Enhanced activity and stability over hierarchical porous mordenite (MOR) for carbonylation of dimethyl ether: Influence of mesopores
-
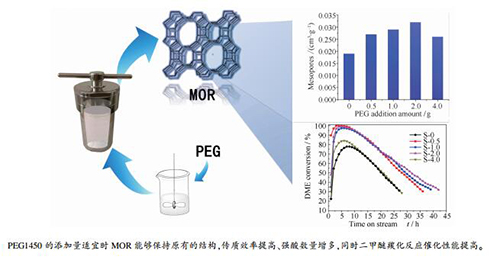
摘要: 本研究通过调整聚乙二醇(PEG 1450)的添加量制备了介孔量不同的梯级孔丝光沸石,并分别对其结构和二甲醚羰基化反应性能进行了表征和评价。结果表明,通过提高PEG1450加入量的方式可以提高丝光沸石的介孔量,但PEG 1450的添加量过高时不利于介孔的形成。当引入的介孔量适宜时丝光沸石能够保持原有的结构,强酸中心数量增多、弱酸和中强酸数量降低,二甲醚的传质效率和二甲醚羰化反应催化性能明显提高。受传质过程和酸分布的影响,梯级孔丝光沸石催化剂上二甲醚羰化反应活性明显改善,二甲醚转化率升高、单程寿命延长,重积炭的形成明显受到抑制。PEG1450的最优添加量为丝光沸石合成时凝胶质量的2%。Abstract: The dimethyl ether (DME) carbonylation reaction over mordenite is greatly affected by the mass transfer process. In this research, hierarchical mordenite catalysts were synthesized and characterized to investigate the influence of mesopores on the structure, mass transfer and catalytic performance. The results show that the medium-strong acid sites decrease while strong acid sites increase over the hierarchical samples. The introduced mesopores can significantly improve the mass transfer efficiency and the carbonylation performances are markedly improved on the hierarchical samples. In addition, the polymerization degree of coke deposition on the deactivated samples decreases although the coke amount increases. Excessive usage of mesopore templates can damage the structure of the MOR catalysts, thus leading to the loss of acid sites and the decrease in catalytic performance.
-
Key words:
- PEG /
- MOR /
- carbonylation /
- mass transfer /
- coke deposition
-
Table 1 Structural properties of the hierarchical MOR samples
Sample SiO2/Al2O3a SBET /(m2·g-1) vMib /(mL·g-1) vMec /(mL·g-1) vTd /(mL·g-1) S-0 17.8 487.1 0.182 0.019 0.201 S-0.5 18.1 490.9 0.179 0.027 0.206 S-1.0 17.7 534.8 0.180 0.029 0.209 S-2.0 17.9 527.4 0.181 0.032 0.213 S-4.0 18.5 505.3 0.174 0.026 0.200 a: determined by XRF; b: volume of micropores; c: volume of mesopores; d: total pore volumes Table 2 Distribution of acid sites over the MOR samples
Sample NH3-TPD/(mmol·g-1) weaka medium-strongb strongc total S-0 0.16 0.46 0.38 1.01 S-0.5 0.16 0.24 0.49 0.89 S-1.0 0.15 0.28 0.52 0.95 S-2.0 0.15 0.25 0.48 0.88 S-4.0 0.07 0.20 0.35 0.62 a: 40-150 ℃; b: 150-270 ℃; c: 270-700 ℃ Table 3 Distribution of acid sites over the MOR samples
Sample Py-FTIR at 150 ℃ Py-FTIR at 300 ℃ OH-IR B acid sites/
(mmol·g-1)L acid sites/
(mmol·g-1)B acid sites/
(mmol·g-1)L acid sites/
(mmol·g-1)B acid in 12 MR1/
(a.u.)B acid in 8 MR2/
(a.u.)S-0 0.53 0.17 0.27 0.03 741 1506 S-0.5 0.44 0.15 0.31 0.02 593 1215 S-1.0 0.46 0.14 0.34 0.02 637 1367 S-2.0 0.42 0.16 0.30 0.03 676 1461 S-4.0 0.35 0.19 0.19 0.03 479 905 1: calculated from the OH-IR peak at 3610 cm-1; 2: calculated from the OH-IR peak at 3590 cm-1 -
[1] MAYER F D, FERIS L A, MARCILIO N R, HOFFMANN R. Why small-scale fuel ethanol production in Brazil does not take off[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev, 2015, 43:687-701. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.11.076 [2] BAEYENS J, KANG Q, APPELS L, DEWIL R, LV Y, TAN, T. Challenges and opportunities in improving the production of bio-ethanol[J]. Prog Energy Combust Sci, 2015, 47:60-88. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2014.10.003 [3] HOCHMAN G, ZILBERMAN D. Corn ethanol and US biofuel policy 10 years later:A quantitative assessment[J]. Am J Agr Econ, 2018, 100(2):570-584. doi: 10.1093/ajae/aax105 [4] VARSHAVSKY Y S, CHERKASOVA T G. Remarks on the process of homogeneous carbonylation of rhodium compounds by N, N-dimethylformamide[J]. J Organomet Chem, 2007, 692(4):887-893. doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2006.10.040 [5] THOMAS C M, MAFUA R, THERRIEN B, RUSANOV E, STOEECKLI-EVANS H, SVSS-FINK G. New diphosphine ligands containing ethyleneglycol and amino alcohol spacers for the rhodium-catalyzed carbonylation of methanol[J]. Chem-A European J, 2002, 8(15):3343-3352. doi: 10.1002/1521-3765(20020802)8:15<3343::AID-CHEM3343>3.0.CO;2-Z [6] VOLKOVA G G, PLYASOVA L M, SALANOV A N, KUSTOVA G N, YURIEVA T M, LIKHOLOBOV V A. Heterogeneous catalysts for halide-free carbonylation of dimethyl ether[J]. Catal Lett, 2002, 80(3):175-179. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5b14d34aaab92390836a1efa864429dc [7] CHEUNG P, BHAN A, SUNLEY G J, IGLESIA E. Selective carbonylation of dimethyl ether to methyl acetate catalyzed by acidic zeolites[J]. Angew Chem-Int Ed, 2006, 45(10):1617-1620. doi: 10.1002/anie.200503898 [8] BHAN A, ALLIAN A D, SUNLEY G J, LAW D J, IGLESIA E. Specificity of sites within eight-membered ring zeolite channels for carbonylation of methyls to acetyls[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129(16):4919-4924. doi: 10.1021/ja070094d [9] CHEUNG P, BHAN A, SUNLEY G J, LAW D J, IGLESIA E. Site requirements and elementary steps in dimethyl ether carbonylation catalyzed by acidic zeolites[J]. J Catal, 2007, 245(1):110-123. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c7490b111ead8941415872f6955e12b9 [10] BHAN A, IGLESIA E. A link between reactivity and local structure in acid catalysis on zeolites[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2008, 41(4):559-567. doi: 10.1021/ar700181t [11] SAN X G, ZHANG Y, SHEN W J, TSUBAKI N. New synthesis method of ethanol from dimethyl ether with a synergic effect between the zeolite catalyst and metallic catalyst[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23:2843-2844. doi: 10.1021/ef900080g [12] ZHANG Y, SAN X G; TSUBAKI N, TAN Y S, CHEN J. Novel ethanol synthesis method via C1 chemicals without any agriculture feedstocks[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2010, 49(11):5485-5488. doi: 10.1021/ie901882s [13] LI X A, SAN X G, ZHANG Y, ICHII T, MENG M, TAN Y S, TSUBAKI N. Direct synthesis of ethanol from dimethyl ether and syngas over combined H-mordenite and Cu/ZnO catalysts[J]. ChemSusChem, 2010, 3(10):1192-1199. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201000109 [14] YANG G H, SAN X G, JIANG N, TANAKA Y, LI X G, JIN Q, TAO K, MENG F Z, TSUBAKI N. A new method of ethanol synthesis from dimethyl ether and syngas in a sequential dual bed reactor with the modified zeolite and Cu/ZnO catalysts[J]. Catal Today, 2011, 164(1):425-428. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.10.027 [15] XUE H F, HUANG, X, ZHAN E, MA M, SHEN W J. Selective dealumination of mordenite for enhancing its stability in dimethyl ether carbonylation[J]. Catal Commun, 2013, 37:75-79. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2013.03.033 [16] LIU J, XUE H, HUANG X, WU P H, HUANG S J, LIU S B, SHEN W. Stability enhancement of H-mordenite in dimethyl ether carbonylation to methyl acetate by pre-adsorption of pyridine[J]. Chin J Catal, 2010, 31(7):729-738. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(09)60081-4 [17] REULE A A C, PRASAD V, SEMAGINA N. Effect of Cu and Zn ion-exchange locations on mordenite performance in dimethyl ether carbonylation[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2018, 263:220-230. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.12.026 [18] JIA X, KHAN W, WU Z, CHOI J, YIP A C K. Modern synthesis strategies for hierarchical zeolites:Bottom-up versus top-down strategies[J]. Adv Powder Technol, 2019, 30(3):467-484. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2018.12.014 [19] XUE H F, HUANG X, DITZEL E, ZHAN E S, MA M, SHEN W J. Dimethyl ether carbonylation to methyl acetate over nanosized mordenites[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2013, 52(33):11510-11515. doi: 10.1021/ie400909u [20] YUAN, Y Y, WANG L, LIU H, TIAN P, YANG M, XU S T, LIU Z M. Facile preparation of nanocrystal-assembled hierarchical mordenite zeolites with remarkable catalytic performance[J]. Chin J Catal, 2015, 36(11):1910-1919. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(15)60960-3 [21] WANG X S, LI R J, YU C C, LIU Y X, ZHANG L Y, XU C M, ZHOU H. Enhancing the dimethyl ether carbonylation performance over mordenite catalysts by simple alkaline treatment[J]. Fuel, 2019, 239:794-803. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.147 [22] ALY H M, MOUSTAFA M E, ABDELRAHMAN E A. Synthesis of mordenite zeolite in absence of organic template[J]. Adv Powder Technol, 2012, 23(6):757-760. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2011.10.003 [23] IDRIS A, KHALIL U, ABDULAZIZ I, MAKERTIHARTHA I G, SUBAGJO, LANIWATI M, AL-BETAR A R, MUKTI R R, MURAZA O. Fabrication zone of OSDA-free and seed-free mordenite crystals[J]. Powder Technol, 2019, 342:992-997. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.09.041 [24] LÓNYI F, VALYON J. On the interpretation of the NH3-TPD patterns of H-ZSM-5 and H-mordenite[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2001, 47(2):293-301. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1387181101003894 [25] GRUNDNER S, MARKOVITS M A, LI G, TROMP M, PIDKO E A, HENSEN E J, JENTYS A, SANCHEZ-SANCHEZ M, LERCHER J A. Single-site trinuclear copper oxygen clusters in mordenite for selective conversion of methane to methanol[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6:7546. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8546 [26] CHENG Z Z, HUANG S Y, LI Y, CAI K, YAO D W, LV J, WANG S P, MA X B. Carbonylation of dimethyl ether over MOR and Cu/H-MOR catalysts:Comparative investigation of deactivation behavior[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2019, 576:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2019.02.032 [27] LI Y, LI Z, HUANG S, CAI K, QU Z, ZHANG J, WANG Y, MA X. Morphology-dependent catalytic performance of mordenite in carbonylation of dimethyl ether:Enhanced activity with high c/b ratio[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2019, 11(27):24000-24005. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b03588 [28] ZHAO N, TIAN Y, ZHANG L, CHENG Q, LYU S, DING T, HU Z, MA X, LI X. Spacial hindrance induced recovery of over-poisoned active acid sites in pyridine-modified H-mordenite for dimethyl ether carbonylation[J]. Chin J Catal, 2019, 40(6):895-904. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63335-8 [29] ZHAO N, CHENG Q, LYU S, GUO L, TIAN Y, DING T, XU J, MA X, LI X. Promoting dimethyl ether carbonylation over hot-water pretreated H-mordenite[J]. Catal Today, 2020, 339:86-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.01.013 [30] GOUNDER R, IGLESIA E. Catalytic consequences of spatial constraints and acid site location for monomolecular alkane activation on zeolites[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131(5):1958-1971. doi: 10.1021/ja808292c [31] BORONAT M, MARTÍNEZ-SÁNCHEZ C, LAW D, CORMA A. Enzyme-like specificity in zeolites:A unique site position in mordenite for selective carbonylation of methanol and dimethyl ether with CO[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130(48):16316-16323. doi: 10.1021/ja805607m [32] BORONAT M, MARTINEZ C, CORMA A. Mechanistic differences between methanol and dimethyl ether carbonylation in side pockets and large channels of mordenite[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2011, 13(7):2603-2612. doi: 10.1039/c0cp01996h [33] XUE H, HUANG X, DITZEL E, ZHAN E, MA M, SHEN W. Coking on micrometer-and nanometer-sized mordenite during dimethyl ether carbonylation to methyl acetate[J]. Chin J Catal, 2013, 34(8):1496-1503. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(12)60607-X [34] ZHOU H, ZHU W, SHI L, LIU H, LIU S, NI Y, LIU Y, HE Y, XU S, LI L, LIU Z. In situ DRIFT study of dimethyl ether carbonylation to methyl acetate on H-mordenite[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2016, 417:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2016.02.032 [35] WANG X S, LI R J, YU C C. ZHANG L, XU C M, ZHOU H. Dimethyl ether carbonylation over nanosheet-assembled hierarchical mordenite[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2019, 274: 227-235. [36] CHAOUATI N, SOUALAH A, CHATER M, TARIGHI M, PINARD L. Mechanisms of coke growth on mordenite zeolite[J]. J Catal, 2016, 344:354-364. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2016.10.011 [37] REULE A C, SAWADA J A, SEMAGINA N. Effect of selective 4-membered ring dealumination on mordenite-catalyzed dimethyl ether carbonylation[J]. J Catal, 2017, 349:98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.03.010 [38] LI Y, SUN C, FAN W, WANG Y, LAN A, HAN P, LI X, DOU T. One-pot synthesis of hierarchical mordenite and its performance in the benzylation of benzene with benzyl alcohol[J]. J Mater Sci, 2015, 50(14):5059-5067. doi: 10.1007/s10853-015-9055-4 -





 下载:
下载: