-
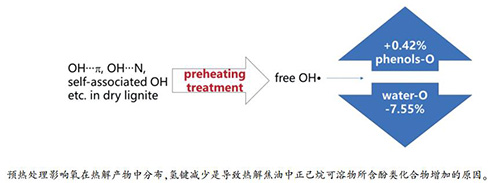
摘要: 以中国呼伦贝尔褐煤为原料,基于工业分析、元素分析、傅里叶变换红外光谱、气相色谱-质谱联用分析,考察140-230℃预热处理对褐煤650℃等温热解氧迁移的影响。结果表明,与未经预热处理的干煤热解相比,褐煤经200℃预热处理后热解,迁移至热解水和半焦中的氧分别下降7.55%和1.43%,迁移至焦油和气体中的氧分别增加6.66%和1.61%,焦油中酚类氧增加一倍。褐煤预热过程中氢键的减少与热解焦油中正己烷可溶物所含酚类化合物的增加,经原位红外漫反射光谱分析,发现源自OH…π、OH…N和羟基自缔合氢键在预热过程中断裂形成自由OH·,导致酚类化合物中苯酚和甲酚含量增加。Abstract: The effect of preheating treatment (140-230 ℃) on the oxygen migration rule of Hulunbuir lignite which is pyrolyzed at 650 ℃ has been discussed by using the proximate and ultimate analyses, the Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy, and the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. Results show that the amount of oxygen migrated to the pyrolysis water and semi-coke is decreased by 7.55% and 1.43%, respectively due to the effect of preheating at 200 ℃. Furthermore, the amount of oxygen transferred to tar and gas is increased by 6.66% and 1.61% respectively, and phenolic oxygen in tar is getting doubled. The decrease of hydrogen bonding and the increase of phenolic compounds are noted as the result of preheating process of lignite, as evidenced by in-situ infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, this could be due to the dissociation of OH…π, OH…N bonds. Hydroxyl self-association hydrogen bonds have also broken down and transformed during the preheating process with the formation of free OH·, which result in the increase of phenol and cresol contents.
-
Key words:
- preheating treatment /
- lignite /
- pyrolysis /
- oxygen migration /
- hydrogen bond
-
表 1 褐煤的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of lignite
Proximate analysis wad/% Ultimate analysis# wdaf/% M A V FC C H O N S 11.44 13.11 33.08 42.37 68.65 4.97 25.92 0.97 0.32 note: # all data are directly detected by vario MACRO cube elementar, detailed measurement methods see section 1.3.1 表 2 不同预热处理温度下热解产物中氧分布
Table 2 Distribution of oxygen in pyrolysis products at different preheating temperatures
Temperature t / ℃ Oxygen distribution w/% char-O water-O tar-O gas-O NO 21.00 41.84 2.41 28.49 140 20.97 39.44 5.00 28.36 170 20.94 37.45 6.20 28.98 200 19.57 34.29 9.07 30.10 230 25.54 32.58 6.40 28.41 表 3 不同预热处理温度下热解焦油各吸收峰透射率
Table 3 Transmittance values of specific functional groups of coal tar obtained from the pyrolysis of preheated lignite
Radical Transmissivity /% NO 140 ℃ 170 ℃ 200 ℃ 230 ℃ -OH (3400 cm-1) 58.84 52.80 46.44 28.45 36.21 C-H (2900 cm-1) 54.15 50.70 41.52 20.48 40.52 C=O (1660 cm-1) 58.43 58.18 53.38 41.25 52.63 C-O (1230 cm-1) 57.59 51.76 44.41 21.45 46.23 表 4 子峰位置及其归属
Table 4 Location and attribution of sub-peaks
The band assignments of sub-peak Position of sub-peak σ /cm-1 Free OH 3611±5 OH…π hydrogen bond 3538±4 Self-associated OH 3415±5 OH…ether hydrogen bond 3300±2 Cyclic OH tetramers 3150±8 Aromatic C-H 3050±2 OH…N hydrogen bond 2940±4 Aliphatic C-H 2857±1 表 5 不同预热温度酚羟基及酚羟基氢键定量
Table 5 Quantitative of phenolic hydroxyl group and hydrogen bond at different preheating temperatures
Temperature t/ ℃ Ar-OH / (mmol·g-1) Free OH / (mmol·g-1) Hydrogen bond /(mmol·g-1) OH…π self-associated OH OH…O cyclic OH tetramers OH…N NO 3.11 0.14 0.73 1.20 0.51 0.08 0.45 140 3.10 0.17 0.73 1.18 0.51 0.08 0.43 170 3.10 0.28 0.68 1.13 0.53 0.08 0.40 200 3.09 0.77 0.54 0.93 0.49 0.06 0.30 note: Ar-OH is phenolic hydroxyl group -
[1] DENG J, ZHAO J Y, XIAO Y, ZHANG Y N, HUANG A C, SHU C M. Thermal analysis of the pyrolysis and oxidation behaviour of 1/3 coking coal[J]. J Therm Anal Calorim, 2017, 129(3):1779-1786. doi: 10.1007/s10973-017-6331-3 [2] YE C P, HUANG H J, LI X H, LI W Y, FENG J. The oxygen evolution during pyrolysis of HunlunBuir lignite under different heating modes[J]. Fuel, 2017, 207:85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.06.062 [3] FENG X B, CAO J P, ZHAO X Y, SONG C, LIU T L, WANG J X, FAN X, WEI X Y. Organic oxygen transformation during pyrolysis of Baiyinhua lignite[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolsis, 2015, 117:106-115. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165237015302369 [4] WANG Z B, WANG C, KANG R N, BIN F, WEI X L. Deoxygenation of Chinese long-flame coal in low-temperature pyrolysis[J]. J Therm Anal Calorim, 2017, 131(3):3025-3033. doi: 10.1007/s10973-017-6753-y [5] MOCHIZUKI Y, NAGANUMA R, TSUBOUCHI N. Influence of inherently-present oxygen-functional groups on coal fluidity and coke strength[J]. Energy Fuels, 2018, 32(2):1657-1664. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b03774 [6] SUN M, MA X X, YAO Q X, YAO Q X, WANG R C, MA Y X, FENG G, SHANG J X, XU L, YANG Y H. GC-MS and TG-FTIR study of petroleum ether extract and residue from low temperature coal tar[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(3):1140-1145. doi: 10.1021/ef101610z [7] HUANG X, CAO J P, SHI P, ZHAO X Y, FENG X B, ZHAO Y P, FAN X, WEI X Y, TAKARADA T. Influences of pyrolysis conditions in the production and chemical composition of the bio-oils from fast pyrolysis of sewage sludge[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2014, 110:353-362. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2014.10.003 [8] 孔娇.煤热解过程中酚类化合物的生成规律[D].太原: 太原理工大学, 2013. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y2395917KONG Jiao. Law of phenolic compounds formation in coal pyrolysis[D].Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2013. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y2395917 [9] 陶建红.褐煤中含氧官能团的测定与研究[J].河南化工, 2010, 27(8):8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3467.2010.08.006TAO Jian-hong. Determination and study of oxygen functional groups in lignite[J]. Henan Chem Ind, 2010, 27(8):8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3467.2010.08.006 [10] SOLOMON P R, SERIO M A, DESPANDE G V, KROO E. Cross-linking reactions during coal conversion[J]. Energy Fuels, 1990, 4(1):42-54. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0225280454/ [11] ZENG C, WU H, HAYASHI J, LI C. Effects of thermal pretreatment in helium on the pyrolysis behaviour of Loy Yang brown coal[J]. Fuel, 2005, 84(12):1586-1592. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=98723441f68aadf796337e9325fc8dc8 [12] 王志青, 白宗庆, 李文, 李保庆, 陈皓侃.吡啶预处理抑制煤热解过程中交联反应的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2008, 36(6):642-644. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract17320.shtmlWANG Zhi-qing, BAI Zong-qing, LI Wen, LI Bao-qing, CHEN Hao-kan. Study on inhibition of crosslinking reaction during coal pyrolysis by pyridine pretreatment[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2008, 36(6):642-644. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract17320.shtml [13] 王知彩, 潘春秀, 任世彪, 雷智平, 王晓玲, 水恒福.先锋褐煤的热处理和水热处理改质[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(9):1033-1037. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18686.shtmlWANG Zhi-cai, PAN Chun-xiu, REN Shi-biao, LEI Zhi-ping, WANG Xiao-ling, SHUI Heng-fu. Heat treatment and hydrothermal treatment of Xianfeng lignite[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(9):1033-1037. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18686.shtml [14] 李文, 李东涛, 陈皓侃, 李保庆. o-烷基化对煤中氢键的调控及对热解特性的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2003, 31(6):514-518. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract16858.shtmlLI Wen, LI Dong-tao, CHEN Hao-kan, LI Bao-qing. Effects of o-alkylation on hydrogen bond and pyrolysis properties in coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2003, 31(6):514-518. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract16858.shtml [15] MIURA K, MAE K, SAKURADA K, HASHWIOTO K. Hash pyrolysis of coal following thermal pretreatment at low-temperature[J]. Energy Fuels, 1992, 6(1):16-21. doi: 10.1021/ef00031a003 [16] ALLARDICE D J. The Science of Victorian Brown Coal[M]. Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann, 1991:103-150. [17] MIURA K, MAE K, LI W, KUSAKAWA T, MOROZUMI F, KUMAMO A. Estimation of hydrogen bond distribution in coal through the analysis of OH stretching bands in diffuse reflectance infrared spectrum measured by in-situ technique[J]. Energy Fuels, 2001, 15(3):599-610. doi: 10.1021/ef0001787 [18] SCHAFER H N S. Determination of carboxyl groups in low rank coal[J]. Fuel, 1984, 63(5):723-726. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(84)90178-9 [19] 董鹏伟, 岳君容, 高士秋, 许光文.热预处理影响褐煤热解行为研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2012, 40(8):898-905. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract17997.shtmlDONG Peng-wei, YUE Jun-rong, GAO Shi-qiu, XU Guang-wen. Effect of thermal pretreatment on pyrolysis behavior of lignite[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 40(8):898-905. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract17997.shtml [20] CAO J P, SHI P, ZHAO X Y, WEI X Y, TAKARADA T. Catalytic reforming of volatiles and nitrogen compounds from sewage sludge pyrolysis to clean hydrogen and synthetic gas over a nickel catalyst[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2014, 123(7):34-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fabe7be168ed37196ac62a1be5bb03f4 [21] PLATONOV V V, POLOVETSKYAYA O S, PROSKURYAKOV V A, SHAVYRINA O V. Pyrolysis kinetics of phenols from lignite semicoking tar[J]. Russ J Appl Chem, 2002, 75(11):1878-1882. doi: 10.1023/A:1022295027623 [22] GENG C C, LI S Y, MA Y, YUE C T, HE J L, SHANG W L. Analysis and identification of oxygen compounds in longkou shale oil and shenmu coal tar[J]. Oil Share, 2012, 29(4):322. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2f6085262e48861350584c1a17a4b14c [23] YANI S, ZHANG D. An experimental study of sulphate transformation during pyrolysis of an Australian lignite[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2010, 91(3):313-321. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.11.002 [24] ZOU L, JIN L J, LI Y, ZHU S W, HU H Q. Effect of tetrahydrofuran extraction on lignite pyrolysis under nitrogen[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2015, 112:113-120. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2015.02.010 [25] LI Z K, WEI X Y, YAN H L, ZONG Z M. Insight into the structural features of Zhaotong lignite using multiple techniques[J]. Fuel, 2015, 153:176-182. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.02.117 [26] LI C Z. Some recent advances in the understanding of the pyrolysis and gasification behaviour of Victorian brown coal[J]. Fuel, 2007, 86(12):1664-1683. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9dd8e1cc925b5df85cc11ee7b35bf753 [27] FILLO J P. An understanding of phenolic compound production in coal gasification processing[D]. Pittsburgh: Carnegie Mellon University, 1979. [28] 谢童英.白音华褐煤热解及酚类化合物分布研究[D].大连: 大连理工大学, 2008. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1247908XIE Tong-ying. Study on pyrolysis and distribution of phenolic compounds from Baiyinhua lignite[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2008. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1247908 [29] HUGGINS C M, PIMENTEL G C. Systematics of the infrared spectral properties of hydrogen bonding systems:Frequency shift, half width and intensity[J]. J Phys Chem, 2002, 60(12):55-57. doi: 10.1021/j150546a004 [30] PAINTER P C, SOBKOWIAK M, YOUTCHEFF J. FT-IR study of hydrogen bonding in coal[J]. Fuel, 1987, 66(7):973-978. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(87)90338-3 [31] FULLER E L, SMYRL N R. Chemistry and structure of coals:Hydrogen bonding structures evaluated by diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy[J]. Appl Spectrosc, 1990, 44(3):451-461. doi: 10.1366-0003702904086056/ [32] CHEN C, JINSHENG GAO A, YAN Y. Observation of the type of hydrogen bonds in coal by FT-IR[J]. Energy Fuels, 1998, 12(3):446-449. doi: 10.1021/ef970100z [33] 陈茺, 许学敏, 高晋生, 颜涌捷, 李伟, 郭新闻.煤中氢键类型的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 1998, 26(2):141-144. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jzsfgdzkxxxb201103010CHEN Chong, XU Xue-min, GAO Jin-sheng, YAN Yong-jie, LI Wei, GUO Xin-wen. Study on hydrogen bond type in coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 1998, 26(2):141-144. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jzsfgdzkxxxb201103010 [34] SOLOMON P R, HAMBLEN D G, CARANGELO R M. Applications of fourier transform IR spectroscopy in fuel science[C]//Coal and Coal Products: Analytical characterization techniques. Washington: American Chemical Society, 1982. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284815153_Applications_of_Fourier_Transform_IR_Spectroscopy_in_Fuel_Science [35] YVRVM Y, ALTUNTA Ç N. Air oxidation of Beypazari lignite at 50℃, 100℃and 150℃[J]. Fuel, 1998, 77(15):1809-1814. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(98)00067-2 -





 下载:
下载: