Influence of different distributions of Ca-mineral in coal on trimodal particulate matter formation during combustion
-
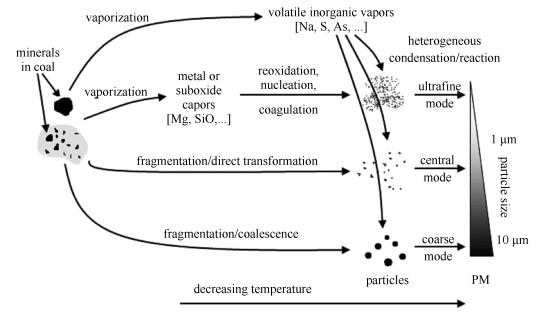
摘要: 通过物理掺混和溶液浸渍两种方式将醋酸钙添加至烟煤中, 分别制得富含外在钙盐的掺钙煤与富含内在钙盐的浸钙煤, 将原煤、掺钙煤和浸钙煤在沉降炉中进行燃烧实验, 炉膛温度1300℃.收集并分析燃烧生成的颗粒物, 研究不同分布形式的钙盐对三模态颗粒物生成的影响.结果表明, 三种煤燃烧生成的超细模态、中间模态和粗模态颗粒物均分别位于小于0.2、0.2-2.0和大于2.0μm粒径范围内; 内、外在钙盐均促进超细模态颗粒物的生成, 其中, 外在钙盐的促进作用更明显; 内在钙盐抑制中间模态颗粒物的生成, 而外在钙盐促进其生成; 对于粗模态颗粒物的生成, 内在钙盐具有促进作用, 外在钙盐作用不明显.Abstract: Calcium acetate was added into a bituminous coal through physically blending and impregnation to obtain the ble-Ca coal rich in excluded Ca-mineral and imp-Ca coal rich in included Ca-mineral, respectively. The raw coal, ble-Ca coal and imp-Ca coal were burned in a drop tube furnace at 1300℃. The generated particulate matters (PMs) were collected and analyzed to study the influence of different distributions of Ca-mineral in coal on trimodal PM formation during combustion. The results showed that for the three coals, PMs with the ultrafine mode, central mode and coarse mode were all in the size range of < 0.2μm, 0.2-2μm and >2μm, respectively. The included and excluded Ca-minerals can both promote the formation of ultrafine mode PM, and the excluded one had more significant effect. The included Ca-mineral can restrain, while the excluded one can promote the formation of central mode PM. The included Ca-mineral can promote the formation of coarse mode PM, while the excluded one did not have obvious effect.
-
Key words:
- coal combustion /
- coal matrix /
- included mineral /
- excluded mineral /
- particulate matter /
- formation mode
-
表 1 原煤特性分析
Table 1 Properties of raw coal
Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis w/% M A V FC C H N S O* 0.68 36.57 21.54 41.21 50.58 3.14 0.82 3.58 4.64 Major ash components w/% Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 SO3 K2O CaO TiO2 Fe2O3 1.00 1.29 32.31 57.03 0.14 1.71 1.73 0.68 0.87 3.24 *: by difference -
[1] YAO Q, LI S Q, XU H W, ZHUO J K, SONG Q. Studies on formation and control of combustion particulate matter in China: A review [J]. Energy, 2009, 34(9): 1296-1309. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2009.03.013 [2] LINAK W P, MILLER C A, SEAMES W S, WENDT J O L, ISHINOMORI T, ENDO Y, MIYAMAE S. On trimodal particle size distributions in fly ash from pulverized-coal combustion[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2002, 29(1): 441-447. doi: 10.1016/S1540-7489(02)80058-X [3] SEAMES W S. An initial study of the fine fragmentation fly ash particle mode generated during pulverized coal combustion[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2003, 81(2): 109-125. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3820(03)00006-7 [4] YU D X, XU M H, YAO H, SUI J C, LIU X W, YU Y, CAO Q. Use of elemental size distributions in identifying particle formation modes[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2007, 31(6): 1921-1928. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223232052_Use_of_elemental_size_distributions_in_identifying_particle_formation_modes [5] QUANN R J. Ash vaporization under simulated pulverized coal combustion conditions[D]. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1982. [6] YU D X, XU M H, YAO H, LIU X W, ZHOU K, LI L, WEN C. Mechanisms of the central mode particle formation during pulverized coal combustion [J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2009, 32(1): 2075-2082. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/245224403_Mechanisms_of_the_central_mode_particle_formation_during_pulverized_coal_combustion [7] KANG S G. Fundamental studies of mineral matter transformation during pulverized coal combustion: Residual ash formation[D]. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1991. [8] HELBLE J J. A model for the air emissions of trace metallic elements from coal combustors equipped with electrostatic precipitators[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 63(2/3): 125-147. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223578384_Model_for_the_air_emissions_of_trace_metallic_elements_from_coal_combustors_equipped_with_electrostatic_precipitators [9] 徐明厚, 于敦喜, 刘小伟.燃煤可吸入颗粒物的形成与排放[M].北京:科学出版社, 2009.XU Ming-hou, YU Dun-xi, LIU Xiao-wei. Formation and Emission of Particulate Matter During Coal Combustion[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. [10] MCLENNAN A R, BRYANT G W, BAILEY C W, STANMORE B R, WALL T F. An experimental comparison of the ash formed from coals containing pyrite and siderite mineral in oxidizing and reducing conditions[J]. Energy Fuels, 2000, 14(2): 308-315. doi: 10.1021/ef990092h [11] 于敦喜, 徐明厚, 姚洪, 刘小伟, ZHANG Lian, WANG Qun-ying, NINOMIYA Y.利用CCSEM对煤中矿物特性及其燃烧转化行为的研究[J].工程热物理学报, 2007, 28(5): 875-878. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB200705050.htmYU Dun-xi, XU Ming-hou, YAO Hong, LIU Xiao-wei, ZHANG Lian, WANG Qun-ying, NINOMIYA Y. Study on coal mineral properties and their transformation behavior during combustion by CCSEM[J]. J Eng Thermophys, 2007, 28(5): 875-878. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB200705050.htm [12] 占中华.矿物特性对燃煤亚微米颗粒物排放特性影响研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学, 2011.ZHAN Zhong-hua. Effect of mineral characteristics on particulate matter emission during pulverized coal combustion[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2011. [13] WANG Q Y, ZHANG L A, SATO A, NINOMIYA Y, YAMASHITA T. Interactions among inherent minerals during coal combustion and their impacts on the emission of PM10. 1. Emission of micrometer-sized particles[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(2): 756-765. doi: 10.1021/ef0603075 [14] SENIOR C L, FLAGAN R C. Synthetic chars for the study of ash vaporization[C]//Twentieth symposium (international) on combustion. The Combustion Institute, 1984: 921-929. [15] ARENILLAS A, PEVIDA C, RUBIERA F, PIS J J. Comparison between the reactivity of coal and synthetic coal models[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(3): 2001-2006. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223372799_Comparison_between_the_reactivity_of_coal_and_synthetic_coal_models [16] 莫鑫. O2/CO2燃烧条件下煤中黄铁矿的转化行为研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学, 2013.MO Xin. Research on transformation of pyrite in coal under O2/CO2 combustion conditions[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2013. [17] NINOMIYA Y, WANG Q Y, XU SY, TERAMAE T, AWAYA I. Evaluation of a Mg-based additive for particulate matter (PM2.5) reduction during pulverized coal combustion[J]. Energy Fuels, 2010, 24(1): 199-204. doi: 10.1021/ef900556s [18] 张洪, 胡光州, 范佳鑫, 蒲文秀, 莫言学, 哈斯, 李迎.矿物在煤粉中的分布规律研究[J].工程热物理学报, 2008, 29(7): 1231-1235. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB200807042.htmZHANG Hong, HU Guang-zhou, FAN Jia-xin, PU Wen-xiu, MO Yan-xue, HA Si, LI Ying. Study on the distribution of mineral in pulverized coals[J]. J Eng Thermophys, 2008, 29(7): 1231-1235. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB200807042.htm [19] ZHANG P A, YU D X, LUO G Q, YAO H. Temperature effect on central mode particulate matter formation in combustion of coals with different mineral compositions[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(8): 5245-5252. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b00784 [20] TERAMAE T, TAKARADA T. Fine ash formation during pulverized coal combustion[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23(3): 2018-2024. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231273778_Fine_Ash_Formation_during_Pulverized_Coal_Combustion [21] YU D X, XU M H, YAO H, LIU X W, ZHOU K. A new method for identifying the modes of particulate matter from pulverized coal combustion[J]. Powder Technol, 2008, 183(1): 105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2007.11.011 [22] 肖海平, 周俊虎, 刘建忠.醋酸钙镁高温脱硫脱硝实验研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27(35): 23-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC200735005.htmXIAO Hai-ping, ZHOU Jun-hu, LIU Jian-zhong. Laboratory study on the high-temperature capture of SO2 and NOx by calcium magnesium acetate[J].Proc Chin Soc Electr Eng, 2007, 27(35): 23-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC200735005.htm [23] 刘洪涛, 韩奎华, 路春美, 李辉. O2/CO2气氛下木醋酸调质石灰石再燃/先进再燃脱硝性能研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(2): 228-234. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(13)60015-8LIU Hong-tao, HAN Kui-hua, LU Chun-mei, LI Hui. Experimental study on reburning/advanced reburning performance of limestone modified by wood vinegar for NO reduction under O2/CO2 atmosphere[J].J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(2): 228-234. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(13)60015-8 [24] GAO X P, RAHIM M U, CHEN X X, WU H W. Significant contribution of organically-bound Mg, Ca and Fe to inorganic PM10 emission during the combustion of pulverized Victorian brown coal[J]. Fuel, 2014, 117(1): 825-832. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259869701_Significant_contribution_of_organically-bound_Mg_Ca_and_Fe_to_inorganic_PM10_emission_during_the_combustion_of_pulverized_Victorian_brown_coal [25] QIU J R, LI F, ZHENG Y, ZHENG C G, ZHOU H C. The influences of mineral behaviour on blended coal ash fusion characteristics[J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(8): 963-969. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(99)00005-8 -





 下载:
下载: