Influence of demineralization on minerals and organic structure in Huadian oil shale
-
摘要: 基于FT-IR和XRD技术研究了逐级酸洗对桦甸油页岩矿物质以及有机结构的影响。结果表明,采用HCl/HF酸洗方法可以有效去除黄铁矿以外的矿物质,但盐酸处理破坏油页岩中高岭石的立体框架结构。油页岩中有机质以脂肪族结构为主,存在形式为无序非晶态聚合体且变质程度较低。酸洗处理对油页岩有机大分子结构影响很小,但对有机结构产生了一定的影响。盐酸处理主要影响含氧官能团和苯环结构,会生成大量羧酸并破坏苯环的多环结构,但对脂肪族化合物的影响较小。氢氟酸处理主要对脂肪族化合物产生影响,破坏脂肪链的桥键结构,脂肪链断裂变短,进而使样品中脂肪族化合物含量降低。盐酸和氢氟酸处理均会破坏油页岩的羟基官能团,尤其对自缔合羟基氢键影响最大。Abstract: Effect of demineralization on minerals and organic structure of Huadian oil shale treated by HCl and HF/HCl sequentially was examined using FT-IR and XRD technology. The results show that HCl/HF treatment can effectively remove minerals except pyrite, but HCl can damage the space frame structure of kaolinite. Organic matter structure with the form of disordered amorphous polymers are mainly composed of aliphatic structure in lower metamorphic grade. Acid treatment effect on shale organic macromolecular structure is very low, but has certain influence on the organic structure. HCl treatment mainly influences oxygen containing functional group and benzene ring structure, generates a large amount of carboxylic acid and destroys the polycyclic structure of benzene ring, but has less effect on aliphatic compounds. HF treatment main affects aliphatic compounds, it can destroy the fat chain bridge bond structure fracture, makes fat chain length shorter and decreases content of aliphatics in the samples. Both HF and HCl treatment can destroy the hydroxyl groups of shale, especially for the associated hydroxyl hydrogen bond.
-
Key words:
- demineralization /
- FT-IR /
- minerals /
- organic structure /
- oil shale
-
表 1 桦甸油页岩的工业分析和物质组成分析
Table 1 Proximate analyses and composition of Huadian oil shale
Proximate analyses wad/% Composition of oil shale w/% M 3.84 kerogen 35.18 A 49.12 carbonate 27.18 V 42.25 silica and clay minerals 34.89 FC 4.79 ignition loss 92.16 表 2 油页岩中矿物质和有机官能团的红外光谱吸收峰
Table 2 Absorption peak for FT-IR spectra of minerals and organic functional groups in oil shale
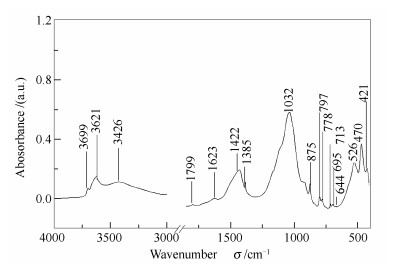
Functional group Absorption bands σ/cm-1 Kaolinite 3 699, 3 621, 1 100a, 1 032, 1 008a, 937a, 913a, 752a, 526, 695, 470, 421 Quartz 1 166a, 797, 778 Muscovite 832a, 713, 412a Serpentine 980a, 565a, 504a, 448a Calcite 1 799, 1 422, 875 As £.CH3 1 385 £.CH2 1 430 Aromatic C=C 1 600 Carboxylic acids 1 709 £:deformation vibration;as:asymmetric;a:hidden absorption peaks detected by second derivative spectra 表 3 样品羟基物质红外光谱分峰拟合各吸收峰参数
Table 3 Parameters of curve-fitting FT-IR spectrum of hydroxyl in samples
Part Position σ/cm-1 Assignment Area percentage/% HD HDA HDB 1# 3 107 OH-N 3.17 7.33 7.27 2# 3 208 ring hydroxyl 12.94 10.95 13.19 3# 3 298 OH-O 10.92 13.00 22.43 4# 3 428 OH-OH 37.43 35.41 28.95 5# 3 559 OH-π 17.02 14.67 14.76 6# 3 624 free OH 18.49 18.61 13.37 表 4 样品含氧官能团红外光谱分峰拟合各吸收峰参数
Table 4 Parameters of curve-fitting FT-IR spectrum of oxygen-containing functional groups in samples
Part Position σ/cm-1 Assignment Area percentage/% HD HAD HDB 1# 1 491 aromatic C=C 18.85 14.39 13.66 2# 1 514 aromatic ring stretch 16.98 3.27 2.36 3# 1 541 aromatic ring stretch 13.06 13.65 9.87 4# 1 569 aromatic ring stretch 10.61 10.02 11.89 5# 1 597 aromatic C=C 10.36 10.65 13.45 6# 1 630 highly conjugated C=O 12.97 17.78 19.55 7# 1 667 conjugated C=O 9.02 12.12 14.67 8# 1 709 COOH 7.43 16.08 16.55 9# 1 730 esters 1.68 1.92 4.77 表 5 样品脂肪族物质的定量峰面积以及结构参数
Table 5 Quantitative peak areas and structure parameters of aliphatic in samples
Type HD HAD HDB Original area 10.04 14.85 17.12 Correct area 22.32 21.16 18.41 A2920/(A2860+ A2950) 1.32 1.30 0.71 表 6 样品脂肪族物质红外光谱分峰拟合各吸收峰参数
Table 6 Parameters of curve-fitting FT-IR spectrum of aliphatic in samples
Part Position σ/cm-1 Assignment Area percentage/% HD HAD HDB 1# 2 851.775 sym. R2CH2 21.57 20.85 21.82 2# 2 873.61 sym. R2CH2 6.75 6.41 8.47 3# 2 894.901 -R3CH 8.23 9.71 6.79 4# 2 922.813 asym. R2CH2 48.89 48.09 35.24 5# 2 949.803 asym. RCH3 15.54 14.94 27.65 -
[1] 何继来, 王擎.爱沙尼亚葛洛特干馏技术的发展与应用[J].东北电力大学学报, 2016, 36(2):76-80. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dbdl201602014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQHE Ji-lai, WANG Qing. The development and application of Estonia gerut carbonization technology[J]. J Northeast Dianli Univ, 2016, 36(2):76-80. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dbdl201602014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [2] 王擎, 张宏喜, 迟铭书, 崔达, 许祥成.蒙脱石对油页岩干酪根热解特性的影响[J].化工进展, 2016, 35(3):766-772. http://www.hgjz.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17851.shtmlWANG Qing, ZHAN Hong-xi, CHI Ming-shu, CUI Da, XU Xiang-cheng. Effect of smectite on the pyrolysis of kerogen isolated from oil shale[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog, 2016, 35(3):766-772. http://www.hgjz.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17851.shtml [3] 畅志兵, 初茉, 张超, 白书霞, 林浩, 马良博.固有碳酸盐和硅酸盐对太姥油页岩热解产物的影响[J].化工学报, 2017, 68(4):1582-1589. http://c.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/hgxb/2017-4.aspxCHANG Zhi-bing, CHU Mo, ZHANG Chao, BAI Shu-xia, LIN Hao, MA Liang-bo. Influence of inherent carbonates and silicates on pyrolytic products of Tailao oil shale[J]. J Chem Ind Eng(China), 2017, 68(4):1582-1589. http://c.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/hgxb/2017-4.aspx [4] WIJAYAN, ZHANG L. A critical review of coal demineralization and its implication on understanding the speciation of organically bound metals and submicrometer mineral grains in coal[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25:1-16. doi: 10.1021/ef1008192 [5] 王擎, 张宏喜, 迟铭书, 崔达, 许祥成.矿物质对桦甸油页岩热解产物影响特性[J].燃料化学学报, 2016, 44(3):328-334. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18797.shtmlWANG Qing, ZHANG Hong-xi, CHI Ming-shu, CUI Da, XU Xiang-cheng. Effect of mine ral matte r on product e volution during pyrolysis of Huadian oil shale[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2016, 44(3):328-334. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18797.shtml [6] LARSEN J W, PAN C S, SHAWVER S. Effect of demineralization on the macromolecular structure of coals[J]. Energy Fuels, 1989, 3(5):557-561. doi: 10.1021/ef00017a004 [7] TEKELY P, NICOLE D, DELPUECH J J, TOTINO E, MULLER J F. Chemical structure changes in coals after low-temperature oxidation and demineralization by acid treatment as revealed by high resolution solid state 13 C NMR[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1987, 15(87):225-231. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0378382087900476 [8] STRYDOM C A, BUNT J R, SCHOBERT H H, RAGHOO M. Changes to the organic functional groups of an inertinite rich medium rank bituminous coal during acid treatment processes[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2011, 92(4):764-770. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2010.09.008 [9] 梁虎珍, 王传格, 曾凡桂, 李美芬, 相建华.应用红外光谱研究脱灰对伊敏褐煤结构的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(2):129-137. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/96c5b9141711cc7930b71645.htmlLIANG Hu-zhen, WANG Chuan-ge, ZENG Fan-gui, LI Mei-fen, XIANG Jian-hua. Effect of demineralization on lignite structure from Yinmin coalfield by FT-IR investigation[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(2):129-137. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/96c5b9141711cc7930b71645.html [10] ZOU X W, YAO J Z, YANG X M, SONG W L, LIN W G. Catalytic effects of metal chlorides on the pyrolysis of lignite[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(2):619-624. doi: 10.1021/ef060477h [11] 张洪, 蒲文秀, 哈斯, 李迎, 刘丹.化学脱灰对低灰煤粉性质的影响[J].工程热物理学报, 2009, 30(4):699-702. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90922X/200904/29907681.htmlZHANG Hong, PU Wen-xiu, HA Si, LI Ying, LIU Dan. Influence of acid treatment on the properties of pulverized coals with low ash content[J]. J Eng Thermophys, 2009, 30(4):699-702. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90922X/200904/29907681.html [12] 地质矿产部地质辞典办公室.地质辞典.四, 矿床地质应用地质分册[M].北京:地质出版社, 1986.The office of Geological Dictionary of Geology and mineral resources. Geological Dictionary. Four, Applied geology fascicle of mineral deposits[M]. Beijing:Geological Press, 1986. [13] 石金明, 向军, 胡松, 孙路石, 苏胜, 徐朝芬, 许凯.洗煤过程中煤结构的变化[J].化工学报, 2010, 61(12):3220-3227. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/fb91bd10e87101f69e3195ee.htmlSHI Jin-ming, XIANG Jun, HU Song, SUN Lu-shi, SU Sheng, XU Chao-fen, XU Kai. Change of coal structure during washing process[J]. J Chem Ind Eng(China), 2010, 61(12):3220-3227. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/fb91bd10e87101f69e3195ee.html [14] WU L M, TONG D S, ZHAO L Z, WANG H, TONG D S, YU W H. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis for hydrothermal transformation of microcrystalline cellulose on montmorillonite[J]. Appl Clay Sci, 2014, 95(3):74-82. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169131714000921 [15] IBARRA J V, PALACIOS J M, DE ANDRÉS A M. Analysis of coal and char ashes and their ability for sulphur retention[J]. Fuel, 1989, 68(7):861-867. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(89)90121-X [16] 闻辂.矿物红外光谱学[M].重庆:重庆大学出版社, 1989.WEN Lu. The infrared spectroscopy of minerals[M]. Chongqing:Chongqing University Press, 1989. [17] DE BENEDETTO G E, LAVIANO R, SABBATINI L, ZAMBONIN P G. Infrared spectroscopy in the mineralogical characterization of ancient pottery[J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2002, 3(3):177-186. doi: 10.1016/S1296-2074(02)01178-0 [18] 韩峰, 张衍国, 蒙爱红, 李清海.云南褐煤结构的FT-IR分析[J].煤炭学报, 2014, 39(11):2293-2299. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=mtxb201411024&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQHAN Feng, ZHANG Yan-guo, MENG Ai-hong, LI Qing-hai. FTIR analysis of Yunnan Lignite[J]. China Coal Soc, 2014, 39(11):2293-2299. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=mtxb201411024&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [19] GHOORAH M, DLUGOGORSKI B Z, OSKIERSKI H C, KENNEDY E M. Study of thermally conditioned and weak acid-treated serpentinites for mineralisation of carbon dioxide[J]. Miner Eng, 2014, 59(5):17-30. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0892687514000429 [20] 孙斌. 油页岩矿物质分解特性研究[D]. 吉林: 东北电力大学, 2013.SUN Bin, Mineral decomposition characteristic research of oil shale[D] Jilin:Northeast Elcetric Power University, 2013. [21] SAKANISHI K, SAITO I, ISHOM F, WATANABE I, MOCHIDA I, OKUYAMA N. Characterization and elution behaviors of organically associated minerals in coals during acid treatment and solvent extraction[J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(11/12):1471-1475. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236102000789 [22] 韩秀伶, 陈开惠.高岭石-多水高岭石演化系列的红外吸收光谱研究[J].地质科学, 1982, (1):71-79.HAN Xiu-ling, CHEN Kai-hui. Study of infrared absorption spectra on the kaolinite-halloysite evolutionary series[J]. Chin J Geol, 1982, (1):71-79. [23] 秦匡宗, 劳永新.茂名和抚顺油页岩组成结构的研究Ⅰ.有机质的芳碳结构[J].燃料化学学报, 1985, 13(2):39-46. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=rlhx198502004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQQIN Kuang-zong, LAO Yong-xin. Study on the structure of oil shale in Maoming and FushunⅠ. Aromatic carbon structure of organic matter[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 1985, 13(2):39-46. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=rlhx198502004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [24] LARSEN J W, PAN C S, SHAWVER S. Effect of demineralization on the macromolecular structure of coals[J]. Energy Fuels, 1989, 3:557-561. doi: 10.1021/ef00017a004 [25] 柏静儒, 潘朔, 林卫生, 贾春霞, 王擎.盐酸酸洗对油页岩小分子溶出行为的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(12):1409-1415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2014.12.001BAI Jing-ru, PAN Shuo, LIN Wei-sheng, JIA Chun-xia, WANG Qing. Influence of hydrochloric acid pickling on dissolution behaviors of small molecules in oil shale[J].J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(12):1409-1415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2014.12.001 [26] WIJAYA N, ZHANG L. A critical review of coal demineralization and its implication on understanding the speciation of organically bound metals and submicrometer mineral grains in coal[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(1):1-16. doi: 10.1021/ef1008192 [27] GENG W, NAKAJIMA T, TAKANASHI H, OHKI A. Analysis of carboxyl group in coal and coal aromaticity by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrometry[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(1):139-144. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.07.027 [28] 魏强, 唐跃刚, 王绍清, 黄帆. 13C-NMR分析混合酸处理脱灰对永兴褐煤结构的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(4):410-415. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18603.shtmlWEI Qiang, TANG Yue-gang, WANG Shao-qing, HUANG Fan. 13C-NMR study on effect of demineralization by mixed acid treatment on Yongxing lignite structure[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(4):410-415. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18603.shtml [29] PATTERSON J H. A review of the effects of minerals in processing of Australian oil shales[J]. Fuel, 1994, 73(3):321-327. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(94)90082-5 [30] IBARRA J V, MUNOZ E, MOLINER R. FTIR study of the evolution of coal structure during the coalification process[J]. Org Geochem, 1996, 24(6):725-735. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0146638096000630 [31] ZHAO Y, LIU L, QIU P H, XIE X, CHEN X Y, LIN D. Impacts of chemical fractionation on Zhundong coal's chemical structure and pyrolysis reactivity[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2017, 155:144-152. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.05.011 [32] LIN R, RITZ G P. Reflectance FT-IR microspectroscopy of fossil algae contained in organic-rich shales[J]. Appl Spectrosc, 1993, 47(3):265-271. doi: 10.1366/0003702934066794 -





 下载:
下载: