-
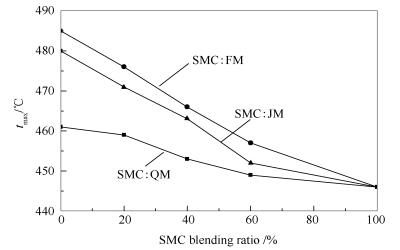
摘要: 利用程序升温热天平研究了神木煤(SMC)分别与气煤(QM)、肥煤(FM)、焦煤(JM)不同比例配合后的共热解交互作用规律,通过分布活化能模型(DAEM)对配合煤的热解动力学进行了考察。结果表明,随着SMC配入比例的增加,配合煤水分集中释放的速率增大,挥发分释放速率峰对应的温度tmax降低,配合煤在塑性固化温度后(>460-480 ℃)的热解过程中抑制作用减弱,表明配合煤黏结性降低。随着升温速率增加,配合煤热解抑制作用增强,表明配合煤黏结性提高。随着黏结煤变质程度加深(QM、FM、JM),配合煤共热解发生促进作用(促进挥发分释放)的温度分别低于、介于、高于黏结煤塑性温度区间,因此,对缓解胶质体膨胀压力及改善胶质体分散性的作用逐渐降低。通过分布热解活化能实验值与理论值的比较,证实了配煤共热解过程中的交互作用规律。Abstract: The pyrolysis characteristic of blended coal and the interaction between Shenmu coal (SMC) and caking coals(Fat coal-FM, gas coal-QM, coking coal-JM) were studied by temperature-programmed thermobalance. The pyrolysis kinetics were analyzed using distributed activation energy model (DAEM). The results indicate that the concentrated release rate of moisture increases and temperature corresponding to the release peak of volatile matter(tmax) for coal blends decreases as increasing SMC blending ratio. The inhibition of blended coal is reduced as increasing SMC blending ratio when pyrolysis temperature surpasses the solidified temperature of metaplast (>460-480 ℃), indicating a poor bonding behavior of metaplast. In addition, the inhibition of blended coal is enhanced and its bonding behavior is improved with increasing heating rate. The effects of relieving swelling pressure and improving dispersity of metaplast gradually reduce as deepening the metamorphic degree of caking coal from QM, FM to JM, since the corresponding temperature for promoting interaction (release of volatile) is below, within, above the plastic temperature range of caking coals, respectively. A comparison of experimental and calculated distributed activation energy model confirms the interaction mechanism of blended coal during co-pyrolysis.
-
Key words:
- Shenmu coal /
- caking coals /
- co-pyrolysis /
- interaction /
- distributed activation energy
-
图 7 热解活化能Ea随煤热解转化率x的变化关系及配煤热解活化能实验值与计算值差值曲线
Figure 7 Relationship between Ea and x and the difference between experimental and calculated value of Ea
(a), (b): blends of SMC and QM; (c), (d): blends of SMC and FM; (e), (f): blends of SMC and JM
■: SMC; ●: caking coal; ▲: 40SMC:60 caking coal (exp); ▼: 40SMC:60 caking coal (cal)表 1 原料煤样的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of coals
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% Mad Aad Vdaf C H O* N S SMC 10.52 4.40 34.02 82.98 4.70 11.10 1.02 0.20 QM 2.24 7.88 34.90 86.37 5.35 6.22 1.18 0.88 FM 0.80 20.74 32.03 87.06 5.39 2.55 1.33 3.67 JM 0.84 13.17 26.72 89.10 4.99 2.28 1.47 2.16 *:by difference -
[1] 李莹. 中国焦化行业现状及发展建议[D]. 北京: 对外经济贸易大学, 2006.LI Ying. The present situation and development proposal of coking industry in China[D]. Beijing: University of International Business and Economics, 2006. [2] 沈大勇.浅谈徐州焦化行业现状及对策建议[J].中国资源综合利用, 2016, 34(5):46-48. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95696A/201605/669294948.htmlSHEN Da-yong. Suggestions and status of Xuzhou coking industry[J]. China Resour Compr Util, 2016, 34(5):46-48. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95696A/201605/669294948.html [3] YE C, WANG Q H, LUO Z Y, XIE G L, JIN K, SIYIL M, CEN K F. Characteristics of coal partial gasification on a circulating fluidized bed reactor[J]. Energy Fuels, 2017, 31:2557-2564. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02889 [4] 孟庆岩, 杨志荣, 黄戒介, 王志青, 李春玉, 房倚天.神木煤与黏结煤配伍制气化焦的黏结特性[J].煤炭转化, 2017, 40(5):45-49. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92653X/201502/664576471.htmlMENG Qing-yan, YANG Zhi-rong, HUANG Jie-jie, WANG Zhi-qing, LI Chun-yu, FANG Yi-tian. Caking property of Shenmu coal and caking coal blending coals for coke-making[J]. Coal Convers, 2017, 40(5):45-49. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92653X/201502/664576471.html [5] 白效言, 裴贤丰, 王岩.焦化企业转型生产气化焦技术经济分析[J].煤质技术, 2016, S1:16-19. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90368X/201606/669390253.htmlBAI Xiao-yan, PEI Xian-feng, WANG Yan. Technology and economic analysis on coking enterprise transformation to produce coke for gasification[J]. Coal Qual Technol, 2016, S1:16-19. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90368X/201606/669390253.html [6] 徐秀丽.气化焦生产及焦粒造气工艺技术经济性探讨[J].煤炭加工与综合利用, 2016, 6:37-40. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90368X/201606/669390253.htmlXU Xiu-li. Technical and economical discussion about gasified coke production and gas making by coke particle[J]. Coal Process Compr Util, 2016, 6:37-40. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90368X/201606/669390253.html [7] YANG Z R, MENG Q Y, HUANG J J, WANG Z Q, LI C Y, FANG Y T. A particle-size regulated approach to producing high strength gasification-coke by blending a larger proportion of long flame coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2018, 177:101-108. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.04.024 [8] DUFFY J, MAHONEY M, STEEL M. Influence of coal thermoplastic properties on coking pressure generation:Part 1- A study of binary coal blends and specific additives[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89:1590-1599. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.08.031 [9] CASCAL M, DIAZ-FAES E, ALVAREZ R. Influence of the permeability of the coal plastic layer on coking pressure[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85:281-288. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2005.06.009 [10] NYATHI M S, MASTALERZ M, KRUSE R. Influence of coke particle size on pore structural determination by optical microscopy[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2013, 118:8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2013.08.004 [11] WU Z Q, WANG S Z, ZHAO J, CHEN L, MENG H Y. Synergistic effect on thermal behavior during co-pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass model components blend with bituminous coal[J]. Bioresource Technol, 2014, 169:220-228. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.06.105 [12] MIURA K, MAKI T. A simple method for estimating f(E) and k0(E) in the distributed activation energy model[J]. Energy Fuels, 1998, 12(5):864-869. doi: 10.1021/ef970212q [13] VAND V. A theory of the irreversible electrical resistance changes of metallic films evaporated in vacuum[J]. Proc Phys Soc, 1942, 55(3):222-246. [14] PITT G J. The kinetics of the evolution of volatile products from coal[J]. Fuel, 1962, 41(3):267-274. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/wiley/modeling-of-coal-pyrolsis-kinetics-MVNm2BphwC [15] CHEN S J, YANG Z, CHEN L, TAO X X, TANG L F, HE H. Wetting thermodynamics of low-rank coal and attachment in flotation[J]. Fuel, 2017, 207:214-225. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.06.018 [16] 姚娜. 生物质快速热解特性实验研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008.YAO Na. Experimental study on the behavior of biomass fast pyrolysis[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008. [17] 王琳俊, 马阳, 刘加勋, 姜秀民.超细煤粉热解特性及热解反应动力学研究[J].锅炉技术, 2015, 46(6):73-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gljs201506016WANG Lin-jun, MA Yang, LIU Jia-xun, JIANG Xiu-min. Study of superfine pulverized coal pyrolysis and thermodynamic parameters[J]. Boiler Technol, 2015, 46(6):73-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gljs201506016 [18] 薛伟. 生物质与褐煤共热解热重实验研究及动力学分析[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2013.XUE Wei. Biomass pyrolysis with lignite thermogravimetric experiment research and dynamic analysis[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2013. -





 下载:
下载: