Effect of swelling treatment by ionic liquid on the structure and pyrolysis performance of the direct coal liquefaction residue
-
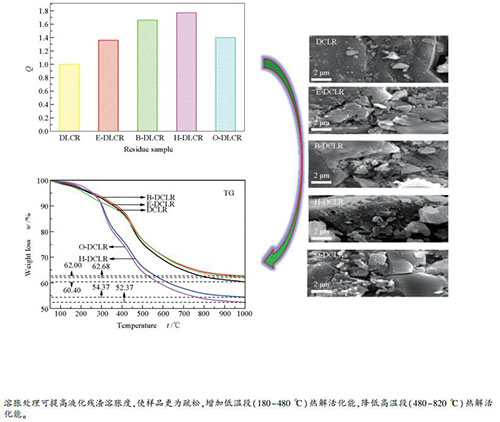
摘要: 采用四种相同阴离子不同有机链长阳离子的离子液体([EMIM][MeSO4]、[BMIM][MeSO4]、[HMIM][MeSO4]和[OMIM][MeSO4])对煤直接液化残渣(DCLR)进行溶胀处理,通过SEM、FT-IR和TG-DTG表征,分析了各离子液体溶胀对煤直接液化残渣溶胀效果、表面形貌、官能团分布、主体结构和热解性能的影响。溶胀结果表明,不同链长离子液体对煤直接液化残渣具有不同的溶胀效果,[HMIM][MeSO4]对残渣溶胀效果最好,其溶胀度高达1.78。FT-IR表明,不同链长离子液体会不同程度地破坏煤中C-H键,使得脂肪族和芳香族类化合物的相对含量有所差异。由TG-DTG可知,不同链长离子液体溶胀对残渣热解性能的影响具有较大差异,其中,以离子液体[OMIM][MeSO4]溶胀对残渣的热解最为有利,失重率高达47.5%;而离子液体[BMIM][MeSO4]溶胀在一定程度上抑制了残渣的热解,其失重率低于未经溶胀处理的残渣。基于Coats-Redfern法的热解动力学分析表明,煤直接液化残渣及其溶胀残渣在低温段(180-480 ℃)的热解过程均符合二级反应动力学,高温段(480-825 ℃)均以三级和四级反应动力学为宜。另外,不同链长离子液体溶胀处理明显改变了残渣的热解活化能,其链越长残渣的热解活化能越高。Abstract: Direct coal liquefaction residue (DCLR) was swelled by four kinds of ionic liquids with the same anion and different organic chain length cations, [EMIM] [MeSO4], [BMIM] [MeSO4], [HMIM] [MeSO4] and[OMIM] [MeSO4], and the effects of swelling treatment with ionic liquids on swelling degree, surface morphology, functional group distribution, the main structure and pyrolysis performance of the direct coal liquefaction residue were analyzed by SEM, FT-IR and TG-DTG characterizations. The swelling results show that different chain length ionic liquid has different swelling degrees for the DCLR, and[HMIM] [MeSO4] presents the best swelling effect with the swelling degree of 1.78. The FT-IR results indicate that the ionic liquid could destroy C-H bond in DCLR, leading to a change in relative content of aliphatic and aromatic compounds. The TG-DTG characterization demonstrates that the pyrolysis performance of the residue is greatly affected by the different organic chain length ionic liquid. And the[OMIM] [MeSO4] ionic liquid is more favorable for the pyrolysis of the residue than others, with the weight loss rate of 47.5%. However, the pyrolysis performance of the residue is restrained by the[BMIM] [MeSO4] ionic liquid, in which the weight loss rate is lower than that of DCLR (without swelling treatment). The pyrolysis kinetic data based on Coats-Redfern method show that the pyrolysis reaction for the direct coal liquid residue and the swelled ones at low temperature (180-480 ℃) obeys a second order law, while the third and fourth order law of reaction is more suitable for the residue pyrolysis at high temperature section (480-825 ℃). In addition, the activation energy of the pyrolysis process for the DCLR is altered obviously by swelling treatment with different organic length ionic liquid, the longer the chain length, the higher the pyrolysis activation energy.
-
Key words:
- direct coal liquefaction residue /
- swelling treatment /
- ionic liquid /
- pyrolysis
-
表 1 残渣样的工业分析与元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of the residue samples
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% Atomic ratio Mad Ad Vdaf FCdaf C H N S O* H/C O/C RDCLR 0.07 16.36 47.40 52.60 65.85 4.28 0.49 0.31 28.62 0.78 0.33 DCLR 3.14 1.99 40.01 59.99 69.66 4.07 1.74 0.24 24.29 0.70 0.26 *: by difference 表 2 残渣样的元素分析
Table 2 Ultimate analysis of the residue samples
Sample ILs Ultimate analysis wdaf/% Atomic ratio C H N S O* H/C O/C DCLR without ILs 69.66 4.07 1.74 0.24 24.29 0.70 0.26 E-DCLR [EMIM][MeSO4] 73.12 4.43 1.41 1.03 20.01 0.73 0.21 B-DCLR [BMIM][MeSO4] 71.19 4.60 2.15 2.12 19.94 0.78 0.21 H-DCLR [HMIM][MeSO4] 69.72 4.91 2.83 2.77 19.77 0.85 0.21 O-DCLR [OMIM][MeSO4] 70.57 5.23 3.02 2.48 18.7 0.89 0.20 *: by difference 表 3 五种残渣样各官能团的相对含量
Table 3 Relative content change of functional groups for five residue samples
Band position/cm-1 Functional groups Area percentage/% DCLR E-DCLR B-DCLR H-DCLR O-DCLR 3600-3500 OH -π 29.39 30.93 29.66 32.39 30.17 3500-3350 self-associated OH 43.84 44.64 40.60 41.70 41.03 3350-3260 OH-ether O 17.01 14.91 19.27 16.43 18.81 3260-3170 cyclic OH 9.76 9.53 10.47 9.48 9.98 2950 aliphatic -CH3 13.64 14.39 18.58 20.35 15.49 2920 asymmetric aliphatic -CH2 41.35 39.95 38.58 37.16 39.32 2890 aliphatic -CH 18.74 18.51 17.56 15.23 16.02 2850 symmetric aliphatic -CH2 26.27 27.14 25.23 27.26 29.17 1690 carboxylic acids C=O 10.69 11.00 11.61 10.78 10.34 1610 conjugated C=O 23.24 23.93 22.04 19.58 20.08 1560 aromatic C=C 10.37 8.95 10.02 10.62 12.56 1440 asymmetric CH3-, CH2- 12.60 14.15 13.58 13.76 13.91 1350 CH3-Ar, R 11.15 9.66 8.44 8.43 8.56 1245 symmetric deformation -CH3 13.60 13.26 14.38 16.70 15.02 1165 C-O phenols 12.65 13.39 14.90 16.57 14.90 1090 grease C-O 5.70 5.66 5.02 3.54 4.61 900-860 five adjacent H deformation 12.51 14.67 9.19 8.07 9.17 860-810 four adjacent H deformations 30.89 25.94 15.74 12.65 13.60 810-750 three adjacent H deformations 54.23 55.67 57.57 56.35 55.06 750-720 two adjacent H deformations 2.37 3.72 17.50 22.91 22.17 表 4 不同反应级数五种残渣样热解动力学参数计算
Table 4 Pyrolysis kinetic parameters of five residue simples with different reaction orders
t /℃ Sample Reaction order Regression equation Correlation coefficient R2 Activation energy E/(kJ·mol-1) Pre-exponential factor A/min-1 2RT/E 180-480 DCLR 1 y=-1097.24x-12.16 0.9243 9.122 0.057 0.328 2 y=-1463.48x-11.36 0.9064 12.167 0.170 0.246 3 y=-1876.53x-10.47 0.8862 15.601 0.530 0.192 4 y=-2337.95x-9.49 0.8684 19.438 1.769 0.154 E-DCLR 1 y=-1388.49x-11.84 0.9261 11.544 0.100 0.259 2 y=-1760.23x-11.05 0.8960 14.635 0.278 0.205 3 y=-2173.02x-10.19 0.8687 18.067 0.818 0.166 4 y=-2633.28x-9.23 0.8461 21.893 2.584 0.137 B-DCLR 1 y=-1491.20x-11.70 0.9370 12.398 0.124 0.241 2 y=-1860.17x-10.92 0.9068 15.465 0.335 0.194 3 y=-2274.60x-10.06 0.8791 18.911 0.975 0.158 4 y=-2736.40x-9.10 0.8556 22.750 3.058 0.132 H-DCLR 1 y=-2708.64x-9.37 0.9777 22.520 2.301 0.133 2 y=-3420.85x-7.92 0.9782 28.441 12.415 0.105 3 y=-4238.92x-6.26 0.9683 35.242 80.794 0.085 4 y=-5165.57x-4.39 0.9548 42.947 638.234 0.070 O-DCLR 1 y=-3236.81x-8.55 0.9758 26.911 6.281 0.111 2 y=-3227.63x-8.56 0.9758 26.834 6.158 0.112 3 y=-4835.02x-5.36 0.9837 40.198 237.540 0.074 4 y= -5808.69x-3.36 0.9745 48.293 2.014×103 0.062 480-825 DCLR 1 y=-1410.38x-11.52 0.9994 11.726 0.140 0.681 2 y=-5248.67x-6.19 0.9718 43.637 107.804 0.183 3 y=-10345.16x+0.79 0.9598 86.010 2.271×105 0.093 4 y=-15983.85x+8.51 0.9578 132.890 7.927×108 0.060 E-DCLR 1 y=-1281.88x-11.66 0.9956 10.658 0.110 0.749 2 y=-4948.00x-6.50 0.9734 41.146 72.412 0.194 3 y=-9815.51x+0.18 0.9620 81.606 1.178×105 0.098 4 y=-15206.24x+7.62 0.9602 126.425 3.100×108 0.063 B-DCLR 1 y=-1349.50x-11.57 0.9966 11.220 0.127 0.711 2 y=-5164.70x-6.25 0.9721 42.939 99.295 0.186 3 y=-10231.48x+0.70 0.9605 85.064 2.070×105 0.094 4 y=-15832.19x+8.40 0.9587 131.629 7.073×108 0.061 H-DCLR 1 y=-805.92x-11.96 0.9905 6.700 0.051 1.191 2 y=-4872.61x-6.10 0.9571 40.511 108.994 0.197 3 y=-10282.43x+1.58 0.9523 85.488 4.998×105 0.093 4 y=-16139.78x+9.94 0.9537 134.186 3.359×109 0.059 O-DCLR 1 y=-747.35x-12.02 0.9909 6.213 0.045 1.285 2 y=-749.45x-12.01 0.9901 6.231 0.045 1.281 3 y=-10092.79x+1.41 0.9538 83.911 4.122×105 0.095 4 y=-15866.43x+9.69 0.9552 131.914 2.571×109 0.061 -
[1] KONG H, KONG X H, WANG J, ZHANG J. Thermodynamic analysis of a solar thermochemical cycle-based direct coal liquefaction system for oil production[J]. Energy, 2019, 179:1279-1287. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.05.019 [2] LV D M, WEI Y C, BAI Z Q, BAI J, KONG L X, GUO Z X, YAN J C, LI W. An approach for utilization of direct coal liquefaction residue:Blending with low-rank coal to prepare slurries for gasification[J]. Fuel, 2015, 145:143-150. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.12.075 [3] 马亚亚, 马凤云, 何芳, 孙志强, 莫文龙, 张晓静.空化洗油微波溶胀对新疆准东西沟煤直接液化性能影响及其动力学分析[J].煤炭学报, 2017, 42(10):2732-2740. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201710030.htmMA Ya-ya, MA Feng-yun, HE Fang, SUN Zhi-qiang, MO Wen-long, ZHANG Xiao-jing. Influence of microwave swelling with cavitated creosote oil on the direct liquefaction performance of xigou coal from xinjiang and its dynamics analysis[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2017, 42(10):2732-2740. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201710030.htm [4] SHU G P, ZHANG Y Z. Research on the maceral characteristics of Shenhua coal and efficient and directional direct coal liquefaction technology[J]. Int J Coal Sci Technol, 2014, 1(1):46-55. doi: 10.1007/s40789-014-0003-8 [5] 郭靖, 马凤云, 玛·伊·拜克诺夫, 周岐雄, 周剑林.溶胀对五彩湾煤低压直接液化性能的影响[J].煤炭学报, 2010, 35(7):1182-1187. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mtxb201007023GUO Jing, MA Feng-yun, TAЙKEHOB M И, ZHOU Qi-xiong ZHOU Jian-lin. Effect of solvent swelling of Wucaiwan coal on hydro-liquefaction properties at lower pressure[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2010, 35(7):1182-1187. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mtxb201007023 [6] 廖静, 马凤云, 孙志强, 刘景梅, 刘月娥, 张晓静.空化洗油机械溶胀对新疆准东西沟煤液化性能的影响[J].煤炭学报, 2016, 41(5):1279-1286. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201605030LIAO Jing, MA Feng-yun, SUN Zhi-qiang, LIU Jing-mei, LIU Yue-e, ZHANG Xiao-jing. Effect of swelling mechanically with cavitated creosote oil on liquefaction properties of Xigou coal from Xinjiang Zhundong[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2016, 41(5):1279-1286. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201605030 [7] ZHANG J B, JIN L J, HU H Q, XUN Y X. Effect of composition in coal liquefaction residue on catalytic activity of the resultant carbon for methane decomposition[J]. Fuel, 2012, 96:462-468. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.12.075 [8] SUN Z Q, MA F Y, LIU X J, WU H H, NIU C G, SU X T, LIU J M. Large-scale synthesis and catalysis of oleic acid-coated Fe2O3 for co-liquefaction of coal and petroleum vacuum residues[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 139:173-177. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.07.025 [9] BAI L, NIE Y, LI Y, DONG H F, ZHANG X P. Protic ionic liquids extract asphaltenes from direct coal liquefaction residue at room temperature[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2013, 108:94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2012.04.008 [10] XU L, TANG M C, DUAN L E, LIU B L, MA X X, ZHANG Y L, ARGYLE M D, FAN M H. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of residue from China Shenhua industrial direct coal liquefaction plant[J]. Thermochim Acta, 2014, 589:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2014.05.005 [11] LI X H, XUE Y L, FENG J, YI Q, LI W Y, GUO X F, LIU K. Co-pyrolysis of lignite and Shendong coal direct liquefaction residue[J]. Fuel, 2015, 144:342-348. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.12.049 [12] CUMMINGS J, SHAH K, ATKIN R, MOGHTADERI B. Physicochemical interactions of ionic liquids with coal; the viability of ionic liquids for pre-treatments in coal liquefaction[J]. Fuel, 2015, 143:244-252. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.11.042 [13] SÖNMEZ Ö, GIRAY E S. An investigation of the effect of pre-swelling on the extraction yield of two different ranked Turkish coals[J]. Energy Sources Part A, 2011, 33(20):1901-1911. doi: 10.1080/15567030903503159 [14] 白金锋, 王勇, 胡浩权, 郭树才, 陈国华.溶胀对扎赉诺尔褐煤热解及液化性能的影响[J].煤炭转化, 2000, 23(4):50-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2000.04.012BAI Jin-feng, WANG Yong, HU Hao-quan, GUO Shu-cai, CHEN Guo-hua. Effect of swelling pretreatment on pyrolysis and liquefaction characteristics of Zalainuer lignite[J]. Coal Convers, 2000, 23(4):50-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2000.04.012 [15] 赵渊, 黄黎明, 马风云, 钟梅.溶胀对新疆淖毛湖煤样结构组成及热解性能的影响[J].过程工程学报, 2018, 18(1):218-224. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgyj201801032ZHAO Yuan, HUANG Li-ming, MA Feng-yun, ZHONG Mei. Effects of swelling on structure, composition and pyrolysis behavior of Xinjiang naomaohu coal[J]. Chin J Process Eng, 2018, 18(1):218-224. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgyj201801032 [16] 刘耀鑫, 伯灵, 冯兆兴, 李晓鹤.溶胀预处理煤热解特性研究[J].煤炭技术, 2018, 37(4):304-306. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtjs201804116LIU Yao-xin, BAI Ling, FENG Zhao-xing, LI Xiao-he. Study on behavior of solvent swelling coal pyrolysis[J]. Coal Technol, 2018, 37(4):304-306. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtjs201804116 [17] SHAH K, ATKIN R, STANGER R, WALL T, MOGHTADERI B. Interactions between vitrinite and inertinite-rich coals and the ionic liquid-[bmim]Cl[J]. Fuel, 2014, 119:214-218. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.11.038 [18] 耿胜楚, 范天博, 刘云义.离子液体[BMIm]BF4在神华煤溶胀预处理中的应用[J].煤炭转化, 2010, 33(2):35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2010.02.009GENG Sheng-chu, FAN Tian-bo, LIU Yun-yi. Application of ionic liquid[Bmim]BF4 in swelling pretreatment of ShenHua coal[J]. Coal Convers, 2010, 33(2):35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2010.02.009 [19] CUI C B, JIANG S G, KOU L W, WANG L Y, ZHANG W Q, WU Z Y, WANG K, SHAO H. Effect of ionic liquids on the pyrolysis of coal[J]. Electron J Geotech Eng, 2016, 21:5203-5216. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtzh201802002 [20] HAYES R, WARR G G, ATKIN R. Structure and nanostructure in lonic liquids[J]. Chem Rev, 2015, 115(13):6357-6426. doi: 10.1021/cr500411q [21] TO T Q, SHAH K, TREMAIN P, SIMMONS B A, MOGHTADERI B, ATKIN R. Treatment of lignite and thermal coal with low cost amino acid based ionic liquid-water mixtures[J]. Fuel, 2017, 202:296-306. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.04.051 [22] JI JIE, WANG D, SUO Z, XU Y, XU S F. Study on direct coal liquefaction residue influence on mechanical properties of flexible pavement[J]. Int J Pavement Res Technol, 2018, 11(4):355-362. doi: 10.1016/j.ijprt.2017.09.006 [23] LV D M, BAI Z Q, WEI Y C, BAI J, KONG L X, GUO Z X, LI X, XU J L, LI W. Properties of direct coal liquefaction residue water slurry:Effect of treatment by low temperature pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2016, 179:135-140. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.03.081 [24] KHARE S, DELL'AMICO M. An overview of conversion of residues from coal liquefaction processes[J]. Can J Chem Eng, 2013, 91(10):1660-1670. doi: 10.1002/cjce.21771 [25] LIU X, ZHOU Z J, HU Q J, DAI Z H, WANG F C. Experimental study on co-gasification of coal liquefaction residue and petroleum coke[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(8):3377-3381. doi: 10.1021/ef200402z [26] YANG J L, WANG Z X, LIU Z Y, ZHANG Y Z. Novel use of residue from direct coal liquefaction process[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23(10):4717-4722. doi: 10.1021/ef9000083 [27] 张德润, 罗蓉, 陈彧, 张胜振, 盛英.基于表面自由能的煤直接液化残渣改性沥青性能分析[J].中国公路学报, 2016, 29(1):22-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.01.003ZHANG De-run, LUO Rong, CHEN Yu, ZHANG Sheng-zhen, SHENG Ying. Performance analysis of DCLR-modified asphalt based on surfacefreer energy[J]. China J Highw Transp, 2016, 29(1):22-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.01.003 [28] LI J, YANG J L, LIU Z Y. Hydrogenation of heavy liquids from a direct coal liquefaction residue for improved oil yield[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2009, 90(4):490-495. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.01.013 [29] ZHOU Y, XIAO N, QIU J S, SUN Y F, SUN T J, ZHAO Z B, ZHANG Y, TSUBAKI N. Preparation of carbon microfibers from coal liquefaction residue[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(15/16):3474-3476. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a21b069f0e3cec20c54efa108857fbf4 [30] LI Y, ZHANG X P, LAI S Y, DONG H F, CHEN X L, WANG X L, NIE Y, SHENG Y, ZHANG S J. Ionic liquids to extract valuable components from direct coal liquefaction residues[J]. Fuel, 2012, 94:617-619. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.10.031 [31] NIE Y, BAI L, DONG H F, ZHANG X P, ZHANG S J. Extraction of asphaltenes from direct coal liquefaction residue by dialkylphosphate ionic liquids[J]. Sep Sci Technol, 2012, 47(2):386-391. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2011.633957 [32] NIE Y, BAI L, LI Y, DONG H F, ZHANG X P, ZHANG S J. Study on extraction asphaltenes from direct coal liquefaction residue with ionic liquids[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2011, 50(17):10278-10282. doi: 10.1021/ie201187m [33] WANG L Y, XU Y L, JIANG S G, YU M, CHU T X, ZHANG W Q, WU Z Y, KOU L W. Imidazolium based ionic liquids affecting functional groups and oxidation properties of bituminous coal[J]. Saf Sci, 2012, 50(7):1528-1534. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2012.03.006 [34] CUMMINGS J, KUNDU S, TREMAIN P, MOGHTADERI B, ATKIN R, SHAH K. Investigations into physicochemical changes in thermal coals during low-temperature ionic liquid treatment[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(11):7080-7088. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b01824 [35] LEI Z P, HU Z Q, ZHANG H, HAN L N, SHUI H F, REN S B, WANG Z C, KANG S G, PAN C C. Pyrolysis of lignite following low temperature ionic liquid pretreatment[J]. Fuel, 2016, 166:124-129. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.10.059 [36] SONG Y H, MA Q N, HE W J. Effect of extracted compositions of liquefaction residue on the structure and properties of the formed-coke[J]. MATEC Web Conf, 2016, 67, 06026. doi: 10.1051/matecconf/20166706026 [37] ZHANG W Q, JIANG S G, WU Z Y, WANG K, SHAO H, QIN T, XI X, TIAN H B. Influence of imidazolium-based ionic liquids on coal oxidation[J]. Fuel, 2018, 217:529-535. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.12.056 [38] SÖNMEZA Ö, YILDIZA Ö, ÇAKIR M Ö, GÖZMENA B, GIRAY E S. Influence of the addition of various ionic liquids on coal extraction with NMP[J]. Fuel, 2018, 212:12-18. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.10.017 [39] CUMMINGS J, TREMAIN P, SHAH K, HELDT E, MOGHTADERI B, ATKIN R, KUNDU S, VUTHALURU H. Modification of lignites via low temperature ionic liquid treatment[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2017, 155:51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.02.040 [40] WU D, LIU G J, SUN R Y. Investigation on structural and thermodynamic characteristics of perhydrous bituminous coal by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetry/mass spectrometry[J]. Energy Fuels, 2014, 28(5):3024-3035. doi: 10.1021/ef5003183 [41] GENG W H, NAKAJIMA T, TAKANASHI H, OHKI A. Analysis of carboxyl group in coal and coal aromaticity by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrometry[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(1):139-144. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=07e793b64c55f0ea6fb1713c86c23c8f [42] LIN X C, WANG C H, IDETA K, MIYAWAKI J, NISHIYAMA Y, WANG Y G, YOON S, MOCHIDA I. Insights into the functional group transformation of a chinese brown coal during slow pyrolysis by combining various experiments[J]. Fuel, 2014, 118:257-264. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.10.081 [43] WANG S Q, TANG Y G, SCHOBERT H H, GUO Y N, GAO W C, LU X K. FT-IR and simultaneous TG/MS/FT-IR study of Late Permian coals from Southern China[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2013, 100:75-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2012.11.021 [44] QI X Y, WANG D M, XIN H H, QI G S. In situ FT-IR study of real-time changes of active groups guring oxygen-free reaction of coal[J]. Energy Fuels, 2013, 27(6):3130-3136. doi: 10.1021/ef400534f [45] WU D, LIU G J, SUN R Y, FAN X. Investigation of structural characteristics of thermally metamorphosed coal by FT-IR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction[J]. Energy Fuels, 2013, 27(10):5823-5830. doi: 10.1021/ef401276h [46] 马亚亚, 马凤云, 莫文龙, 樊星.酸洗脱灰处理对新疆和丰低阶煤结构和萃取性能的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(6):649-660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2019.06.002MA Ya-ya, MA Feng-yun, MO Wen-long, FAN Xing. Influence of acid treatment on the structure and extraction performance of Xinjiang Hefeng low-rank coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2019, 47(6):649-660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2019.06.002 [47] 周俊虎, 方磊, 程军, 刘建忠, 岑可法.神华煤液化残渣的热解特性[J].燃烧科学与技术, 2006, 12(4):295-299. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-8740.2006.04.002ZHOU Jun-hu, FANG Lei, CHENG Jun, LIU Jian-zhong, CEN Ke-fa. Pyrolysis properties of Shenhua coal liquefaction residue[J]. J Combust Sci Technol, 2006, 12(4):295-299. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-8740.2006.04.002 [48] ZHU P, LUO A Q, ZHANG F, LEI Z P, ZHANG J L, ZHANG J S. Effects of extractable compounds on the structure and pyrolysis behaviours of two Xinjiang coal[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2018, 133:128-135. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2018.04.012 [49] 畅志兵, 初茉, 孙任晖, 杨小敏, 吕海龙.煤直接液化残渣与褐煤共热解动力学研究[J].煤炭科学技术, 2015, 43(3):138-141+39. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtkxjs201503032CHANG Zhi-bing, CHU Mo, SUN Ren-hui, YANG Xiao-min, LV Hai-long. Study on co-pyrolysis kinetics of coal direct liquefaction residue and lignite[J]. Coal Sci Technol, 2015, 43(3):138-141+39. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtkxjs201503032 -





 下载:
下载: