Effect of different ashing temperatures on the sintering characteristics of ash from combustion of coal and biomass blends
-
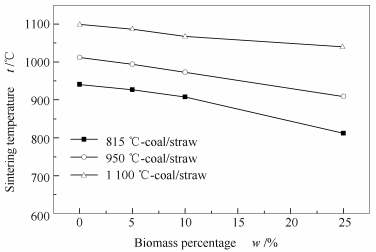
摘要: 选取晋城无烟煤和麦秆作为研究对象,利用压差法烧结温度测定装置测量不同灰化温度下煤和麦秆混合灰的烧结温度,再利用SEM-EDS以及XRD对灰样进行烧结特性分析。结果表明,不论灰化温度高低,随着麦秆的添加,煤和麦秆混合灰的烧结温度都呈现降低趋势,其降低幅度略有差别。灰化温度较低时,煤和麦秆混合灰的烧结温度低于灰化温度较高情况下混合灰的烧结温度。SEM-EDS分析表明,低温灰化得到的样品中出现较多不规则的纤维结构;较高温度下获得的灰样中出现较多致密的球状颗粒,这表明矿物质发生熔融形成球状颗粒。XRD分析表明,低温灰化烧结后的煤和麦秆混合灰样中因含有较多的含钾等碱金属系助融矿物质,导致混合灰样的烧结温度降低。然而,像钙长石等含钙矿物质本身具有较高的熔点,因此,在1 100℃时混合灰样具有较高的烧结温度。Abstract: Effect of ashing temperature on sintering behavior of ashes from combustion of coal and straw blends was investigated. Blends of a Chinese anthracite, Jincheng coal, and wheat straw were burned at three different temperatures. The resulting ash samples were then subjected to the sintering temperature measurement using a pressure-drop sintering device, morphological and mineralogical characterization with scanning electron microscope (SEM) fitted with X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray diffractometry analyzer (XRD), respectively. For the same coal and biomass blends but different ashing temperatures, their sintering temperatures decrease in different extent. In addition, sintering temperatures of the blends under lower ashing temperature are lower than that under the higher ashing temperature. SEM imaging show that the texture of ash samples from lower ashing temperature is irregular, loose and more fibrous. The ashes under higher ashing temperature are mostly in spherical-shape, indicating ash melting has occurred during combustion. The XRD analysis reveals that blends of ash from Jincheng coal and straw under low ashing temperature has low sintering temperature due to more fluxing minerals, like K-containing mineral. The high sintering temperature of the ash blends depends on the Ca-containing minerals like anorthite with high melting temperature.
-
表 1 样品的工业分析、元素分析和灰成分分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analysis and ash compositions of Jincheng coal and straw
Proximate analysis wad/% Ultimate analysis wad/% M V A FC C H O N S Jincheng coal 2.23 8.46 20.1 69.21 65.81 3.25 6.72 0.94 0.95 Wheat straw 9.89 68.39 5.22 16.5 45.55 5.7 46.53 1.32 0.15 Ash composition w/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO Na2O K2O SO3 TiO2 P2O5 Cl Jincheng coal 52.5 29 4.44 5.18 1.12 1.25 1.87 1.97 1.05 0.254 - Wheat straw 30.09 1.67 1.01 4.8 5.09 13.24 32.6 3.45 0.15 7.72 1.97 -
[1] 唐建业, 陈雪莉, 乔治, 刘爱彬, 王辅臣.添加秸秆类生物质对长平煤灰熔融特性的影响[J].化工学报, 2014, 65(12):4948-4957. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ201412041.htmTANG Jian-ye, CHEN Xue-li, QIAO Zhi, LIU Ai-bin, WANG Fu-chen. Influence of agro-biomass addition on Changping coal ash melting characteristics[J]. CIESC J, 2014, 65(12):4948-4957. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ201412041.htm [2] HAYKIRI-ACMA H, YAMAN S, KUCUKBAYRAK S. Effect of biomass on temperatures of sintering and initial deformation of lignite ash[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(10):3063-3068. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.06.003 [3] ZHENG Y J, JENSEN P A, JENSEN A D, SANDER B, JUNKER H. Ash transformation during co-firing coal and straw[J]. Fuel, 2007, 86(7/8):1008-1020. [4] KAZAGIC A, SMAJEVIC I. The research here presented therefore represents a precondition for the adoption of clean coal technologies[J]. Energy, 2007, 32:2006-2016. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2007.03.007 [5] VASSILEV S V, BAXTER D, ANDERSEN L K, VASSILEVAC G. An overview of the chemical composition of biomass[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(5):913-933. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.10.022 [6] LUAN C, YOU C F, ZHANG D K. Composition and sintering characteristics of ashes from co-firing of coal and biomass in a laboratory-scale drop tube furnace[J]. Energy, 2014, 69:562-570. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.03.050 [7] LIU H F, XU M H, ZHANG Q, ZHAO H, LI W F. Effective utilization of water hyacinth resource by co-gasification with coal:rheological properties and ash fusion temperatures of hyacinth-coal slurry[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2013, 52(46):16436-16443. doi: 10.1021/ie402163c [8] FANG X, JIA L. Experimental study on ash fusion characteristics of biomass[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2012, 104:769-774. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.055 [9] SAMI M, ANNAMALAI K, WOOLDRIDGE M. Co-firing of coal and biomass fuel blends[J]. Prog Energy Combust Sci, 2001, 27:171-214. doi: 10.1016/S0360-1285(00)00020-4 [10] DEMIRBAS A. Combustion characteristics of different biomass fuels[J]. Prog Energy Combust Sci, 2004, 30(2):219-230. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2003.10.004 [11] KHAN A A, JONG W, JANSENS P J, SPLIETHOFF H. Biomass combustion in fluidized bed boilers:Potential problems and remedies[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2009, 90(1):21-50. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2008.07.012 [12] GAYAN P, ADANEZ J, LUIS F, DIEGO D, GARCI'A-LABIANO F, CABANILLAS A, BAHILLO A, AHO M, VEIJONEN K. Circulating fluidised bed co-combustion of coal and biomass[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(3):277-286. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2003.08.003 [13] DEMIRBAS A. Sustainable cofiring of biomass with coal[J]. Energy Convers Manage, 2003, 44(9):1465-1479. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(02)00144-9 [14] KUPKA T, MANCINI M, IRMER M, WEBER R. Investigation of ash deposit formation during co-firing of coal with sewage sludge, saw-dust and refuse derived fuel[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(12):2824-2837. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.01.024 [15] LIN W G, DAM-JOHANSEN K, FRANDSEN F. Agglomeration in bio-fuel fired fluidized bed combustors[J]. Chem Eng J, 2003, 96(1/3):171-185. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223943234_Agglomeration_in_Bio-Fuel_Fired_Fluidized_Bed_Combustors [16] VAMVUKA D, KAKARAS E. Ash properties and environmental impact of various biomass and coal fuels and their blends[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2011, 92(3):570-581. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2010.11.013 [17] TEIXEIRA P, LOPES H, GULYURTLU I, LAPA N, ABELHA P. Evaluation of slagging and fouling tendency during biomass co-firing with coal in a fluidized bed[J]. Biomass Bioenergy, 2012, 39:192-203. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.01.010 [18] GOGEBAKAN Z, GOGEBAKAN G, SELCUK N, SELCUK E. Investigation of ash deposition in a pilot-scale fluidized bed combustor co-firing biomass with lignite[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2009, 100(2):1033-1036. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.037 [19] JING N J, WANG Q H, LUO Z, CEN K F. Effect of different reaction atmospheres on the sintering temperature of Jincheng coal ash under pressurized conditions[J]. Fuel, 2011, 90(8):2645-2651. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.04.013 [20] LI J B, ZHU M M, ZHANG Z Z, ZHANG, K, SHEN, G Q, ZHANG D K. Characterisation of ash deposits on a probe at different temperatures during combustion of a Zhundong lignite in a drop tube furnace[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2016, 144:155-163. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.12.024 [21] VASSILEV S V, KITANOB K, SHOHEI T, TSURUE T. Influence of mineral and chemical composition of coal ashes on their fusibility[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1995, 45(1):27-51. doi: 10.1016/0378-3820(95)00032-3 [22] YANG J G, DENG F R, ZHAO H, CEN K. Mineral conversion and microstructure change in the melting process of Shenmu coal ash[J]. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng, 20010, 2(10):165-170. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/239096050_Mineral_conversion_and_microstructure_change_in_the_melting_process_of_Shenmu_coal_ash [23] WU H W, BRYANT G, WALL T. The effect of pressure on ash formation during pulverized coal combustion[J]. Energy Fuels, 2000, 14(4):745-750. doi: 10.1021/ef990080w [24] WU X J, ZHANG Z X, PIAO G L, HE X, CHEN Y S, KOBAYASHI N, MORI S, ITAYA Y. Behavior of mineral matters in Chinese coal ash melting during gasfication reaction char-CO2/H2O[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23:2420-2428. doi: 10.1021/ef801002n [25] VUTHALURU H B, ZHANG D K. Effect of Ca-and Mg-bearing minerals on particle agglomeration defluidisation during fluidised-bed combustion of a South Australian lignite[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2001, 69(1):13-27. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3820(00)00129-6 -





 下载:
下载: