Comparison of mercury emission from around 300 MW coal-fired power generation units between pulverized boiler and circulating fluidized-bed boiler
-
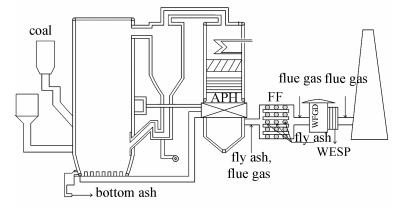
摘要: 选取某地330 MW煤粉炉(PC炉)和350 MW循环流化床锅炉(CFB)的燃煤电厂进行汞排放特性的研究。采用30B法和安大略法对两个燃煤电厂的除尘器入口、除尘器出口、脱硫塔出口和湿式电除尘器出口的烟气进行了取样和汞浓度分析,采集了入炉煤和副产物底渣、飞灰及脱硫石膏样品。通过样品中汞含量的分布,探讨了PC炉与CFB锅炉机组现有污染物控制设备对汞的协同脱除作用。结果表明,350 MW CFB电厂除尘器出口烟气平均汞浓度降低至0.43 μg/m3,布袋除尘器对汞的捕获效率达到98.9%,相应的燃烧副产物中飞灰是汞的主要富集对象。对于330 MW PC炉电厂,除尘器入口和除尘器出口烟气汞浓度均高于350 MW CFB电厂,烟气汞浓度从除尘器入口、除尘器出口到脱硫塔出口依次降低,在脱硫塔出口烟气汞浓度降低至0.42 μg/m3,静电除尘器和湿式脱硫塔对烟气汞的捕获效率分别为75.0%和22.4%,相应的产物中飞灰和脱硫石膏中汞都有一定程度的富集。Abstract: The mercury emission characteristics are investigated and compared at a coal-fired power plant with 330 MW pulverized coal (PC) boiler and a coal-fired power plant with 350 MW circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boiler. EPA 30B method and Ontario method were used to test the mercury concentration in flue gas at the inlet of dust extraction unit, outlet of dust extraction unit, outlet of desulfurization unit, and outlet of wet dust extraction unit. The feed coal, bottom ash, fly ash and gypsum sample were collected at the same time together with gas sampling. The effect of the existing air pollution control device on mercury control was discussed toward PC and CFB units based on the mercury distribution data. The results show that the mercury concentration at fabric filter (FF) outlet of CFB power plant is decreased to 0.43 μg/m3 and the mercury removal efficiency of FF reaches 98.9%. A predominating portion of mercury is enriched in fly ash. With respect to a PC power plant, the mercury concentrations at inlet and outlet of ESP are both higher than those in the CFB power plant, and the mercury concentration gradually drops from electrostatic precipitator (ESP) inlet to wet flue gas desulfurization (WFGD) outlet. The mercury concentration reaches a low value of 0.42 μg/m3 at the WFGD outlet, and the mercury removal efficiency of ESP and WFGD is 75.0% and 22.4%, respectively, which can meet the ultra low mercury emission controlling.
-
表 1 入炉煤的工业分析和平均汞含量
Table 1 Proximate analysis and average mercury content of feed coal samples

表 2 除尘器入口30B法测试得到的烟气汞浓度
Table 2 Mercury concentration in inlet flue gas of dust collector detected by 30B method

表 3 除尘器入口OHM法测试得到的烟气汞浓度
Table 3 Mercury concentration in inlet flue gas of dust collector detected by OHM method

表 4 除尘器出口30B法测试得到的烟气汞浓度
Table 4 Mercury concentration in outlet flue gas of dust collector detected by 30B method

表 5 湿式脱硫塔出口30B法测试得到的烟气汞浓度
Table 5 Mercury concentration in outlet flue gas of wet desulfurization tower detected by 30B method

表 6 湿式电除尘器出口30B法测试得到的烟气汞浓度
Table 6 Mercury concentration in outlet flue gas of wet ESP detected by 30B method

表 7 两电厂各固相废弃物中的汞含量
Table 7 Mercury content in solid wastes for two power plants

表 8 330 MW PC电厂五级ESP飞灰的汞含量
Table 8 Mercury content in fly ash from ESP for a 330 MW PC power plant

-
[1] 杨爱勇, 严智操, 惠润堂, 申智勇, 庄柯.中国煤中汞的含量、分布与赋存状态研究[J].科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(32): 93-100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201532017.htmYANG Ai-yong, YAN Zhicao, HUI Runtang, SHEN Zhiyong, ZHUANG Ke. The abundance, distribution, and modes of occurrence of Hg in Chinese coals[J]. Sci Technol Eng, 2105, 15(32): 93-100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201532017.htm [2] 国家环境保护部. GB13223—2011火电厂大气污染物排放标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011.Ministry of Environmental Protection. GB13223—2011 Pollutant emission standard in thermal power plant[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2011. [3] WU S, YANG W, ZHOU J, WANG H, XIE Z. Effects of properties of activated carbon on its activity for mercury removal and mercury desorption from used activated carbons[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(3): 1946-1950. doi: 10.1021/ef502868s [4] WANG S, ZHANG Y, GU Y, WANG J, LIU Z, ZHANG Y, CAO Y, ROMERO C E, PAN W. Using modified fly ash for mercury emissions control for coal-fired power plant applications in China[J]. Fuel, 2016, 181: 1230-1237. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.02.043 洪亚光, 段钰锋, 朱纯, 周强, 佘敏, 杜鸿飞.载硫椰壳活性炭喷射脱汞实验研究[J].工程热物理学报, 2015, 36(5): 1135-1138.HONG Ya-guang, DUAN Yu-feng, ZHU Chun, SHE Min, DU Hong-fei. Experimental study on mercury adsorption of S-impregnated coconut shell activated carbon by duct injection[J]. J Eng Thermophys, 2015, 36(5): 1135-1138. [6] ZHANG L, WANG S, MENG Y, HAO J. Influence of Mercury and Chlorine Content of Coal on Mercury Emissions from Coal-Fired Power Plants in China[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2012, 46(11): 6385-6392. doi: 10.1021/es300286n [7] 许月阳, 薛建明, 王宏亮, 李兵, 管一明, 刘珺.燃煤烟气常规污染物净化设施协同控汞的研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34(23): 3924-3931. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC201423013.htmXU Yue-yang, XUE Jian-ming, WANG Hong-liang, LI Bing, GUAN Yi-ming, LIU Jun. Research on mercury collaborative control by conventional pollutants purification facilities of coal-fired power plants[J]. Proc Chin Soc Electrical Eng, 2014, 34(23): 3924-3931. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC201423013.htm [8] 程乐鸣, 周星龙, 郑成航, 王勤辉, 方梦祥, 施正伦, 骆仲泱, 岑可法.大型循环流化床锅炉的发展[J].动力工程, 2008, 28(6): 817-826. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10079-2008073542.htmCHENG Le-ming, ZHOU Xing-long, ZHENG Cheng-hang, WANG Qin-hui, FANG Meng-xiang, SHI Zheng-lun, LUO Zhong-yang, CEN Ke-fa. Development of large-scale circulating fluidized bed boiler[J]. J Power Eng, 2008, 28(6): 817-826. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10079-2008073542.htm [9] HU Y, CHENG H. Control of mercury emissions from stationary coal combustion sources in China: Current status and recommendations[J]. Environ Pollut, 2016, 218: 1209-1221. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.077 [10] CHEN B, LI J S, CHEN G Q, WEI W D, YANG Q, YAO M T, SHAO J A, ZHOU M, XIA X H, DONG K Q, XIA H H, CHEN H P. China's energy-related mercury emissions: Characteristics, impact of trade and mitigation policies[J]. J Clean Prod, 2017, 141: 1259-1266. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.200 [11] YU L, YIN L, XU Q, XIONG Y. Effects of different kinds of coal on the speciation and distribution of mercury in flue gases[J]. J Energy Inst, 2015, 88(2): 136-142. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2014.06.006 [12] RALLO M, HEIDEL B, BRECHTEL K, MAROTO-VALER M M. Effect of SCR operation variables on mercury speciation[J]. Chem Engineer J, 2012, 198-199: 87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.080 [13] EOM Y, JEON S, NGO T, KIM J, LEE T. Heterogeneous mercury reaction on a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalyst[J]. Catal Lett, 2008, 121(3/4): 219-225. doi: 10.1007/s10562-007-9317-0 [14] ZHOU Z, LIU X, ZHAO B, CHEN Z, SHAO H, WANG L, XU M. Effects of existing energy saving and air pollution control devices on mercury removal in coal-fired power plants[J]. Fuel Process Technol 2015, 131: 99-108. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.11.014 [15] CAO Y, CHENG Q, CHEN C, LIU M, WANG C, PAN W. Abatement of mercury emissions in the coal combustion process equipped with a fabric filter baghouse[J]. Fuel 2008, 87: 3322-3330. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.05.010 [16] PUDASAINEE D, KIM J, YOON Y, SEO Y. Oxidation, reemission and mass distribution of mercury in bituminous coal-fired power plants with SCR, CS-ESP and wet FGD[J]. Fuel, 2012, 93: 312-318. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.10.012 [17] ZHANG L, ZHUO Y, CHEN L, XU X, CHEN C. Mercury emissions from six coal-fired power plants in China[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2008, 89(11): 1033-1040. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2008.04.002 [18] 段钰锋, 江贻满, 杨立国, 王运军.循环流化床锅炉汞排放和吸附实验研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2008, 28(32): 1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC200832002.htmDUAN Yu-feng, JIANG Yi-man, YANG Li-guo, WANG Yun-jun. Experimental study on mercury emission and adsorption in circulating fluidized bed boiler[J]. Proc Chin Soc Electrical Eng, 2014, 28(32): 1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC200832002.htm [19] CHENG C, CAO Y, ZHANG K, PAN W. Co-effects of sulfur dioxide load and oxidation air on mercury re-emission in forced-oxidation limestone flue gas desulfurization wet scrubber[J]. Fuel, 2013, 116: 505-511. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256712446_Co-effects_of_sulfur_dioxide_load_and_oxidation_air_on_mercury_re-emission_in_forced-oxidation_limestone_flue_gas_desulfurization_wet_scrubber [20] YUE C, WANG J, HAN L, CHANG L, HU Y, WANG H. Effects of pretreatment of Pd/AC sorbents on the removal of Hg0 from coal derived fuel gas[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 135: 125-132. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.11.038 [21] RRUPP E C, WILCOX J. Mercury chemistry of brominated activated carbons-Packed-bed breakthrough experiments[J]. Fuel, 2014, 117: 351-353. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.09.017 [22] CHANG J C S, ZHAO Y. Pilot plant testing of elemental mercury reemission from a wet scrubber[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 22(1): 338-342. http://oaspub.epa.gov/eims/eimscomm.getfile?p_download_id=461002 [23] XIN M, GUSTIN M S, LADWIG K. Laboratory study of air-water-coal combustion product (fly ash and FGD solid) mercury exchange[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(16): 2260-2267. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2006.01.029 -





 下载:
下载: