Methanol converting to propylene on weakly acidic and hierarchical porous MFI zeolite
-
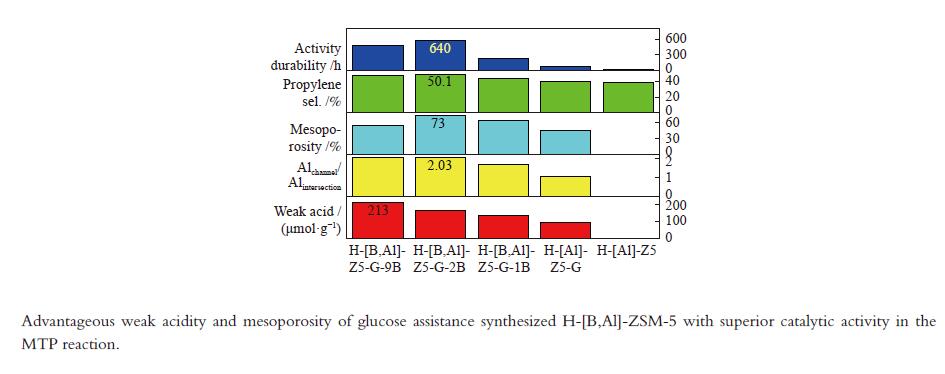
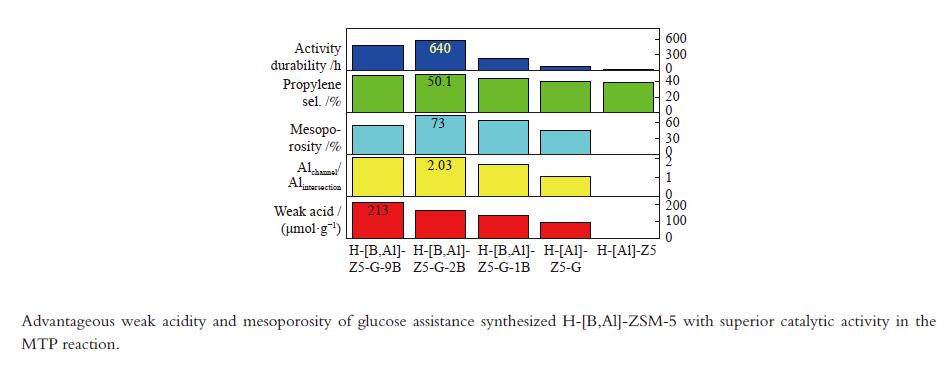
摘要: 使用葡萄糖辅助模板合成了H-[B,Al]-ZSM-5 沸石并用于催化甲醇转化制丙烯。优越的丙烯选择性和活性持久性关联于有利于丙烯生成的高的弱酸/强酸比例以及有利于改善反应物扩散的防止快速积炭的高的介孔率。较多的位于MFI沸石直/正弦孔道的骨架铝增加了产物丙烯/乙烯比归因于促进的丙烯生成。低的酸密度有助于高的丙烯/乙烯比。B/Al比为2 且(Al2+B2)/Si 比为0.01的HZ5-G-2B 样品用于甲醇制丙烯反应,在原料CH3OH/H2O(1∶1.2) 重时空速为1.8 h−1 、480 °C反应条件下,丙烯选择性为51.6%,
${\rm{C}}_{2-4}^ {=} $ 烯烃选择性为83.7%,甲醇完全转化。丙烯/乙烯比为2。催化活性保持580 h稳定。Abstract: H-[B,Al]-ZSM-5 zeolites were synthesized with glucose as assistant template to catalyze methanol converting toward propylene. The superior catalytic performance in terms of the propylene selectivity and the activity longevity was related to high ratio of weak acid to strong acid for favorable production of propylene and to high mesoporosity for improved diffusion of reactants and prevention from fast coking. More framework Al siting in the straight or sinusoidal channels of the MFI zeolite could also enhance the propylene/ethylene ratio due to the promotional effect on propylene formation. Low weak acid density was conducive to the production of high propylene/ethylene ratio. With the B/Al ratio of 2 and the (Al2+B2)/Si ratio of 0.01, HZ5-G-2B was applied in the methanol to propylene reaction at CH3OH/H2O (1∶1.2) WHSV of 1.8 h−1 and 480 °C. Propylene selectivity of 51.6%, the${\rm{C}}_{{2-4}}^ {=} $ selectivity of 83.7% and complete conversion of methanol were achieved. The propylene/ethylene ratio was 2. The catalytic activity kept stable for 580 h.-
Key words:
- H-[B /
- Al]-ZSM-5 /
- weak acidity /
- mesoporosity /
- MTP
-
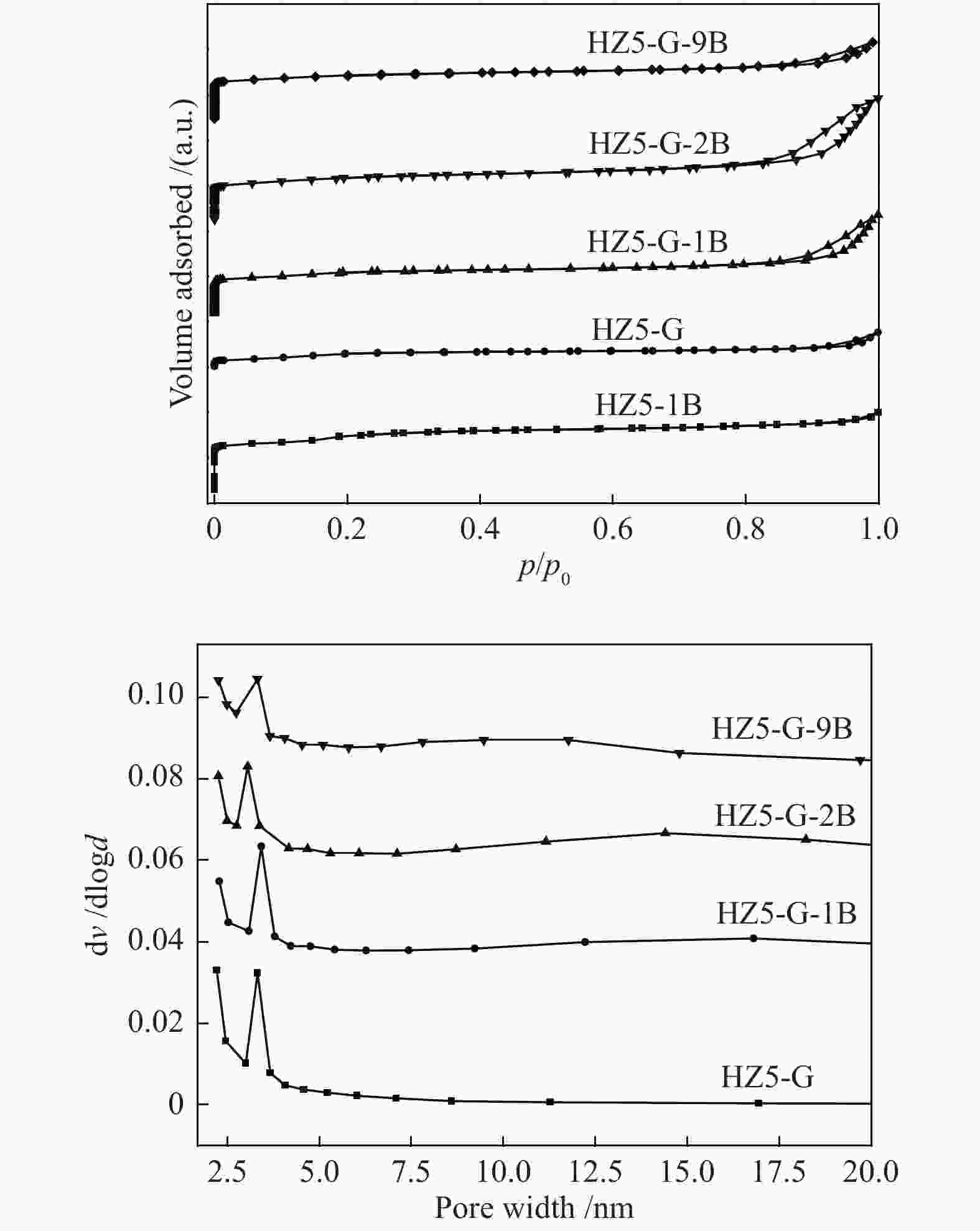
Table 1 Textural properties of synthetic samples
Sample Measured molar ratio* Crysta-llinity/% BET area/(m2·g−1) Pore volume/(cm3·g−1) Mesoporosity/% Si/Al2 B/Al (Al2+B2)/Si micro meso total micro meso total HZ5-G-9B 220 5.1 0.030 98 279 58 337 0.12 0.14 0.26 53 HZ5-G-2B 230 1.3 0.010 95 254 72 326 0.11 0.30 0.41 73 HZ5-G-1B 224 0.7 0.008 89 295 48 343 0.13 0.23 0.36 63 HZ5-G 218 0 0.005 96 316 57 373 0.14 0.10 0.22 45 HZ5-1B − − − − 382 33 415 0.17 0.02 0.19 10 HZ5 220 0 0.005 − − − − − − − − *: charged Si/Al2=200, B/Al=9, 2, 1, 0, 0 Table 2 Percentage of deconvoluted peak areas for synthetic samples
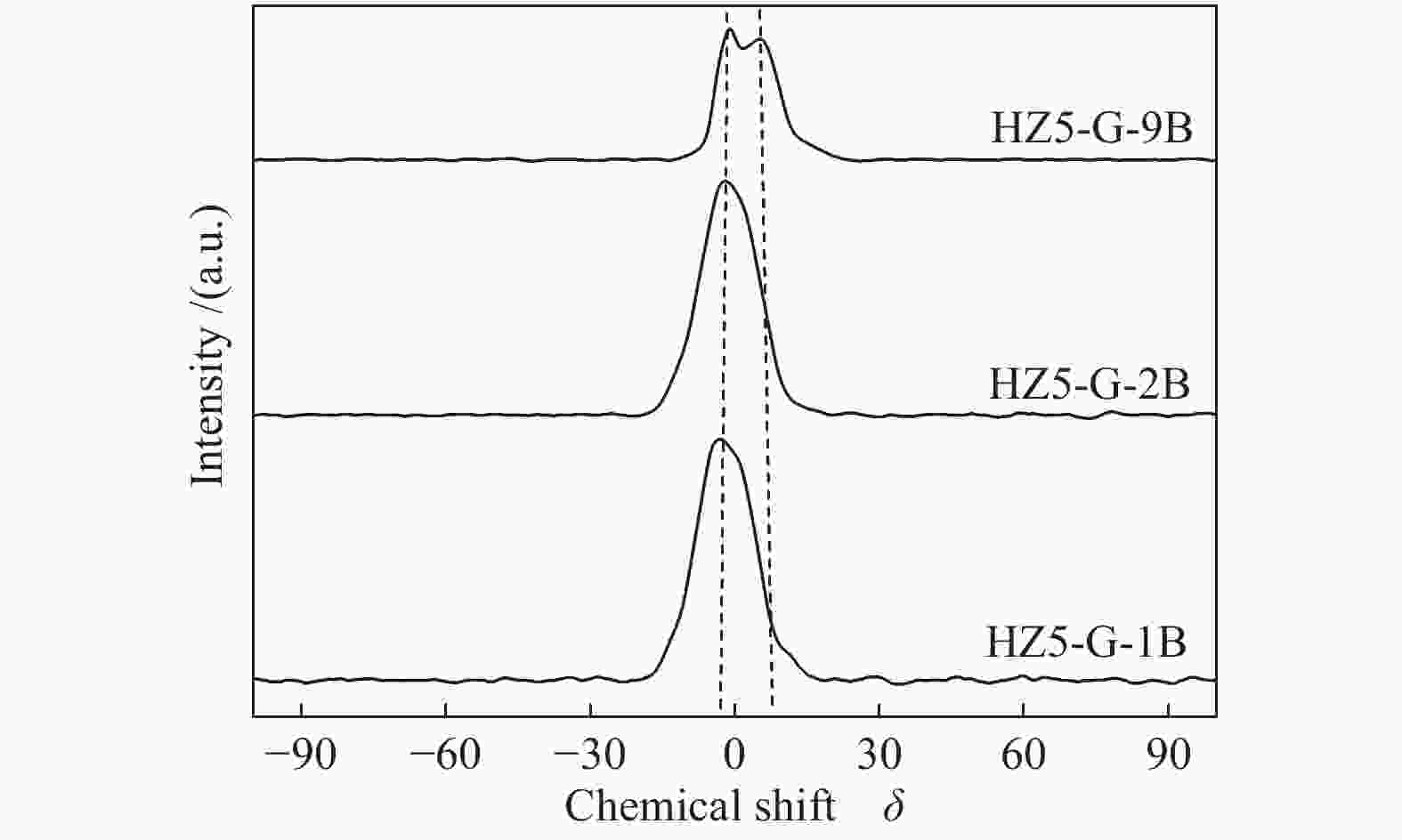
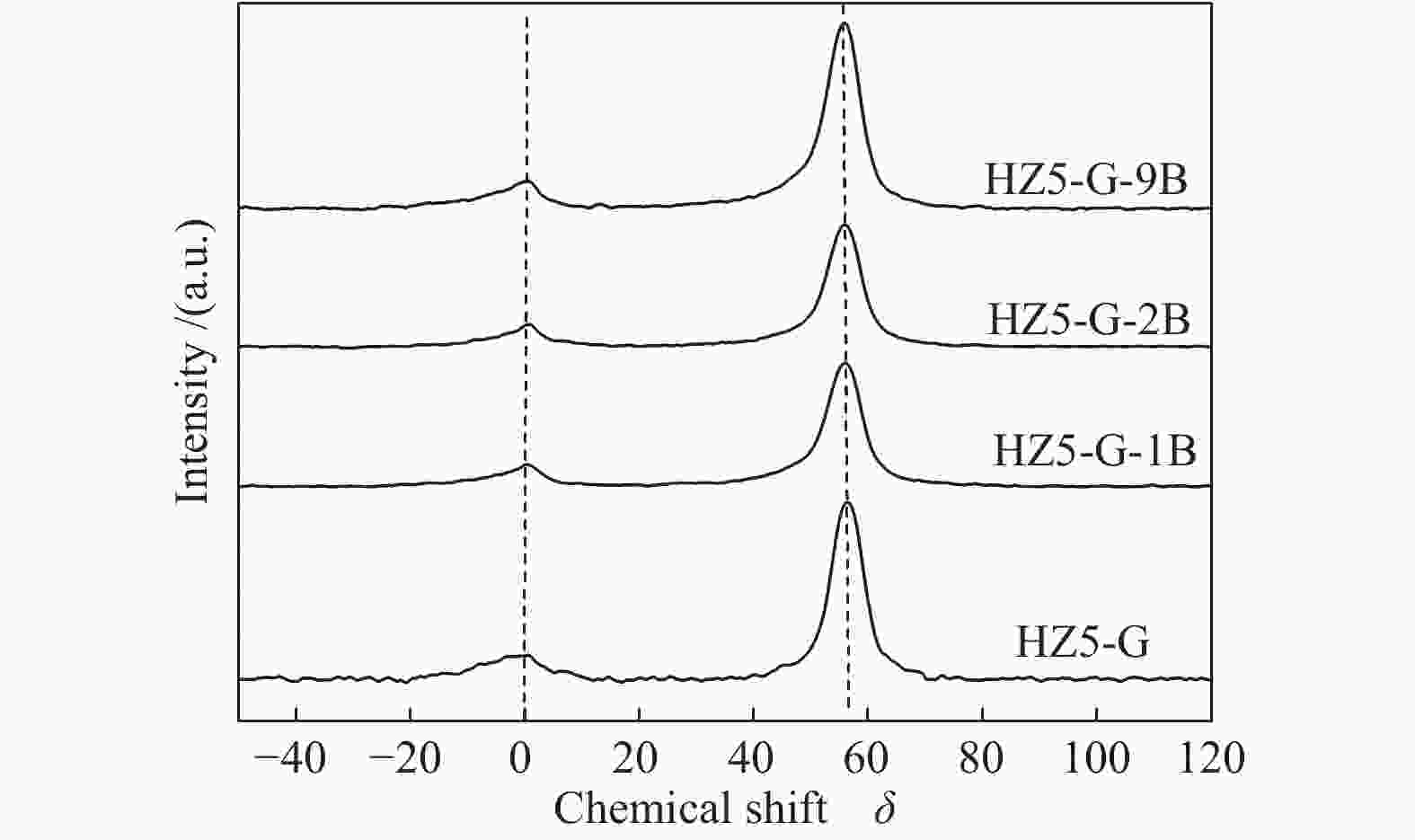
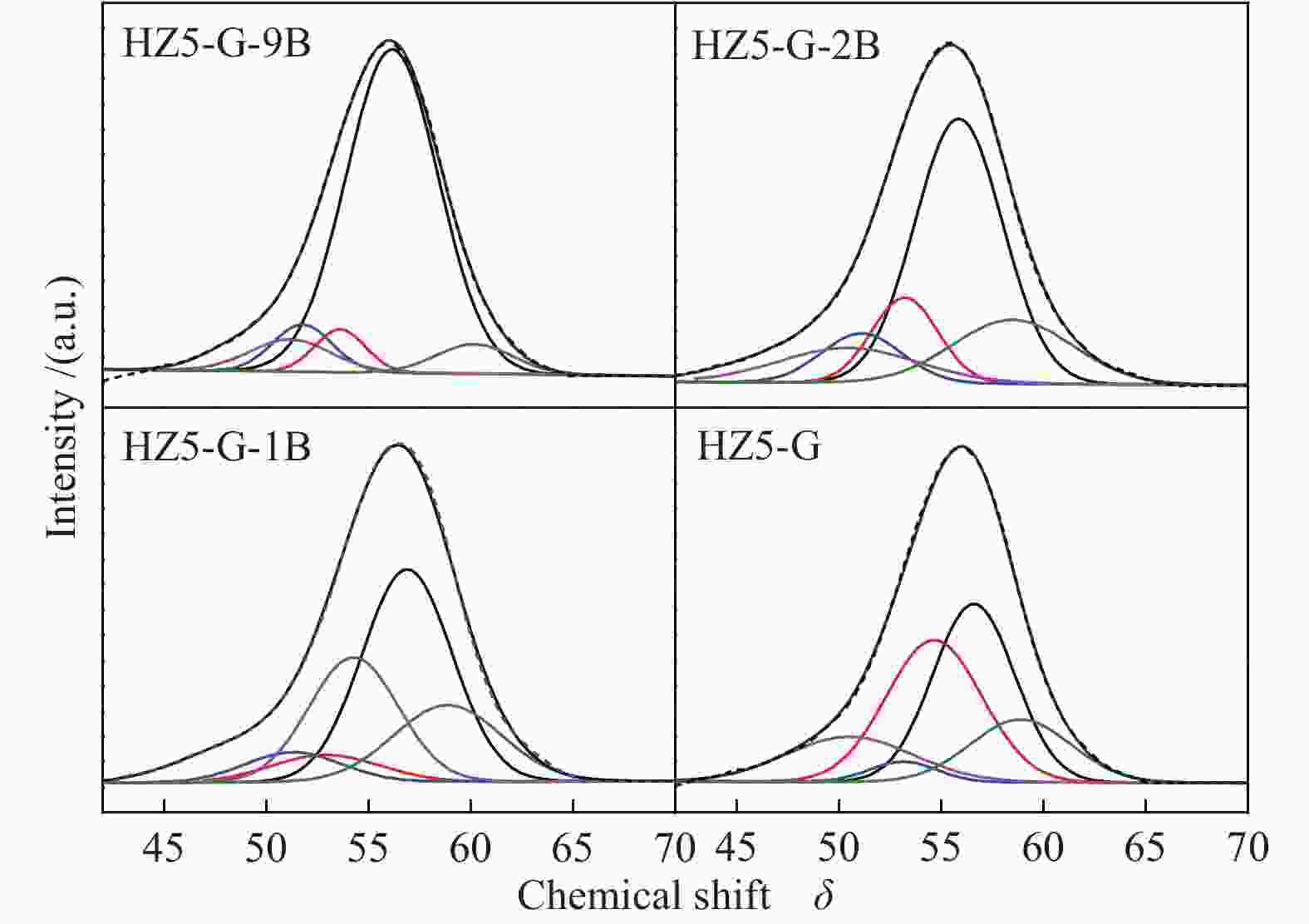
Sample Percentage/% Al56/Al54 52 53 54 56 58 HZ5-G-9B 12 13 20 47 8 2.04 HZ5-G-2B 8 12 23 45 9 2.03 HZ5-G-1B 10 13 25 42 10 1.68 HZ5-G 12 14 30 31 12 1.03 Table 3 Surface acidity of synthetic samples
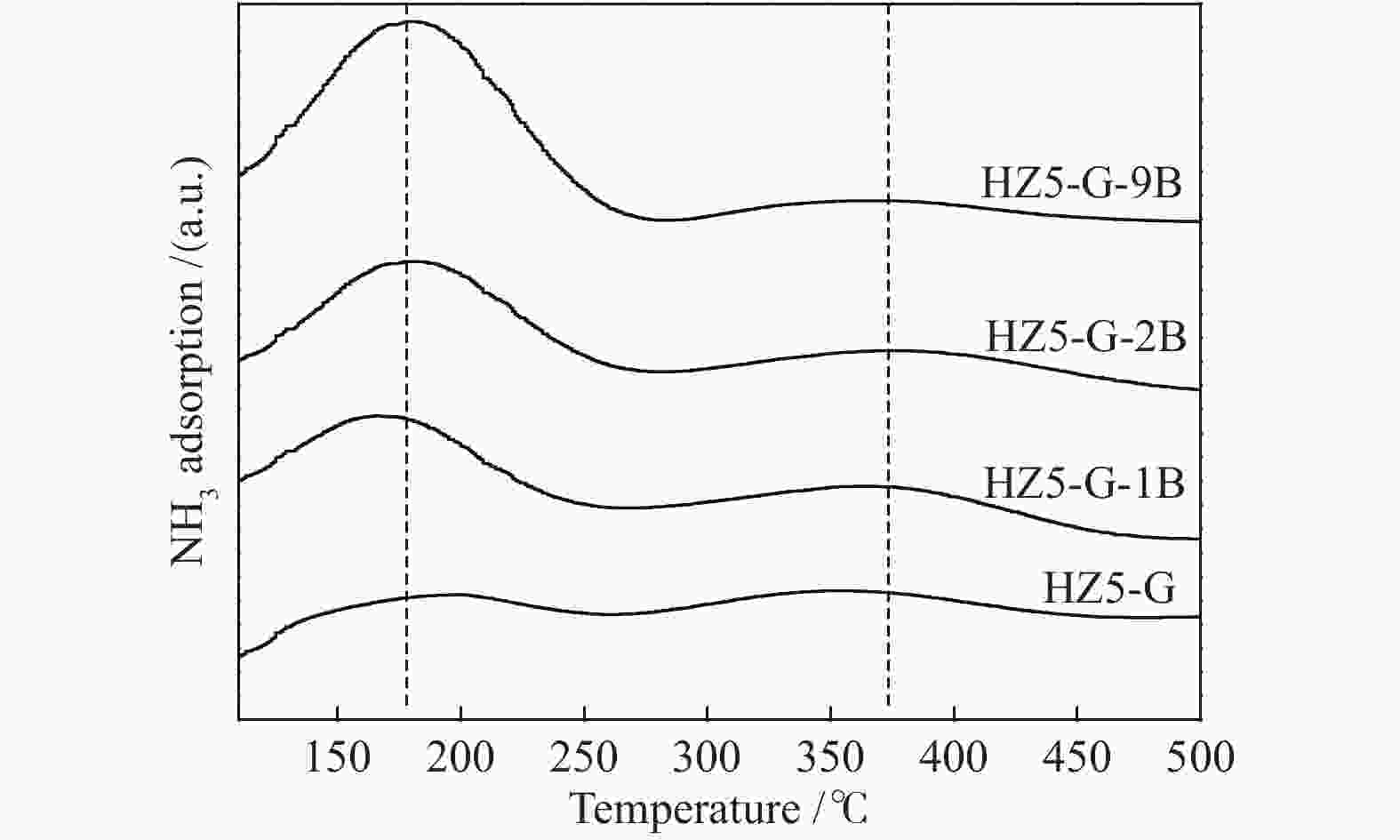
Sample Temp./°C Acid amount/(μmol NH3·g−1) W/S
ratioWeak acid density/
(μmol·m−2)Acid/(μmol·g−1) weak strong weak strong B L HZ5-G-9B 170 373 213 38 5.6 0.63 130 3 HZ5-G-2B 175 374 167 41 4.1 0.51 126 3 HZ5-G-1B 174 369 139 40 3.5 0.41 94 4 HZ5-G 168 362 92 42 2.2 0.25 80 1 Table 4 Catalytic activity of synthetic samples for MTP
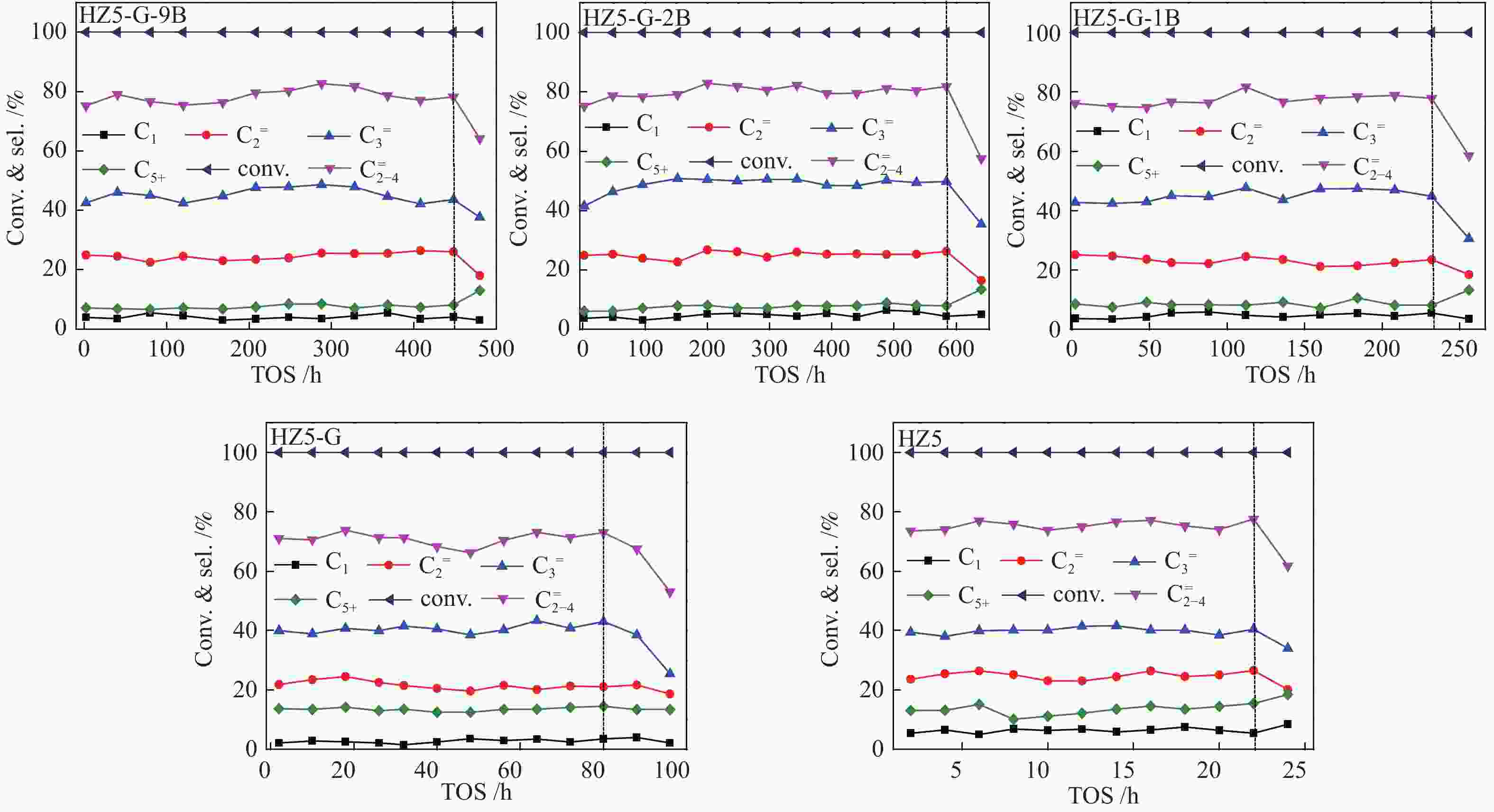
Sample TOS/h Product selectivity/% P/E HTI C1 ${\rm{C}}_{2}^ {=} $ C2 ${\rm{C}}_{3}^ {=} $ C3 ${\rm{C}}_{4}^ {=} $ C4 ${\rm{C}}_{5+} $ ${\rm{C} }_{{2-4}}^ {=}$ HZ5-G-9B 480 3.4 25.4 0.3 47.9 3.4 10.4 0.7 7.1 83.7 1.9 0.05 HZ5-G-2B 580 3.7 22.8 0.3 50.1 2.1 11.6 0.7 6.4 84.5 2.2 0.04 HZ5-G-1B 230 4.3 24.1 0.5 44.4 3.3 11.4 0.6 7.6 79.9 1.8 0.05 HZ5-G 80 1.8 25.2 0.6 41.1 4.3 12.6 0.7 13.5 78.9 1.6 0.07 HZ5 23 6.5 24.9 0.5 38.9 4.9 11.5 0.8 15.7 75.3 1.5 0.08 -
[1] HAW J F, SONG W, MARCUS D M, NICHOLAS J B. The mechanism of methanol to hydrocarbon catalysis[J]. Acc Chem Res,2003,36:317−326. doi: 10.1021/ar020006o [2] INOUE M, DHUPATEMIYA P, PHATANASRI S, INUI T. Synthesis course of the Ni-SAPO-34 catalyst for methanol-to-olefin conversion[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,1999,28(1):19−24. doi: 10.1016/S1387-1811(98)00278-9 [3] ZHAO T S, TAKEMOTO T, TSUBAKI N. Direct synthesis of propylene and light olefins from dimethyl ether catalyzed by modified H-ZSM-5[J]. Catal Commun,2006,7(9):647−650. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2005.11.009 [4] LEE K Y, LEE S W, IHM S K. Acid strength control in MFI zeolite for the methanol-to-hydrocarbons(MTH) reaction[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2014,53(24):10072−10079. [5] PALČIČ A, ORDOMSKY V V, QIN Z, GEORGIEVA V, VALTCHEV V. Tuning zeolite properties for highly efficient synthesis of propylene from methanol[J]. Chem-Eur J,2018,24(50):13136−13149. doi: 10.1002/chem.201803136 [6] UNNEBERG E, KOLBOE S. H--ZSM-5 as catalyst for methanol reactions[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,1995,124:345−354. doi: 10.1016/0926-860X(95)00005-4 [7] CHU C T-W, KUEHL G H, LAGO R M, CHANG C D. lsomorphous substitution in zeolite frameworks II catalytic properties ofZSM-5[J]. J Catal,1985,89:1569−1571. [8] YANG Y, SUN C, DU J, YUE Y, HUA W, ZHANG C, SHEN W, XU H. The synthesis of endurable B-Al-ZSM-5 catalysts with tunable acidity for methanol to propylene reaction[J]. Catal Commun,2012,24(26):44−47. [9] YARIPOUR F, SHARIATINIA Z, SAHEBDELFAR S, IRANDOUKHT A. Effect of boron incorporation on the structure, products selectivities and lifetime of H-ZSM-5 nanocatalyst designed for application in methanol-to-olefins (MTO) reaction[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2015,203:41−53. [10] LIANG T, CHEN J, QIN Z, LI J, WANG P, WANG S, WANG G, DONG M, FAN W, WANG J. Conversion of methanol to olefins over H-ZSM-5 zeolite: Reaction pathway is related to the framework Aluminum siting[J]. ACS Catal,2016,6:7311−7325. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01771 [11] TAO J, ZHANG J, FAN S, MA Q, GAO X, ZHAO T S. Effects of boron modification on the activity of HZSM-5 toward MTP[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2020,48(9):1105−1111. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(20)30074-8 [12] CUI N, GUO H, ZHOU J, LI L, GUO L, HUA Z. Regulation of framework Al distribution of high-silica hierarchically structured ZSM-5 zeolites by boron-modification and its effect on materials catalytic performance in methanol-to-propylene reaction[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2020,306:110411. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110411 [13] HU Z, ZHANG H, WANG L, ZHANG H, ZHANG Y, XU H, SHEN W, TANG Y. Highly stable boron-modified hierarchical nanocrystalline ZSM-5 zeolite for the methanol to propylene reaction[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2014,4(9):2891−2895. doi: 10.1039/C4CY00376D [14] DING J, JIA Y, CHEN P, ZHAO G, LIU Y, LU Y. Thin-felt hollow-B-ZSM-5/SS-fiber catalyst for methanol-to-propylene: toward remarkable stability improvement from mesoporosity-dependent diffusion enhancement[J]. Chem Eng J, 2019, 361: 588−598. [15] KIM J, CHOI M, RYOO R. Effect of mesoporosity against the deactivation of MFI zeolite catalyst during the methanol-to-hydrocarbon conversion process[J]. J Catal,2010,269(1):219−228. [16] TAO J, ZHANG J, FAN S, ZHAO T S. Cocrystalline synthesis of ZSM-5/ZSM-11 and catalytic activity for methanol to propylene[J]. Cryst Res Technol,2020,55:2000027. doi: 10.1002/crat.202000027 [17] LIU H, ERNST H, FREUDDE D, SCHEFFLER F, SCHWIEGER W. In situ 11B MAS NMR study of the synthesis of a boron-containing MFI type zeolite[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2002,54(3):319−330. doi: 10.1016/S1387-1811(02)00392-X [18] CHEN T H, WOUTERS B H, GROBET P J. Aluminium coordinations in zeolite mordenite by 27Al multiple quantum MAS NMR spectroscopy[J]. Eur J Inorg Chem,2000,2:281−285. [19] YOKOI T, MOCHIZUKI H, NAMBA S, KONDO J N, TATSUMI T. Control of the Al distribution in the framework of ZSM-5 zeolite and its evaluation by solid-state NMR technique and catalytic properties[J]. J Phys Chem C,2015,119(27):15303. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b03289 [20] LI J, MA H, CHEN Y, XU Z, LI C, YING W. Conversion of methanol to propylene over hierarchical HZSM-5: Effect of Al spatial distribution[J]. Chem Commun,2018,54:6032−6035. doi: 10.1039/C8CC02042F [21] RODRÍGUEZ-GONZÁLEZ L, HERMES F, BERTMER M, RODRÍGUEZ-CASTELLÓN E, JIMÉNEZ-LÓPEZ A, SIMON U. The acid properties of H-ZSM-5 as studied by NH3-TPD and 27Al-MAS-NMR spectroscopy[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2007,328(2):174−182. [22] CHU C T-W, CHANG C D. Isomorphous substitution in zeolite frameworks. 1. acidity of surface hydroxyls in [B]-, [Fe]-, [Ga]-, and [AI]-ZSM-5[J]. J Phys Chem,1985,89(30):1569−1571. [23] CHANG C D, CHU C T-W, SOCHA R F. Methanol conversion to olefins over ZSM-5 I. effect of temperature and zeolite SiO2/A12O3[J]. J Catal,1984,86(2):289−296. [24] ZHU Q, KONDO J N, SETOYAMA T, YAMAGUCHI M, DOMEN K, TATSUMI T. Activation of hydrocarbons on acidic zeolites: superior selectivity of methylation of ethene with methanol to propene on weakly acidic catalysts[J]. Chem Commun,2008,71(41):5164−5166. [25] KIM S, PARK G, WOO M H, KWAK G, KIM S K. Control of hierarchical structure and framework-Al distribution of ZSM-5 via adjusting crystallization temperature and their effects on methanol conversion[J]. ACS Catal,2019,9:2880−2892. -






 下载:
下载: