Experimental research on the control of heavy metal emissions from 330 MW coal-fired unit by heterogeneous agglomeration
-
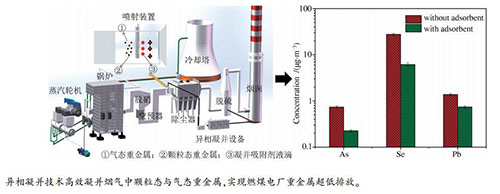
摘要: 湖北某电厂1号机组容量为330 MW,配备双室四电场静电除尘器,为了考察异相凝并技术对细颗粒物以及重金属脱除效率的影响,对1号机组除尘器前后,脱硫塔后进行颗粒物与重金属采样测试。结果表明,在烟道中喷射凝并吸附剂后,ESP入口颗粒态重金属占比增加,其中,Se元素在PM2.5和PM10上增加尤为明显,而气态的重金属含量有所降低,表明凝并吸附剂增强了颗粒态重金属的凝并效果,小颗粒态与气态重金属通过异相凝并过程转移至大颗粒态。喷入凝并吸附剂后,石膏中重金属含量显著降低,说明能够进入脱硫石膏的重金属含量减少,异相凝并提升了ESP对重金属的脱除作用;在尾部烟道末端烟囱排放口采样点,重金属含量相较于未喷入凝并吸附剂的工况,有着明显的降低,表明了经过异相凝并之后,排放至大气中的重金属显著减少,异相凝并对于重金属的控制起到关键作用。Abstract: In order to investigate the influence of spraying the agglomeration adsorbent on the removal efficiency of fine particles and heavy metals, the sampling and tests on particles and heavy metals were carried out before and after the dedusters and the desulfurization towers in the Unit 1 of a power plant in Hubei Province with a capacity of 330 MW and equipped with a double-chamber four-electric-field electrostatic precipitator. The test results show that after spraying the agglomeration adsorbent in the flue, the proportion of the particulate heavy metals at the ESP inlet increases, the Se element increasing significantly in PM2.5 and PM10, while the heavy metal content in the gas phase decreases, indicating that the agglomeration adsorbent can improve the coagulation efficiency of particulate heavy metals, leading to the small particulate and heavy metals in gas phase being transferred to large particulates. In gypsum, the content of heavy metals is significantly reduced after agglomeration, indicating that heavy metals can join the desulfurized gypsum. Also, the heterogeneous agglomeration enhances the effect of ESP on the removal of heavy metals. At the point before final discharge to the chimney, there is a significant decrease in the content of heavy metals compared with the non-agglomerated condition, which indicates that the heavy metals discharged into the atmosphere after agglomeration are significantly reduced, and the heterogeneous agglomeration plays a key role in the control of heavy metals.
-
Key words:
- heterogeneous agglomeration /
- particle /
- heavy metals /
- arsenic /
- selenium /
- lead
-
表 1 煤样的元素分析和工业分析
Table 1 Ultimate analysis and proximate analysis of coal samples
Ultimate analysis w/% Heavy metals content /(μg·g-1) Proximate analysis w/% Qnet, ar /(MJ·kg-1) C H N S O As Se Pb Mt-ar Mad Aar Vdaf 60.2 2.7 0.7 1.5 4.9 4.1 1.8 53.3 8.30 6.9 23.0 16.0 22.6 表 2 异相凝并系统参数
Table 2 Parameters for an agglomeration system
Project Unit Parameter Adsorbent supply capacity kg/h 2-4 Dilution water supply capacity kg/h 18000 Compressed air supply capacity m3/min 30 Installed power of agglomeration device kW < 50 Installed power of air compressor kW 180 表 3 采样参数
Table 3 Sampling parameters
Sampling site Adsorbent Suction volume /L Load/MW Before ESP with 20 300 After ESP with 1045 300 After WFGD with 1230 300 Before ESP without 20 300 After ESP without 1465 300 After WFGD without 1800 300 表 4 颗粒物采样
Table 4 Particle sampling concentration results in size
Sampling site Adsorbent 2.5-10 μm/(mg·m-3) 1-2.5 μm/(mg·m-3) < 1 μm/(mg·m-3) Before ESP with 31.0 44.0 98.5 Before ESP without 183.5 927.0 102.0 After ESP with 0.49 2.08 1.69 After ESP without 0.07 0.02 3.50 表 5 固体样中重金属的含量
Table 5 Concentrations of heavy metals in solid samples
Sample w/(μg·g-1) As Se Pb limestone 9.02 3.88 10.43 Slag 0.37 0.11 15.09 ESP fly ash without adsorbent 18.80 8.09 234.01 ESP fly ash with adsorbent 19.53 9.19 243.96 Gypsum without adsorbent 11.10 6.76 15.56 Gypsum with adsorbent 7.52 2.19 10.89 表 6 脱硫废水中重金属的含量
Table 6 Concentrations of heavy metals in a desulfurization wastewater
Sample w/(μg·g-1) As Se Pb Desulfurization wastewater 0.85 1.64 0.13 表 7 各元素质量平衡率
Table 7 Mass balance rate for each element
Adsorbent MBR /% As Se Pb With 97.45 103.82 90.88 Without 96.11 98.87 87.45 表 8 各元素在各产物中的富集
Table 8 The enrichment of each element in each product
Adsorbent element With /% Without /% As Se Pb As Se Pb Fly ash 95.13 96.45 98.38 92.87 89.21 98.07 Slag 0.32 0.20 1.07 0.33 0.21 1.12 Gypsum 4.53 2.84 0.54 6.79 9.23 0.81 Desulfurization wastewater 0.70 2.93 0.01 0.71 3.07 0.01 Air 0.01 0.47 0.01 0.01 1.32 0.01 -
[1] International Energy Agency (IEA). World Energy Outlook 2018[M].Paris: OECD Publishing, 2018 [2] 郭新彪, 魏红英.大气PM2.5对健康影响的研究进展[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(13): 1171-1177. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=45934939GUO Xin-biao, WEI Hong-ying. Research progress on the impact of atmospheric PM2.5 on health[J]. Sci Bull, 2013, 58(13): 1171-1177. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=45934939 [3] 付高平.成都市微细颗粒物(PM2.5)形成机理及对人类健康危害研究[D].成都: 西南交通大学, 2014.FU Gao-ping. Research on the formation mechanism of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Chengdu and its harm to human health[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014. [4] NEAS L M. Fine particulate matter and cardiovascular disease[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 65-66: 55-67. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378382099000764 [5] PUI D Y H, CHEN S C, ZUO Z L. PM2.5 in China: Measurements, sources, visibility and health effects, and mitigation[J]. Particuology, 2014, 13: 1-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JCSP201402001.htm [6] CHEN G Y, SUN Y N, WANG Q, YAN B B, CHENG Z J, MA W C. Partitioning of trace elements in coal combustion products: A comparative study of different applications in China[J]. Fuel, 2019, 240: 31-39. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236118320271 [7] ZHOU C C, LIU G J, WU D, FANG T, WANG R W, FAN X. Mobility behavior and environmental implications of trace elements associated with coal gangue: A case study at the Huainan Coalfield in China[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 95: 193-199. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24050719 [8] 华伟, 孙和泰, 祁建民, 黄治军, 石志鹏, 段伦博.燃煤电厂超低排放机组重金属铅、砷排放特性[J].热力发电, 2019, 48(10): 65-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RLFD201910012.htmHUA Wei, SUN He-tai, QI Jian-min, HUANG Zhi-jun, SHI Zhi-peng, DUAN Lun-bo. Heavy metal lead and arsenic emission characteristics of ultra-low emission units in coal-fired power plants[J]. Therm Power Gener, 2019, 48(10): 65-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RLFD201910012.htm [9] WEI F, ZHANG J Y, ZHENG C G. Agglomeration rate and action forces between atomized particles of agglomerator and inhaled-particles from coal combustion[J]. J Environ Sci, 2005, 17(2): 335-339. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HJKB200502034.htm [10] LI H L, ZHANG J Y, ZHAO Y C, WU C Y, ZHENG C G. Wettability of fly ashes from four coal-fired power plants in China[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2011, 50(13): 7763-7771. doi: 10.1021/ie2001378 [11] 李志超, 段钰锋, 王运军, 黄治军, 孟素丽, 沈解忠. 300 MW燃煤电厂ESP和WFGD对烟气汞的脱除特性[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(4): 491-498. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18171.shtmlLI Zhi-chao, DUAN Yu-feng, WANG Yun-jun, HUANG Zhi-jun, MENG Su-li, SHEN Jie-zhong. The removal characteristics of flue gas mercury by ESP and WFGD in 300 MW coal-fired power plants[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(4): 491-498. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18171.shtml [12] 李海龙, 张军营, 赵永椿, 张凯, 张立麒, 郑楚光.燃煤飞灰物理化学特性及其润湿机理研究[J].工程热物理学报, 2009, 30(9): 1597-1600. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=31431892LI Hai-long, ZHANG Jun-ying, ZHAO Yong-chun, ZHANG Kai, ZHANG Li-qi, ZHENG Chu-guang. Study on the physical and chemical properties of coal-fired fly ash and its wetting mechanism[J]. J Eng Thermophys, 2009, 30(9): 1597-1600. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=31431892 [13] 魏凤.燃煤亚微米颗粒的形成和团聚机制的研究[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2005.WEI Feng. Research on the formation and agglomeration mechanism of coal-fired sub-micron particles[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2005. [14] RAJNIAK P, STEPANEK F, DHANASEKHARAN K, FAN R, MANCINELLI C, CHERN R T. A combined experimental and computational study of wet granulation in a Wurster fluid bed granulator[J]. Powder Technol, 2009, 189(2): 190-201. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0032591008001885 [15] HU B, YI Y, LIANG C, YUAN Z L, ROSZAK S, YANG L J. Experimental study on particles agglomeration by chemical and turbulent agglomeration before electrostatic precipitators[J]. Powder Technol, 2018, 335: 186-194. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0032591018302882 [16] 郭沂权, 赵永椿, 李高磊, 张军营. 300MW燃煤电站化学团聚强化飞灰细颗粒物排放控制的研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(3): 754-763. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zgdjgcxb201903012GUO Yi-quan, ZHAO Yong-chun, LI Gao-lei, ZHANG Jun-ying. Research on enhanced fly ash fine particulate emission control by chemical agglomeration of 300MW coal-fired power stations[J].Proc CSEE, 2019, 39(3): 754-763. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zgdjgcxb201903012 [17] GUO Y Q, ZHANG J Y, ZHAO Y C, WANG S L, JIANG C, ZHENG C G. Chemical agglomeration of fine particles in coal combustion flue gas: Experimental evaluation[J].Fuel, 2017, 3: 557-569. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S001623611730577X [18] VIEBKE C, PICULELL, NILSSON S. On the mechanism of gelation of helix-forming biopolymers[J]. Macromolecules, 1994, 27(15): 4160-4166. doi: 10.1021/ma00093a017 [19] 张凯.超细颗粒物微观团聚机理数值模拟研究[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2009.ZHANG Kai. Numerical simulation study on the micro-aggregation mechanism of ultrafine particles[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2009. [20] LINAK W, WENDT J. Toxic metal emissions from incineration-mechanisms and control[J]. Prog Energy Combust Sci, 1993, 19(2): 145-185. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0360128593900146 [21] 祁倩倩.新疆燃煤电厂重金属分布规律及天然气锅炉汞的排放研究[D].新疆: 新疆师范大学, 2015.QI Qian-qian. Research on the distribution of heavy metals in Xinjiang coal-fired power plants and mercury emissions from natural gas boilers[D]. Xinjiang: Xinjiang Normal University, 2015. [22] 李敬伟.燃煤烟气中可凝结颗粒物及典型有机污染物的排放特性实验研究[D].浙江: 浙江大学, 2018.LI Jing-wei. Experimental study on the emission characteristics of condensable particulate matter and typical organic pollutants in coal-fired flue gas[D]. Zhejiang: Zhejiang University, 2018. [23] ZHAO S L, DUAN Y F, LU J C, GUPTA R, PUDASAINEE D, LIU S, LIU M. Chemical speciation and leaching characteristics of hazardous trace elements in coal and fly ash from coal-fired power plants[J]. Fuel, 2018, 232: 463-469. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236118309694 [24] 张凯华, 张锴, 潘伟平. 300MW燃煤电站砷、汞排放特征研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(7): 839-844. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18219.shtmlZHANG Kai-hua, ZHANG Kai, PAN Wei-ping. Research on arsenic and mercury emission characteristics of 300MW coal-fired power station[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(7): 839-844. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18219.shtml -





 下载:
下载: