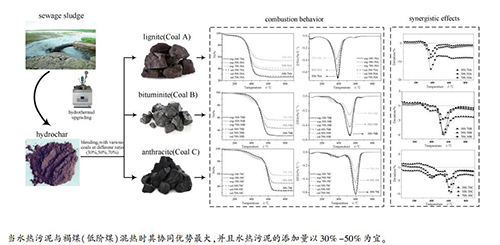
Synergistic effects in co-combusting of hydrochar derived from sewage sludge with different-rank coals
-
摘要: 以城市污泥衍生的水热污泥(SS-derived hydrochar)为对象,结合傅里叶红外光谱分析(FT-IR)、X射线荧光光谱分析(XRF)和X射线衍射分析(XRD)等对比研究了水热污泥与三种不同品阶煤(褐煤、烟煤和无烟煤)在有机/无机结构与燃料特性上的异同;同时,通过热重(TG)与偏差分析(Deviation)考察水热污泥与各阶煤在不同混合比例条件下的协同燃烧行为及其作用机制。结果表明,污泥经过水热处理后其有机结构和燃烧行为均提升至与煤相似的水平,该过程不仅改善污泥的燃烧特性,并增强其与煤之间的协同燃烧效应。水热污泥中适量的轻质组分与(碱)碱土金属能在混合燃烧过程中加速煤的失重速率,其对三种煤的促进作用可达4.4%-16.1%(褐煤)、1.9%-9.4%(烟煤)和4.8%-12.1%(无烟煤)。总体而言,水热污泥与褐煤混合而成的燃料在燃料性能上具有较大的优势,并且其混合比例以30%(水热污泥):70%(褐煤)与50%(水热污泥):50%(褐煤)为宜。Abstract: Differences on organic/inorganic structures and fuel properties between sewage sludge-derived hydrochar and different-rank coals were investigated and compared with the help of FT-IR, XRF and XRD technologies. Meanwhile, the combustion behavior under various blending ratio and its synergistic effects was identified via TG and deviation analysis. The results demonstrates that the organic structures and combustion behaviors of hydrochar are similar to those of coals, which not only improves the combustion properties of sewage sludge, but also enhances the synergistic effects in co-combustion of hydrochar and coals. During the co-combustion process, light volatiles and (alkaline) alkaline-earth metals in hydrochar could accelerate the weight loss rate for coals, reaching 4.4%-16.1%, 1.9%-9.4% and 4.8%-12.1% for lignite, bitumite and anthracite, respectively. In general, the blends with 30% hydrochar and 70% lignite or 50% hydrochar and 50% lignite are better than other blends in terms of comprehensive combustion evolutions.
-
Key words:
- sewage sludge /
- hydrothermal carbonization /
- coal /
- co-combustion /
- synergistic effects
-
表 1 污泥、水热污泥及各种煤的原料特性
Table 1 Properties of sewage sludge, SS-derived hydrochar, and coals
Sample Proximate analysis wd/% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% QHHV/ (J·g-1) V FC A C H O N S SS 39.30 4.20 56.50 50.02 6.42 40.12 3.02 0.42 9403 Hydrochar 21.71 1.91 76.38 13.55 2.09 83.01 1.09 0.26 6637 Coal A 50.32 42.94 6.74 59.87 4.55 34.10 0.98 0.50 24306 Coal B 29.35 56.36 14.29 68.53 4.05 25.76 0.92 0.74 27959 Coal C 12.02 72.27 15.71 66.09 3.26 29.77 0.47 0.41 27989 note: V:volatile matters; A:ash; FC:fixed carbon; O (oxygen) was calculated by difference based on dry ash-free base;
QHHV:higher heating value表 2 单独燃烧的温度区间与特征温度点
Table 2 Combustion stages and characteristic temperatures of biowastes and coals
Sample Temperature range t/℃ Weight loss w/% Residues
w/%Characteristic temperatures t/℃ stage 1 stage 2 stage 3 stage 2 stage 3 ti tmax tb SS 50-155 155-375 375-615 26.76 10.81 57.33 227 298 595 Hydrochar 50-120 145-355 355-615 9.94 12.02 75.19 249 390 600 Coal A 50-140 - 255-537 - 87.24 5.48 328 395 626 Coal B - - 374-712 - 83.66 14.77 455 552 715 Coal C - - 325-739 - 82.13 15.96 539 608 740 表 3 混合燃料的基本特性
Table 3 Proximate, ultimate and HHV analyses of mixed fuels
Sample Proximate analysis wd/% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% QHHV /(MJ·kg-1) A V FC C H O N S cal-V exp-V 30S:70A 26.63 42.73 30.64 45.59 4.14 48.83 1.01 0.43 19.0 20.2 50S:50A 40.62 36.27 23.11 37.79 3.48 57.36 0.99 0.38 15.5 16.4 70S:30A 54.63 30.59 14.78 28.96 2.98 66.73 1.00 0.33 11.9 12.6 30S:70B 32.33 26.15 41.52 52.88 3.51 42.06 0.95 0.60 21.6 21.6 50S:50B 45.37 24.82 29.81 41.37 3.19 53.94 1.00 0.50 17.3 17.7 70S:30B 57.95 23.65 18.40 30.31 2.69 65.59 1.01 0.40 13.0 13.2 30S:70C 34.17 14.88 50.95 50.44 2.49 46.04 0.67 0.36 21.6 21.7 50S:50C 45.80 17.22 36.98 40.24 2.35 56.36 0.72 0.33 17.3 17.4 70S:30C 57.69 19.01 23.30 30.79 2.18 65.91 0.82 0.30 13.0 13.2 note: V, volatile matters; A, ash; FC, fixed carbon; HHV, higher heating value; cal-V, calculated value; exp-V, experimental value; d, on dry base; daf, on dry ash-free base 表 4 水热污泥与煤混合燃烧的动力学参数
Table 4 Co-combustion kinetic parameters for hydrochar and coals
Sample Stage 2 Stage 3 region/℃ E1/(kJ·mol-1) A1/min-1 R2 region/℃ E2/ (kJ·mol-1) A2/min-1 R2 Hydrochar 150-370 19.31 0.02 0.9649 370-600 21.39 0.02 0.9710 Coal A - - - - 240-500 60.09 7.08 0.9791 Coal B - - - - 375-625 97.15 298.47 0.9964 Coal C - - - - 500-700 136.85 1344.17 0.9896 30S:70A - - - - 220-530 50.82 32.46 0.9925 50S:50A - - - - 230-520 39.23 5.44 0.9843 70S:30A - - - - 225-515 30.20 0.12 0.9712 30S:70B 260-420 40.23 0.02 0.9939 420-625 84.34 50.38 0.9846 50S:50B 200-410 30.20 <0.01 0.9990 410-625 68.77 4.64 0.9793 70S:30B 185-445 20.93 <0.01 0.9759 445-625 60.22 1.35 0.9803 30S:70C 250-485 26.97 <0.01 0.9993 485-690 125.50 1098.58 0.9981 50S:50C 225-480 21.21 <0.01 0.9978 480-690 107.09 903.05 0.9950 70S:30C 225-480 20.92 <0.01 0.9842 480-690 99.20 797.74 0.9838 note: E1 and A1 are the activation energy and pre-exponential factor for stage 2, respectively, while E2 and A2 are for stage 3 表 5 水热污泥与煤混合燃烧的性能评价
Table 5 Combustibility index values for hydrochar and coals
Sample Characteristic temperature (t/℃) DTG/(%·℃-1) S×1010 R×104 ti tb tmax (dw/dt)max (dw/dt)mean Hydrochar 249 600 390 0.10 0.03 0.81 2.20 Coal A 328 626 395 0.94 0.11 15.35 20.44 Coal B 455 715 552 0.75 0.10 5.07 11.67 Coal C 539 740 608 0.86 0.10 4.00 12.15 30S:70A 322 495 387 0.69 0.08 10.76 15.31 50S:50A 303 486 375 0.60 0.07 9.41 13.74 70S:30A 302 478 375 0.39 0.05 4.47 8.93 30S:70B 450 624 533 0.55 0.08 3.48 8.86 50S:50B 427 615 532 0.42 0.07 2.62 6.78 70S:30B 406 612 530 0.25 0.05 1.24 4.05 30S:70C 522 685 600 0.63 0.08 2.70 9.02 50S:50C 515 678 600 0.46 0.06 1.54 6.58 70S:30C 469 675 597 0.29 0.05 0.29 4.17 -
[1] PARSHETTI G K, LIU Z G, JAIN A, SRINIVASAN M P, BALASUBRAMANIAN R. Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge for energy production with coal[J]. Fuel, 2013, 111:201-210. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.04.052 [2] LEE Y J, LEE D W, PARK J H, BAE J S, KIM J G, KIM J H, PARK S J, JEON C H, CHOI Y C. Two-in-one fuel combining sewage sludge and bioliquid[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng, 2016, 4(6):3276-3284. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00314 [3] WANG Z Q, HONG C, XING Y, LI Y F, FENG L H, JIA M M. Combustion behaviors and kinetics of sewage sludge blended with pulverized coal:With and without catalysts[J]. Waste Manage, 2018, 74:288-296. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.01.002 [4] XIE C D, LIU J Y, XIE W M, KUO J H, LU X W, ZHANG X C, HE Y, SUN J, CHANG K L, XIE W H, LIU C, SUN S Y, BUYUKADA M, EVRENDILEK F. Quantifying thermal decomposition regimes of textile dyeing sludge, pomelo peel, and their blends[J]. Renewable Energy, 2018, 122:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.01.093 [5] 张光义, 马大朝, 彭翠娜, 许光文.水热处理抗生素菌渣制备固体生物燃料[J].化工学报, 2013, 64(10):3741-3749. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201310035ZHANG Guang-yi, MA Da-zhao, PENG Cui-na, XU Guang-wen. Hydrothermal treatment of antibiotic mecelial dregs for solid bio-fuel preperation[J]. J Chem Ind Eng, 2013, 64(10):3741-3749. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201310035 [6] 庄修政, 黄艳琴, 阴秀丽, 吴创之.基于响应面法优化污泥燃料的水热制备工艺[J].新能源进展, 2017, (05):325-332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2017.05.001ZHUANG Xiu-zheng, HUANG Yan-qin, YIN Xiu-li, WU Chuang-zhi. Optimization of hydrothermal process for solid fuel derived from sewage sludge by response surface methodology[J]. Adv New Renewable Energy, 2017, 5(5):325-332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2017.05.001 [7] 庄修政, 黄艳琴, 阴秀丽, 吴创之.污泥水热处理制备清洁燃料的研究进展[J].化工进展, 2018, 37(1):311-318. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgjz201801040ZHUANG Xiu-zheng, HUANG Yan-qin, YIN Xiu-li, WU Chuang-zhi. Research on clean solid fuel derived from sludge employing hydrothermal treatment[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog, 2018, 37(1):311-318. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgjz201801040 [8] ZHAO P T, SHEN Y F, GE S F, CHEN Z Q, YOSHIKAWA K. Clean solid biofuel production from high moisture content waste biomass employing hydrothermal treatment[J]. Appl Energy, 2014, 131:345-367. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.06.038 [9] HE C, GIANNIS A, WANG J Y. Conversion of sewage sludge to clean solid fuel using hydrothermal carbonization:Hydrochar fuel characteristics and combustion behavior[J]. Appl Energy, 2013, 111(11):257-266. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261913003887 [10] HE C, WANG K, YANG Y, WANG J Y. Utilization of sewage-sludge-derived hydrochars toward efficient cocombustion with different-rank coals:Effects of subcritical water conversion and blending scenarios[J]. Energy Fuels, 2014, 28(9):6140-6150. doi: 10.1021/ef501386g [11] ZHUANG X, ZHAN H, HUANG Y, SONG Y, YIN X, WU C. Conversion of industrial biowastes to clean solid fuels via hydrothermal carbonization (HTC):Upgrading mechanism in relation to coalification process and combustion behavior[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2018, 267:17-29. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.002 [12] OTERO M, GOMEZ X, GARCIA A I, MORAN A. Effects of sewage sludge blending on the coal combustion:A thermogravimetric assessment[J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 69(11):1740-1750. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.05.077 [13] LIU Z G, QUEK A, HOEKMAN S K, SRINIVASAN M P, BALASUBRAMANIAN R. Thermogravimetric investigation of hydrochar-lignite co-combustion[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2012, 123:646-652. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.063 [14] LIN Y, LIAO Y, YU Z, FANG S, MA X. The investigation of co-combustion of sewage sludge and oil shale using thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Thermochim Acta, 2017, 653:71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2017.04.003 [15] SMITH A M, SINGH S, ROSS A B. Fate of inorganic material during hydrothermal carbonisation of biomass:Influence of feedstock on combustion behaviour of hydrochar[J]. Fuel, 2016, 169:135-145. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.12.006 [16] CHEN W D, WANG F, KANHAR A H. Sludge acts as a catalyst for coal during the Co-combustion process investigated by thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Energies, 2017, 10(12). [17] CAO J P, LI L Y, MORISHITA K, XIAO X B, ZHAO X Y, WEI X Y, TAKARADA T. Nitrogen transformations during fast pyrolysis of sewage sludge[J]. Fuel, 2013, 104(2):1-6. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S001623611000431X [18] ZHUANG X Z, HUANG Y Q, SONG Y P, ZHAN H, YIN X L, WU C Z. The transformation pathways of nitrogen in sewage sludge during hydrothermal treatment[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2017, 245:463-470. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.195 [19] MAGDZIARZ A, DALAI A K, KOZINSKI J A. Chemical composition, character and reactivity of renewable fuel ashes[J]. Fuel, 2016, 176:135-145. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.02.069 [20] SONIBARE O O, HAEGER T, FOLEY S F. Structural characterization of Nigerian coals by X-ray diffraction, Raman and FT-IR spectroscopy[J]. Energy, 2010, 35(12):5347-5353. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2010.07.025 [21] BAYSAL M, YURUM A, YILDIZ B, YURUM Y. Structure of some western Anatolia coals investigated by FT-IR, Raman, C-13 solid state NMR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2016, 163:166-176. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.07.009 [22] XIE C D, LIU J Y, ZHANG X C, XIE W M, SUN J, CHANG K L, KUO J H, XIE W H, LIU C, SUN S Y, BUYUKADA M, EVRENDILEK F. Co-combustion thermal conversion characteristics of textile dyeing sludge and pomelo peel using TGA and artificial neural networks[J]. Appl Energy, 2018, 212:786-795. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.12.084 [23] MUTHURAMAN M, NAMIOKA T, YOSHIKAWA K. A comparison of co-combustion characteristics of coal with wood and hydrothermally treated municipal solid waste[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2010, 101(7):2477-2482. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.060 [24] XIE W H, HUANG J L, LIU J Y, ZHAO Y J, CHANG K L, KUO J H, HE Y, SUN J, ZHENG L, XIE W M, SUN S Y, BUYUKADA M, EVRENDILEK F. Assessing thermal behaviors and kinetics of (co-) combustion of textile dyeing sludge and sugarcane bagasse[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2018, 131:874-883. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.025 -





 下载:
下载: