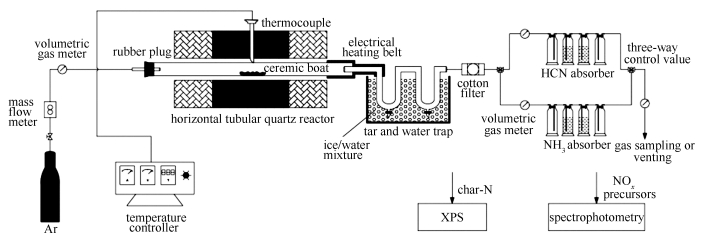
Characteristics of NOx precursors and their formation mechanism during pyrolysis of herb residues
-
摘要: 以凉茶药渣(HTW)和青霉素菌渣(PMW)为对象,结合热重(TGA)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)表征,在水平管式反应器上对比研究了热解NOx前驱物的生成特征,考察了热力因素和燃料理化特性的影响。结果表明,蛋白质N为主要原料N结构,HTW占全部,PMW超过80%,决定了主导NOx前驱物为NH3;热力因素不改变此主导性,但会影响前驱物生成路径,改变组分比例及总产率,其强弱顺序为:高温快速>高温慢速>低温快速≈低温慢速;基于高温快速热解,大粒径和低含水率可分别降低总产率5%-11%和4%-6%;燃料组分影响NH3产率,低温或慢速下,N结构差别使PMW>HTW;高温快速下,灰分元素差异使PMW < HTW;半焦N结构及N分布表明,典型热解条件下总产率为20%-45%,与药渣种类无关,可为其清洁利用提供参考。Abstract: Based on two herb residues-herbal tea waste (HTW) and penicillin mycelial waste (PMW), characteristics of NOx precursors during their pyrolysis were investigated in a horizontal tubular reactor with the help of XPS and TGA technologies. Effects of thermal conditions and physicochemical properties of fuels were discussed and compared. The results demonstrate that protein-N is the main nitrogen form for both HTW and PMW, determining the dominance of NH3 among NOx precursors at any operational conditions. Thermal conditions would still change the ratio and total yield by intrinsically influencing their formation pathways. Subsequently, the effects could be sequenced as follows:high temperatures with rapid pyrolysis > high temperatures with slow pyrolysis > low temperatures with rapid pyrolysis ≈ low temperatures with slow pyrolysis. Moreover, at high temperatures with rapid pyrolysis, increase in particle size or decrease in moisture content would result in reduction of total yield by 5%-11% and 4%-6%, respectively. In addition, NH3 yield is produced at low temperatures or slow pyrolysis with sequence of PMW > HTW and vice versa, depending on components in the fuels. Consequently, analyses on nitrogen forms in char and nitrogen distribution indicate that total yield of 20%-45% is observed to be independent of fuel type under typical pyrolysis conditions, which may provide helpful guidance for the clean reutilization of herb residues.
-
Key words:
- HTW /
- PMW /
- NOx precursors /
- pyrolysis /
- NH3 /
- total yield
-
表 1 药渣原料特性
Table 1 Properties of herb residues
Sample Proximate analysis wd/% Ultimate analysis wdsf/% V FC A C H S N Oa HTW 67.71 15.63 16.66 51.14 6.80 0.18 3.37 38.51 PMW 78.95 12.73 8.32 48.73 7.14 0.57 8.05 35.52 Ash analysis (expressed as w/% of metal oxides) SiO2 Al2O3 MgO Na2O Fe2O3 P2O5 CaO K2O TiO2 ZnO CuO SrO 21.98 7.92 7.66 0.40 4.82 4.56 20.78 7.64 0.44 0.09 0.03 0.08 0.39 0.14 3.62 2.85 0.50 30.82 22.64 19.15 0.01 0.09 0.02 0.03 a: by difference 表 2 实验因素及操作条件
Table 2 Operational conditions chosen for the experiments
Conditions Value range Pyrolysis temperature t/℃ 300, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 Heating rate r/(℃·min-1) slow pyrolysis: 15; rapid pyrolysis: about 103 Particle size d/μm 0-300, 300-600, 600-900 Moisture content w/% 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 -
[1] 许光文, 纪文峰, 刘周恩, 万印华, 张小勇.轻工生物质过程残渣高值化利用必要性与技术路线分析[J].过程工程学报, 2009, 9(3):618-624. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGYJ200903037.htmXU Guang-wen, JI Wen-feng, LIU Zhou-en, WAN Yin-hua, ZHANG Xiao-yong. Necessity and technical route of value-added utilization of biomass process residues in light industry[J]. Chin J Process Eng, 2009, 9(3):618-624. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGYJ200903037.htm [2] ZENG X, SHAO R Y, WANG F, DONG P W, YU J, XU G W. Industrial demonstration plant for the gasification of herb residue by fluidized bed two-stage process[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2016, 206:93-98. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.075 [3] DONG L, XU G W, SUDA T, MURAKAMI T. Potential approaches to improve gasification of high water content biomass rich in cellulose in dual fluidized bed[J].Fuel Process Technol, 2010, 91(8):882-888. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.12.012 [4] 邹艳敏, 吴静波, 仰榴青, 赵江丽, 吴向阳.中药渣的综合利用研究进展[J].江苏中医药, 2008, 40(12):113-115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSZY200812083.htmZOU Yan-min, WU Jing-bo, YANG Liu-qing, ZHAO Jiang-li, WU Xiang-yang. Research development on the comprehensive utilization of Chinese herb residues[J]. Jiangsu J Tradit Chin Med, 2008, 40(12):113-115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSZY200812083.htm [5] 冼萍, 钟莉莹, 王孝英.两面针药渣的热解气化利用特性分析[J].可再生能源, 2007, 25(1):26-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCNY200701007.htmXIAN Ping, ZHONG Li-ying, WANG Xiao-ying. The analyses of residue of anthoxylumnitidum decoction asgasification feedstock[J]. Renewable Energy Resour, 2007, 25(1):26-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCNY200701007.htm [6] WANG P, ZHAN S H, YU H B, XUE X F, HONG N. The effects of temperature and catalysts on the pyrolysis of industrial wastes (herb residue)[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2010, 101(9):3236-3241. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.082 [7] GUO F Q, DONG Y P, DONG L, JING Y Z. An innovative example of herb residues recycling by gasification in a fluidized bed[J]. Waste Manage, 2013, 33(4):825-832. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.12.009 [8] GUO F Q, DONG Y P, ZHANG T H, DONG L, GUO C W, RAO Z H. Experimental study on herb residue gasification in an air-blown circulating fluidized bed gasifier[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2014, 53(34):13264-13273. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272144046_Experimental_Study_on_Herb_Residue_Gasification_in_an_Air-Blown_Circulating_Fluidized_Bed_Gasifier [9] 杨帅, 张兆玲, 孟剑锋, 董玉平, 梁敬翠, 盖超, 范鹏飞.循环流化床中菌渣热解气化特性的研究[J].高校化学工程学报, 2015, 29(4):997-1002. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXHX201504031.htmYANG Shuai, ZHANG Zhao-ling, MENG Jian-feng, DONG Yu-ping, LIANG Jing-cui, GAI Chao, FAN Peng-fei. Study on pyrolysis gasification of fungus residues in circulating fluidized beds[J]. J Chem Eng Chin Univ, 2015, 29(4):997-1002. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXHX201504031.htm [10] 尤占平, 郝长生, 焦永刚, 赵亮, 封春红.两种抗生素菌渣热解及燃烧特性对比研究[J].工业安全与环保, 2016, 42(5):41-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYAF201605015.htmYOU Zhan-ping, HAO Chang-sheng, JIAO Yong-gang, ZHAO Liang, FENG Chun-hong. Pyrolysis and combustion characteristics comparison studies of two kinds of antibiotic residues[J]. Ind Safety Environ Prot, 2016, 42(5):41-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYAF201605015.htm [11] 贡丽鹏.土霉素菌渣热解技术的研究[D].石家庄:河北科技大学, 2012.GONG Li-peng. Research on pyrolysis technology of terramycin bacterial residue[D]. Shijiazhuang:Hebei University of Science & Technology, 2012. [12] HANSSON K M, SAMUELSSON J, TULLIN C, AMAND L E. Formation of HNCO, HCN, and NH3 from the pyrolysis of bark and nitrogen-containing model compounds[J].Combust Flame, 2004, 137(3):265-277. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2004.01.005 [13] GB 13271-2014, 锅炉大气污染物排放标准[S].GB 13271-2014, Emission standard of air pollutants for boiler[S]. [14] BALAT M, BALAT M, KIRTAY E, BALAT H. Main routes for the thermo-conversion of biomass into fuels and chemicals. Part 1:Pyrolysis systems[J].Energ Convers Manage, 2009, 50(12):3147-3157. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2009.08.014 [15] TIAN F J, LI B Q, CHEN Y, LI C Z. Formation of NOx precursors during the pyrolysis of coal and biomass. Part Ⅴ. Pyrolysis of a sewage sludge[J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(17):2203-2208. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00139-4 [16] BECIDAN M, SKREIBERG O, HUSTAD J E. NOx and N2O precursors (NH3 and HCN) in pyrolysis of biomass residues[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(2):1173-1180. doi: 10.1021/ef060426k [17] YUAN S, ZHOU Z J, LI J, CHEN X L, WANG F C. HCN and NH3 released from biomass and soybean cake under rapid pyrolysis[J]. Energy Fuels, 2010, 24(11):6166-6171. doi: 10.1021/ef100959g [18] REN Q Q, ZHAO C S, WU X, LIANG C, CHEN X P, SHEN J Z, WANG Z. Formation of NOx precursors during wheat straw pyrolysis and gasification with O2 and CO2[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(5):1064-1069. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.12.001 [19] CHEN H F, WANG Y, XU G W, YOSHIKAWA K. Fuel-N evolution during the pyrolysis of industrial biomass wastes with high nitrogen content[J]. Energies, 2012, 5(12):5418-5438. doi: 10.3390/en5125418 [20] TIAN F J, YU J L, MCKENZIE L J, HAYASHI J, LI C Z. Conversion of fuel-N into HCN and NH3 during the pyrolysis and gasification in steam:A comparative study of coal and biomass[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(2):517-521. doi: 10.1021/ef060415r [21] AZNAR M, ANSELMO M S, MANYA J J, MURILLO M B. Experimental study examining the evolution of nitrogen compounds during the gasification of dried sewage sludge[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23:3236-3245. doi: 10.1021/ef801108s [22] KELEMEN S R, AFEWORKI M, GORBATY M L, KWIATEK P J, SANSONE M, WALTERS C C, COHEN A D. Thermal transformations of nitrogen and sulfur forms in peat related to coalification[J]. Energy Fuels, 2006, 20(2):635-652. doi: 10.1021/ef050307p [23] TIAN Y, ZHANG J, ZUO W, CHEN L, CUI Y N, TAN T. Nitrogen conversion in relation to NH3 and HCN during microwave pyrolysis of sewage sludge[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2013, 47(7):3498-3505. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235904520_Nitrogen_Conversion_in_Relation_to_NH3_and_HCN_during_Microwave_Pyrolysis_of_Sewage_Sludge [24] WEI L H, WEN L, YANG T H, ZHANG N. Nitrogen transformation during sewage sludge pyrolysis[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(8):5088-5094. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b00792 [25] ZHANG J, TIAN Y, CUI Y N, ZUO W, TAN T. Key intermediates in nitrogen transformation during microwave pyrolysis of sewage sludge:A protein model compound study[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2013, 132:57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.008 [26] CHEN H F, NAMIOKA T, YOSHIKAWA K. Characteristics of tar, NOx precursors and their absorption performance with different scrubbing solvents during the pyrolysis of sewage sludge[J]. Appl Energy, 2011, 88(12):5032-5041. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.07.007 [27] TIAN K, LIU W J, QIAN T T, JIANG H, YU H Q. Investigation on the evolution of N-containing organic compounds during pyrolysis of sewage sludge[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2014, 48(18):10888-10896. doi: 10.1021/es5022137 [28] BEIS S H, ONAY O, KOCKAR O M. Fixed-bed pyrolysis of safflower seed:Influence of pyrolysis parameters on product yields and compositions[J]. Renewable Energy, 2002, 26(1):21-32. doi: 10.1016/S0960-1481(01)00109-4 [29] TIAN F J, YU J L, MCKENZIE L J, HAYASHI J, LI C Z. Formation of NOx precursors during the pyrolysis of coal and biomass. Part Ⅸ. Effects of coal ash and externally loaded-Na on fuel-N conversion during the reforming of coal and biomass in steam[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(10/11):1411-1417. [30] REN Q Q, ZHAO C S, WU X, LIANG C, CHEN X P, SHEN J Z, TANG G Y, WANG Z. Effect of mineral matter on the formation of NOx precursors during biomass pyrolysis[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2009, 85(1/2):447-453. [31] REN Q Q, ZHAO C S, WU X, LIANG C, CHEN X P, SHEN J Z, WANG Z. Catalytic effects of Fe, Al and Si on the formation of NOx precursors and HCl during straw pyrolysis[J]. J Therm Anal Calorim, 2010, 99(1):301-306. doi: 10.1007/s10973-009-0150-0 [32] ZHOU J Q, GAO P, DONG C Q, YANG Y P. TG-FTIR analysis of nitrogen conversion during straw pyrolysis:A model compound study[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(12):1427-1432. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(16)30001-9 [33] 袁帅, 李军, 陈雪莉, 代正华, 周志杰, 王辅臣.吡咯型氮快速热解中NH3和HCN生成机理研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2011, 39(11):801-805. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/Y2011/V39/I06/413YUAN Shuai, LI Jun, CHEN Xue-li, DAI Zheng-hua, ZHOU Zhi-jie, WANG Fu-chen. Study on NH3 and HCN formation mechanisms during rapid pyrolysis of pyrrolic nitrogen[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2011, 39(11):801-805. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/Y2011/V39/I06/413 -





 下载:
下载: