Effect of inorganic acid elution on microcrystalline structure and spontaneous combustion tendency of Shengli lignite
-
摘要: 利用XRD、Raman、XPS和FT-IR表征技术,研究无机酸洗脱(HCl、H2SO4、HCl-HF)处理的胜利褐煤微晶结构的变化,采用自行设计的表面吸附仪-GC联用装置,对样品进行不同温度的低温脉冲氧化实验,考察了煤样在不同温度下氧吸附量的变化规律,通过低温脉冲氧吸附规律与TG/DTG和固定床燃烧实验关联,考察了煤样的自燃倾向。结果表明,无机酸洗脱对矿物质的脱除使得煤结构的有序度增加,石墨化程度提高,无机酸洗脱煤样与原煤相比吸氧量明显下降。随着吸附温度的升高,各煤样吸氧量明显增加,且随着脱除矿物质程度的增加,吸氧量呈减小的趋势,导致自燃倾向降低。Abstract: XRD, Raman, XPS and FT-IR were used to examine microcrystalline structure changes of Shengli lignite eluted by inorganic acid (HCl, H2SO4 and HCl-HF). By adopting a designed surface adsorption instrument-GC, the samples were oxidized at low temperature through pulse method to investigate their oxygen adsorption under different temperatures. Via low-temperature oxidation, TG/DTG and fixed bed combustion tests, the spontaneous combustion tendency of coal samples were investigated. The results show that the removal of minerals increases the degree of order and graphitization of the coal structure. Compared with raw coal, oxygen absorption of inorganic acid elution samples decreases obviously. With the increase of adsorption temperature, oxygen absorption capacity increases significantly, but decreases with the increasing level of removed minerals, which reduces spontaneous combustion tendency of the treated coal.
-
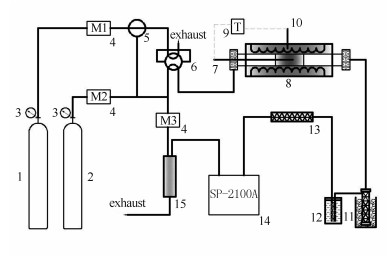
图 1 低温氧化反应实验流程示意图
1: adsorbed gas; 2: carrier gas; 3: pressure reducing valve4: mass flow meter; 5: triple valve; 6: six-port valve; 7: temperature thermocouple; 8: adsorbor; 9: temperature controller; 10: temperature control thermocouple; 11: ice-bath; 12: cold-hydrazine; 13: purifier; 14: chromatographic; 15: thermal conductivity cell
Figure 1 Experiment flowchart of low temperature oxidation
表 1 煤样的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analysis of coal samples
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis w/% Mad Ad Vd FCd C H N S O* SR 1.52 13.92 33.37 52.71 57.59 3.58 0.89 1.81 22.21 SC 2.14 7.53 39.77 52.70 61.42 3.34 0.86 1.74 25.10 SS 2.60 5.35 33.26 58.79 58.16 4.21 0.87 1.78 27.03 SFC 2.18 1.14 41.97 56.89 64.90 4.88 0.91 1.69 26.48 *:by difference 表 2 洗脱煤样及所对应灰分中主要金属元素含量
Table 2 Metal ion percentage in coal samples and ashes
Coal sample Coal based/ash based w/% Al3+ Na+ Ca2+ Si4+ Fen+ K+ Mnn+ SR 2.40/35.50 0.58/8.59 0.41/6.08 3.11/46.09 0.11/1.69 0.08/1.18 0.06/0.88 SC 0.90/32.94 0.00/0.16 0.01/0.19 2.89/64.58 0.03/0.92 0.03/1.18 0.00/0.03 SS 0.87/31.21 0.00/0.12 0.05/6.01 0.75/61.36 0.04/1.03 0.00/0.12 0.00/0.15 SFC 0.11/41.77 0.00/1.03 0.01/2.10 0.14/53.31 0.00/1.22 0.00/0.13 0.00/0.45 表 3 煤样的微晶结构参数
Table 3 Microcrystalline structure parameters of coal samples
Coal
sampled002 /nm La /nm Lc /nm N fa SR 0.366 1.220 0.754 2.062 0.519 SC 0.357 1.471 0.773 2.162 0.531 SS 0.354 1.816 0.802 2.263 0.547 SFC 0.353 2.474 0.853 2.413 0.563 表 4 煤样的Raman结构参数
Table 4 Raman structure parameters of coal samples
Coal sample SR SC SS SFC ID/IG 0.921 8 0.885 5 0.857 3 0.843 4 IS/IG 0.445 4 0.352 5 0.237 9 0.209 7 ID/I(VR+VL+GR) 0.463 0 0.721 1 0.739 5 0.750 4 表 5 煤样的XPS C 1s拟合结果
Table 5 XPS C 1s fitting results of coal samples
E/eV Carbon form Content wmol/% SR SC SS SFC 284.6 C-C, C-H 83.91 84.80 81.77 79.42 286.4 C-O 10.84 8.58 9.29 10.62 287.5 C=O 3.14 3.55 4.98 5.88 289.0 COO- 2.11 3.07 3.96 4.08 表 6 煤样氧消耗量与氧化温度的关系
Table 6 Relationship between O2 consumption of coals and oxidation temperature
TEMP t/℃ O2 consumption/(×10-2 mmol·g-1) SR SC SS SFC 60 0.13 0.19 0.18 0.15 90 0.39 0.73 0.46 0.25 110 0.53 0.86 0.64 0.46 140 1.86 1.53 1.10 0.64 160 8.45 3.09 3.03 2.62 -
[1] 曾凡桂, 谢克昌.煤结构化学的理论体系与方法论[J].煤炭学报, 2004, 4(29): 443-447. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB200404015.htmZENG Fan-gui, XIE Ke-chang. Theoretical system and methodology of coal structural chemistry[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2004, 4(29): 443-447. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB200404015.htm [2] 石婷, 邓军, 王小芳, 文振翼.煤自燃初期的反应机理研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2004, 32(6): 652-657. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16607.shtmlSHI Ting, DENG Jun, WANG Xiao-fang, WEN Zhen-yi. Mechanism of spontaneous combustion of coal at initial stage[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2004, 32(6): 652-657. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16607.shtml [3] GOUWS M J, GIBBON G J, WADE L, PHILLIPS H R. An adiabatic apparatus to establish the spontaneous combustion propensity of coal[J]. Min Sci Technol, 1991, 13(3): 417-422. doi: 10.1016/0167-9031(91)90890-O [4] 秦波涛, 王德明, 李增华, 马汉鹏.以活化能的观点研究煤炭自燃机理[J].中国安全科学学报, 2005, 15(1): 11-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK200501003.htmQIN Bo-tao, WANG De-ming, LI Zeng-hua, MA Han-peng. Study on the mechanism of coal spontaneous combustion with activated energy view[J]. China Safety Sci J, 2005, 15(1): 11-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK200501003.htm [5] TIAN L, YANG W, CHEN Z, WANG X, YAGN H, CHEN H. Sulfur behavior during coal combustion in oxy-fuel circulating fluidized bed condition by using TG-FTIR[J]. J Energy Inst, 2016, 89(2): 264-270. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2015.01.020 [6] MARTIN R R, MACPHEE J A, YOUNGER C. Sequential derivation and the SIMS imaging of coal[J]. Energy Source, 1989, 11(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1080/00908318908908936 [7] 舒新前.煤炭自燃的热分析研究[J].中国煤田地质, 1994, 25(2): 25-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT402.005.htmSHU Xin-qian. The thermogravity analysis study on the spontaneous combustion of coal[J]. Coal Geology China, 1994, 25(2): 25-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT402.005.htm [8] 戴广龙.煤低温氧化过程中微晶结构变化规律研究[J].煤炭学报, 2011, 36(2): 322-325. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201102032.htmDAI Guang-long. Research on microcrystalline structure change regularity in the coal low temperature oxidation process[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2011, 36(2): 322-325. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201102032.htm [9] LI Y, YANGH, HU J, WANG X, CHEN H. Effect of catalysts on the reactivity and structure evolution of char in petroleum coke steam gasification[J]. Fuel, 2014, 117(Part B): 1174-1180. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274022208_Effect_of_catalysts_on_the_reactivity_and_structure_evolution_of_char_in_petroleum_coke_steam_gasification?_sg=9KtgfZkTvR_QRfQthbDUeZptlgspWBc1erWVlPtqA7R88An920qHsO_y-nDjtKjX5WtIOo2mYYsk_xTTif6Zaw [10] LI X, HAYASHI J, LI C Z. FT-Raman spectroscopic study of the evolution of char structure during the pyrolysis of a Victorian brown coal[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(12): 1700-1707. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/244067993_FT-Raman_Spectroscopic_Study_of_the_Evolution_of_Char_Structure_During_the_Prolysis_of_a_Victorian_Brown_Coal [11] NEMANICH R J, GLASS J T, LUCOVSKY G, SHRODER R E. Raman scattering characterization of carbon bonding in diamond and diamond like thin films[J]. J Vac Sci Technol A, 1988, 6(3): 1783-1787. doi: 10.1116/1.575297 [12] LI X, LI C Z.Volatilisation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal. Part VII. Raman spectroscopic study on the changes in char structure during the catalytic gasification in air[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(10/11): 1509-1507. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/244067894_Volatilisation_and_catalytic_effects_of_alkali_and_alkaline_earth_metallic_species_during_the_pyrolysis_and_gasification_of_Victorian_brown_coal_Part_VII_Raman_spectroscopic_study_on_the_changes_in_ch [13] LI X, LI C Z. FT-Raman spectroscopic characterisation of chars from the pyrolysis of coals of varying rank[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2005, 33(4): 385-390. [14] SONIBARE O O, HAEGER T, FOLEY S F. Structural characterization of Nigerian coals by X-ray diffraction, Raman and FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Energy, 2010, 35(12): 5347-5353. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2010.07.025 [15] ESTRADE-SZWARCKOPF H. XPS photoemission in carbonaceous materials: A "defect" peak beside the graphitic asymmetric peak[J]. Carbon, 2004, 42(8): 1713-1721. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/239211487_XPS_photoemission_in_carbonaceous_materials_A_defect_peak_beside_the_graphitic_asymmetric_peak [16] WANG B, PENG Y, VINK S. Diagnosis of the surface chemistry effects on fine coal flotation using saline water[J]. Energy Fuels, 2013, 27(8): 4869-4874. doi: 10.1021/ef400909r [17] HU Y, LI P, HU N, HU S, DOU S, YANG G. Inorganic element functional group database on pulverized coal surface based on XPS method[J]. Data Sci J, 2007, 6: S317-S323. doi: 10.2481/dsj.6.S317 [18] XIA W, YANG J, LIANG C. Investigation of changes in surface properties of bituminous coal during natural weathering processes by XPS and SEM[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 293: 293-298. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.12.151 [19] KOZLOWSKI M. XPS study of reductively and non-reductively modified coals[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(3): 259-265. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2003.08.004 [20] DONG P, CHEN G, ZENG X, CHU M, GAO S, XU G. Evolution of inherent oxygen in solid fuels during pyrolysis[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(4): 2268-2276. doi: 10.1021/ef5028839 [21] MIURA K, MAE K, LI W, KUSAKAWA T, MOROZUMI F, KUMANO A. Estimation of hydrogen bond distribution in coal through the analysis of OH stretching bands in diffuse reflectance infrared spectrum measured by in-situ technique[J]. Energy Fuels, 2001, 15(3): 599-610. doi: 10.1021/ef0001787 [22] GENG W, NAKAJIMA T, TAKANASHI H, OHKI A. Analysis of carboxyl group in coal and coal aromaticity by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrometry[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(1): 139-144. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.07.027 [23] QI X, GUO X, XUE L, ZHENG C. Effect of iron on Shenfu coal char structure and its influence on gas ification reactivity[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2014, 110: 401-407. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2014.10.011 [24] LU L, SAHAJWALLA V, HARRIS D. Characteristics of chars prepared from various pulverized coals at different temperatures using drop-tube furnace[J]. Energy Fuels, 2000, 14(4): 869-876. doi: 10.1021/ef990236s [25] HECKLEY E. The structural changes of hydrothermally treated biochar caused by ball-milling[D]. Norcester: Worcester Polytechnic Institute, 2014. [26] XIA W, YANG J, LIANG C. Investigation of changes in surface properties of bituminous coal during natural weathering processes by XPS and SEM[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 293: 293-298. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.12.151 [27] KOZLOWSKI M. XPS study of reductively and non-reductively modified coals[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(3): 259-265. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2003.08.004 [28] KELEMEN S R, AFEWORKI M, GORBATY M L, COHEN A D. Characterization of organically bound oxygen forms in lignites, peats, and pyrolyzed peats by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and solid-state 13C NMR methods[J]. Energy Fuels, 2002, 16(6): 1450-1462. doi: 10.1021/ef020050k [29] 胡艺.污泥干燥及干污泥与煤混烧官能团演化研究[D].湖北:武汉大学, 2010: 40-42.HU-Yi. Research on sewage sludge drying and functionality evolution during co-combustion of dry sewag sludge and coal[D]. Hubei:Wuhan University, 2010: 40-42. [30] 杨永良, 李增华, 尹文宣, 潘尚昆.易自然煤漫反射红外光谱特征[J].煤炭学报, 2007, 32(7): 729-733.YANG Yong-liang, LI Zeng-hua, YIN Wen-xuan, PAN Shang-kun. Infrared diffuse reflectance spectral signature of spontaneous combustion coal[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2007, 32(7): 729-733. -





 下载:
下载: