Effect of solvent extraction pretreatments on the variation of macromolecular structure of low rank coals
-
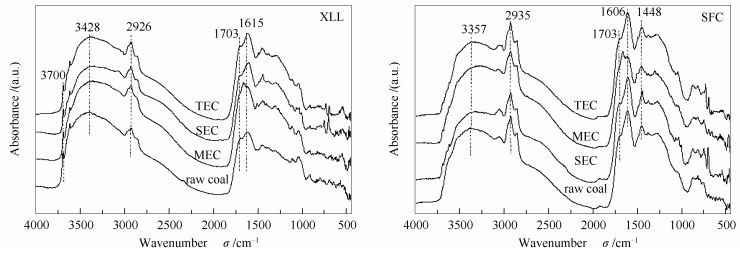
摘要: 为了研究溶剂预处理对低阶煤的固有大分子结构的影响,本研究对锡林郭勒褐煤(XLL)和神府次烟煤(SFC)分别进行了四氢呋喃(THF)索氏抽提、二硫化碳/N-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮(CS2/NMP)混合溶剂抽提及热溶处理,并对所得抽余煤进行了傅里叶红外漫反射光谱分析(DRIFT)、热重分析(TGA)、压汞法分析(MI)和溶胀度测定。结果表明,溶剂抽提导致煤大分子结构重排和再缔合。其中,THF索式抽提和CS2/NMP混合溶剂抽提可以改变非共价键交联作用,特别是氢键作用分布,从而不同程度地松弛煤大分子结构。然而,高温溶剂热溶处理主要促进了煤大分子的共价键交联,尤其是对锡林郭勒褐煤(XLL)。所有抽取煤的溶胀都受Fickian扩散控制,且所有抽取煤的溶胀活化能都低于原煤。Abstract: In order to understand the effects of solvent pretreatment on the inherent macromolecular structure of low rank coal, Xilinguole lignite (XLL) and Shenfu sub-bituminous coal (SFC) were extracted by tetrahydrofuran (THF) soxhlet extraction, carbon disulfide/N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (CS2/NMP) mixed solvent extraction and thermal dissolution, respectively. The extracted coals were characterized by diffuse reflection FT-IR spectroscopy (DRIFT), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), mercury intrusion method (MI) and swelling ratio determination. The results indicated that the extraction resulted in the arrangement and reassociation of coal inherent macromolecules. THF Soxhlet extraction and CS2/NMP mixed solvent extraction can relax the macromolecular structure of coal to varying degrees by changing the non-covalent bond cross-linking, especially the distribution of hydrogen bond interactions. However, thermal dissolutions at high temperature mainly increased the covalent cross linking of coal macromolecules, especially for XLL. Swelling of all extracted coals was limited by Fickian diffusion, and the extracted coal showed lower swelling activation energy than the corresponding raw coals.
-
Key words:
- pretreatment /
- extraction /
- macromolecular structure /
- swelling /
- diffusion
-
Table 1 Ultimate and proximate analyses of XLL and SFC
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% Mad Ad Vdaf C H N S O* XLL 15.77 11.01 40.34 62.67 4.83 0.98 0.44 31.08 SFC 7.40 5.58 32.44 75.95 5.18 1.05 0.33 17.49 *: by difference Table 2 Extraction yields of XLL and SFC
Sample Yield w/% SE ME TE XLL 4.4 6.6 11.4 SFC 10.3 14.0 16.9 Table 3 Elemental analyses results of raw coals and extracted coals
Sample Element content wdaf/% Atomic ratio N C S H O* H/C O/C XLL 0.98 62.67 0.44 4.83 31.08 0.93 0.37 SEC(XLL) 1.05 62.05 0.47 4.77 31.66 0.92 0.38 TEC(XLL) 0.95 64.82 0.51 4.65 29.07 0.86 0.34 MEC(XLL) 1.27 61.65 0.62 4.79 31.67 0.93 0.39 SFC 1.05 75.95 0.33 5.18 17.49 0.82 0.17 SEC(SFC) 1.02 76.18 0.32 5.16 17.32 0.81 0.17 TEC(SFC) 1.03 78.13 0.39 4.92 15.53 0.76 0.15 MEC(SFC) 1.18 74.53 0.54 5.01 18.74 0.81 0.19 *: by difference Table 4 MIP results of raw coals and extracted coals
Sample Total pore area S/(m2·g-1) Average pore diameter d/nm Bulk density ρ/(g·mL-1) Apparent density ρ/(g·mL-1) Porosity /% XLL 8.26 269 0.8119 1.4792 45.11 SEC(XLL) 9.06 497.5 0.5459 1.4182 61.51 MEC(XLL) 8.01 348.9 0.6336 1.1372 44.29 TEC(XLL) 10.40 404.3 0.5632 1.3807 59.21 SFC 10.77 261.3 0.659 1.228 46.35 SEC(SFC) 7.39 405.2 0.619 1.153 46.33 MEC(SFC) 6.89 447.7 0.638 1.256 49.21 TEC(SFC) 10.2 272.2 0.665 1.236 46.18 Table 5 Swelling ratios of raw coals and extracted coals
Swelling solvent XLL SFC raw coal MEC SEC TEC raw coal MEC SEC TEC Toluene 0.90 1.04 0.86 0.92 1.03 1.24 1.06 1.07 Methanol 1.16 1.22 1.09 1.13 1.15 1.13 1.02 1.18 THF 1.21 1.29 1.00 1.30 1.60 1.42 1.31 1.69 Pyridine 1.48 1.32 1.28 1.35 1.70 1.71 1.47 1.58 Table 6 Swelling kinetic parameters of raw coals and extracted coals
Sample Q∞ n K×100 Ea/(kJ·mol-1) XLL 1.28-1.81 0.07-0.25 10.0-67.4 27.20 SEC(XLL) 1.41-1.62 0.13-0.16 26.5-48.4 8.04 MEC(XLL) 1.25-1.54 0.15-0.28 14.4-61.5 20.50 TEC(XLL) 1.35-1.50 0.10-0.15 33.9-63.4 8.80 SFC 1.67-1.80 0.04-0.09 55.9-60.9 5.31 SEC(SFC) 1.62-1.70 0.04-0.06 60.9-72.9 2.63 MEC(SFC) 1.66-1.80 0.03-0.06 68.2-87.8 3.54 TEC(SFC) 1.54-1.62 0.04-0.07 45.9-63.1 4.51 Table 7 Effective diffusion coefficients of raw coals and extracted coals
Sample De /(m2·h-1) Correlation coefficient XLL 6.1×10-8 0.96 SEC(XLL) 7.0×10-8 0.94 MEC(XLL) 4.2×10-8 0.96 TEC(XLL) 4.4×10-8 0.98 SFC 5.4×10-8 0.91 SEC(SFC) 5.6×10-8 0.93 MEC(SFC) 7.4×10-8 0.91 TEC(SFC) 5.7×10-8 0.97 -
[1] XIE K C, LI F, FENG J, LIU J S. Study on the structure and reactivity of swollen coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 64(1):241-251. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=04e4eb948b2dc8bf0a4df15a007d284d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [2] MARZEC A. Macromolecular and molecular model of coal structure[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1986, 14(86):39-46. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8a1613578a557c277afc85fd19cb6c48&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] ⅡNO M. Network structure of coals and association behavior of coal-derived materials[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 62(2):89-101. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3f767e5ce8ea5e40909b234c58c0b870&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [4] MARZEC A. Towards an understanding of the coal structure:A review[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2002, 77(25):25-32. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=996a7e2cc36e5b89bcd4f69460716f3a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] KRZESIN'SKA M. Averaged structural units in bituminous coals studied by means of ultrasonic wave velocity measurements[J]. Energy Fuels, 2001, 15(4):930-935. doi: 10.1021/ef0100101 [6] MONDRAGON F, QUINTERO G, JARAMILLO A, FERNANDEZA J, HALLB P J. The catalytic liquefaction of coal in the presence of ethanol[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1998, 53(3):171-181. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3820(97)00046-5 [7] STEPHENS H, KOTTENSTETTE R. Studies of coal reactivity for direct liquefaction[J]. Fuel, 1990, 70(3):386-392. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c5c97abf6cf19fbf34a1a0e05d73dec0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [8] JOSEPH J T. Liquefaction behavior of solvent-swollen coals[J]. Fuel, 1991, 70(2):139-144. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(91)90144-Y [9] MAE K, MAKI T, OKUTSU H, MIURA K. Examination of relationship between coal structure and pyrolysis yields using oxidized brown coals having different macromolecular networks[J]. Fuel, 2000, 79(3/4):417-425. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a3d76a8b29a2bd5ebf3eff110f989529&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [10] JOSEPH J T. Beneficial effects of preswelling on conversion and catalytic activity during coal liquefaction[J]. Fuel, 1991, 70(3):459-464. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(91)90139-2 [11] SHUI H F, LIU J L, WANG Z C, CAO M X, WEI X Y. Effect of pre-swelling of coal at mild temperatures on its hydro-liquefaction properties[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2009, 90(7/8):1047-1051. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2ea594c1b66d610ce43ac1cfcc222e2f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [12] MATHEWS J P, BURGESS-CLIFFORD C, PAINTER P. Interactions of Illinois No. 6 bituminous coal with solvents:A review of solvent swelling and extraction literature[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(3):1279-1294. doi: 10.1021/ef502548x [13] ⅡNO M, TAKANOHASHI T, OHSUGA H, TODA K. Extraction of coals with CS2-N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone mixed solvent at room temperature:Effect of coal rank and synergism of the mixed solvent[J]. Fuel, 1988, 67(12):1639-1647. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(88)90208-6 [14] SHIN Y J, SHEN Y W. Preparation of coal slurry with organic solvents[J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 68(2):389-393. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.049 [15] HU H Q, SHA G Y, CHEN G H. Effect of solvent swelling on liquefaction of Xinglong coal at less severe conditions[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 68(1):33-34. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3820(00)00101-6 [16] SHUI H F, WANG Z C, CAO M X. Effect of pre-swelling of coal on its solvent extraction and liquefaction properties[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(13/14):2908-2913. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a5ad33cb2e4615bd2c6262ebe20dc60d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [17] PINTO F, GULYURTLU I, LOBO L S, CABRITA I. Effect of coal pre-treatment with swelling solvents on coal liquefaction[J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(6):629-634. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(98)00193-8 [18] SZELIGA J, MARZEC A. Swelling of coal in relation to solvent electron-donor numbers[J]. Fuel, 1983, 62(10):1229-1231. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(83)90070-4 [19] PAINTER P C, PARK Y, SOBKOWIAK M, COLEMAN M M. Coal solubility and swelling. 2. Effect of hydrogen bonding on calculations of molecular weight from swelling measurements[J]. Energy Fuels, 1990, 4(4):384-393. doi: 10.1021/ef00022a009 [20] PAINTER P C, PARK Y, GRAF J F. Coal solubility and swelling[J]. Energy Fuels, 1990, 4(4):393-397. doi: 10.1021/ef00022a010 [21] LUCHT L M, PEPPAS N A. Macromolecular structure of coals:2. Molecular weight between crosslinks from pyridine swelling experiments[J]. Fuel, 1987, 66(6):803-809. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(87)90128-1 [22] NISHIOKA M. Evidence for the associated structure of bituminous coal[J]. Fuel, 1993, 72(12):1719-1724. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(93)90361-5 [23] OTAKE Y, SUUBERG E M. Temperature dependence of solvent swelling and diffusion process in coals[J]. Energy Fuels, 1997, 11(6):1155-1164. doi: 10.1021/ef970020v [24] QIN Z H, ZONG Z M, LIU J Z, MA H M, YANG M J, WEI X Y. Solubilities of lithotypes in carbon disulfide-N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone mixed solvent[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 1997, 25(6):549-553. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289181581_Solubilities_of_lithotypes_in_carbon_bisulfide-N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone_mixed_solvent [25] YOSHIDA T, TAKANOHASHI T, SAKANISHI K, SAITO I, FUJITA M, MASHIMO K. The effect of extraction condition on 'HyperCoal' production (1) under room-temperature filtration[J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(11/12):1463-1469. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ef0b52b3acf171cdb938430bc4980079&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [26] MIURA K, NAKAGAWA H, ASHIDA R, IHARA T. Production of clean fuels by solvent skimming of coal at around 350℃[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(6):733-738. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2003.09.019 [27] YOSHIDA T, LI C, TAKANOHASHI T, MATSUMURA A, SATO S, SAITO I. Effect of extraction condition on "HyperCoal" production (2) effect of polar solvents under hot filtration[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2004, 86(1):61-72. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2003.12.003 [28] WANG Z C, SHUI H F, PAN C X, LI L, REN S B, LEI Z P, KANG S G, WEI C, HU J C. Structural characterization of the thermal extracts of lignite[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2014, 120(120):8-15. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=60f10b63ef847a642be18b04c57081dc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [29] WANG Z C, LI L, SHUI H F, LEI Z P, REN S B, KANG S G. High temperature thermal extraction of Xianfeng lignite and FT-IR characterization of its extracts and residues[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2011, 39(6):401-406. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(11)60027-3 [30] WANG Z C, SHUI H F, PEI Z N, GAO J S. Study on the hydrothermal treatment of Shenhua coal[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(4):527-533. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=403d56cd654a34d96169b49f4c2b54e6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [31] OKOLO G N, EVERSON R C, NEOMAGUS H W J P, ROBERTS M J, SAKUROVS R. Comparing the porosity and surface areas of coal as measured by gas adsorption, mercury intrusion and SAXS techniques[J]. Fuel, 2015, 141(141):293-304. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7427a87b41e023d0394bd457267dbf98&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [32] ⅡNO M, TAKANOHASHI T, OBARA S, TSUETA H, SANKAWA Y. Characterization of the extracts and residues from CS2-N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone mixed solvent extraction[J]. Fuel, 1989, 68(12):1588-1593. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(89)90299-8 [33] OTAKE Y, SUUBERG E M. Solvent swelling rates of low rank coals and implications regarding their structure[J]. Fuel, 1998, 77(8):901-904. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(97)00256-1 [34] PANDE S, SHARMA D K. Studies of kinetics of diffusion of N-methyl-2-pyrrlidone (NMP), ethylenediamine (EDA) and NMP+EDA (1:1, vol/vol) mixed solvent system in Chinakuri coal by solvent swelling techniques[J]. Energy Fuels, 2001, 15(5):1063-1068. doi: 10.1021/ef9902395 [35] ESTAPE D, GODIA F, SOLA C. Determination of glucose and ethanol effective diffusion coefficients in Ca-alginate gel[J]. Enzyme Microb Technol, 1992, 14(5):396-401. doi: 10.1016/0141-0229(92)90009-D [36] RITGER P L, PEPPAS N A. Transport of penetrants in the macromolecular structure of coals, 7. Transport in thin coal sections[J]. Fuel, 1987, 66(10):1379-1388. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(87)90185-2 -





 下载:
下载: