Effect of promoter and CO2 content in the feed on the performance of CuFeZr catalyst in the synthesis of higher alcohol from syngas
-
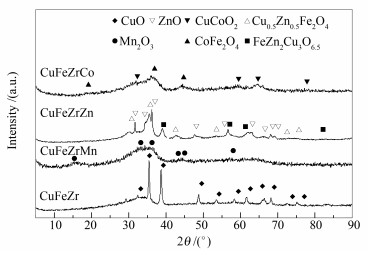
摘要: 考察了不同助剂 (Mn、Zn、Co) 对CuFeZr催化剂用于合成气制混合醇的影响.借助BET、XRD、H2-TPR等对其物化性质进行了表征, 结果表明, 加入助剂可减小颗粒粒径并且增强对CO的吸附能力以及催化剂表面碱性, 其中, 加入Zn可以增强CuFe间的相互作用, 改善CuFeZr催化剂的还原性质, 提高对CO的吸附能力, 以及提供最强的表面碱性.用固定床反应器对催化剂的反应性能进行了评价, 反应结果表明, 加入Zn可以显著提高CuFeZr催化剂用于合成气制混合醇的反应活性及醇选择性, 使醇时空收率从0.026 g/(gcat·h) 提高至0.071 g/(gcat·h).由于循环条件下, 反应产物CO2同时也是原料气的组成成分, 进一步地探究了原料气中CO2浓度对催化剂反应性能的影响.结果表明, 加入CO2可提高CO转化率和醇以及烃的收率, 但阻碍链增长反应并使得产物烯烷比降低.其中, 在所考察浓度范围内, 原料气中含有2.5%的CO2最有利于醇和烃的生成尤其是低碳醇和低碳烃的生成.Abstract: The effect of various promoting additives (Mn, Zn, Co) on the performance of CuFeZr catalyst in the synthesis of higher alcohol from syngas was investigated. The results of nitrogen physisorption, XRD and H2-TPR characterization show that these additives can reduce the particle size and enhance the surface basicity and the adsorption capacity towards CO. Especially, the doping of Zn in the CuFeZr catalyst can effectively enhance the interaction between Cu and Fe, strengthen the surface basicity, and improve the reducibility and CO adsorption ability. For the synthesis of higher alcohol from syngas over the CuFeZr catalyst, the catalytic evaluation results in a fixed bed reactor illustrate that the activity and selectivity to alcohols are greatly enhanced by the addition of Zn promoter; the space time yield (STY) of ROH is increased from 0.026 to 0.071 g/(gcat·h). Meanwhile, it was found that CO2 in the feed can improve the CO conversion as well as the STY to alcohols and hydrocarbons, but suppress the chain growth and decrease the ratio of olefin to paraffin; proper amount of CO2 (2.5%) is beneficial to the formation of alcohols and hydrocarbons of short chains.
-
Key words:
- higher alcohols synthesis /
- CuFeZr catalyst /
- syngas /
- promoting additives /
- CO2
-
Table 1 Textural properties of various catalysts
Catalyst Molar ratioa ABET/(m2·g-1) Pore volume v/(cm3·g-1) Pore size d/nm CuFeZr 1.8:1.3:1.0 91.0 0.3 10.8 CuFeZrMn 1.8:1.3:1.0:1.8 186.3 0.4 7.9 CuFeZrZn 1.8:1.2:1.0:1.9 137.9 0.3 7.0 CuFeZrCo 1.8:1.2:1.0:1.8 72.9 0.2 11.5 a: metal molar ratios were determined by ICP-AES analysis Table 2 Average performance of the CuFeZrX catalysts in CO hydrogenation
Catalyst CO conv. x/% Selectivity s/% Yield/(g·gcat-1·h-1) Alcohol distribution w/% Hydrocarbon distribution w/% ROH CHn CO2 alcohol CHn MeOH C2-5OH C6+OH CH4 C2-4 C5+ CuFeZr 12.1 13.2 51.2 35.6 0.026 0.091 18.2 34.9 46.9 13.9 36.9 49.2 CuFeZrMn 15.8 17.6 70.5 11.9 0.037 0.104 9.6 35.2 55.2 7.0 25.8 67.2 CuFeZrZn 19.7 24.1 66.0 9.9 0.071 0.114 10.3 40.6 49.2 7.4 31.9 60.7 CuFeZrCo 6.3 16.0 30.4 53.6 0.018 0.115 36.2 56.1 7.7 25.0 55.2 19.8 reaction conditions: 210 ℃, 6 MPa, GHSV=6 000 h-1 Table 3 Performance of the CuFeZrZn catalysts in CO hydrogenation in the CO2 rich feed
CO2 concentration w/% CO conv. x/% Selectivity s/% Yield/(g·gcat-1·h-1) Alcohol distribution w/% Hydrocarbon distribution w/% ROH CHn CO2 alcohol CHn MeOH C2-5OH C6+OH CH4 C2-4 C5+ 0 17.2 23.4 51.0 25.6 0.068 0.148 11.1 40.2 48.7 7.8 33.7 58.5 2.5 17.7 22.63 59.08 18.28 0.076 0.197 12.1 39.7 48.2 9.9 38.6 51.5 5 19.1 21.38 56.29 22.33 0.073 0.193 11.8 48.6 39.6 9.0 35.1 55.9 reaction conditions: 210 ℃, 6 MPa, GHSV=6 000 h-1 Table 4 Alcohol and alkane chain growth factors for CO hydrogenation in the feed containing different amounts of CO2
CO2/CO (%) Chain growth factor α ROH hydrocarbon 0 0.78 0.82 2.5 0.72 0.67 5 0.71 0.66 -
[1] ANDERSSON R, BOUTONNET M, JARAS S. Correlation patterns and effect of syngas conversion level for product selectivity to alcohols and hydrocarbons over molybdenum sulfide based catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen, 2012, 417/418(3): 119-128. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X11007514 [2] ANDERSSON R, BOUTONNET M, JARAS S. Effect of CO2 in the synthesis of mixed alcohols from syngas over a K/Ni/MoS2 catalyst[J]. Fuel, 2013, 107: 715-723. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.11.044 [3] XU R, WEI W, LI W H, HU T D, SUN Y H. Fe modified CuMnZrO2 catalysts for higher alcohols synthesis from syngas: Effect of calcination temperature[J]. J Mol Catal A: Chem, 2005, 234(1/2): 75-83. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1381116905001068 [4] LIN M, FANG K, LI D, SUN Y H. CO hydrogenation to mixed alcohols over co-precipitated Cu-Fe catalysts[J]. Catal Commun, 2008, 9(9): 1869-1873. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2008.03.004 [5] XU R, ZHANG S, ROBERTS C B. Mixed alcohol synthesis over a K promoted Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst in supercritical hexanes[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2013, 52(41): 14514-14524. doi: 10.1021/ie3024017 [6] YANG X, WEI Y, SU Y, ZHOU L. Characterization of fused Fe-Cu based catalyst for higher alcohols synthesis and DRIFTS investigation of TPSR[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2010, 91(9): 1168-1173. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2010.03.032 [7] HUBER G W, IBORRA S, CORMA A. Synthesis of transportation fuels from biomass: Chemistry, catalysts, and engineering[J]. Chem Rev, 2006, 106(9): 4044-4098. doi: 10.1021/cr068360d [8] SUBRAMANI V, GANGWAL S K. A review of recent literature to search for an efficient catalytic process for the conversion of syngas to ethanol[J]. Energy Fuels, 2008, 22(2): 117-136. doi: 10.1021/ef700411x?src=recsys&journalCode=enfuem [9] SLAA J C, OMMEN J G V, ROSS J R H. The synthesis of alcohols using Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 (Ce or Mn) catalysts[J]. Top Catal, 1995, 2(1): 79-89. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256426666_The_synthesis_of_alcohols_using_CuZnOA12O3_Ce_or_Mn_catalysts [10] SLAA J C, OMMEN J G V, ROSS J R H. The synthesis of higher alcohols using modified Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts[J]. Catal Today, 1992, 15(1): 129-148. doi: 10.1016/0920-5861(92)80125-7 [11] HERMAN R G. Advances in catalytic synthesis and utilization of higher alcohols[J]. Catal Today, 2000, 55(3): 233-245. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(99)00246-1 [12] ZHANG Q W, LI X H, FUJIMOTO K R. Pd-promoted Cr/ZnO catalyst for synthesis of methanol from syngas[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen, 2006, 309(1): 28-32. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2006.04.026 [13] SMITH K J, ANDERSON R B. A chain growth scheme for the higher alcohols synthesis[J]. J Catal, 1984, 85(2): 428-436. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(84)90232-X [14] MEI D, ROUSSEAU R, KATHMANN S M, GLEZAKOU V A, ENGELHARD M H, JIANG W, WANG C, GERBER M, WHITE J, STEVENS D. Ethanol synthesis from syngas over Rh-based/SiO2 catalysts: A combined experimental and theoretical modeling study[J]. J Catal, 2010, 271(2): 325-342. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2010.02.020 [15] PRIETO G, CONCEPCION P, MARTINEZ A, MENDOZA E. New insights into the role of the electronic properties of oxide promoters in Rh-catalyzed selective synthesis of oxygenates from synthesis gas[J]. J Catal, 2011, 280(2): 274-288. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2011.03.025 [16] LI Z R, XIE Y N. Structures and performance of Pd-Mo-K/Al2O3 catalysts used for mixed alcohol synthesis from synthesis gas[J]. Catal Lett, 2000, 65(1): 43-48. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/226853392_Structures_and_performance_of_Pd-Mo-KAl2O3_catalysts_used_for_mixed_alcohol_synthesis_from_synthesis_gas [17] SHI X R, JIAO H, HERMANN K, WANG J. CO hydrogenation reaction on sulfided molybdenum catalysts[J]. J Mol Catal A: Chem, 2009, 312(1/2): 7-17. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1381116909003161 [18] XIANG M L, LI D B, XIAO H C, ZHANG J L, QI H J, LI W H, ZHONG B, SUN Y H. Synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas over Fischer-Tropsch elements modified K/beta-Mo2C catalysts[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(4/5): 599-603. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236107000920 [19] LIU C C, LIN M G, FANG K G, SUN Y H. Preparation of nanostructured molybdenum carbides for CO hydrogenation[J]. RSC Adv, 2014, 144(4): 20948-20954. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2014/ra/c4ra01586j#!divAbstract [20] DING M, LIU J, ZHANG Q, TSUBAKI N, WANG T, MA L L. Preparation of copper-iron bimodal pore catalyst and its performance for higher alcohols synthesis[J]. Catal Commun, 2012, 28: 138-142. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2012.08.027 [21] DING M Y, QIU M H, LIU J G, LI Y P, WANG T J, MA L L, WU C Z. Influence of manganese promoter on co-precipitated Fe-Cu based catalysts for highe alcohols synthesis[J]. Fuel, 2013, 109(7): 21-27. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236112004541 [22] 王野.以铝为载体的铜钴催化剂用于CO加氢的结构和性能[D].福建:厦门大学, 2012.WANG Ye. Structure and catalytic performance of alumina-supported copper-cobalt catalysts for carbon monoxide hydrogenation[D]. Fujian: Xiamen University, 2012. [23] WANG J, CHERNAVSKⅡ P A, WANG Y, KHODAKOV A Y. Influence of the support and promotion on the structure and catalytic performance of copper-cobalt catalysts for carbon monoxide hydrogenation[J]. Fuel, 2013, 103(1): 1111-1122. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236112006151 [24] FANG K, LI D, LIN M, XIANG M, WEI W, SUN Y H. A short review of heterogeneous catalytic process for mixed alcohols synthesis via syngas[J]. Catal Today, 2009, 147(2): 133-138. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2009.01.038 [25] GAO W, ZHAO Y F, LIU J M, HUANG Q W, HE S, LI C M, ZHAO J W, WEI M. Catalytic conversion of syngas to mixed alcohols over CuFe-based catalysts derived from layered double hydroxides[J]. Catal Sci Technol, 2013, 3(5): 1324-1332. doi: 10.1039/c3cy00025g [26] LU Y, YU F, HU J, LIU J. Catalytic conversion of syngas to mixed alcohols over Zn-Mn promoted Cu-Fe based catalyst[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen, 2012, 429-430(25): 48-58. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X12002049 [27] 林明桂, 房克功, 李德宝, 孙予罕. Zn、Mn助剂对CuFe合成低碳醇催化剂的影响[J]. 2008, 24(5): 833-838. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLHX200805019.htmLIN Ming-gui, FANG Ke-gong, LI De-bao, SUN Yu-han. Effect of Zn and Mn promoters on copper-iron based catalysts for higher alcohol synthesis[J]. Acta Phys Chem Sin, 2008, 24(5): 833-838. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLHX200805019.htm [28] LUK H T, MONDELLI C, FERRÉ D C, STEWART J A, PÉREZ-RAMÍREZ J. Status and prospects in higher alcohols synthesis from syngas[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2017, 46(5): 1358-1426. doi: 10.1039/C6CS00324A [29] LU Y, CAO B, YU F, LIU J, BAO Z, GAO J. High selectivity higher alcohols synthesis from syngas over three-dimensionally ordered macroporous Cu-Fe catalysts[J]. ChemCatChem, 2014, 6(2): 473-478. doi: 10.1002/cctc.v6.2 [30] HAN X Y, FANG K G, SUN Y H. Effects of metal promotion on CuMgFe catalysts derived from layered double hydroxides for higher alcohol synthesis via syngas[J]. RSC Adv, 2015, 5(64): 51868-51874. doi: 10.1039/C5RA05846E [31] HAN X Y, FANG K G, ZHOU J, ZHAO L, SUN Y H. Synthesis of higher alcohols over highly dispersed Cu-Fe based catalysts derived from layered double hydroxides[J]. J Colloid Interf Sci, 2016, 470(6): 162-171. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021979715302320 [32] DING M Y, TU J L, QIU M H, WANG T J, MA L L, LI Y P. Impact of potassium promoter on Cu-Fe based mixed alcohols synthesis catalyst[J]. Appl Energy, 2015, 138: 584-589. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.01.010 [33] XIANG Y Z, CHITRY V, LIDDICOAT P, FELFER P, CAIRNEY J, RINGER S, KRUSE N. Long-chain terminal alcohols through catalytic CO hydrogenation[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135(19): 7114-7117. doi: 10.1021/ja402512r [34] SMIT E D, WECKHUYSEN B M. The renaissance of iron-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: on the multifaceted catalyst deactivation behaviour[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2008, 37(12): 2758-2781. doi: 10.1039/b805427d [35] MUNNIK P, DE JONGHP E, DE JONGK P. Control and impact of the nanoscale distribution of supported cobalt particles used in Fischer-Tropsch catalysis[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136(20): 7333-7340. doi: 10.1021/ja500436y [36] SCHULZ H. Short history and present trends of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen, 1999, 186(1/2): 3-12. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X9900160X [37] NEWSOME D S. Water-gas shift reaction[J]. Catal Rev, 1980, 21(2): 275-318. doi: 10.1080/03602458008067535 [38] HALL W K, KOKES R J, EMMETT P H. Mechanism studies of the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis-the addition of radioactive methanol, carbon dioxide and gaseous formaldehyde[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1957, 79(12): 2983-2989. doi: 10.1021/ja01569a001 [39] XU L G, BAO S Q, HOUPT D J, LAMBERT S H, DAVIS B H. Role of CO2 in the initiation of chain growth and alcohol formation during the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Catal Today, 1997, 36(3): 347-355. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(96)00244-1 [40] LU G, ZHANG C F, CANG Y Q, ZHU Z B, NI Y H, CHEN L J, YU F. Synthesis of mixed alcohols from CO2 contained syngas on supported molybdenum sulfide catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen, 1997, 150(2): 243-252. doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(96)00285-2 [41] DING M Y, QIU M H, WANG T J, MA L L, WU C Z, LIU J G. Effect of iron promoter on structure and performance of CuMnZnO catalyst for higher alcohols synthesis[J]. Appl Energy, 2012, 97(9): 543-547. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261911007896 [42] SHI L M, CHU W. Catalytic properties for higher-alcohol synthesis of CuCo based catalysts promoted by transition elements (Zn, Mo)[J]. J Mol Catal A: Chem, 2011, 25(4): 316-321. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-FZCH201104007.htm [43] LIU J G, DING M Y, WANG T J, MA L L. Promoting effect of cobalt addition on higher alcohols synthesis over copper-based catalysts[J]. Adv Mater Res, 2012, 550/553: 270-275. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.550-553 [44] MIRANDA L S, ANDREW C, JAMES J S. Reduction processes in Cu/SiO2, Co/SiO2, and CuCo/SiO2 catalysts[J]. Catal Today, 2012, 182(1): 60-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.07.026 [45] DING M Y, YANG Y, WU B S, LI Y W, WANG T J, MA L L. Study on reduction and carburization behaviors of iron-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst[J]. Appl Energy, 2014, 61(10): 2267-2270. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876610214034821 [46] CORTES J, DROGUETT S. Temperature programmed desorption of CO from supported cobalt[J]. J Catal, 1975, 38(s1/s3): 477-481. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0021951775901104 [47] CHENG X, WANG L, WANG Z, ZHANG M, MA C. Catalytic performance of NO reduction by CO over activated semicoke supported Fe/Co catalysts[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2016, 55(50): 12710-12722. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.6b00804 [48] AN X, WU B S, WAN H J, LI T Z, TAO Z C, XIANG H W, LI Y W. Comparative study of iron-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst promoted with potassium or sodium[J]. Catal Commun, 2007, 8(12): 1957-1962. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2007.03.016 [49] ZHANG C H, YANG Y, TENG B T, LI T Z, ZHENG H Y, XIANG H W, LI Y W. Study of an iron-manganese Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst promoted with copper[J]. J Catal, 2006, 237(2): 405-415. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2005.11.004 [50] WANG J, CHERNAVSKⅡ P A, WANG Y, KHODAKOV A Y. Influence of the support and promotion on the structure and catalytic performance of copper-cobalt catalysts for carbon monoxide hydrogenation[J]. Fuel, 2013, 103: 1111-1122. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.07.055 [51] XIANG Y, KRUSE N. Tuning the catalytic CO hydrogenation to straight-and long-chain aldehydes/alcohols and olefins/paraffins[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 13058. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13058 -





 下载:
下载: