Effect of framework Al siting on catalytic performance in methanol to aromatics over ZSM-5 zeolites
-
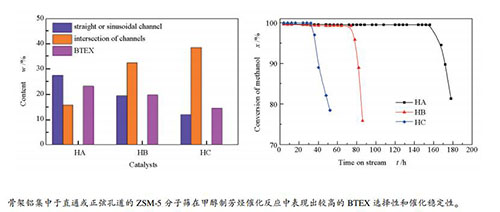
摘要: 采用水热合成法,在合成过程中通过添加矿化剂、尿素和改变硅源,制备了不同骨架铝落位的ZSM-5分子筛。通过SEM、XRD、BET、XRF、MAS NMR、NH3-TPD和Py-FTIR等表征手段对分子筛的形貌、织构、骨架铝落位和酸性进行了系统研究,同时考察了不同ZSM-5分子筛催化剂甲醇制芳烃的催化性能。研究结果表明,制备的ZSM-5分子筛均具有结晶度高和形貌均一等特点,但在骨架铝落位和酸性方面存在显著差异。椭球状ZSM-5分子筛的骨架铝主要分布于直通孔道或正弦孔道中,并表现出较多的酸性位。块状分子筛中骨架铝主要落位在孔道交叉处,且具有较低的强酸量。在甲醇制芳烃反应中,骨架铝主要位于直通或正弦孔道并表现出较多酸性位的椭球状ZSM-5分子筛催化剂具有较高的活性稳定性和芳烃选择性。Abstract: ZSM-5 zeolites with different framework Al (AlF) siting were hydrothermally synthesized by adding mineralizer, urea, or by changing the silicon source. The morphology, textural properties, AlF siting, and acidity of different ZSM-5 zeolites were characterized using SEM, XRD, BET, XRF, MAS NMR, NH3-TPD, and Py-IR. Furthermore, the conversion of methanol to aromatics (MTA) was used to investigate the catalytic performance of different catalysts.The results suggested that different ZSM-5 zeolites were highly crystalline with a uniform morphology, but there were large differences in AlF siting and acidity. The AlF in the ellipsoidal ZSM-5 sample was mainly distributed in straight or sinusoidal channels and displayed more acidic sites. AlF of bulk ZSM-5 was mainly located at the intersection of channels, and it showed the lowest amount of strong acid sites. The ellipsoidal ZSM-5 catalyst in which AlF was mainly located in straight or sinusoidal channels exhibited more acidic sites and higher stability and aromatic selectivity during the MTA reaction.
-
Key words:
- ZSM-5 zeolites /
- framework Al siting /
- methanol to aromatics
-
表 1 不同形貌ZSM-5分子筛的硅铝比和织构性质
Table 1 Si/Al ratios and textural properties of different ZSM-5 samples
Sample Si/Ala Relative crystallinity /%b BET surface area A/(m2·g-1)c Microporous area A/(m2·g-1)c External surface area A/(m2·g-1)c HA 43.16 94 393.85 318.30 75.55 HB 44.78 100 378.85 314.80 64.04 HC 41.06 91 403.05 334.80 68.25 a: determined by XRF; b: calculated from XRD patterns; c: obtained by N2-adsorption at -196 ℃ 表 2 不同ZSM-5分子筛样品中的骨架铝落位
Table 2 Framework Al (AlF) siting of different ZSM-5 zeolite samples
Sample AlF distribution /% Al(54) Al(56) HA 15.96 27.65 HB 32.63 19.63 HC 38.63 12.19 表 3 NH3-TPD和Py-FTIR表征的不同ZSM-5分子筛的酸性质
Table 3 Acidic properties of various ZSM-5 zeolites measured by NH3-TPD and Py-FTIR
Sample Acidity /(μmol·g-1) a Acidity /(μmolPy·g-1) b weak strong Brønsted Lewis 200 ℃ 350 ℃ 200 ℃ 350 ℃ HA 166.22 171.97 155.49 138.11 13.38 9.15 HB 149.54 185.73 148.23 131.04 10.90 8.11 HC 154.93 149.72 143.62 118.59 13.57 12.80 a: determined by NH3-TPD; b: calculated from Py-FTIR spectra 表 4 不同ZSM-5分子筛催化剂上产物分布
Table 4 Product distribution of different ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts
Catalyst Product distribution /% a CH4 C2-5- C2-5= C5+ non-aromatics BTEX b C9+ aromatics HA 1.20 34.69 5.69 21.10 23.33 13.99 HB 2.08 38.97 5.74 23.12 19.86 10.23 HC 2.81 35.35 6.31 27.69 14.66 13.18 a: analyzed at time-on-stream of 12 h; b: benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene -
[1] HOLLANDER M A D, WISSNK M, MAKKEE M. Gasoline conversion:Reactivity towards cracking with equilibrated FCC and ZSM-5 catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2002, 223(1/2):85-102. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=468d9b40f3549da1246e4060b6216b29&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [2] YANG L Z, LIU Z Y, LIU Z, PENG W Y, LIU Y Q, LIU C G. Correlation between H-ZSM-5 crystal size and catalytic performance in the methanol-to-aromatics reaction[J]. Chin J Catal, 2017, 38(4):683-690. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(17)62791-8 [3] HU H, ZHANG Q, CEN J. Catalytic activity of Pt modified hierarchical ZSM-5 catalysts in benzene alkylation with methanol[J]. Catal Lett, 2015, 145(2):715-722. doi: 10.1007/s10562-014-1458-3 [4] SOHN J R, DECANIO S J, FRITZ P O. Acid catalysis by dealuminated zeolite Y. 2. The roles of aluminum[J]. J Phys Chem, 1986, 90/20(20):4847-4851. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=k1txISpY6JfiU22g8t1HQfex2CW4X35Rd/qyCufUqJI= [5] MACHT J, CARR R T, IGLESIA E. Consequences of acid strength for isomerization and elimination catalysis on solid acids[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131(18):6554-6565. doi: 10.1021/ja900829x [6] DEDECEK J, BALGOV A, VENDUL A, PASHKOVA V. Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolites with defined distribution of Al atoms in the framework and multinuclear MAS NMR analysis of the control of Al distribution[J]. Chem Mater, 2012, 24(16):3231-3239. doi: 10.1021/cm301629a [7] PARK S, BILIGETU T, WANG Y, NISHITOBA T, KONDO J W, YOKOI T. Acidic and catalytic properties of ZSM-5 zeolites with different Al distributions[J]. J Catal, 2017, 353:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.06.026 [8] BILIGETU T, WANG Y, NISHITOBA T, YOKOI T. Al distribution and catalytic performance of ZSM-5 zeolites synthesized with various alcohols[J]. Catal Today, 2018, 303:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.12.032 [9] YOKOI T, MOCHIZUKI H, NAMB A, KONDO J N, TATSUMI T. Control of the Al distribution in the framework of ZSM-5 zeolite and its evaluation by solid-state NMR technique and catalytic properties[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2015, 119:15303-15315. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b03289 [10] KIM J H, NAMBA S, YASHIMA T. Shape selectivity of ZSM-5 type zeolite for alkylation of ethylbenzene and ethanol[J]. Bull Chem Soc Jpn, 1988, 61:1051-1055. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.61.1051 [11] LIANG T Y, CHEN J L, QIN Z F, LI J F, WANG P F, WANG S, WANG G F, DONG M, FAN W B, WANG J G. Conversion of methanol to olefins over HZSM5 zeolite:Reaction pathway is related to the framework aluminum siting[J]. ACS Catal, 2016, 6(11):7311-7325. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01771 [12] NA J D, LIU G Z, ZHOU T Y, DING G C, HU S L, WANG L. Synthesis and catalytic performance of ZSM-5/MCM-41 zeolites with varying mesopore size by surfactant-directed recrystallization[J]. Catal Lett, 2013, 143(3):267-275. doi: 10.1007/s10562-013-0963-0 [13] GREGG S J, SING K S W. Adsirption, Surface Area and Porosity[M]. London:Academic Press, 1982, 154. [14] AGUADO J, SERRANO D P, ESCOLA J M, RODRIGUEZ J M. Low temperature synthesis and properties of ZSM-5 aggregates formed by ultra-small nanocrystals[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2004, 75(1):41-49. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cbc586f5512d10772bbad06fa686ac15&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [15] GOBIN O C, REITMEIER S J, JENTYS A, LERCHER J A. Comparison of the transport of aromatic compounds in small and large MFI particles[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2009, 113(47):20435-20444. doi: 10.1021/jp907444c [16] WU G, WU W, WANG X, ZAN W, WANG W, LI C. Nanosized ZSM-5 zeolites:Seed-induced synthesis and the relation between the physicochemical properties and the catalytic performance in the alkylation of naphthalene[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2013, 180(6):187-195. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1387181112006609 [17] SKLENAK S, DĚEDEČCEK J, LI C. Aluminium siting in the ZSM-5 framework by combination of high resolution 27Al NMR and DFT/MM calculations[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2009, 11(8):1237-1247. doi: 10.1039/B807755J [18] YOKOI T, MOCHIZUKI H, NAMBA S, KONDO J, TATSUMI T. Control of the Al distribution in the framework of ZSM-5 zeolite and its evaluation by solid-State NMR technique and catalytic properties[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2015, 119(27):15303-15315. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b03289 [19] LIU S Y, REN J, ZHU S J, ZHANG H K, LV E J, XU J, LI Y W. Synthesis and characterization of the Fe-substituted ZSM-22 zeolite catalyst with high ndodecane isomerization performance[J]. J Catal, 2015, 330:485-496. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.07.027 [20] YANG G H, TSUBAKI N, SHAMOTO J, YONEYAMA Y, ZHANG Y. Confinement effect and synergistic function of H-ZSM-5/Cu-ZnO-Al2O3 capsule catalyst for one-step controlled synthesis[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132(23):8129-8136. doi: 10.1021/ja101882a [21] KUBELKOVA L, NOVAKOVA J. Reactivity of surface species on zeolites in methanol conversion[J]. J Catal, 1990, 124:441-450. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(90)90191-L [22] WANG K, DONG M, LI J F, LIU P, ZHANG K, WANG J G, FAN W B. Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite hollow spheres for catalytic conversion of methanol to aromatics[J]. Catal Sci Technol, 2017, 7:560-564. doi: 10.1039/C6CY02476A [23] BLASZKOWSKI S, SANTEN R. The mechanism of dimethyl ether formation from methanol catalyzed by zeolite protons[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1996, 118(21):5152-5153. doi: 10.1021/ja954323k -





 下载:
下载: