Emission characteristics and control of NOx from oil sludge char fluidized bed combustion
-
摘要: 为无害化处理油泥焦,采用小型流化床反应器,研究了不同温度、不同颗粒粒径下油泥焦的燃烧氮氧化物释放特性,并借助空气分级燃烧技术降低NOx排放。SEM电镜和物理吸附结果表明,油泥焦颗粒表面结构致密、孔道稀疏,不利于其内部有机质充分燃烧。燃烧实验结果表明,油泥焦燃烧产生的NOx主要来源于焦炭氮,来自挥发性氮的较少。适当降低燃烧温度、减小颗粒粒径既能保证油泥焦充分燃烧,又能抑制氮氧化物排放。实施空气分级燃烧时,通过优化过量空气系数、二次风比例和二次风入口位置,能够获得显著的NOx减排效果,同时可以有效抑制飞灰产生,有助于烟气终极处理。Abstract: To realize innocent treatment of oil sludge char, a lab-scale fluidized bed reactor was employed to study combustion of the oil sludge char in the term of nitrogen oxide emission characteristics at various different temperatures and particle sizes, as well as the reduction in the emission of NOx by using air-staging combustion technology. According to the results of scanning electron microscope and physical adsorption analyses of oil sludge char, the surface structure of the sludge char is dense and its pores are sparse, which is not conducive to the full combustion of organic matter inside. The combustion experiments of oil sludge char show that the generated NOx is mainly from coke-N and less from volatile-N. Reduction in the combustion temperature and the particle size to a proper extent can not only ensure full combustion of oil sludge char, but also inhibit NOx emission. When conducting air-staging combustion, by optimizing the excess air ratio, proportion of secondary air and position of secondary air inlet, the NOx emission is considerably reduced, and meanwhile the generation of fly ash is restrained, and these are beneficial for the ultimate treatment of the flue gas.
-
Key words:
- oil sludge char /
- fluidized bed /
- combustion /
- NOx emission /
- air-staging combustion
-
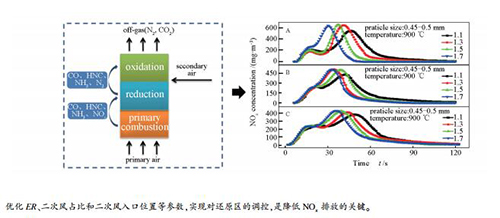
图 7 不同ER和二次风位置条件下的NOx排放和N转化率变化
Figure 7 Variation of NOx emission and N conversion with different ER and secondary air locations
(a): particle size: 0.45-0.5 mm; temperatures: 900℃; —■—: 1.1; —●—: 1.3; —▲—: 1.5; : 1.7 (b): : NOx concentration of A; : NOx concentration of B; : NOx concentration of C; —□—: fuel-N conversion of A; —○—: fuel-N conversion of B; —△—: fuel-N conversion of C
表 1 油泥焦的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of the oil sludge char
Proximate analysis war/% Ultimate analysis wd/% QHHV
/(MJ·kg-1)M V A FC* N C H S O* 2.37 4.52 75.64 17.47 0.53 16.29 0.48 0.35 4.87 5.31 ar: as received basis; d: dry basis;*: calculated by difference 表 2 油泥焦灰的熔融特性
Table 2 Melting properties of the oil sludge char ash
Initiator DT ST HT FT Temperature t/℃ 1100 1150 1180 1420 表 3 油泥焦灰的XRF分析
Table 3 XRF analysis of the oil sludge char ash
Component Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 SO3 K2O CaO TiO2 MnO Fe2O3 Others Percent w/% 2.07 2.49 13.70 60.73 0.62 2.04 2.79 8.22 0.75 0.14 5.98 0.47 表 4 油泥焦原料的BET分析
Table 4 BET analysis of the raw materials of the oil sludge char
Parameter Value Surface area A/(m2·g-1) 12.344 Pore volume v/(cm3·g-1) 0.034 Pore size d/nm 10.992 -
[1] XU N, WANG W X, HAN P F, LU X P. Effects of ultrasound on oily sludge deoiling[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2009, 171(1/3):914-917. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ef2e5219db957c03c1b5914182fd829b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [2] HU G J, LI J B, ZENG G M. Recent development in the treatment of oily sludge from petroleum industry:A review[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2013, 261:470-490. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.069 [3] SCHMIDT H, KAMINSKY W. Pyrolysis of oil sludge in a fluidised bed reactor[J]. Chemosphere, 2001, 45:285-290. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00542-7 [4] SHEN L, ZHANG D K. An experimental study of oil recovery from sewage sludge by low-temperature pyrolysis in a fluidised-bed[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82:465-472. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00294-6 [5] GONG Z Q, DU A, WANG Z B, FANG P W. Experimental study on pyrolysis characteristics of oil sludge with a tube furnace reactor[J]. Energy Fuels, 2017, 31(8):8102-8108. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b01363 [6] 高昌胜, 魏茂, 蒋文广, 李相国, 吕阳.基于含油污泥热解残渣的路基材料制备与性能评价[J].硅酸盐通报, 2019, 38(6):1895-1900. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gsytb201906043GAO Chang-sheng, WEI Mao, JIANG Wen-guang, LI Xiang-guo, LV Yang. Preparation and performance evaluation of roadbed materials based on pyrolysis residue of oily sludge[J]. Bull Chin Ceram Soc, 2019, 38(6):1895-1900. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gsytb201906043 [7] ROS A, LILLO-RÍDENAS M A, FUENTE E, MONTES-MORÁN M A, MARTÍN M J, LINARES-SOLANO A. High surface area materials prepared from sewage sludge-based precursors[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 65(1):132-140. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.017 [8] 彭海军, 李志光, 夏兴良, 郭开, 苏猛飞, 何纯莲.污泥热解残渣催化市政破膜污泥的热解作用[J].环境化学, 2014, 33(3):508-514. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjhx201403020PENG Hai-jun, LI Zhi-guang, XIA Xin-liang, GUO Kai, SU Meng-fei, HE Chun-lian. Catalysis of sludge residual carbon to municipal disintegration-membrance sludge pyrolysis[J]. Environ Chem, 2014, 33(3):508-514. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjhx201403020 [9] ZHANG H F, LV C X, LI J, WU Q, HU Y K, DONG C Q. Solid waste mixtures combustion in a circulating fluidized bed:Emission properties of NOx, dioxin, and heavy metals[J]. Energy Proc, 2015, 75:987-992. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2015.07.322 [10] FAN W D, LIN Z C, LI Y Y, KUANG J G. Effect of air-staging on anthracite combustion and NOx formation[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23(1):111-120. doi: 10.1021/ef800343j [11] MLADENOVIĆ M, DAKIĆ D, NEMODA S. The combustion of biomass-The impact of its types and combustion technologies on the emission of nitrogen oxide[J]. Hem Ind, 2015, 70:33-33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000004749785 [12] TRIKKELA A, KUUSIKA R, MARTINS A, PILU T, STENCEL J M. Utilization of estonian oil shale semicoke[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2008, 89:756-763. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2008.01.010 [13] 洪勇, 卢啸风, 王泉海, 杨宇.油页岩半焦在流化床内的燃烧特性研究[J].热能动力工程, 2016, 31(3):92-96. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rndlgc201603015HONG Yong, LU Xiao-feng, WANG Quan-hai, YANG Yu. Study on combustion characteristics of oil shale semi-coke in fluidized bed[J]. J Eng Therm Energy Power, 2016, 31(3):92-96. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rndlgc201603015 [14] BIEŃ J D, BIEŃ J B, NOWAK W. Combustion of char received after sewage sludge pyrolysis in the circulating fluidized bed[J]. J Chin Inst Chem Eng, 2001, 32(5):415-418. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c45e41423de9e5e5d945c08aaee635bb [15] 胡文斌, 杨海瑞, 吕俊复, 岳光溪, 张建胜.煤着火特性的热重分析研究[J].电站系统工程, 2005, 21(2):8-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-006X.2005.02.003HU Wen-bin, YANG Hai-rui, LU Jun-fu, YUE Guang-xi, ZHANG Jian-sheng. Study on ignition properties of coals by using thermogravimetry[J]. Power Syst Eng, 2005, 21(2):8-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-006X.2005.02.003 [16] KILPINEN P, HUPA M. Homogeneous N2O chemistry at fluidized bed combustion conditions:A kinetic modeling study[J]. Combust Flame, 1991, 85(1/2):94-104. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d737f699db836c6c13e4d1d0fba2ce94&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [17] 张秀霞, 周志军, 周俊虎, 姜树栋, 刘建忠, 岑可法. N2O在焦炭表面异相生成和分解机理的密度泛函数理论研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2011, 39(11):806-811. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2011.11.002ZHANG Xiu-xia, ZHOU Zhi-jun, ZHOU Jun-hu, JIANG Shu-dong, LIU Jian-zhong, CEN Ke-fa. A density functional study of heterogeneous formation and decomposition of N2O on the surface of char[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2011, 39(11):806-811. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2011.11.002 [18] 牛欣, 肖军.污泥化学链燃烧过程中氮迁移转化特性研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(4):505-512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.04.016NIU Xin, XIAO Jun. Nitrogen transformation in chemical looping combustion of sewage sludge[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(4):505-512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.04.016 [19] 葛亚昕, 张光义, 崔丽杰, 高士秋.高含水菌渣流化床燃烧NOx、SO2排放特性[J].化工学报, 2017, 68(8):3250-3257. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201708036GE Ya-xin, ZHANG Guang-yi, CUI Li-jie, GAO Shi-qiu. Characteristics of NOx and SO2 emission from combustion of antibiotic mycelial residue with high water content in fluidized bed reactor[J]. J Chem Ind Eng (Chin), 2017, 68(8):3250-3257. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201708036 [20] 王苑, 罗永浩, 林鹏云, 季俊杰.煤在燃烧过程中灰层有效扩散系数的实验研究与应用[J].动力工程学报, 2010, 30(8):573-577. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlgc201008003WANG Yuan, LUO Yong-hao, LIN Peng-yun, JI Jun-jie. Study on gas diffusion through ash layer during coal combustion process and the application[J]. Chin J Power Eng, 2010, 30(8):573-577. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlgc201008003 [21] 周志军, 周宁, 陈瑶姬, 周俊虎, 刘建忠, 岑可法.低挥发分煤燃烧特性及NOx生成规律的试验研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2010, 30(29):55-61. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201029009ZHOU Zhi-jun, ZHOU Ning, CHEN Yao-ji, ZHOU Jun-hu, LIU Jian-zhong, CEN Ke-fa. Experimental research on the combustion and NOx generation characteristics of low volatile coal[J]. Proc CSEE, 2010, 30(29):55-61. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201029009 [22] 陈萍, 顾明言, 汪嘉伦, 卢坤, 林郁郁.含氮煤焦还原NO反应路径研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(3):279-286. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb201903004CHEN Ping, GU Ming-yan, WANG Jia-lun, LU Kun, LIN Yu-yu. Reaction pathways for the reduction of NO by nitrogen-containing char[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2019, 47(3):279-286. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb201903004 [23] ISHIZUKA H, HYVARINEN K, MORITA A, SUZUKI A, YANO K, HIROSE R. Experimental study on NOx reduction in CFB coal combustion[C]//Circulating Fluidized Bed Technology. Proceedings of the Second International Conference On Circulating Fluidized Beds. France: Compiégne, 1988: 437-444. [24] WERTHER J, OGADA T. Sewage sludge combustion[J]. Proc Energy Combust Sci, 1999, 25(1):55-116. doi: 10.1016/S0360-1285(98)00020-3 [25] LEDESMA E B, NELSON P F, MACKIE J C. An experimental and kinetic modeling study of the reduction of NO by coal volatiles in a flow reactor[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2000, 28(2):2345-2351. doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(00)80646-3 [26] PERMCHART W, KOUPRIANOV V I. Emission performance and combustion efficiency of a conical fliodized-bed combustor firing various biomass fuels[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2004, 92(1):83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2003.07.005 [27] 马辉, 赵俊平, 张小东.优化二次风布置降低NOx放浓度[J].电站系统工程, 2015, 31(1):71-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzxtgc201501023MA Hui, ZHAO Jun-ping, ZHANG Xiao-dong. Optimization of secondary air layout to reduce NOx emissions[J]. Power Syst Eng, 2015, 31(1):71-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzxtgc201501023 -





 下载:
下载: