Syngas-derived olefins over iron-based catalysts: Effects of basic properties of MgO nanocrystals
-
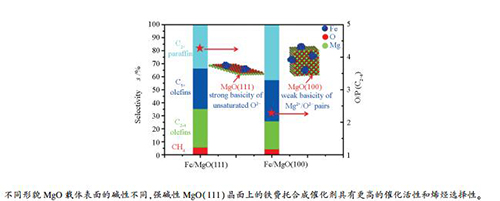
摘要: 本研究采用等量浸渍法、化学沉淀法和超声浸渍法合成了一系列具有良好外露晶面的Fe/MgO催化剂。采用X射线粉末衍射、高分辨透射电子显微镜、CO2程序升温脱附、H2程序升温还原、X射线光谱学和N2物理吸附等物理化学方法对催化剂进行了表征。MgO纳米晶载体的碱性会影响费-托合成产物的选择性。在超声浸渍过程中,MgO纳米晶载体的碱性得到了保持。研究结果显示,Fe/MgO催化剂的碱性会提高CO解离速率和产物中烯烃的选择性。此外,相比于MgO(100)晶面,MgO(111)晶面负载铁基催化剂具有更高的活性(TOF)和烯烃选择性。MgO(111)晶面上更有利于CO的吸附,抑制二次加氢反应,提高产物中烯烃的收率。Abstract: A series of Fe/MgO catalysts with well-defined exposed crystal planes were synthesized by impregnation, deposition-precipitation and ultrasonic impregnation methods. The catalysts were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, CO2 temperature-programmed desorption, H2 temperature-programmed reduction, X-ray spectroscopy and N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms. The characterization results indicate that the basicity of MgO supports strongly affect the catalytic performance of iron-based catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. It is found that the strong basicity sites of MgO supports remain during the ultrasonic impregnation process. The intrinsic basicity of Fe/MgO catalysts enhances dissociative CO adsorption and promotes the olefin selectivity. In addition, the catalyst of iron particles on the (111) crystal planes of MgO nanosheets presents higher TOF value and olefins selectivity than that of the catalyst using the (100) crystal planes of MgO nanocubes as a support. The effect of basic properties of MgO nanocrystals facilitates CO chemisorption, suppressing H2 adsorption and olefin desorption on the corresponding Fe/MgO catalysts.
-
Key words:
- Fischer-Tropsch synthesis /
- iron /
- MgO /
- preparation method
-
Table 1 Physicochemical property of the as-synthesized samples
Samples Surface area A/(m2·g-1) Total pore volume v/(cm3·g-1) Average Pore size d/nm MgO-ns 42.4 0.33 25.0 Fe/MgO-ns-UI 38.8 0.29 26.2 Fe/MgO-ns-IM 50.4 0.46 21.8 Fe/MgO-ns-DP 64.9 0.47 21.3 Table 2 XPS and ICP analysis results of the reduced Fe/MgO catalysts
Catalyst Binding energy of Fe 2p3/2 Iron content on the surfacea /% Bulk iron contentb/% Fe3O4 Fe0 Fe/MgO-ns-UI 710.4 706.2 1.6 4.9 Fe/MgO-ns-DP 710.8 - 2.6 6.5 Fe/MgO-ns-IM 710.8 706.3 0.7 5.3 a: obtained by XPS measurement and the samples were pretreated with hydrogen at 420 ℃ for 3 h; b: obtained by ICP measurement Table 3 Catalytic performance of iron-based catalysts with MgO supports for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis a
Catalyst CO conv.x/% TOF b/
(×10-2 s-1)Hydrocarbon selectivity s/% CH4 C2-40 C2-4= C5+ olefins O/P(C2-4) Fe/MgO-ns-IM 55.6 1.26 14.7 11.2 14.6 59.5 50.0 1.3 Fe/MgO-ns-DP 38.0 2.74 15.8 10.2 15.5 58.5 49.9 1.5 Fe/MgO-ns-UI 35.5 5.73 12.1 7.3 29.6 51.0 60.6 4.1 Fe/MgO-c-UI 35.7 4.34 13.6 9.6 21.5 55.3 53.1 2.2 a: reaction condition: 1.0 MPa, 300 ℃, H2/CO=1, 8 L/(h·g); b: TOF was based on the amount of the total H2 uptake -
[1] CHENG K, KANG J, KING D L, VIJAYANAND S, ZHOU C, ZHANG Q, WANG Y. Advances in catalysis for syngas conversion to hydrocarbons[J]. Adv Catal, 2017, 60:125-208. [2] KOMATSU T, FUKUI Y. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on RuTi intermetallic compound catalyst[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2005, 279(1/2):173-180. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X04008567 [3] LIU C, ZHANG Y, ZHAO Y, WEI L, HONG J, WANG L, CHEN S, WANG G, LI J. The effect of the nanofibrous Al2O3 aspect ratio on Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over cobalt catalysts[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(2):570-581. doi: 10.1039/C6NR07529K [4] DAVIS B H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis:Comparison of performances of iron and cobalt catalysts[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2007, 46:8938-8945. doi: 10.1021/ie0712434 [5] TORRES GALVIS H M, DE JONG K P. Catalysts for production of lower olefins from synthesis gas:A review[J]. ACS Catal, 2013, 3(9):2130-2149. doi: 10.1021/cs4003436 [6] ZHAI P, XU C, GAO R, LIU X, LI M, LI W, FU X, JIA C, XIE J, ZHAO M, WANG X, LI Y, ZHANG Q, WEN X, MA D. Highly tunable selectivity for syngas-derived alkenes over zinc and sodium-modulated Fe5C2 catalyst[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55(35):9902-9907. http://www.chemeurope.com/en/publications/988869/highly-tunable-selectivity-for-syngas-derived-alkenes-over-zinc-and-sodium-modulated-fe5c2-catalyst.html [7] SSUN J, CHEN Y, CHEN J. Towards stable Fe-based catalysts with suitable active phase for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis to lower olefins[J]. Catal Commun, 2017, 91:34-37. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.12.008 [8] ASAMI K, KOMIYAMA K, YOSHIDA K, MIYAHARA H. Synthesis of lower olefins from synthesis gas over active carbon-supported iron catalyst[J]. Catal Today, 2018, 303:117-122. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.09.010 [9] TORRES GALVIS H M, BITTER J H, KHARE C B, RUITENBEEK M, IULIAN DUGULAN A, DE JONG. K P. Supported iron nanoparticles as catalysts for sustainable production of lower olefins[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6070):835-838. doi: 10.1126/science.1215614 [10] LI J, CHENG X, ZHANG C, YANG Y, LI Y. Effects of alkali on iron-based catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis:CO chemisorptions study[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2015, 396:174-180. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.10.006 [11] PARK J C, YEO S C, CHUN D H, LIM J T, YANG J, LEE H, SUNG-JUN H, LEE H M, KIM C S, JUNG H. Highly activated K-doped iron carbide nanocatalysts designed by computational simulation for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. J Mater Chem A, 2014, 2(35):14371-14379. doi: 10.1039/C4TA02413C [12] YANG J, SUN Y, TANG Y, LIU Y, WANG H, TIAN L, WANG H, ZHANG Z, XIANG H, LI Y. Effect of magnesium promoter on iron-based catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. J Mater Chem A, 2006, 245(1/2):26-36. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1381116905006151 [13] CHENG Y, LIN J, WU T, WANG H, XIE S, PEI Y, YAN S, QIAO M, ZONG B. Mg and K dual-decorated Fe-on-reduced graphene oxide for selective catalyzing CO hydrogenation to light olefins with mitigated CO2 emission and enhanced activity[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2017, 204:475-485. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.11.058 [14] CAGNOLI M V, MARCHETTI S G, GALLEGOS N G, ALVAREZ A M, MERCADER R C, YERAMIAN A A. Influence of the support on the activity and selectivity of high dispersion Fe catalysts in the Fischer-Tropsch reaction[J]. J Catal, 1990, 123(1):21-30. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(90)90154-C [15] CAGNOLI M V, MARCHETTI S G, GALLEGOS N G, ALVAREZ A L, YERAMIAN A A, MERCADER R C. Effect of thermal pretreatment on the structural properties of Fe/MgO catalysts in hydrocarbon synthesis from CO and H2[J]. Mater Chem Phys, 1991, 27(4):403-418. doi: 10.1016/0254-0584(91)90137-J [16] ARSALANFAR M, MIRZAEI A A, BOZORGZADEH H R, SAMIMIC A, GHOBADIA R. Effect of support and promoter on the catalytic performance and structural properties of the Fe-Co-Mn catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. J Ind Eng Chem, 2014, 20(4):1313-1323. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2013.07.011 [17] KAKE Z, HU J, KÜBEL C, RICHARDS R. Efficient Preparation and Catalytic Activity of MgO(111) Nanosheets[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2006, 118(43):7435-7439. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3757 [18] LI Z, CIOBANU C V, HU J, JUAN-PEDRO PALOMARES-BA'EZ, JOSE'-LUIS RODRI'GUEZ-LO'PEZD, RYAN RICHARDS. Experimental and DFT studies of gold nanoparticles supported on MgO(111) nano-sheets and their catalytic activity[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2011, 13(7):2582-2589. doi: 10.1039/c0cp01820a [19] HACQUART R, KRAFFT J, COSTENTIN G, JUPILLE J. Evidence for emission and transfer of energy from excited edge sites of MgO smokes by photoluminescence experiments[J]. Surf Sci, 2005, 595(1/3):172-182. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ026076871 [20] Li Y, AFZAAL M, O'BRIEN P. The synthesis of amine-capped magnetic (Fe, Mn, Co, Ni) oxide nanocrystals and their surface modification for aqueous dispersibility[J]. J Mater Chem, 2006, 16(22):2175-2180. doi: 10.1039/b517351e [21] KAKE Z, HUA W, DENG W, RICHARDS R M. Preparation of MgO nanosheets with polar (111) surfaces by ligand exchange and esterification-synthesis, structure, and application as catalyst support[J]. Eur J Inorg Chem, 2012, 2012(17):2869-2876. doi: 10.1002/ejic.v2012.17 [22] LIANG M, KANG W, XIE K. Comparison of reduction behavior of Fe2O3, ZnO and ZnFe2O4 by TPR technique[J]. J Nat Gas Chem, 2009, 18(1):110-113. doi: 10.1016/S1003-9953(08)60073-0 [23] LIU Y, CHEN J, BAO J, ZHANG Y. Manganese-modified Fe3O4 microsphere catalyst with effective active phase of forming light olefins from syngas[J]. ACS Catal, 2015, 5(6):3905-3909. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b00492 [24] MILLS P, SULLIVAN J L. A study of the core level electrons in iron and its three oxides by means of x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy[J]. J Phys D:Appl Phys, 1983, 16:723-732. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/16/5/005 [25] BIESINGERA M C, PAYNE B P, GROSVENOR A P, LAU L W M, GERSON A R, SMART R S C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides:Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 257(7):2717-2730. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.051 [26] NORDMANN T, KUSCHEL O, WOLLSCHLÄGER J. Epitaxial growth of ultrathin MgO layers on Fe3O4(001) films[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2016, 381:28-31. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.133 [27] DRY M E, OOSTHUIZEN J G. The correlation between catalyst surface basicity and hydrocarbon selectivity in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. J Catal, 1968, 11(11):18-24. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0021951768900043 [28] LU J, YANG L, XU B, WU Q, ZHANG D, YUAN S, ZHAI Y, WANG X, FAN Y, HU Z. Promotion effects of nitrogen doping into carbon nanotubes on supported iron Fischer-Tropsch catalysts for lower olefins[J]. ACS Catal, 2014, 4(2):613-621. doi: 10.1021/cs400931z [29] GALLEGOS N G, ALVAREZ A M, CAGNOLI M V, BENGOA J F, MARCHETTI S G, MERCADER R C, YERAMIAN A A. Selectivity to olefins of Fe/SiO2-MgO catalysts in the Fischer-Tropsch reaction[J]. J Catal, 1996, 161:132-142. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1996.0170 -





 下载:
下载: