Changes in chemical structure and solvation of heavy oil components during thermal upgrading of a vacuum residue
-
摘要: 以委内瑞拉减压渣油为原料, 采用微型反应釜, 研究了其在410℃、2.0MPa氮气初压下, 不同反应停留时间的热改质过程生成油的化学结构组成及其重组分溶剂化变化规律.通过1H-NMR技术研究了热改质过程生成油中沥青质和重胶质不同化学位移归属氢的转化路径; 并结合改进的Brown-Ladner法分析了热改质过程生成油中沥青质和重胶质的平均分子结构参数变化; 采用蒸汽压渗透法考察了热改质过程生成油中沥青质和重胶质在甲苯溶液中所形成的复合超分子结构的平均相对分子质量.结果表明, 随着热改质程度的加深, 沥青质和重胶质的H/C原子比减小, 供氢能力逐渐下降, 沥青质和重胶质的芳香环共轭程度和fA在体系生焦后(45min) 显著提高; 沥青质的聚集趋势相关值在热改质15min前变化不大, 15min后显著增强, 而重胶质在整个热改质过程中, 其聚集趋势相关值的增势较为缓和; 沥青质和重胶质的聚集趋势相关值差异逐渐增大, 15min时增加了1.5%、25min时增加了50.8%、45min时增加了142.3%, 表明沥青质和重胶质的结构差异越来越明显; 重胶质溶剂化沥青质的能力逐步减弱, 体系的溶剂化参数从0时的32.9%逐步降到15min时的29.5%、25min时的14.1%和45min时的9.6%;热改质生成油的斑点实验等级逐渐增加, 体系的胶体稳定性逐渐降低.Abstract: The Venezuelan vacuum residue was used as a feedstock for thermal upgrading experiments to investigate the changes in chemical structure and composition and the solvation interaction of heavy oil components in a micro-batch reactor at 410℃ with an initial pressure of nitrogen 2.0MPa. The 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance measurement was applied to analyze the reaction pathway of hydrogen atoms with different chemical shift of the heavy oil components. The average molecular structural parameters of asphaltenes and heavy resins in the oil produced by thermal upgrading of the feedstock were calculated and analyzed by the modified Brown-Lander methods. The vapor pressure osmometry was used to determine the average molecular weights of supramolecular structures formed by asphaltenes and heavy resins in toluene. The results show that both H/C atomic ratio and hydrogen donating ability of asphaltenes and heavy resins decrease with reaction time, and the conjugate degree of aromatic ring system and fA become greater clearly after 45min. The aggregation of asphaltenes rises slowly and increases sharply after 15 min, while there is a slight change of aggregation for the heavy resins during the whole reaction time, and the differences in aggregation correlation values between asphaltenes and heavy resins are increased by 1.5% at 15min, 50.8% at 25min, and 142.3% at 45min, respectively. The solvation interaction of heavy resins with asphaltenes weakens with time, and the solvation parameters decrease from 32.9% at the beginning to 29.5% at 15min, 14.1% at 25min, and 9.6% at 45min, respectively. The changes may contribute to the dropping of thermal colloidal stability of resins and the increasing of spot ratings.
-
Key words:
- thermal upgrading /
- asphaltenes /
- heavy resins /
- chemical structure and composition /
- solvation
-
表 1 委内瑞拉减压渣油性质
Table 1 Properties of the Venezuelan vacuum residue
ρ20/
(g·cm-3)μ100/
(mm2·s-1)Conradson carbon
residue w/%w/% H/C
(atomic ratio)n-C7Asp.
w/%w/(μg·g-1) C H S N Ni V 1.053 2 58 530 25.57 83.74 9.58 4.65 0.90 1.36 17.48 40.34 33.66 表 2 VNVR热改质过程生成油中沥青质和重胶质的元素组成及其不同归属氢含量
Table 2 CHSN elemental composition and 1H-NMR analysis of asphaltenes and heavy resins in the oil produced by thermal upgrading of VNVR
Items Asphaltenes Heavy resins 0 min 15 min 25 min 45 min 0 min 15 min 25 min 45 min H w /% 7.32 7.16 6.84 6.15 8.85 8.11 7.84 7.12 C w/% 81.77 82.69 83.06 83.45 82.22 83.53 83.71 84.04 N w/% 2.01 1.97 1.94 2.00 1.52 1.58 1.74 1.79 S w/% 5.50 5.08 4.86 4.67 4.66 4.77 4.59 4.82 Odi w/% 3.40 3.10 3.30 3.73 2.75 2.01 2.12 2.23 H/C (atomic ratio) 1.08 1.04 0.99 0.89 1.29 1.17 1.12 1.02 HA/HT 0.122 0.134 0.145 0.197 0.097 0.144 0.162 0.196 Hα/HT 0.199 0.214 0.235 0.227 0.215 0.219 0.225 0.262 Hβ/HT 0.487 0.483 0.471 0.425 0.516 0.471 0.455 0.406 Hγ/HT 0.192 0.169 0.149 0.151 0.172 0.166 0.158 0.136 Odi: estimated by difference; HA: hydrogen attached to aromatic ring with chemical shift between 6.0 and 9.0; Hα: hydrogen on naphthenic ring or alkyl chain adjacent to aromatic ring with chemical shift between 2.0 and 4.0; Hβ: hydrogen on naphthenic ring or alkyl chain with two or more positions from an aromatic ring with chemical shift between 1.0 and 2.0; Hγ: terminal methyl protons of paraffins or of alkyl side-chains three or more positions from an aromatic ring with chemical shift between 0.5 and 1.0; HT: hydrogen in total of HA, Hα, Hβ and Hγ 表 3 VNVR热改质过程生成油中沥青质和重胶质的平均分子结构参数
Table 3 Average molecular structural parameters of asphaltenes and heavy resins from reaction oil during thermal upgrading of VNVR
Items Asphaltenes Heavy resins 0 min 15 min 25 min 45 min 0 min 15 min 25 min 45 min fA 0.55 0.57 0.59 0.66 0.44 0.52 0.55 0.61 fN 0.19 0.20 0.21 0.20 0.20 0.19 0.19 0.20 fP 0.26 0.23 0.20 0.14 0.36 0.29 0.26 0.19 HAU/CA 0.41 0.42 0.42 0.40 0.58 0.55 0.54 0.53 usw 933.1 857.1 833.9 821.2 594.3 554.7 535.1 509.3 CT* 63.5 59.0 57.7 57.1 40.7 39.6 37.3 35.7 HT* 68.3 61.4 57.0 50.5 52.6 44.9 41.9 36.3 ST* 1.6 1.4 1.3 1.2 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 NT* 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.1 0.6 0.6 0.7 0.7 OT* 2.0 1.7 1.7 1.9 1.0 0.7 0.6 0.7 RT* 15.1 14.4 14.8 15.6 7.7 8.2 8.2 8.7 RA* 10.8 10.3 10.6 11.7 4.8 5.6 5.7 6.2 RN* 4.3 4.1 4.1 3.9 2.9 2.6 2.5 2.5 RN*/RA* 0.40 0.40 0.39 0.33 0.59 0.46 0.44 0.40 CA* 36.5 35.0 35.7 39.1 18.4 20.8 21.2 22.5 fA: ratio of aromatic carbon to total carbons; fN: ratio of naphthenic carbon to total carbons; fP: ratio of paraffinic carbons to total carbons; HAU/CA: condensation degree parameter of aromatic ring system; usw: unit sheet weight 表 4 VNVR热改质过程生成油斑点实验等级
Table 4 Spot ratings of oil from thermal upgrading of VNVR
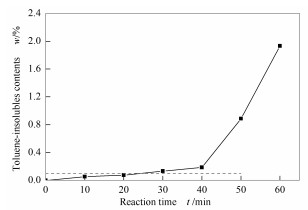
Reaction time t /min Spot ratings 0 2 15 2 25 4 45 5 -
[1] 姚国欣.委内瑞拉超重原油和加拿大油砂沥青加工现状及发展前景[J].中外能源, 2012, 17(1): 3-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201201003.htmYAO Guo-xin. Current status and development prospects for processing of Venezuelan extra-heavy crude and Canadian oil sand bitumen[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2012, 17(1): 3-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201201003.htm [2] LI S H, LIU C G, QUE G H, LIANG W J, ZHU Y J. Colloidal structures of three Chinese petroleum vacuum residues[J]. Fuel, 1996, 75(8): 1025-1029. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(95)00315-0 [3] ZHAO B, SHAW J M. Composition and size distribution of coherent nanostructures in Athabasca bitumen and Maya crude oil[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(5): 2795-2804. doi: 10.1021/ef070119u [4] INDO K, RATULOWSKI J, DINDORUK B, GAO J L, ZUO J L, MULLINS O C. Asphaltene nanoaggregates measured in a live crude oil by centrifugation[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23(9): 4460-4469. doi: 10.1021/ef900369r [5] CHANG C L, FOGLER H S. Stabilization of asphaltenes in aliphatic solvents using alkylbenzene-derived amphiphiles. 2. Study of the asphaltene-amphiphile interactions and structures using fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and small-angle x-ray scattering techniques[J]. Langmuir, 1994, 10(6): 1758-1766. doi: 10.1021/la00018a023 [6] GONZÁLEZ G, NEVES G B M, SARAIVA S M, LUCAS E F, SOUSA M D A D. Electrokinetic characterization of asphaltenes and the asphaltenes-resins interaction[J]. Energy Fuels, 2003, 17(4): 879-886. doi: 10.1021/ef020249x [7] LEÓN O, CONTRERAS E, ROGEL E, DAMBAKLI G, ESPIDEL J, ACEVEDO S. The influence of the adsorption of amphiphiles and resins in controlling asphaltene flocculation[J]. Energy Fuels, 2001, 15(5): 1028-1032. doi: 10.1021/ef010032n [8] LEÓN O, CONTRERAS E, ROGEL E, DAMBAKLI G, ACEVEDO S, CARBOGNANI L, ESPIDEL J. Adsorption of native resins on asphaltene particles: A correlation between adsorption and activity[J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18(13): 5106-5112. doi: 10.1021/la011394q [9] DANIEL M G, ANDERSEN S I. Thermodynamic characterization of asphaltene-resin interaction by microcalorimetry[J]. Langmuir, 2004, 20(11): 4559-4565. doi: 10.1021/la0499315 [10] SOORGHALI F, ZOLGHADR A, AYATOLLAHI S. Effects of native and non-native resins on asphaltene deposition and the change of surface topography at different pressures: An experimental investigation[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(9): 5487-5494. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b00366 [11] 王齐, 郭磊, 王宗贤, 沐宝泉, 郭爱军, 刘贺.委内瑞拉减压渣油供氢热转化基础研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2012, 40(11): 1317-1322. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(13)60001-8WANG Qi, GUO Lei, WANG Zong-xian, MU Bao-quan, GUO Ai-jun, LIU He. Hydrogen donor visbreaking of Venezuelan vacuum residue[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 40(11): 1317-1322. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(13)60001-8 [12] GOULD K A, WIEHE I A. Natural hydrogen donors in petroleum resids[J]. Energy Fuels, 2006, 21(3): 1199-1204. [13] WANG Z X, JI S F, LIU H, CHEN K, GUO A J. Hydrogen transfer of petroleum residue subfractions during thermal processing under hydrogen[J]. Energy Technol, 2015, 3(3): 259-264. doi: 10.1002/ente.201402190 [14] GUO A J, WANG Z Q, ZHANG H J, ZHANG X J, WANG Z X. Hydrogen transfer and coking propensity of petroleum residues under thermal processing[J]. Energy Fuels, 2010, 24(5): 3093-3100. doi: 10.1021/ef100172r [15] BROWN J K, LADNER W R. A study of the hydrogen distribution in coal-like materials by high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy Ⅱ. A comparison with infra-red measurement and the conversion to carbon structure[J]. Fuel, 1960, 39: 87-96. [16] 刘贺, 陈坤, 王宗贤, 郭爱军. 1H-NMR评价不同重油缓和热转化过程中的相对供氢能力[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(10): 1191-1198. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18273.shtmlLIU He, CHEN Kun, WANG Zong-xian, GUO Ai-jun. Evaluation of relative hydrogen-donating abilities of different heavy oils during mild thermal conversion by 1H-NMR[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(10): 1191-1198. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18273.shtml [17] DICKIE J P, YEN T F. Macrostructures of asphaltic fractions by various instrumental methods[J]. Anal Chem, 1967, 39(14): 1847-1852. doi: 10.1021/ac50157a057 [18] 李传, 王继乾, 隋李涛, 崔敏, 邓文安.委内瑞拉稠油沥青质的XPS研究[J].石油学报:石油加工, 2013, 29(3): 459-463. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXJG201303017.htmLI Chuan, WANG Ji-qian, SUI Li-tao, CUI Min, DENG Wen-an. Study on XPS of Venezuela heavy oil asphaltene[J]. Acta Pet Sin (Pet Proc Sect), 2013, 29(3): 459-463. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXJG201303017.htm [19] 王治卿.渣油热反应体系胶体化学与氢转移行为研究[D].青岛:中国石油大学(华东), 2006.WANG Zhi-qing. Research on the colloidal stability and hydrogen-transfer of vacuum residue during thermal conversion[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum, 2006. [20] SEDGHI M, GOUAL L, WELCH W, KUBELKA J. Effect of asphaltene structure on association and aggregation using molecular dynamics[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2013, 117(18): 5765-5776. doi: 10.1021/jp401584u -





 下载:
下载: