Preparation of CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox composite by bacterial cellulose promoted sol-gel method and its catalytic performance in the toluene degradation at low temperature
-
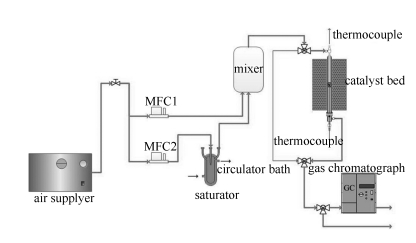
摘要: 以绿色廉价的天然椰果细菌纤维素(BC)为造孔剂,采用溶胶凝胶法制备了CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox复合氧化物催化剂,通过TG/DTG、N2低温物理吸脱附、XRD、H2-TPR、O2-TPD和Raman等手段对催化剂进行了表征,并对其在固定床上挥发性有机物(VOCs)降解的催化性能进行了研究。结果表明,利用BC精细的纤维网状结构和亲水性能与活性金属盐溶液形成凝胶,可有效制备介孔结构的复合氧化物催化剂。制备过程中,凝胶形式和成胶温度对催化剂降解甲苯的活性有较大影响;采用醇凝胶形式在70 ℃时制备的ACCZ-70催化剂完全降解甲苯的温度为205 ℃,明显低于已有文献报道的催化剂,这主要归因于该催化剂具有良好的低温还原性和高达0.81的氧空穴浓度。而采用水凝胶制备的催化剂降解甲苯时,在120-140 ℃存在吸附现象。Abstract: Mesoporous CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox composite was prepared by a simple sol-gel method with environmentally benign bacterial cellulose (BC) as a pore former and characterized by TG/DTG, N2 adsorption-desorption, XRD, H2-TPR, O2-TPD and Raman; its catalytic activity in the degradation of toluene at low temperature was investigated in a fixed-reactor. The results indicated that BC with ultra fine three-dimensional networks and excellent compatibility is beneficial to the formation of gel with nitrate solution, to prepare the mesoporous catalyst. The catalyst performance of CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox composite is significantly affected by the gel-form and gelling temperature during the preparation process. Over the ACCZ-70 catalyst prepared by alcohol gelling at 70 ℃, the temperature for a complete degradation of toluene (T100) reaches 205 ℃, much lower than those reported in open literature; the excellent activity of ACCZ-70 is ascribed to its high reducibility at low temperature and high concentration of oxygen vacancies (0.81). In addition, adsorption phenomenon was observed in the range of 120-140 ℃ during the toluene degradation over WCCZ catalysts prepared by water gelling.
-
Key words:
- bacterial cellulose /
- sol-gel /
- multiple oxide catalysts /
- VOCs
-
表 1 不同CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox催化剂的制备参数
Table 1 Preparation parameters of the different CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox catalysts
Catalyst Gel form Gel temperature t/℃ WCCZ-70 water gel 70 ACCZ-70 alcohol gel 70 WCCZ-80 water gel 80 ACCZ-80 alcohol gel 80 表 2 CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox催化剂的比表面积、总孔容和平均孔径
Table 2 ABET, vpand dpof different CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox catalysts
Catalyst ABET /(m2·g-1) vp /(cm3·g-1) dp /nm WCCZ-70 33.3 0.11 10.3 ACCZ-70 38.1 0.13 10.7 WCCZ-80 42.7 0.12 9.7 ACCZ-80 24.1 0.09 10.8 表 3 CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox催化剂氢气消耗量
Table 3 H2 consumptions of different CuCe0.75Zr0.25Ox catalysts
Catalyst H2 consumption /(μmol·g-1) α β γ total WCCZ-70 13.0 95.0 37.6 145.6 ACCZ-70 16.0 50.0 78.0 144.0 WCCZ-80 14.0 98.6 35.1 147.7 ACCZ-80 15.0 50.0 70.0 135.0 -
[1] ZHONG Z M, SHA Q E, ZHENG J Y, YUAN Z B, GAO Z J, OU J M, ZHENG Z Y, LI C, HUANG Z J. Sector-based VOCs emission factors and source profiles for the surface coating industry in the Pearl River Delta region of China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2017, 583(1):19-28. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969716328613 [2] ZHANG Z X, ZHENG J, SHANGGUAN W F. Low-temperature catalysis for VOCs removal in technology and application:A state-of-the-art review[J]. Catal Today, 2016, 264(15):270-278. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920586115007087 [3] KAMIMURA Y, SHIMOMUR M, ENDO A. Simple template-free synthesis of high surface area mesoporous ceria and its new use as a potential adsorbent for carbon dioxide capture[J]. J Colloid Interf Sci, 2014, 436(15):52-62. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/25265586 [4] YE L Q, ZHANG Y L, SONG C C, LI Y Y, JIANG B. A simple sol-gel method to prepare superhydrophilic silica coatings[J]. Mater Lett, 2017, 188(1):316-318. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308083416_A_simple_sol-gel_method_to_prepare_superhydrophilic_silica_coatings [5] MIN J E, LEE Y J, PARK H G, ZHANG C D, JUN K W. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane on Ni-MgO-Al2O3 catalysts prepared by sol-gel method:Effects of Mg/Al ratios[J]. J Ind Eng Chem, 2015, 26(25):375-383. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1226086X14006777 [6] MARCELLO R D, EDUARDO H M N, WANDER L V. Use of a design-of-experiments approach for preparing ceria-zirconia-alumina samples by sol-gel process[J]. Ceram Int, 2016, 42(8):9488-9495. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.03.021 [7] TANG W X, WU X F, LIU G, LI S D, LI D Y, LI W H, CHEN Y F. Preparation of hierarchical layer-stacking Mn-Ce composite oxide for catalytic total oxidation of VOCs[J]. J Rare Earth, 2015, 33(1):62-69. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60384-7 [8] ZHANG X, WU D F. Ceramic monolith supported Mn-Ce-M ternary mixed-oxide (M=Cu, Ni or Co) catalyst for VOCs catalytic oxidation[J]. Ceram Int, 2016, 42(15):16563-16570. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.07.076 [9] LU H F, KONG X X, HUANG H F, ZHOU Y, CHEN Y F. Cu-Mn-Ce ternary mixed-oxide catalysts for catalytic combustion of toluene[J]. J Environ Sci, 2015, 32(1):102-107. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jes-e201506012 [10] MANMEET S D, JEFFREY M C. Mechanical and structural property analysis of bacterial cellulose composites[J]. Carbohyd Polym, 2016, 144(25):447-453. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27083837 [11] WANG J Q, LU X K, NG P F, LEE K I, FEI B, XIN J H, WU J Y. Polyethylenimine coated bacterial cellulose nanofiber membrane and application as adsorbent and catalyst[J]. J Colloid Interf Sci, 2015, 440(15):32-38. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021979714007991 [12] ZHANG D Y, QI L M. Synthesis of mesoporous titania networks consisting of anatase nanowires by templating of bacterial cellulose membranes[J]. Chem Commun, 2005, 21:2735-2737. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15917937 [13] ZHANG T, ZHENG Y D, LIU S M, YUE L N, GAO Y, YAO Y. Bacterial cellulose membrane supported three-dimensionally dispersed silver nanoparticles used as membrane electrode for oxygen reduction reaction in phosphate buffered saline[J]. J Electroanal Chem, 2015, 750(1):43-48. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S157266571500226X [14] ZHOU P P, WANG H H, YANG J Z, TANG J, SUN D P, TANG W H. Bacteria cellulose nanofibers supported palladium(0) nanocomposite and its catalysis evaluation in heck reaction[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2012, 51(16):5743-5748. doi: 10.1021/ie300395q [15] YANG J Z, TANG W H, LIU X L, CHAO C, LIU J G, SUN D P. Bacterial cellulose-assisted hydrothermal synthesis and catalytic performance of La2CuO4 nanofiber for methanol steam reforming[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(25):10813-10818. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.01.015 [16] LIU S S, YAN W N, CAO X C, ZHOU Z F, YANG R Z. Bacterial-cellulose-derived carbon nanofiber-supported CoFe2O4 as efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(11):5351-5360. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.01.121 [17] FORESTI M L, VÁZQUEZ A, BOURY B. Applications of bacterial cellulose as precursor of carbon and Composites with metal oxide, metal sulfide and metal nanoparticles:A review of recent advances[J]. Carbohyd Polym, 2017, 157(10):447-467. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27987949 [18] LI S M, HAO Q L, ZHAO R Z, LIU D L, DUAN H Z, DOU B J. Highly efficient catalytic removal of ethyl acetate over Ce/Zr promoted copper/ZSM-5 catalysts[J]. Chem Eng J, 2016, 285(1):536-543. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894715013686 [19] DOU B J, LI S M, LIU D L, ZHAO R Z, LIU J G, HAO Q L, BIN F. Catalytic oxidation of ethyl acetate and toluene over Cu-Ce-Zr supported ZSM-5/TiO2 catalysts[J]. RSC Adv, 2016, 6(59):53852-53859. doi: 10.1039/C6RA06421C [20] WANG Y L, ZHANG S N, MAI Y W, WAN Y Z, LIM S H, HE F, HUANG Y. Preparation and Thermo-Mechanical Characterization of Hydroxyapatite/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocomposites[J]. Nanotech Precis Eng, 2009, 7(2):95-101. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288810559_Preparation_and_Thermo-Mechanical_Characterization_of_HydroxyapatiteBacterial_Cellulose_Nanocomposites [21] ZHANG Q L, XU L S, NING P, GU J J, GUAN Q Q. Surface characterization studies of CuO-CeO2-ZrO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 317:955-961. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.09.017 [22] ZHOU G L, LAN H, GAO T T, XIE H M. Influence of Ce/Cu ratio on the performance of ordered mesoporous CeCu composite oxide catalysts[J]. Chem Eng J, 2014, 246(15):53-63. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894714002071 [23] ZHANG Y W, WEN J, WANG J, PAN D C, SHEN M Q, LU Y F. Synthesis of monodisperse CexZr1-xO2 nanocrystals and the size-dependent enhancement of their properties[J]. Nano Res, 2011, 4(5):494-504. doi: 10.1007/s12274-011-0105-1 [24] CAI T, HUANG H, DENG W, DAI Q G, LIU W, WANG X Y. Catalytic combustion of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene at low temperature over Mn-modified Co3O4 catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2015, 166-167:393-405. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.047 [25] HE C, YU Y K, YUE L, QIAO N L, LI J J, SHEN Q, YU W J, CHEN J S, HAO Z P. Low-temperature removal of toluene and propanal over highly active mesoporous CuCeOx catalysts synthesized via a simple self-precipitation protocol[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2014, 147:156-166. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.08.039 [26] RIVAS B, LÓPEZ-FONSECA R, GUTIÉRREZ-ORTIZ MÁ, GUTIÉRREZ-ORTIZ J I. Combustion of chlorinated VOCs using K-CeZrO4 catalysts[J]. Catal Today, 2011, 176(1):470-473. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.10.044 [27] YANG P, YANG S S, SHI Z N, MENG Z H, ZHOU R X. Deep oxidation of chlorinated VOCs over CeO2-based transition metal mixed oxide catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2015, 162:227-235. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.06.048 [28] LIAO Y N, FU M L, CHEN L M, WU J L, HUANG B C, YE D Q. Catalytic oxidation of toluene over nanorod-structured Mn-Ce mixed oxides[J]. Catal Today, 2013, 216(1):200-228. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8734806 [29] LU H F, ZHOU Y, HAN W F, HUANG H F, CHEN Y F. Promoting effect of ZrO2 carrier on activity and thermal stability of CeO2-based[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2013, 464:101-108. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X13003189 -





 下载:
下载: