Activation and mechanism of chars from partial gasification of lignite at different steam concentrations
-
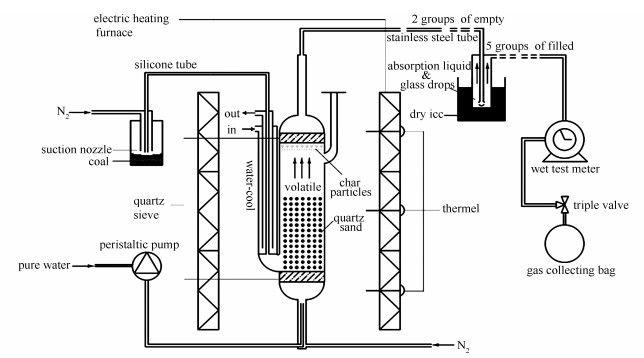
摘要: 以胜利褐煤为原料,利用流化床/固定床石英反应器,进行褐煤气化实验,采用BET、Raman、FT-IR、微波消解ICP-AES、TGA等技术表征半焦。结果表明,在800 ℃水蒸气气氛中,醚基裂解造成芳环间短链或无定形碳含量减少,从而削弱石墨化进程,进而提高芳香结构的缺陷程度,是半焦活化的内在原因。提高水蒸气浓度(10%-25%),半焦的反应性降低,是因为气化过程中半焦的活性位再生能力变弱,而反应(Ar,R-CO-Ar,R+2H2O→Ar,R-O-Ar,R+2H2+CO2)增强,导致醚基含量增加,是半焦活性位再生能力变弱的内在原因。继续提高水蒸气浓度(25%-40%),半焦的反应性略有提高,是因为芳香小环(3-5环)缺陷结构含量增加,而反应(Ar,R-CH=CH2+H2O→Ar,R-CO-CH3+H2)和反应(Ar,R-+H-→Ar,R-H)增强是芳香小环缺陷结构含量增加的内在原因。Abstract: The char samples were prepared from the partial gasification of Shengli lignite in a fluidised-bed/fixed-bed reactor, and characterised by BET, Raman, FT-IR, microwave digestion ICP-AES, and TGA. The results indicate that at 800 ℃ and steam atmosphere the decomposition of ether group is made by the inherent char activation, leading to the decrease in the content of short chain or amorphous carbon between aromatic rings to prevent the graphitizing and the enhancement in the degree of defective aromatic structure. With the increasing of steam concentration (10%-25%) the char reactivity is reduced, which is attributed to the weakening of the regeneration of active sites by forming more ether group via the reaction "Ar, R-CO-Ar, R+2H2O→Ar, R-O-Ar, R+2H2+CO2". However, with the continual increasing of steam concentration (25%-40%) the char reactivity is slightly promoted because the content of defective aromatic structure (3-5 rings) is increased due to the enhancement of the reaction (Ar, R-CH=CH2+H2O→Ar, R-CO-CH3+H2) and the reaction (Ar, R-+H-→Ar, R-H).
-
Key words:
- lignite /
- fluidized-bed /
- active site /
- char structure
-
表 1 煤样和半焦的工业分析及元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analysis of Shengli lignite and chars
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% Mad Vd Ad FCd C H O* N S Shengli lignite 5.69 26.25 12.96 60.79 70.97 5.24 20.72 1.46 1.61 700-char-N2 2.21 10.08 21.50 68.42 86.24 2.06 9.10 1.50 1.10 700-char-10% H2O 2.24 9.56 22.84 67.60 86.49 2.01 9.42 1.28 0.81 700-char-25% H2O 2.30 8.88 24.57 66.55 88.08 2.08 7.83 1.33 0.68 700-char-40% H2O 3.59 9.97 23.99 66.04 89.28 1.93 6.78 1.32 0.69 800-char-N2 2.67 8.23 23.13 68.64 89.63 1.73 5.71 2.00 0.93 800-char-10% H2O 2.05 7.10 30.43 62.47 90.86 1.77 4.88 1.54 0.96 800-char-25% H2O 2.52 7.59 34.98 57.43 90.93 1.76 5.09 1.43 0.79 800-char-40% H2O 2.72 6.93 44.68 48.39 86.05 1.72 10.31 1.49 0.43 *: means calculated by subtraction -
[1] 徐秀峰, 崔洪, 顾永达, 陈诵英, 吴东.煤焦制备条件对其气化反应性的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 1996, 24(5): 404-410. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10112-1014417058.htmXU Xiu-feng, CUI Hong, GU Yong-da, CHEN Song-ying, WU Dong. Influence of charring conditions of coal chars on their gasification reactivity by air[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 1996, 24(5): 404-410. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10112-1014417058.htm [2] 谢克昌, 王永刚, 凌开成, 凌大琦.东山煤焦的CO2加压气化动力学研究[J].煤炭学报, 1991, 16(2): 103-109. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB199102013.htmXIE Ke-chang, WANG Yong-gang, LING Kai-cheng, LING Da-qi. Kinetics of CO2 pressurised gasification of DongShan char[J]. J China Coal Soc, 1991, 16(2): 103-109. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB199102013.htm [3] 朱子彬, 马智华, 林石英, 平户瑞穗, 堀尾正靭.高温下煤焦气化反应特性 (Ⅱ):细孔构造对煤焦气化反应的影响[J].化工学报, 1994, 45(2): 155-161. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ199402004.htmZHU Zi-bin, MA Zhi-hua, LIN Shi-ying, Mitsuho Hirato, Masayuki Horio. Characteristics of coal char gasification at high temperature (Ⅱ): The effect of pore structure on coal char gasification[J]. CIESC J, 1994, 45(2): 155-161. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ199402004.htm [4] RADOVIC L R, STECZKO K, WALKER P L, JENKINS R G. Combined effects of inorganic constituents and pyrolysis conditions on the gasification reactivity of coal chars[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1985, 10(3): 311-326. doi: 10.1016/0378-3820(85)90038-4 [5] LIZZIO A A, JIANG H, RADOVIC L R. On the kinetics of carbon (char) gasification: Reconciling models with experiments[J]. Carbon, 1990, 28(1): 7-19. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(90)90087-F [6] LI X, HAYASHI J, LI C. Volatilisation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal. Part Ⅶ. Raman spectroscopic study on the changes in char structure during the catalytic gasification in air[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(10/11): 1509-1517. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236101001284 [7] LI X, LI C. Volatilisation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal. Part Ⅷ. Catalysis and changes in char structure during gasification in steam[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(10/11): 1518-1525. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236101001284 [8] LI T, ZHANG L, DONG L, LI C Z. Effects of gasification atmosphere and temperature on char structural evolution during the gasification of Collie sub-bituminous coal[J]. Fuel, 2014, 117: 1190-1195. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.08.040 [9] TAY H L, KAJITANI S, ZHANG S, LI C Z. Effects of gasifying agent on the evolution of char structure during the gasification of Victorian brown coal[J]. Fuel, 2013, 103: 22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.02.044 [10] 王永刚, 孙加亮, 张书.反应气氛对褐煤气化反应性及半焦结构的影响[J].煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8): 1765-1771. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201408051.htmWANG Yong-gang, SUN Jia-liang, ZHANG Shu. Impacts of the gas atmosphere on the gasification reactivity and char structure of the brown coal[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2014, 39(8): 1765-1771. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201408051.htm [11] 许修强, 王永刚, 陈国鹏, 陈宗定, 秦中宇, 戴谨泽, 张书, 许德平.水蒸气对褐煤原位气化半焦反应性能及微观结构的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(5): 546-553. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18622.shtmlXU Xiu-Qiang, WANG Yong-gang, CHEN Guo-peng, CHEN Zong-ding, QIN Zhong-yu, DAI Jin-ze, ZHANG Shu, XU De-ping. Effects of steam on the reactivity and microstructure of char from in-situ gasification of brown coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(5): 546-553. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18622.shtml [12] 许修强, 王永刚, 陈宗定, 白磊, 张锟俊, 杨萨莎, 张书.胜利褐煤半焦冷却处理对其微观结构及反应性能的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(1): 1-8. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18547.shtmlXU Xiu-qiang, WANG Yong-gang, CHEN Zong-ding, BAI Lei, ZHANG Kun-jun, YANG Sa-sha, ZHANG Shu. Influence of cooling treatments on char microstructure and reactivity of Shengli brown coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(1): 1-8. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18547.shtml [13] 向银花, 王洋, 张建民, 张守玉, 房倚天, 董众兵.部分气化焦的水蒸气气化动力学[J].化工学报, 2003, 54(3): 368-373. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ200303017.htmXIANG Yin-hua, WANG Yang, ZHANG Jian-min, ZHANG Shou-yu, FANG Yi-tian, DONG Zhong-bing. Kinetic on steam gasification of partially gasified char[J]. CIESC J, 2003, 54(3): 368-373. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ200303017.htm [14] LI C Z. Some recent advances in the understanding of the pyrolysis and gasification behaviour of Victorian brown coal[J]. Fuel, 2007, 86(12/13): 1664-1683. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236107000361 [15] MIN Z, YIMSIRI P, ASADULLAH M, ZHANG S, LI C Z. Catalytic reforming of tar during gasification. Part Ⅱ. Char as a catalyst or as a catalyst support for tar reforming[J]. Fuel, 2011, 90(7): 2545-2552. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.03.027 [16] WU H, QUYN D M, LI C Z. Volatilisation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal. Part Ⅲ. The importance of the interactions between volatiles and char at high temperature[J]. Dent Traumatol, 2002, 81(8): 1033-1039. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S001623610200011X [17] ZHANG L X, HUANG J J, FANG Y T, WANG Y. Gasification reactivity and kinetics of typical chinese anthracite chars with steam and CO2[J]. Energy Fuels, 2006, 20(3): 1201-1210. doi: 10.1021/ef050343o [18] YE D P, AGNEW J B, ZHANG D K. Gasification of a South Australian low-rank coal with carbon dioxide and steam: Kinetics and reactivity studies[J]. Fuel, 1998, 77(11): 1209-1219. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(98)00014-3 [19] ZHANG S, HAYASHI J I, LI C Z. Volatilisation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal. Part Ⅸ. Effects of volatile-char interactions on char-H2O and char-O2 reactivities[J]. Fuel, 2011, 90(4): 1655-1661. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.11.008 [20] CHEN W H, LIN B J. Hydrogen and synthesis gas production from activated carbon and steam via reusing carbon dioxide[J]. Appl Energy, 2013, 101(1): 551-559. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261912004758 [21] ROMÁN S, GONZÁLEZ J F, GONZÁLEZ-GARCÍA C M, ZAMORA F. Control of pore development during CO2 and steam activation of olive stones[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2008, 89(8): 715-720. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2007.12.015 [22] 向银花, 王洋, 张建民, 董众兵, 李斌.煤焦气化过程中比表面积和孔容积变化规律及其影响因素研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2002, 30(2): 108-112. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RLHX200202002.htmXIANG Yin-hua, WANG Yang, ZHANG Jian-min, DONG Zhong-bing, LI Bin. Study on structural properties and their affecting factors during gasificaiton of chars[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2002, 30(2): 108-112. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RLHX200202002.htm [23] TAY H L, KAJITANI S, ZHANG S, LI C Z. Inhibiting and other effects of hydrogen during gasification: Further insights from FT-Raman spectroscopy[J]. Fuel, 2014, 116: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.07.066 -





 下载:
下载: