Effects of Cl ions on low-temperature NO conversion by NH3 over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts
-
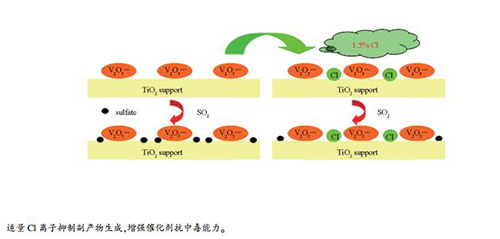
摘要: 考察添加不同含量Cl离子对浸渍法制备的Cl-V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂低温NO转化率的影响。随着Cl离子质量添加量从0增加到2.5%,Cl-V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂NO转化率先升高后降低,结合在含有SO2和H2O的SCR实验结果,确定1.5% Cl-V2O5-WO3/TiO2为性能最优催化剂。在反应温度为149-362℃,NO转化率大于95%;在145-385℃,NO转化率大于90%。采用XRF、BET、XRD、TG、FT-IR和H2-TPR等方法表征了催化剂的物理化学性能和结构。结果表明,在反应气氛中加入SO2和H2O后,催化剂比表面积和孔容均减小,副反应产物含有NH4+和SO42-。适量Cl离子可以抑制硫物种沉积,减少副反应产物生成,增强催化剂抗中毒能力。Abstract: The Cl-V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts were prepared by impregnation methods. With the Cl ions content increased from 0 to 2.5%, the NO conversion of Cl-V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts increased at first and then decreased. Combined with the experimental results, 1.5% Cl-V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst was the optimal catalyst, NO conversion was higher than 95% in the range of 149-362℃, and NO conversion was higher than 90% in the temperature range of 145-385℃. The catalysts were characterized by XRF, BET, XRD, TG, FT-IR and H2-TPR. The specific surface area and pore volume of the catalysts decreased in different degrees after adding SO2 and H2O in reactant gas. The poisoned catalysts deposited sulfur species and contained NH4+ and SO42-. Adding appropriate amount of Cl ions inhibited the formation of side byproducts and enhanced the poisoning resistance of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst.
-
Key words:
- Cl ions /
- low temperature SCR /
- sulfur resistance /
- catalyst poisoning
-
表 1 反应气氛中通入SO2后Cl-3VWT催化剂的NO转化率趋势线
Table 1 Trend lines describing the effect of SO2 on NO conversion over the Cl-3VWT catalysts
Sample Equation of trend line Correlation coefficient R2 0Cl-3VWT Y=99.28-0.39X 0.98 1.25Cl-3VWT Y=99.58-0.19X 0.99 1.5Cl-3VWT Y=99.33-0.02X 0.99 2.5Cl-3VWT Y=98.56-0.27X 0.98 表 2 Cl-3VWT催化剂的比表面积
Table 2 Specific surface area of the Cl-3VWT catalysts
No. Sample Specific surface area A/(m2·g-1) 1 0Cl-3VWT 82 2 0.5Cl-3VWT 82 3 1Cl-3VWT 83 4 1.25Cl-3VWT 83 5 1.5Cl-3VWT 84 6 2.5Cl-3VWT 84 表 3 催化剂的物理性质对比
Table 3 Comparison of physical properties of the Cl-3VWT catalysts
Characterization 0Cl-3VWT 0Cl-3VWTSH 1.5Cl-3VWT 1.5Cl-3VWTSH Specific surface area A/(m2·g-1) 82 70 84 73 Pore volume v/(cm3·g-1) 0.32 0.28 0.33 0.29 Average pore diameter d/nm 15.6 15.6 16.1 16.1 Component weight fraction/% XRF TiO2 90.0 90.8 88.6 88.9 V2O5 3.01 2.07 2.95 2.50 WO3 5.92 4.36 5.94 5.26 Cl 0.00 0.00 1.46 1.43 SO3 0.13 1.70 0.10 0.70 Temperature range t/℃ weight loss fraction/% TG 25-600 2.83 5.45 3.03 5.94 25-100 1.28 1.48 1.22 2.42 220-440 0.62 2.68 0.63 2.40 -
[1] CHENG Y F, ZHENG G J, WEI C, MU Q, ZHENG B, WANG Z B, GAO M, ZHANG Q, HE K B, CARMICHAEL G, PÖSCHL U, SU H. Reactive nitrogen chemistry in aerosol water as a source of sulfate during haze events in China[J]. Sci Adv, 2016, 2(12):1-11. http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC5176349/ [2] LIETTI L, NOVA I, FORZATTI P. Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO by NH3 over TiO2-supported V2O5-WO3 and V2O5-MoO3 catalysts[J]. Top Catal, 2000, 11/12(1/4):111-122. http://www.springerlink.com/content/t4w8123685543214/ [3] BOSCH H, JANSSEN F. Catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides:A review on the fundamentals and technology[J]. Catal Today, 1988, 2(4):369-531. doi: 10.1016/0920-5861(88)80002-6 [4] BUSCA G, LIETTI L, RAMIS G, BERTI F. Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia over oxide catalysts:A review[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 1998, 18(1/2):1-36. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092633739800040X [5] NOVA I, LIETTI L, CASAGRANDE L, DALL'ACQUA L, GIAMELLO E, FORZATTI P. Characterization and reactivity of TiO2-supported MoO3 De-NOx SCR catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 1998, 17(3):245-258. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(98)00015-0 [6] KOBAYASHI M, KUMA R, MORITA A. Low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over V2O5 supported on TiO2-SiO2-MoO3[J]. Catal Lett, 2006, 112(1/2):37-44. http://www.springerlink.com/content/47643v348257p766/ [7] PHIL H H, REDDY M P, KUMAR P A, JU L K, HYO J S. SO2 resistant antimony promoted V2O5/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR of NOx at low temperatures[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2008, 78(3/4):301-308. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337307002858 [8] SONG L Y, CHAO J D, FANG Y J, HE H, LI J, QIU W G, ZHANG G Z. Promotion of ceria for decomposition of ammonia bisulfate over V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction[J]. Chem Eng J, 2016, 303(1):275-281. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894716307732 [9] LIU F D, HE H. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over manganese substituted iron titanate catalyst:Reaction mechanism and H2O/SO2 inhibition mechanism study[J]. Catal Today, 2010, 153(3/4):70-76. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920586110001288 [10] WU X D, YU W C, SI Z C, WENG D. Chemical deactivation of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalyst by combined effect of potassium and chloride[J]. Front Env Sci Eng, 2013, 7(3):420-427. doi: 10.1007/s11783-013-0489-0 [11] ZHANG B K, LIU J, DAI G L, CHANG M, ZHENG C G. Insights into the mechanism of heterogeneous mercury oxidation by HCl over V2O5/TiO2 catalyst:Periodic density functional theory study[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2015, 35(3):2855-2865. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2014.06.051 [12] LISI L, LASORELLA G, MALLOGGI S, RUSSO G. Single and combined deactivating effect of alkali metals and HCl on commercial SCR catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2004, 50(4):251-258. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2004.01.007 [13] HOU Y Q, CAI G Q, HUANG Z G, HAN X J, GUO S J. Effect of HCl on V2O5/AC catalyst for NO reduction by NH3 at low temperatures[J]. Chem Eng J, 2014, 247(6):59-65. http://www.scholarmate.com/scmwebsns/publication/view?des3Id=UgaswVKxPB%252BG6oipsysktA%253D%253D [14] SU C, NOTOYA F, SASAOKA E. Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 at low temperature using halogen ions-modified Al2O3, ZrO2, and TiO2 as catalysts[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2003, 42(23):5770-5774. doi: 10.1021/ie030235u [15] WANG P, WANG Q S, MA X X, GUO R T, PAN W G. The influence of F and Cl on Mn/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3:A comparative study[J]. Catal Commun, 2015, 71(5):84-87. [16] 晁晶迪, 何洪, 宋丽云, 房玉娇, 梁全明, 张桂臻, 邱文革, 张然. Pr掺杂对V2O5-MoO3/TiO2催化剂NH3-SCR反应活性的影响[J].高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(3):523-530. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdxxhxxb201503018CHAO Jing-di, HE Hong, SONG Li-yun, FANG Yu-jiao, LIANG Quan-ming, ZHANG Gui-zhen, QIU Wen-ge, ZHANG Ran. Promotional effect of Pr-doping on the NH3-SCR activity over the V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst[J]. Chem J Chin Univ, 2015, 36(3):523-530. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdxxhxxb201503018 [17] LIANG Q M, LI J, HE H, LIANG W J, ZHANG T J, FAN X. Effects of SO2 on the low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over CeO2-V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts[J]. Front Env Sci Eng, 2017, 11(4):153-159. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zggdxxxswz-hjkxygc201704017 [18] ZHANG T J, LI J, HE H, SONG Q Q, LIANG Q M. NO oxidation over Co-La catalysts and NOx reduction in compact SCR[J]. Front Environ Sci Eng, 2017, 11(2):67-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zggdxxxswz-hjkxygc201702006 [19] SONG L Y, ZHAN Z C, LIU X J, HE H, QIU W G, ZI X H. NOx selective catalytic reduction by ammonia over Cu-ETS-10[J]. Chin J Catal, 2014, 35(7):1030-1035. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60035-8 [20] LI P, LIU Z Y, LI Q C, WU W Z, LIU Q Y. Multiple roles of SO2 in Selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over V2O5/AC catalyst[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2014, 53(19):7910-7916. doi: 10.1021/ie4031488 [21] WANG Y L, LI X X, ZHAN L, LI C, QIAO W M, LING L C. Effect of SO2 on activated carbon honeycomb supported CeO2-MnOx catalyst for NO removal at low temperature[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2015, 54(8):2274-2278. doi: 10.1021/ie504074h [22] SOH B W, NAM I S. Effect of support morphology on the sulfur tolerance of V2O5/Al2O3 catalyst for the reduction of NO by NH3[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2003, 42(13):2975-2986. doi: 10.1021/ie020861b [23] MAO L Q, T-RAISSI A, HUANG C P, MURADOV N Z. Thermal decomposition of (NH4)2SO4 in presence of Mn3O4[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(10):5822-5827. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.11.011 [24] BETKE U, WICKLEDER M S. Sulfates of the refractory metals:Crystal structure and thermal behavior of Nb2O2(SO4)3, MoO2(SO4), WO(SO4)2, and two modifications of Re2O5(SO4)2[J]. Inorg Chem, 2011, 50(3):858-872. doi: 10.1021/ic101455z [25] YU W C, WU X D, SI Z C, WENG D. Influences of impregnation procedure on the SCR activity and alkali resistance of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2013, 283(20):209-214. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016943321301194X [26] ZHANG L, LI L L, CAO Y, YAO X J, GE C Y, GAO F, DENG Y, TANG C J, DONG L. Getting insight into the influence of SO2 on TiO2/CeO2 for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2015, 165(18):589-598. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337314006420 [27] WAQIF M, BAZIN P, SAUR O, LAVALLEY J C, BLANCHARD G, TOURET O. Study of ceria sulfation[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 1997, 11(2):193-205. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(96)00040-9 [28] YANG S J, GUO Y F, CHANG H Z, MA L, PENG Y, QU Z, YAN N Q, WANG C Z, LI J H. Novel effect of SO2 on the SCR reaction over CeO2:Mechanism and significance[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2013, 136/137(12):19-28. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337313000489/pdfft?md5=98aa98124dd18b0fdb55419d27fc2c56&pid=1-s2.0-S0926337313000489-main.pdf -





 下载:
下载: