Effect of coordinating groups of chelating agents on the hydrodesulfurization over CoMo/γ-Al2O3 catalysts
-
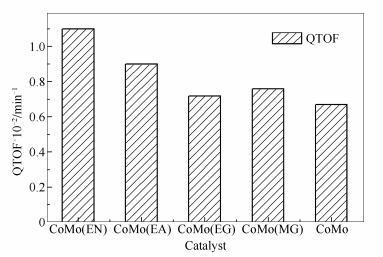
摘要: 选择四种不同配位基团的双齿配位分子乙二胺(EN)、乙醇胺(EA)、乙二醇(EG)和丙二酸(MA)对CoMo/γ-Al2O3催化剂改性,比较了它们对二苯并噻吩HDS性能的影响。结果表明,其活性顺序为CoMo(EN)> CoMo(EA)> CoMo(EG)≈CoMo(MA)> CoMo,反应以直接脱硫路径为主,随反应温度升高,加氢路径的占比增加,加入配合物后可以促进加氢路径脱硫,CoMo(EN)催化剂具有最高的加氢活性。采用UV-vis、EA、XPS和HRTEM等手段对催化剂进行表征,结果表明,-NH2与Co2+有强络合作用,-COOH主要是静电作用,而-OH与钴离子没有相互作用。配位基团和Co2+的相互作用,与HDS活性直接相关。配合物与Co2+的结合可以有效生成Co-Mo-S活性相,且配合物碳化减弱载体与活性相的相互作用,有利于生成有更高本征活性的II型活性相。
-
关键词:
- 有机配合物 /
- 双齿配位分子 /
- CoMo/γ-Al2O3 /
- 加氢脱硫 /
- 二苯并噻吩
Abstract: The modified CoMo/γ-Al2O3 catalyst was prepared by addition of ethylene diamine (EN), ethanolamine (EA), ethylene glycol (EG) or malonic acid (MA). The effect of four bidentate molecules with different coordination groups on the dibenzothiophene HDS was compared. And the catalytic activity is determined in the sequence of CoMo (EN) > CoMo (EA) > CoMo (EG)≈CoMo (MA) > CoMo. For all catalysts, the direct desulfurization route is dominated, but with the increase of reaction temperature, the desulfurization by hydrogenation route become more apparent. Chelating agents facilitate the HDS reaction through hydrogenation route. CoMo (EN) catalyst presents the highest hydrogenation ability. The catalysts were characterized by UV-vis, EA, XPS and HRTEM. The results show that NH2 group has a strong complexing interaction with Co2+. COOH group mainly has an electrostatic interaction with cobalt ion. Meanwhile, OH group hardly interacts with Co2+. It is noted that the HDS activity is directly related to the interaction between coordinating groups and Co2+. The combination of coordinating molecules with Co2+ leads to the effective formation of Co-Mo-S active center, and the carbonization of chelating decreases the interaction of the support with active phases, facilitating the formation of type Ⅱ active phases which has a higher intrinsic catalytic activity.-
Key words:
- organic chelating agent /
- bidentate molecule /
- CoMo/γ-Al2O3 /
- hydrodesulfurization /
- dibenzothiophene
-
表 1 反应后催化剂S和C含量分析
Table 1 Analysis of S and C contents of spent catalysts
Catalyst S contents w/% C contents w/% Degree of sulfidation* /% CoMo (EN) 6.49 2.35 87 CoMo (EA) 6.04 1.97 81 CoMo (EG) 5.78 2.24 77 CoMo (MA) 5.81 2.13 78 CoMo 5.50 2.26 71 *:the calculation of sulfidity is based on transformation all Mo and Co atoms into MoS2 and CoS 表 2 反应后催化剂表面成分分析
Table 2 Surface components determined by XPS of the spent catalysts
Catalyst Mo 3d5/2 E/eV FWHM E/eV Relative percentage/% S/Mo CoMo (EN) 229.1 1.31 49 1.9 231.7 2.00 19 232.8 2.20 32 CoMo (EA) 228.9 1.34 41 1.8 231.2 2.50 29 232.7 1.63 30 CoMo (EG) 228.9 1.32 38 1.7 230.5 2.88 31 232.6 1.57 31 CoMo (MA) 229.0 1.46 37 1.7 231.1 2.24 28 232.8 1.72 35 CoMo 229.0 1.31 27 1.6 230.5 2.90 34 232.7 1.90 39 表 3 反应后催化剂(Co)MoS2晶粒的平均宽度和平均堆叠层数
Table 3 Average slab length and stacking number of (Co)MoS2 grains in spent catalysts
Catalyst Average slab length /nm Average stacking number CoMo(EN) 2.97 1.87 CoMo(EA) 2.89 1.80 CoMo(EG) 2.86 1.67 CoMo(MA) 2.85 1.63 CoMo 2.80 1.58 -
[1] 王腾飞, 张晔, 葛晖, 唐明兴, 周立公, 吕占军, 李学宽.硫代硫酸铵预硫化的Mo/AC催化剂加氢脱硫性能的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(2):202-207. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18575.shtmlWANG Teng-fei, ZHANG Ye, GE Hui, TANG Ming-xing, ZHOU Li-gong, LÜ Zhan-jun, LI Xue-kuan. Hydrodesulfurization of thiophene over Mo/AC catalyst presulfided by ammonium thiosulfate[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(2):202-207. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18575.shtml [2] 范强.柴油超深度加氢脱硫技术长周期生产国Ⅴ柴油的工业应用[J].当代石油石化, 2016, 4(12):21-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6809.2016.12.005FAN Qiang. Industrial application of diesel ultra deep hydrodesulfurization technology producing V diesel oil[J]. Pet Petrochem Today, 2016, 24(12):21-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6809.2016.12.005 [3] TOPSOE H. The role of Co-Mo-S type structures in hydrotreating catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2007, 322:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2007.01.002 [4] HIROSHIMA K, MOCHIZUKI T, HONMA T. High HDS activity of CoMo/Al2O3 modified by some chelates and their surface fine structures[J]. Appl Sur Sci, 1997, 21(6):433-436. [5] LELIAS M A, KOOYMAN P J, MARIEY L. Effect of NTA addition on the structure and activity of the active phase of cobalt-molybdenum sulfide hydrotreating catalysts[J]. J Catal, 2009, 267(1):179. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021951709002401 [6] ESCOBAR J, BARRERA M C, GUTIERREZ A W. Benzothiophene hydrodesulfurization over NiMo/alumina catalysts modified by citric acid. Effect of addition stage of organic modifier[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2017, 156:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.09.028 [7] CIROSPEREZ J, GOMEZ, SERRA M. On the role of triethylene glycol in the preparation of highly active Ni-Mo/Al2O3, hydrodesulfurization catalysts:A spectroscopic study[J]. Appl Catal B:Enriron, 2015, 166-167:560-567. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.039 [8] HUI G, LI X, QIN Z. Effects of carbon on the sulfidation and hydrodesulfurization of CoMo hydrating catalysts[J]. Korean J Chem Eng, 2009, 26(2):576-581. doi: 10.1007/s11814-009-0098-6 [9] BUI N Q, GEANTET C, BERHAULT G. Maleic acid, an efficient additive for the activation of regenerated CoMo/Al2O3, hydrotreating catalysts[J]. J Catal, 2015, 330:374-386. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.07.031 [10] GE H, WEN X D, RAMOS M A. Carbonization of ethylenediamine coimpregnated CoMo/Al2O3 catalysts sulfided by organic sulfiding agent[J]. ACS Catal, 2014, 4(8):2556-2565. doi: 10.1021/cs500477x [11] CATTANEO R, WEBER T, SHIDO T. A quick EXAFS study of the sulfidation of NiMo/SiO2, hydrotreating catalysts prepared with chelating ligands[J]. J Catal, 2000, 191(1):225-236. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1999.2784 [12] IWAMOTO R, KAGAMI N, ⅡNO A. Effect of polyethylene glycol addition on hydrodesulfurization activity over CoO-MoO3/Al2O3 catalyst[J]. J Jpn Pet Inst, 2005, 48(4):237-242. doi: 10.1627/jpi.48.237 [13] VALENCIA D, KLIMOVA T. Kinetic study of NiMo/SBA-15 catalysts prepared with citric acid in hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene[J]. Catal Commun, 2012, 21(9):77-81. http://www.academia.edu/6956002/Effect_of_citrate_addition_in_NiMo_SBA15_catalysts_on_selectivity_of_DBT_hydrodesulfurization [14] INFANTES M A, ROMERO P A, SANCHEZ G V, Role of Cs on hydrodesulfurization activity of RuS2 catalysts supported on a mesoporous SBA-15 type material[J]. ACS Catal, 2011, 1(3):175-186. doi: 10.1021/cs100053e [15] 左东华, 聂红, Vrinat M, 石亚华, Lacroix M, 李大东.硫化态NiW/AI2O3催化剂加氢脱硫活性相的研究Ⅰ. XPS和HREM表征.催化学报, 2004, 25(4):309-314.ZUO Dong-hua, NIE Hong, VRINAT M, SHI Ya-hua, LACROIX M, LI Da-dong. Study on the hydrodesulfurization active phase in sulfided NiW/Al2O3 catalyst Ⅰ. XPS and HREM characterization[J]. Chin J Chem, 2004, 25(4):309-314. [16] RANA M S, RAMIREZ J, GUTIERREZ A A, ANCHEYTA J, CEDENO L, MAITY S K. Support effects in CoMo hydrodesulfurization catalysts prepared with EDTA as a chelating agent[J]. J Catal, 2007, 246(1):100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2006.11.025 [17] 白天忠, 刘继华, 柳伟, 宋永一, 孙厚祥, 包洪洲.柴油加氢脱硫机理的研究进展[J].广东化工, 2011, 38(9):92-93. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdhg201109048BAI Tian-zhong, LIU Ji-hua, LIU Wei, SONG Yong-yi, SUN Hou-xiang, BAO Hong-zhou. Study on the mechanism of diesel hydrodesulfurization[J]. Guangdong Chem Ind, 2011, 38(9):92-93. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdhg201109048 [18] 徐永强, 赵瑞玉, 商红岩, 赵会吉, 刘晨光.二苯并噻吩和4-甲基二苯并噻吩在Mo和CoMo/γ-Al2O3催化剂上加氢脱硫的反应机理[J].石油学报, 2003, 19(5):14-21.XU Yong-qiang, ZHAO Rui-yu, SHANG Hong-yan, ZHAO Hui-ji, LIU Chen-guang. Mechanism of hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and 4-methyldibenzothiophene on Mo/γ-Al2O3 and CoMo/γ-Al2O3[J]. Acta Pet Sin, 2003, 19(5):14-21. [19] PAPADOPOULOU C, VAKROS J, MATRALIS H K. Preparation, characterization, and catalytic activity of CoMo/γ-Al2O3 catalysts prepared by equilibrium deposition filtration and conventional impregnation techniques[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2004, 274(1):159-166. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2003.11.041 [20] QIU L, XU G. Peak overlaps and corresponding solutions in the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of hydrodesulfurization catalysts[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2010, 256(11):3413-3417. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.12.043 [21] BERIT H, HENRIK T. A density functional study of the chemical differences between type Ⅰ and type Ⅱ MoS2-based structures in hydrotreating catalysts[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2005, 109(6):2245-2253. doi: 10.1021/jp048842y [22] RINALDI N, KUBOTA T, OKAMOTO Y. Effect of citric acid addition on Co-Mo/B2O3/Al2O3 catalysts prepared by a post-treatment Method[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2009, 48(23):10414-10424. doi: 10.1021/ie9008343 [23] VALENCIA D, KLIMOVA T. Citric acid loading for MoS2-based catalysts supported on SBA-15. New catalytic materials with high hydrogenolysis ability in hydrodesulfurization[J]. Appl Catal B:Enriron, 2013, 129(2):137-145. -





 下载:
下载: