Structure characteristics and association behavior of coal and petroleum C7-asphaltenes
-
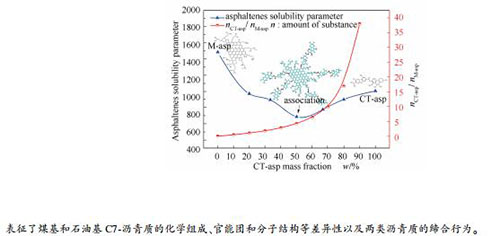
摘要: 采用核磁(NMR)、小角散射分析(SAXS)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)、改进的B-L法等手段,研究了煤基C7-沥青质(CT-asp)和石油基C7-沥青质(M-asp)两类沥青质的化学组成、官能团和分子结构等组成结构特征以及差异性,进而通过极性溶剂中沥青质稳定参数研究两类沥青质的缔合行为和聚集体尺寸以及两者之间的氢键和酸碱作用。结果表明,CT-asp分子芳香环数较少且有较多短烷基侧链,且芳香度较高,较高含量氧杂原子以芳香醚和酚羟基赋存形态为主;而M-asp的芳香核尺寸和平均相对分子质量明显高于CT-asp,芳香环数虽较多且有较多长烷基支链,且芳香度较小;两类沥青质缔合聚集程度关联物质的量比(nCT-asp/nM-asp)及其分子结构特征,源于杂原子官能团的氢键和酸碱作用是两类沥青质缔合的主要作用力。Abstract: The structural characteristics and differences of coal tar and petroleum C7-asphaltenes were studied, such as chemical composition, functional groups and molecular structure, using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), improved B-L method and other methods. Furthermore, the association behavior and aggregation size of two different types of asphaltenes as well as the hydrogen bonds and acidic-basic interaction were analyzed by asphaltenes solubility parameters in polar solvents. The experiment results showed that the coal tar asphaltenes (CT-asp) was mainly composed of less aromatic rings with more short alkyl branched chains and possessed a high aromaticity degree. The higher content oxygen heteroatoms of CT-asp were mostly presented as aromatic ether bonds and phenolic hydroxyl groups. The aromatic nucleus size and the average relative molecular weight of petroleum asphaltenes (M-asp) were larger than that of CT-asp. The M-asp consisted primarily of more aromatic rings with more long alkyl branched chains and possessed a low aromaticity degree. The association and aggregation degree between CT-asp and M-asp was associated with the amount of substance ratio (nCT-asp/nM-asp) and their molecular structure characteristics. The association force of two types mainly was the hydrogen bonds and the acidic-basic interaction from heteroatomic functional groups.
-
Key words:
- coal tar /
- petroleum /
- C7-asphaltene /
- molecular structure /
- association behavior
-
表 1 煤基沥青质和石油基沥青质的元素分析
Table 1 Elemental analysis of CT-asp and M-asp
Element analysis CT-asp M-asp C w/% 78.38 82.13 H w/% 6.17 7.48 S w/% 0.36 2.23 N w/% 1.68 4.90 Total(C H S N) w/% 86.59 96.74 H/C (atomic ratio) 0.95 1.09 表 2 煤基沥青质和石油基沥青质的杂原子官能团(O、N和S)分析
Table 2 XPS curve-resolution results for O, N and S
Atom type Binding energy
E/eVAtomic ratio per 100 carbons /% CT-asp M-asp Oxygen type C=O 531.8 2.10 1.14 and content C-O-C, C-OH, C-O 532.9 4.72 1.29 COO- 534.1 1.65 0.49 total - 8.47 2.92 Nitrogen type pyridinic-N 398.8 0.33 0.97 and content pyrrolic-N 399.9 1.20 1.02 quaternary-N 401.1 0.76 0.24 total - 2.29 2.23 Sulfur type alkyl sulfides 163.4 0.13 1.07 and content thiophenes 164.8 0.09 0.50 sulfoxides 165.6 0.14 - total - 0.37 1.57 表 3 沥青质C-O键的类型(原子比)
Table 3 FT-IR curve-resolution results for C-O bond
Peak position
/cm-1Assignment Atomic ratio /% CT-asp M-asp 1043 alkyl ether group (-C-O-C-) 12.30 24.02 1175 C-O vinration of phenols 34.02 35.95 1290 aromatic ether groups 40.75 31.00 1715 carboxyl group (-COOH) 12.93 9.03 phenols/(phencols+ether) 39.08 39.50 表 4 沥青质的1H-NMR平均结构参数
Table 4 Average molecular structural parameters of CT-asp and M-asp from 1H-NMR
Structural parameter Value CT-asp M-asp HA watom/% 37.8 8.6 Hα watom/% 42.6 22.6 Hβ watom/% 15.9 49.3 Hγ watom/% 3.7 19.5 M (relative molecular mass VPO) 416 1950 fA (aromatic carbon weight ratio) 0.71 0.53 fN (naphthenic carbon weight ratio) 0.18 0.17 fP (alkyl carbon weight ratio) 0.11 0.33 RT (total rings per average molecule) 5.76 28.63 RA (aromatic rings per average molecule) 4.34 20.87 RN (naphthenic rings per average molecule) 1.42 7.76 CA (aromatic carbons per average molecule) 19.34 66.62 CN (naphthenic carbons per average molecule) 4.92 23.28 CP (alkyl carbons per average molecule) 2.91 43.34 CS (saturated carbons per average molecule) 7.83 66.62 HA/CA (aromatic rings condensation degree) 0.78 0.42 σ (aromatic rings substitution degree) 0.48 0.59 表 5 沥青质的13C-NMR平均结构参数
Table 5 Average structural parameters of CT-asp and M-asp from 13C-NMR
Chemical shift Type of carbon Atomic ratio per 100 carbons /% CT-asp M-asp 0-25 methyl 12.9 17.0 25-50 methylene 13.1 31.0 50-70 methoxy, ether, alcohol 3.7 1.1 90-135 aromatic carbon bound to hydrogen 47.3 28.0 135-148 bridgehead or alkyl-substituted aromatic carbon 9.6 18.7 148-171 oxy-aromatic carbon 7.2 2.0 171-220 carboxyl, ester, carbonyl, ketone 6.1 2.2 0-90 aliphatic carbon (Cal) 29.7 49.1 90-220 aromatic carbon (Car) 70.3 50.9 表 6 沥青质缔合体的氢键分布
Table 6 Hydrogen bonds distribution of asphaltenes aggregation
Position /cm-1 Abbreviation Atomic ratio /% CT-asp M-asp MC-asp 3610 free OH groups 0.70 1.31 2.01 3530 OH-π HBs 17.31 35.10 23.99 3400 OH-OH self associated 35.74 53.07 41.60 3300 OH-ether O HBs 21.63 4.66 17.33 3200 tightly bound cyclic OH tetramers 13.57 5.23 10.71 3150 OH-N (acidic/basic strctures) 11.05 0.62 4.35 表 7 沥青质的酸碱官能团
Table 7 Acidic and basic groups of CT-asp and M-asp
Functional groups Atomic ratio /% Functional groups Atomic ratio /% CT-asp M-asp CT-asp M-asp Neutral C=O 2.10 1.14 acidic alkyl sulfides 0.15 1.07 Neutral C-O- C 2.87 0.50 basic thiophenes 0.09 0.50 Acidic C-OH, C-O 1.84 0.79 neutral sulfoxides 0.04 0 Acidic COO- 1.65 0.49 neutral sulfones 0.08 0 Basic pyridinic-N 0.33 0.97 total of acid 3.64 2.35 Neutral pyrrolic-N 1.20 1.02 total of 1.18 1.71 Basic quaternary-N 0.76 0.24 relative acidity 2.46 0.64 -
[1] KAN T, SUN X, WANG H, LI C, MUHAMMAD U. Production of gasoline and diesel from coal tar via its catalytic hydrogenation in serial fixed beds[J]. Energy Fuels, 2012, 26(6):3604-3611. doi: 10.1021/ef3004398 [2] 张倩玉, 许志明, 赵锁奇.低温煤焦油常渣C5沥青质的分离与表征[J].燃料化学学报, 2016, 44(11):1318-1325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2016.11.006ZHANG Qian-yu, XU Zhi-ming, ZHAO Suo-qi. Separation and characterization of C5-asphaltene from low temperature coal tar[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2016, 44(11):1318-1325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2016.11.006 [3] ANGELES M J, LEYVA C, ANCHEYTA J, RAMÍREZ S. A review of experimental procedures for heavy oil hydrocracking with dispersed catalyst[J]. Catal Today, 2014, 220-222, 274-294. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0920586113003908 [4] LI C, DU J, YANG T, DENG W. Exploratory investigation on the slurry-phase hydrocracking reaction behavior of coal tar and petroleum-based heavy oil mixed raw material[J]. Energy Fuels, 2019, 33(9):8471-8482. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b02031 [5] 盛强, 王刚, 金楠, 张淇源, 高成地, 高金森.石油沥青质的微观结构分析和轻质化[J].化工进展, 2019, 38(3):1147-1159. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgjz201903001SHENG Qiang, WANG Gang, JIN Nan, ZHANG Qi-yuan, GAO Cheng-di, GAO Jin-sen. Petroleum asphaltene micro-structure analysis and lightening[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog, 2019, 38(3):1147-1159. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgjz201903001 [6] 张文, 龙军, 任强, 蔡新恒.沥青质分子聚集行为研究进展[J].化工进展, 2019, 38(5):2158-2163. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgjz201905011ZHANG Wen, LONG Jun, REN Qiang, CAI Xin-heng. Research progress on aggregation behavior of asphaltene[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog, 2019, 38(5):2158-2163. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgjz201905011 [7] 隆建, 沈本贤, 赵基钢, 凌昊, 卢俊财.减压渣油掺炼煤焦油改善常压溶剂脱沥青过程的机理[J].石油学报(石油加工), 2012, 28(1):69-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2012.01.013LONG Jian, SHEN Ben-xian, ZHAO Ji-gang, LING Hao, LU Jun-cai. Mechanism of improving atmospheric solvent deasphalting process by vacuum residue blending with coal tar[J]. Acta Pet Sin(Pet Process Sect):2012, 28(1):69-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2012.01.013 [8] 孟兆会, 杨圣斌, 杨涛, 郭蓉.减压渣油掺炼煤焦油相容性及加氢处理研究[J].石油炼制与化工, 2014, 45(5):25-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2014.05.005MENG Zhao-hui, YANG Sheng-bin, YANG Tao, GUO Rong. Study on stability of vacuum residue blending coal tar and hydrocracking of mixture[J]. Chin Pet Process Petrochem Technol, 2014, 45(5):25-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2014.05.005 [9] 胡建宏, 程相林, 李国宁, 武建军, 汲伟, 王永刚, 王柏川.煤沥青可溶组分在甲苯中缔合行为的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(7):774-778. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18443.shtmlHU Jian-hong, CHENG Xiang-lin, LI Guo-ning, WU Jian-jun, JI Wei, WANG Yong-gang, WANG Bai-chuan. Association behavior of coal tar pitch soluble components in toluene[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(7):774-778. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18443.shtml [10] YUDIN I K, NIKOLAENKO G L, GORODETSKII E E, KOSOV V I, MELIKYAN V R, MARKHASHOV E L, FROT D, BRIOLANT Y. Mechanisms of asphaltene aggregation in toluene-heptane mixtures[J]. J Pet Sci Eng, 1998, 20(3/4):297-301. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410598000333 [11] HAJI-AKBARI N, TEERAPHAPKUL P, FOGLER H S. Effect of asphaltene concentration on the aggregation and precipitation tendency of asphaltenes[J]. Energy Fuels, 2014, 28(2):909-919. doi: 10.1021/ef4021125 [12] ANISIMOV M A, GANEEVA Y M, GORODETSKII E E, DESHABO V A, KOSOV V I, KURYAKOV V N, YUDIN D I, YUDIN I K. Effects of resins on aggregation and stability of asphaltenes[J]. Energy Fuels, 2014, 28(10):6200-6209. doi: 10.1021/ef501145a [13] KRAIWATTANAWONG K, FOGLER H S, GHARFEH S G, SINGH P, THOMASON W H, CHAVADEJ S. Effect of asphaltene dispersants on aggregate size distribution and growth[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23(3):1575-1582. doi: 10.1021/ef800706c [14] GRAY M R, TYKWINSKI R R, STRYKER J M, TAN X. Supramolecular assembly model for aggregation of petroleum asphaltenes[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(7):3125-3134. doi: 10.1021/ef200654p [15] GABRIENKO A A, MARTYANOV O N, KAZARIAN S G. Effect of temperature and composition on the stability of crude oil blends studied with chemical imaging[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(11):7114-7123. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b01880 [16] AGRAWALA M, YARRANTON H W. An asphaltene association model analogous to linear polymerization[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2001, 40(21):4664-4672. doi: 10.1021/ie0103963 [17] RAKOTONDRADANY F, FENNIRI H, RAHIMI P, GAWRYS K L, KILPATRICK P K, GRAY M R. Hexabenzocoronene model compounds for asphaltene fractions:Synthesis & characterization[J]. Energy Fuels, 2006, 20(6):2439-2447. doi: 10.1021/ef060130e [18] LI P, ZONG Z, LI Z, WANG Y, LIU F, WEI X. Characterization of basic heteroatom-containing organic compounds in liquefaction residue from Shenmu-Fugu subbituminous coal by positive-ion electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 132:91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.12.026 [19] DU J, DENG W, LI C, ZHANG Z, YANG T, GUO R. Reactivity and structure changes of coal tar asphaltene during slurry-phase hydrocracking[J]. Energy Fuels, 2017, 31(2):1858-1865. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02992 [20] XIONG G, LI Y, JIN L, HU H. In situ FT-IR spectroscopic studies on thermal decomposition of the weak covalent bonds of brown coal[J]. J Anal Appl Pyroysisl, 2015, 115:262-267. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2015.08.002 [21] FERGOUG T, BOUHADDA Y. Determination of Hassi Messaoud asphaltene aromatic structure from 1H & 13C NMR analysis[J]. Fuel, 2014, 115:521-526. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.07.055 [22] DUTTA MAJUMDAR R, BAKE K D, RATNA Y, POMERANTZ A E, MULLINS O C, GERKEN M, HAZENDONK P. Single-core PAHs in petroleum-and coal-derived asphaltenes:Size and distribution from solid-state NMR spectroscopy and optical absorption measurements[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30(9):6892-6906. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b02815 [23] ALHUMAIDAN F S, HAUSER A, RANA M S, LABABIDI H M S, BEHBEHANI M. Changes in asphaltene structure during thermal cracking of residual oils:XRD study[J]. Fuel, 2015, 150:558-564. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.02.076 [24] SCHNEIDER M H, ANDREWS A B, MITRA-KIRTLEY S, MULLINS O C. Asphaltene molecular size by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(5):2875-2882. doi: 10.1021/ef700216r [25] JIN N, WANG G, HAN S, MENG Y, XU C, GAO J. Hydroconversion behavior of asphaltenes under liquid-phase hydrogenation conditions[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30(4):2594-2603. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b02765 [26] SUN Z, LI D, MA H, TIAN P, LI X, LI W, ZHU Y. Characterization of asphaltene isolated from low-temperature coal tar[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 138:413-418. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.05.008 [27] XIA W, YANG J. Reverse flotation of Taixi oxidized coal[J]. Energy Fuels, 2013, 27(12):7324-7329. doi: 10.1021/ef4017224 [28] EYSSAUTIER J, LEVITZ P, ESPINAT D, JESTIN J, GUMMEL J, GRILLO I, BARRE L. Insight into asphaltene nanoaggregate structure inferred by small angle neutron and X-ray scattering[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2011, 115(21):6827-6837. doi: 10.1021/jp111468d [29] 张庆, 邓文安, 李传, 吴乐乐.稠油沥青质的基本化学组成结构与缔合性研究[J].石油炼制与化工, 2014, 45(6):20-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2014.06.007ZHANG Qing, DENG WEN-an, LI Chuan, WU Le-le. Study on basic chemical structure and association of asphaltene in heavy oil[J]. Chin Pet Process Petrochem Technol, 2014, 45(6):20-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2014.06.007 [30] JUYAL P, MERINO-GARCIA D, ANDERSEN S I. Effect on molecular interactions of chemical alteration of petroleum asphaltenes[J]. Energy Fuels, 2005, 19(4):1272-1281. doi: 10.1021/ef050012b [31] LIU X, HIRAJIMA T, NONAKA M, SASAKI K. Investigation of the changes in hydrogen bonds during low-temperature pyrolysis of lignite by diffuse reflectance FT-IR combined with forms of water[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2015, 54(36):8971-8978. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b02474 [32] 张龙力, 王春岚, 赵元生, 杨国华, 杨朝合.塔河常压渣油沥青质含硫官能团形态与其性质的关系研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2012, 40(9):1081-1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.09.009ZHANG Long-li, WANG Chun-lan, ZHAO Yuan-sheng, YANG Guo-hua, YANG Chao-he. Study on the relationship between sulfur functionalities and the characteristics of THAR asphaltene[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 40(9):1081-1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.09.009 -





 下载:
下载: