Effect of chemical structure and sulfur speciation of high-sulfur coking coals on sulfur transformation during pyrolysis
-
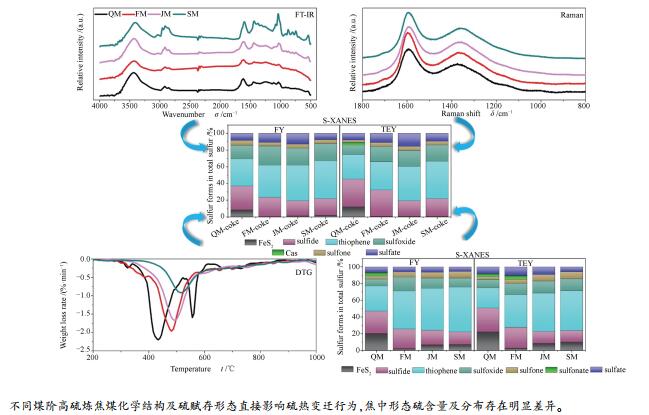
摘要: 利用红外、拉曼、热重及XANES等技术对不同煤阶高硫炼焦煤的化学结构、原煤及焦样形态硫分布进行了准确判定, 对煤中化学结构及硫赋存形态与硫的热变迁行为进行了关联分析。结果表明, 高硫炼焦煤中硫的热变迁行为不仅与硫赋存形态有关, 而且受化学结构不同的高硫炼焦煤热解挥发分释放特性的影响。较低煤阶高硫炼焦煤中脂肪结构热分解产生大量挥发分, 且挥发分释放温区较宽, 形态硫分解产生的活性硫与挥发分中富氢组分相结合, 形成更多的含硫气体转移到气相中, 提高了热解脱硫率, 焦炭体相中噻吩硫相对含量高于表面, 硫化物硫则与之相反。煤化程度升高, 煤中稳定噻吩类硫含量增多, 挥发分释放量减少, 热解脱硫率降低, 且形态硫在焦炭体相与表面的分布差异不明显。无机硫脱除率与黄铁矿硫分解程度直接相关, 热解过程中也将形成部分新的无机硫滞留于焦中。煤结构及有机硫的赋存形态决定了有机硫脱除率, 煤阶升高时有机硫脱除率明显降低。Abstract: The chemical structure, content and distribution of sulfur forms in coal and coke of four high-sulfur coking coals were characterized by FT-IR, Raman, TG, and sulfur K-edge XANES technique, and effects on sulfur transformation during pyrolysis were also investigated. The results show that sulfur transformation behavior is related to the sulfur forms in coal as well as the release of volatile matters during pyrolysis. For lower rank coking coals, decomposition of unstable aliphatic structure releases plenty of volatiles with wider range. The interactions between sulfur radicals from cleavage of sulfur forms and hydrogen-rich radicals in volatiles promote release of sulfur into gas phase. This increases total sulfur removal and results in the higher content of thiophene in coke bulk than that on coke surface, while sulfide compounds have an opposite distribution. The degree of aromatization and relative content of thiophene increase with increasing coal rank, leading to lower desulfurization rate and unapparent difference of sulfur distribution between bulk and surface of coke. Inorganic sulfur removal is related to degree of decomposition of pyrite directly, and inter-conversions of sulfur species during pyrolysis process would generate new inorganic sulfur and retain in coke ultimately. Organic sulfur removal is determined by the coal structure and organic sulfur forms, and decreases obviously with increasing coal rank.
-
Key words:
- high-sulfur coking coal /
- pyrolysis /
- chemical structure /
- sulfur forms /
- XANES
-
表 1 高硫炼焦煤分析数据
Table 1 Analysis of the high-sulfur coking coals
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysisw/% Sulfur form wd/% G Y/mm Mad Ad Vdaf Cdaf Hdaf Ndaf Sd O* Ss Sp So* QM 0.81 9.93 42.28 74.99 5.32 1.41 2.42 15.59 0.01 0.86 1.55 94 17.9 FM 0.19 9.14 28.48 83.35 4.84 1.35 3.88 6.19 0.07 0.07 3.74 100 33.2 JM 0.71 8.53 24.72 90.46 4.83 1.59 1.42 1.57 0.04 0.16 1.22 93 25 SM 0.61 10.94 16.19 90.91 4.34 1.42 2.32 0.72 0.03 0.30 1.99 19 - note: ad: air dried basis; d: dry basis; daf: dry and ash-free basis; Sp: pyritic sulfur; Ss: sulfate sulfur; So: organic sulfur; *: by difference 表 2 高硫炼焦煤灰成分分析
Table 2 Ash composition of the high-sulfur coking coals
Sample Ash composition w/% AI SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO TiO2 SO3 K2O Na2O P2O5 QM 56.98 24.64 6.16 5.17 1.39 1.44 1.48 1.34 0.38 0.28 0.34 FM 47.44 37.76 2.62 3.46 0.22 1.77 3.18 1.93 0.66 0.09 0.10 JM 49.84 39.07 3.13 1.84 0.32 1.62 0.90 0.31 0.84 0.34 0.07 SM 48.53 41.31 3.84 1.72 0.31 1.39 0.56 0.16 0.45 0.10 0.07 表 3 高硫炼焦煤红外光谱结构参数
Table 3 Structure parameters of FT-IR spectra of the high-sulfur coking coals
Sample fa I1 I2 I3 QM 0.59 0.17 0.03 1.02 FM 0.68 0.22 0.05 1.94 JM 0.74 0.30 0.07 2.00 SM 0.77 0.38 0.08 2.55 表 4 拉曼光谱分峰拟合结构参数
Table 4 Sructure parameters from curve fitting of Raman spectra
Sample W-D/cm-1 W-G/cm-1 FWHM-G/cm-1 ID/IG ID/I(GR+VR+VL) IS/IG QM 1373 1592 74.13 0.50 0.26 0.26 FM 1365 1594 66.36 0.61 0.22 0.30 JM 1360 1592 67.12 0.66 0.29 0.28 SM 1353 1593 63.68 0.67 0.32 0.34 表 5 高硫炼焦煤的热重分析结果
Table 5 Thermogravimetric analysis results of the high-sulfur coking coals
Sample Temperature t/℃ wmax /(%·min-1) ti> teo tf tef tmax QM 300 387 855 600 433, 560 -2.19, -1.48 FM 320 426 850 580 482 -1.96 JM 345 453 850 573 494 -1.67 SM 400 485 850 600 517 -0.91 note: ti:initial temperature; teo: extrapolated onset temperature; tf: final temperature; tef: extrapolated final temperature; tmax: maximum weight loss temperature; wmax: maximum weight loss rate 表 6 高硫炼焦煤单独热解焦产率, 焦中硫含量及脱硫率
Table 6 Coke yield, sulfur content in coke and desulfurization rate during pyrolysis of the high-sulfur coking coals
Sample Coke yield w/% Sulfur content in coke/% Total sulfur removal/% Inorganic sulfur removal/% Organic sulfur removal/% QM 61.00 1.84 53.62 71.06 47.19 FM 72.33 3.26 39.23 16.07 41.26 JM 75.00 1.26 33.45 42.21 32.12 SM 79.67 2.45 15.87 37.74 12.71 -
[1] 么秋香, 杜美利, 王水利, 刘静, 杨建利, 上海涛.高硫煤中形态硫的热解迁移特性[J].煤炭转化, 2012, 35(2):17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2012.02.004YAO Qiu-xiang, DU Mei-li, WANG Shui-li, LIU Jing, YANG Jian-li, SHANG Hai-tao.Charateristics of sulfur forms transformation in high sulfur coal transformation[J].Coal Convers, 2012, 35(2):17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2012.02.004 [2] 李梅, 杨俊和, 夏红波, 常海洲, 孙慧.典型炼焦高硫煤热解过程中硫迁移规律研究[J].煤炭转化, 2013, 36(4):41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2013.04.010LI Mei, YANG Jun-he, XIA Hong-bo, CHANG Hai-zhou, SUN Hui.Behavior of sulfur transformation during pyrolysis of high-sulfur coking coals[J].Coal Convers, 2013, 36(4):41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2013.04.010 [3] 李梅, 杨俊和, 张启锋, 常海洲, 孙慧.用XPS研究新西兰高硫煤热解过程中氮、硫官能团的转变规律[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(11):1287-1293. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb201311002LI Mei, YANG Jun-he, ZHANG Qi-feng, CHANG Hai-zhou, SUN Hui.XPS study on transformation of N-and S-functional groups during pyrolysis of high sulfur New Zealand coal[J].J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(11):1287-1293. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb201311002 [4] YAN J, YANG J, LIU Z.SH radical:The key intermediate in sulfur transformation during thermal processing of coal[J].Environ Sci Technol, 2005, 39(13):5043-5051. doi: 10.1021/es048398c [5] ZHANG G, DU Y, ZHANG Y, XU Y.Desulfurization reaction model and experimental analysis of high sulfur coal under hydrogen atmosphere[J].J Ind Eng Chem, 2014, 20(2):487-493. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c816523ce1edbb70e5b49b7ff9b28f81 [6] CHEN H, LI B, YANG J, ZHANG B.Transformation of sulfur during pyrolysis and hydropyrolysis of coal[J].Fuel, 1998, 77(6):487-493. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(97)00275-5 [7] GU Y, YPERMAN J, REGGERS G, CARLEER R, VANDEWIJNGAARDEN J.Characterisation of volatile organic sulphur compounds release during coal pyrolysis in inert, hydrogen and CO2 atmosphere[J].Fuel, 2016, 184:304-313. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.06.085 [8] JORJANI E, YPERMAN J, CARLEER R, REZAI B.Reductive pyrolysis study of sulfur compounds in different Tabas coal samples (Iran)[J].Fuel, 2006, 85(1):114-120. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3f3aeb264de28d25709ea46efa847faa [9] 刘粉荣, 李文, 李保庆, 白宗庆.常压程序升温还原-质谱法研究遵义煤在热解过程中硫的变迁行为[J].燃料化学学报, 2008, 36(1):6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2008.01.002LIU Fen-rong, LI Wen, LI Bao-qing, BAI Zong-qing.Sulfur transformation during pyrolysis of Zunyi coal by atmosphere pressure-temperature programmed reduction-mass spectrum[J].J Fuel Chem Technol, 2008, 36(1):6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2008.01.002 [10] 苏海强.内蒙高硫煤配煤炼焦的研究与应用[J].燃料与化工, 2011, 42(3):43-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3709.2011.03.019SU Hai-qiang.Study and application of blending coking of Inner mongolia high sulfur coal[J].Fuel Chem Process, 2011, 42(3):43-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3709.2011.03.019 [11] 温增光, 邓彤.利用现有装置大比例使用高硫煤生产焦炭的实践探索[J].煤化工, 2017, 45(5):57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9598.2017.05.014WEN Zeng-guang, DENG Tong.Practical exploration of coking with large proportion high sulfur coal using the existing equipment[J].Coal Chem Ind, 2017, 45(5):57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9598.2017.05.014 [12] ORREGO-RUIZ J, CABANZO R, MEJIA-OSPINO E.Study of colombian coals using photoacoustic fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[J].Int J Coal Geol, 2011, 85(3):307-310. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f4bd2fcb76d8c21a091af94aac8184f5 [13] HE X, LIU X, NIE B, SUN D.FT-IR and Raman spectroscopy characterization of functional groups in various rank coals[J].Fuel, 2017, 206:555-563. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.05.101 [14] IBARRA J, MOLINER R, BONET A J.FT-I.R.investigation on char formation during the early stages of coal pyrolysis[J].Fuel, 1994, 73(6):918-924. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(94)90287-9 [15] IBARRA J, MU OZ E, MOLINER R.FT-IR study of the evolution of coal structure during the coalification process[J].Org Geochem, 1996, 24(6/7):725-735. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222789181_FTIR_Study_of_the_Evolution_of_Coal_Structure_during_the_Coalification_Process [16] LI K, KHANNA R, ZHANG J, BARATI M, LIU Z, XU T, YANG T, SAHAJWALLA V.Comprehensive investigation of various structural features of bituminous coals using advanced analytical techniques[J].Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(11):7178-7189. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b02064 [17] LI X, HAYASHI J, LI C-Z.FT-Raman spectroscopic study of the evolution of char structure during the pyrolysis of a victorian brown coal[J].Fuel, 2006, 85(12/13):1700-1707. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5f1d929e70499f5b83966ba0dfc5e28c [18] HINRICHS R, BROWN M, VASCONCELLOS M, ABRASHEV M, KALKREUTH W.Simple procedure for an estimation of the coal rank using micro-Raman spectroscopy[J].Int J Coal Geol, 2014, 136:52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2014.10.013 [19] MORGA R, JELONEK I, KRUSZEWSKA K.Relationship between coking coal quality and its micro-Raman spectral characteristics[J].Int J Coal Geol, 2014, 134/135:17-23. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6ff41f755f42d3d02c7caf60bfcd3d4b [20] BAYSAL M, YURUM A, YILDIZ B, YURUM Y.Structure of some western Anatolia coals investigated by FT-IR, Raman, 13C solid state NMR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction[J].Int J Coal Geol, 2016, 163:166-176. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.07.009 [21] GUEDES A, VALENTIM B, PRIETO A C, RODRIGUES S, NORONHA F.Micro-Raman spectroscopy of collotelinite, fusinite and macrinite[J].Int J Coal Geol, 2010, 83(4):415-422. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2010.06.002 [22] WANG M, HU Y, WANG J, CHANG L, WANG H.Transformation of sulfur during pyrolysis of inertinite-rich coals and correlation with their characteristics[J].J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2013, 104(10):585-592. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7cfea0e528f783636a751ecbfb431df5 [23] SHEN Y, WANG M, HU Y, KONG J, WANG J, CHANG L, BAO W.Transformation and regulation of sulfur during pyrolysis of coal blend with high organic-sulfur fat coal[J].Fuel, 2019, 249:427-433. [24] PRIETZEL J, BOTZAKI A, TYUFEKCHIEVA N, BRETTHOLLE M, THIEME J, KLYSUBUN W.Sulfur speciation in soil by S K-Edge XANES spectroscopy:Comparison of spectral deconvolution and linear combination fitting[J].Environ Sci Technol, 2011, 45(7):2878-2886. doi: 10.1021/es102180a [25] LIU L, FEI J, CUI M, HU Y, WANG J.XANES spectroscopic study of sulfur transformations during co-pyrolysis of a calcium-rich lignite and a high-sulfur bituminous coal[J].Fuel Process Technol, 2014, 121:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2013.12.008 [26] WALDO G, MULLINS O, PENNER-HAHN J, CRAMER S.Determination of the chemical environment of sulphur in petroleum asphaltenes by X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J].Fuel, 1992, 71(1):53-57. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/001623619290192Q [27] 尹浩, 刘桂建, 刘静静.煤热解过程中含硫气体的释放特征[J].环境化学, 2012, 31(3):330-334. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjhx201203010YIN Hao, LIU Gui-jian, LIU Jing-jing.Release of sulfur containing gases during coal pyrolysis[J].Environ Chem, 2012, 31(3):330-334. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjhx201203010 [28] 秦跃强, 陈雪莉, 陈汉鼎, 刘海峰.添加CaO对煤热解过程中砷和硫迁移转化的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(2):147-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.02.003QIN Yue-qiang, CHEN Xue-li, CHEN Han-ding, LIU Hai-feng.Effects of adding CaO on the release and transformation of arsenic and sulfur during coal pyrolysis[J].J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(2):147-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.02.003 [29] GUAN R, LI W, LI B.Effects of Ca-based additives on desulfurization during coal pyrolysis[J].Fuel, 2003, 82(15/17):1961-1966. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f2bad4d050b18bff815c25bc4baeeb29 [30] WANG B, ZHAO S, HUANG Y, ZHANG J.Effect of some natural minerals on transformation behavior of sulfur during pyrolysis of coal and biomass[J].J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2014, 105:284-294. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.11.015 -





 下载:
下载: