Research progress on emission and control technologies of arsenic, selenium and lead in coal-fired power plants
-
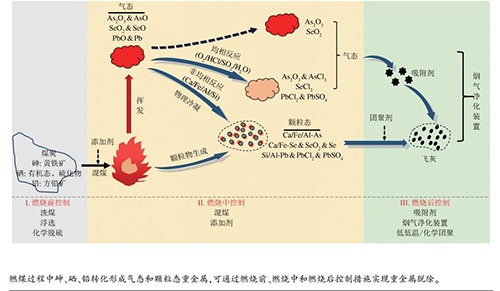
摘要: 煤炭是中国重要的能源资源,而中国煤中重金属砷、硒、铅含量较高,燃煤电厂已经成为重要的砷、硒、铅排放源之一。针对电厂燃煤带来严峻的砷、硒、铅污染问题,本文首先介绍了燃煤释放的砷、硒、铅排放量大且危害性强,概述了世界各国关于重金属排放控制的相关政策法规,指出中国对燃煤重金属砷、硒、铅的排放控制势在必行;其次从煤中赋存形态、燃烧过程中的形态转化和质量分布三个方面阐释了燃煤过程中砷、硒、铅的迁移转化规律,重点描述了砷、硒、铅在颗粒物上的形态特征和尺度分布;最后综述了燃烧前、燃烧中和燃烧后对砷、硒、铅的排放控制技术,详述了吸附剂捕集和烟气净化装置协同脱除的研究进展,并论述了低低温除尘器和团聚技术对砷、硒、铅的强化脱除潜力。以期为燃煤电厂重金属砷、硒、铅超低排放的实现提供参考和指导。Abstract: Coal is the most significant source of energy generation in China, but the high content of arsenic/selenium/lead in coal has made coal-fired power plants become one of the main anthropogenic emission sources of them. To solve the serious problem on arsenic/selenium/lead pollution from coal-fired power plants, this paper firstly introduces the discharge and harmfulness of arsenic/selenium/lead released from coal-fired power plants, and summarizes the relevant domestic and foreign regulations on heavy metals emission control, then points out that it is necessary to control their emission from coal-fired power plants in China. Secondly, the migration and transformation behaviors of arsenic/selenium/lead during coal combustion are illustrated from the perspectives of occurrence form, speciation transformation and mass distribution, focusing on their speciation characteristics and size distribution in particulate matters. Finally, the control technologies pre-, in- and post-combustion are reviewed, and the research progress on their removal by adsorbents and air pollution control devices (APCDs) is described in detail. Meanwhile, the potential for strengthening the removal by electrostatic precipitators equipped with low temperature economizer and agglomeration technologies is discussed. In conclusion, it is aimed to provide reference and guidance for realization of ultra-low emission of arsenic/selenium/lead in coal-fired power plants.
-
图 2 不同电厂不同级飞灰中砷的结合形态[43]
Figure 2 Arsenic speciation in fly ashes collected from different hoppers of four power plants[43]
: non-specifically adsorbed As; : specifically adsorbed As; : calcite-bound As; : amorphous and poorly-crystalline Fe/Al-bound As; : well-crystallized Fe/Al-bound As
(with permission from Elsevier)表 1 全球煤中砷、硒、铅的平均含量
Table 1 The average content of arsenic, selenium and lead in coals over the world
表 2 美国燃煤电厂重金属砷、硒、铅排放限值[15]
Table 2 Emission limits for arsenic, selenium and lead from coal-fired power plants in the United States[15]
TEs Existing coal-fired power plants /(μg·m-3) New or reconstructed coal-fired power plants /(μg·m-3) As 2.7 0.4 Se 8.2 6.8 Pb 2.7 2.7 表 3 烟气中砷、硒、铅的质量分布
Table 3 Mass distribution of arsenic, selenium and lead in the flue gas
TEs Vapor phases /% Particulate phases /% References As 0.01-32.4 67.6-99.99 Guo[53]; Zhao et al[54]; Yi et al[55]; Zhou et al[56]; Sandelin et al[57]; Nalbandian et al[58]; Ratafia-Brown et al[59]; Córdoba et al[60] Se 13.3-61.7 38.3-86.7 Guo[53]; Yi et al[55]; Meij et al[61]; Sandelin et al[57]; Nalbandian et al[58]; Ratafia-Brown et al[59]; Córdoba et al[60] Pb 0.02-30.5 69.5-99.98 Zhao et al[54]; Zhou et al[56]; Sandelin et al[57]; Nalbandian et al[58]; Ratafia-Brown et al[59]; Deng et al[62]; Sun[63] 表 4 烟气净化装置对砷、硒、铅的脱除效率
Table 4 Removal efficiency of arsenic, selenium and lead by air pollution control devices
APCDs Removal efficiency /% References As Se Pb ESP 72.3-99.98 34.2-90.7 91.85-99.95 Hua et al[108]; Chang et al[105]; Meij et al[109]; Zhang et al[110] FF 99 65 95.12 Deng et al[62]; Brekke et al[111] EFF 90-99.85 - 90-99.95 Wang et al[112]; Zhao et al[103] WFGD 7.69-85.8 12.5-66.7 35.67-77.81 Li et al[113]; Deng et al[62]; Cheng et al[104]; Chang et al[105] WESP 83.33 23.06 32.87-84.38 Wang et al[106]; Zhao et al[103] -
[1] 中华人民共和国自然资源部.中国矿产资源报告2019[R].北京: 自然资源部, 2019.http://www.mnr.gov.cn/sj/sjfw/kc_19263/zgkczybg/201910/t20191022_2473040.html.Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. China Mineral Resources 2019. http://www.mnr.gov.cn/sj/sjfw/kc_19263/zgkczybg/201910/t20191022_2473040.html. [2] XU M, YAN R, ZHEN C, QIAO Y, HAN J, SHENG C. Status of trace element emission in a coal combustion process:A review[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2003, 85:215-237. [3] ZHAO Y, YANG J, MA S, ZHANG S, LIU H, GONG B, ZHANG J, ZHENG C. Emission controls of mercury and other trace elements during coal combustion in China:A review[J]. Int Geol Rev, 2017, 60(5/6):638-670. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2017.1362671 [4] CHENG S. Heavy metal pollution in China:Origin, pattern and control[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2003, 10(3):192-198. doi: 10.1065/espr2002.11.141.1 [5] TCHOUNWOU P B, YEDJOU C G, PATLOLLA A K, SUTTON D J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment[J]. Exp Suppl, 2012, 101:133-164. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6 [6] TIAN H Z, ZHU C Y, GAO J J, CHENG K, HAO J M, WANG K, HUA S B, WANG Y, ZHOU J R. Quantitative assessment of atmospheric emissions of toxic heavy metals from anthropogenic sources in China:Historical trend, spatial distribution, uncertainties, and control policies[J]. Atmos Chem Phys, 2015, 15(17):10127-10147. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/HZ_Tian/publication/276177637_Quantitative_assessment_of_atmospheric_emissions_of_toxic_heavy_metals_from_anthropogenic_sources_in_China_Historical_trend_spatial_distribution_uncertainties_and_control_policies/links/55f8ce0508ae07629de06cd7.pdf [7] DAI S, LUO Y, SEREDIN V V, WARD C R, HOWER J C, ZHAO L, LIU S, ZHAO C, TIAN H, ZOU J. Revisiting the late Permian coal from the Huayingshan, Sichuan, southwestern China:Enrichment and occurrence modes of minerals and trace elements[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2014, 122:110-128. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516213002838 [8] TIAN H Z, LU L, HAO J M, GAO J J, CHENG K, LIU K Y, QIU P P, ZHU C Y. A review of key hazardous trace elements in Chinese coals:Abundance, occurrence, behavior during coal combustion and their environmental impacts[J]. Energy Fuels, 2013, 27(2):601-614. doi: 10.1021/ef3017305 [9] FINKELMAN R B. Trace and Minor Elements in Coal[M]. US:Organic Geochemistry, Springer, 1993. [10] RILEY K W, FRENCH D H, FARRELL O P, WOOD R A, HUGGINS F E. Modes of occurrence of trace and minor elements in some Australian coals[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2012, 94:214-224. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516211001352 [11] RILEY K W, FRENCH D H, LAMBROPOULOS N A, FARRELL O P, WOOD R A, HUGGINS F E. Origin and occurrence of selenium in some Australian coals[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2007, 72(2):72-80. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516206002072 [12] SWAINE D J, GOODARZI F. Environmental aspects of trace elements in coal[M]. Dordrecht Kluwer, 1995. [13] MUKHERJEE S, SRIVASTAVA S K. Trace elements in high-sulfur assam coals from the Makum coalfield in the northeastern region of India[J]. Energy Fuels, 2005, 19(3):882-891. doi: 10.1021/ef049775+ [14] KETRIS M P, YUDOVICH Y E. Estimations of Clarkes for carbonaceous biolithes:World averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2009, 78(2):135-148. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516209000123 [15] National emission standards for hazardous air pollutants from coaland oil-fired electric utility steam generating units and standards of performance for fossil-fuel-fired electric utility, industrial-commercial- institutional, and small industrial[S]. Federal Register, 2016. [16] NIU Y, LIU X, WANG S, HUI S E, SHADDIX C R. A numerical investigation of the effect of flue gas recirculation on the evolution of ultra-fine ash particles during pulverized coal char combustion[J]. Combust Flame, 2017, 184:1-10. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010218017302043 [17] WEI Q, DAI S, LEFTICARIU L, COSTIN G. Electron probe microanalysis of major and trace elements in coals and their low-temperature ashes from the Wulantuga and Lincang Ge ore deposits, China[J]. Fuel, 2018, 215:1-12. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236117314047 [18] 刘晶, 陆晓华, 郭欣.煤中痕量砷和汞的形态分析[J].华中理工大学学报, 2000, 28(7):71-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HZLG200007030.htmLIU Jing, LU Xiao-hua, GUO Xin. Speciation analysis of arsenic and mercury in coal[J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol, 2000, 28(7):71-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HZLG200007030.htm [19] SENIOR C L, ZENG T, CHE J, AMES M R, SAROFIM A F, OLMEZ I, HUGGINS F E, SHAH N, HUFFMAN G P, KOLKER A, MROCZKOWSKI S, PALMER C, FINKELMAN R. Distribution of trace elements in selected pulverized coals as a function of particle size and density[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 63(2):215-241. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378382099000983 [20] KOLKER A, SAROFIM A, PALMER C A, SENIOR C L, HUGGINS F E. Toxic substances from coal combustion phase coal selection and characterization[R]. 1998. [21] 郭欣, 郑楚光, 刘迎晖, 刘晶, 陆晓华.煤中汞, 砷, 硒赋存形态的研究[J].工程热物理学报, 2001, 22:763-766. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90922X/20016/5989548.htmlGUO Xin, ZHENG Cuo-guang, LIU Ying-hui, LIU Jing, LU Xiao-hua. The study of the mode of occurrence of mercury, arsenic and selenium in coal[J]. J Eng Therm, 2001, 22:763-766. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90922X/20016/5989548.html [22] SWAINE D J. Trace Elements in Coal[M]. Netherlands:Elsevier Ltd, 1990. [23] SAVAGE K S, TINGLE T N, PEGGY A O, WAYCHUNAS G A, BIRD D K. Arsenic speciation in pyrite and secondary weathering phases, Mother Lode Gold District, Tuolumne County, California[J]. Appl Geochem, 2000, 15(8):1219-1244. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0883292799001158 [24] HUGGINS F E, HUFFMAN G P. Modes of occurrence of trace elements in coal from XAFS spectroscopy[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 1994, 32(1/4):31-53. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0140670196893891 [25] FINKELMAN R B, Modes of occurrence of environmentally-sensitive trace elements in coal. in environmental aspects of trace elements in coal, 1995, 24-50. [26] 刘瑞卿.煤转化过程中砷、硒、铅的热稳定性及转化行为研究[D].太原: 中国科学院山西煤炭化学研究所, 2009.LIU Rui-qing. A study on thermal stability and transformation behavior of arsenic, selenium and lead during coal conversion[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009. [27] 刘瑞卿, 杨建丽, 刘振宇.热处理条件对煤中硒释放行为的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2011, 39(4):241-245. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=37865546LIU Rui-qing, YANG Jian-li, LIU Zhen-yu. Influence of thermal treatment condition on release behavior of selenium in coals[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2011, 39(4):241-245. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=37865546 [28] ZHOU C, LIU G, XU Z, SUN H, LAM P K S. Effect of ash composition on the partitioning of arsenic during fluidized bed combustion[J]. Fuel, 2017, 204:91-97. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S001623611730618X [29] ZHOU C, LIU G, XU Z, SUN H, KWAN SING LAM P. Retention mechanisms of ash compositions on toxic elements(Sb, Se and Pb) during fluidized bed combustion[J]. Fuel, 2018, 213:98-105. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236117313674 [30] SHEN F, LIU J, ZHANG Z, DAI J. Online analysis and kinetic behavior of arsenic release during coal combustion and pyrolysis[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2015, 49(22):13716-23. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26488499 [31] LIU H, WANG C, SUN X, ZHANG Y, ZOU C. Volatilization of arsenic in coal during isothermal oxy-fuel combustion[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30(4):3479-3487. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236117305276 [32] SHEN F, LIU J, DONG Y, GU C. Insights into the effect of chlorine on arsenic release during MSW incineration:An on-line analysis and kinetic study[J]. Waste Manag, 2018, 75:327-332. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956053X18300515 [33] WINTER R M, MALLEPALLI R R, HELLEM K P, SZYDLO S W. Determination of As, Cd, Cr, and Pb species formed in a combustion environment[J]. Combust Sci Technol, 1994, 101(1/6):45-58. doi: 10.1080/00102209408951865 [34] FRANDSEN F, DAM-JOHANSEN K, RASMUSSEN P. Trace elements from combustion and gasification of coal-An equilibrium approach[J]. Prog Energ Combust Sci, 1994, 20(2):115-138. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0360128594900078 [35] 张小锋, 姚强.吸附剂与铅反应的热力学平衡分析[J].工程热物理学报, 2006, 27(6):1054-1056. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCRB200606049.htmZHANG Xiao-Feng, YAO Qiang. Thermodynamic equilibrium analysis for reaction between sorbents and lead[J]. J Eng Therm, 2006, 27(6):1054-1056. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCRB200606049.htm [36] YAN R. Possible interactions between As, Se and Hg during coal combustion[J]. Combust Flame, 2000, 120. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236101001053 [37] LI Q, MENG A, JIA J, ZHANG Y. Investigation of heavy metal partitioning influenced by flue gas moisture and chlorine content during waste incineration[J]. J Environ Sci, 2010, 22(5):760-768. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1001074209601741 [38] JIAO F, ZHANG L, YAMADA N, SATO A, NINOMIYA Y. Effect of HCl, SO2 and H2O on the condensation of heavy metal vapors in flue gas cooling section[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2013, 105:181-187. [39] CONTRERAS M L, AROSTEGUI J M, ARMESTO L. Arsenic interactions during co-combustion processes based on thermodynamic equilibrium calculations[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(3):539-546. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236108003918 [40] SEAMES W S, WENDT J O L. Regimes of association of arsenic and selenium during pulverized coal combustion[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2007, 31(2):2839-2846. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1540748906003294 [41] LUO Y, GIAMMAR D E, HUHMANN B L, CATALANO J G. Speciation of selenium, arsenic, and zinc in class c fly ash[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(7):2980-2987. doi: 10.1021/ef2005496 [42] YANG Y, HU H, XIE K, HUANG Y, LIU H, LI X, YAO H, NARUSE I. Insight of arsenic transformation behavior during high-arsenic coal combustion[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2019, 37(4):4443-4450. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1540748918304826 [43] GONG H, HUANG Y, HU H, FU B, MA T, LI S, XIE K, LUO G, YAO H. Insight of particulate arsenic removal from coal-fired power plants[J]. Fuel, 2019, 257. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236119313729 [44] SHEN F, LIU J, ZHANG Z, YANG Y. Temporal measurements and kinetics of selenium release during coal combustion and gasification in a fluidized bed[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2016, 310:40-47. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389416301571 [45] SHAH P, STREZOV V, PRINCE K, NELSON P F. Speciation of As, Cr, Se and Hg under coal fired power station conditions[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(10/11):1859-1869. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236107005194 [46] FU B, HOWER J C, DAI S, MARDON S M, LIU G. Determination of chemical speciation of arsenic and selenium in high-as coal combustion ash by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy:Examples from a Kentucky stoker ash[J]. ACS Omega, 2018, 3(12):17637-17645. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b02929 [47] MA T, HUANG Y, DENG S, FU B, LUO G, WANG J, HU H, YUAN C, YAO H. The relationship between selenium retention and fine particles removal during coal combustion[J]. Fuel, 2020, 265. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236119322136 [48] HUANG Y, GONG H, HU H, FU B, YUAN B, LI S, LUO G, YAO H. Migration and emission behavior of arsenic and selenium in a circulating fluidized bed power plant burning arsenic/selenium-enriched coal[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 127920. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045653520321159 [49] HUANG Y, HU H, GONG H, XING H, YUAN B, FU B, LI A, YAO H. Mechanism study of selenium retention by iron minerals during coal combustion[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2020. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1540748920305903 [50] 麻银娟.煤中挥发性微量元素Hg、As、Pb燃烧固化的热力学模拟与实验研究[D].焦作: 河南理工大学, 2011.MA Yin-juan. Thermodynamics simulation and experiment study of volatile trace elements in coal during combustion[D]. Jiaozuo: Institutes of Technology of Henan, 2011. [51] 王丽.超低排放机组中汞、砷和硒等重金属的迁移特性研究[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.WANG Li. Study on the partitioning characteristics of Hg, As, Se and other hazardous elements in ultra low emission coal fired power plants[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. [52] SENIOR C, OTTEN B V, WENDT J O L, SAROFIM A. Modeling the behavior of selenium in Pulverized-Coal Combustion systems[J]. Combust Flame, 2010, 157(11):2095-2105. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010218010001288 [53] 郭欣.煤燃烧过程中汞, 砷, 硒的排放与控制研究[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2005.GUO Xin. Experimental and mechanism study on the mercury, arsenic and selenium transformation and emission control during coal combustion[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2005. [54] ZHAO S, DUAN Y, LI Y, LIU M, LU J, DING Y, GU X, TAO J, DU M. Emission characteristic and transformation mechanism of hazardous trace elements in a coal-fired power plant[J]. Fuel, 2018, 214:597-606. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236117312012 [55] YI H, HAO J, DUAN L, TANG X, NING P, LI X. Fine particle and trace element emissions from an anthracite coal-fired power plant equipped with a bag-house in China[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(10/11):2050-2057. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236107004383 [56] ZHOU C, LIU G, FANG T, WU D, LAM P K S. Partitioning and transformation behavior of toxic elements during circulated fluidized bed combustion of coal gangue[J]. Fuel, 2014, 135:1-8. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236114006000 [57] SANDELIN K, BACKMAN R. Trace elements in two pulverized coal-fired power stations[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2001, 35(5):826-834. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11351523 [58] NALBANDIAN H. Trace element emissions from coal[R]. 2012. [59] RATAFIA-BROWN J A. Overview of trace element partitioning in flames and furnaces of utility coal-fired boilers[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1994, 39(1/3):139-157. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0378382094901775 [60] CÓRDOBA P, OCHOA-GONZALEZ R, FONT O, IZQUIERDO M, QUEROL X, LEIVA C, LÓPEZ-ANTÓN M A, DÍAZ-SOMOANO M, ROSA MARTINEZ-TARAZONA M, FERNANDEZ C, TOMÁS A. Partitioning of trace inorganic elements in a coal-fired power plant equipped with a wet flue gas desulphurisation system[J]. Fuel, 2012, 92(1):145-157. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236111004224 [61] MEIJ R, TE WINKEL H. The emissions of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from modern coal-fired power stations[J]. Atmos Environ, 2007, 41(40):9262-9272. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1352231007003937 [62] 邓双, 张凡, 刘宇, 石应杰, 王红梅, 张辰, 王相凤, 曹晴.燃煤电厂铅的迁移转化研究[J].中国环境科学, 2013, 33:1199-1206. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=46850231DENG Shuang, ZHANG Fan, LIU Yu, SHI Ying-jie, WANG Hong-mei, ZHANG Chen, WANG Xiang-feng, CAO Qing. Lead emission and speciation of coal-6red power plants in China[J]. China Environ Sci, 2013, 33:1199-1206. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=46850231 [63] 孙喆.燃煤电站砷, 铅, 镉, 铬的迁移规律[D].华北电力大学, 2015.SUN Zhe. Transformation of arsenic, lead, cadmium and chromium in coal fire power plant[D]. North China Electric Power University, 2015. [64] BIN H, LIN Z, YANG Y, FEI L, CAI L, LINJUN Y. PM2.5 and SO3 collaborative removal in electrostatic precipitator[J]. Powder Technol, 2017, 318:484-490. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0032591017304667 [65] 盘思伟, 张凯, 张宇, 刘小伟.大型燃煤机组颗粒物与痕量元素的排放特性[J].热能动力工程, 2016, (31):84-89. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_rndlgc201610015.aspxPAN Si-wei, ZHANG Kai, ZHANG Yu, LIU Xiao-wei. The Particulate matter and trace elements emission characteristics of large coal-fired units[J]. J Eng Thermal Energy Tower, 2016, (31):84-89. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_rndlgc201610015.aspx [66] FU B, LIU G, SUN M, HOWER J C, MIAN M M, WU D, WANG R, HU G. Emission and transformation behavior of minerals and hazardous trace elements (HTEs) during coal combustion in a circulating fluidized bed boiler[J]. Environ Pollut, 2018, 242(Pt B):1950-1960. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0269749118325417 [67] ZHAO Y, ZHANG J, HUANG W, WANG Z, LI Y, SONG D, ZHAO F, ZHENG C. Arsenic emission during combustion of high arsenic coals from Southwestern Guizhou, China[J]. Energy Convers Manage, 2008, 49(4):615-624. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890407002683 [68] TIAN C, GUPTA R, ZHAO Y, ZHANG J. Release behaviors of arsenic in fine particles generated from a typical high-arsenic coal at a high temperature[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30(8):6201-6209. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00279 [69] MULHOLLAND J A, SAROFIM A F. Mechanisms of inorganic particle formation during suspension heating of simulated aqueous wastes[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1991, 25(2):268-274. doi: 10.1021/es00014a008 [70] 张小锋, 姚强, 宋蔷, 李水清.燃烧中铅元素排放特性的实验研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2007, (32):18-23. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb200732004ZHANG Xiao-feng, YAO Qiang, SONG Qiang, LI Shui-qing. Experimental study on the emission characteristics of lead during combustion[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2007, (32):18-23. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb200732004 [71] YAO H, NARUSE I. Behavior of lead compounds during municipal solid waste incineration[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2009, 32(2):2685-2691. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1540748908002599 [72] AKERS D, DOSPOY R. Role of coal cleaning in control of air toxics[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1994, 39(1/3):73-86. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0378382094901732 [73] 王文峰, 秦勇, 宋党育.煤中有害元素的洗选洁净潜势[J].燃料化学学报, 2003, 31(4):295-299. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract16814.shtmlWANG F, QIN Y, SONG D Y. Cleaning potential of hazardous elements during coal washing[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2003, 31(4):295-299. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract16814.shtml [74] FINKELMAN R B. Modes of occurrence of potentially hazardous elements in coal:Levels of confidence[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1994, 39(1/3):21-34. [75] 张振桴, 樊金串, 晋菊芳, 杨幼村, 宋丽君杨煌.煤中砷, 铅, 铍, 铬等元素的存在状态[J].燃料化学学报, 1992, 20(2):206-212. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=846794ZHANG Zhen-fu, FAN Jin-chuan, JIN Ju-fang, YANG You-cun, SONG Li-jun, YANG Huang. Mode of occurrence of Pb, As, Be, Cr in coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 1992, 20(2):206-212. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=846794 [76] 王明仕, 郑宝山, FINKELMAN R B, 胡军, 吴代赦, 李社红.煤中砷赋存状态与其脱洗率的关系[J].燃料化学学报, 2005, 33(2):253-256. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=15831752WANG Ming-shi, ZHENG Bao-shan, FINKELMAN R B, HU Jun, WU Dai-she, LI She-hong. Relationship between occurrence mode of arsenic in coal and its washing rate[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2005, 33(2):253-256. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=15831752 [77] 张博.煤中有害微量元素的洁净潜势分析[J].洁净煤技术, 2015, 21(4):20-24. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb200003002ZHANG Bo. Cleaning potentiality analysis of harmful microelements in coal[J]. Clean Coal Technol, 2015, 21(4):20-24. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb200003002 [78] 喻秋梅.煤燃烧中重金属对环境污染的研究[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 1996.YU Qiu-mei. Investigation of environmental pollution of heavy metals during coal combustion[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1996. [79] LIU H, WANG C, ZHANG Y, HUANG X, GUO Y, WANG J. Experimental and modeling study on the volatilization of arsenic during co-combustion of high arsenic lignite blends[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2016, 108:1336-1343. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S135943111631331X [80] JIAO F, NINOMIYA Y, ZHANG L, YAMADA N, SATO A, DONG Z. Effect of coal blending on the leaching characteristics of arsenic in fly ash from fluidized bed coal combustion[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2013, 106:769-775. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378382012004043 [81] 张成, 许豪, 姚洪, 谭鹏, 胡红云, 方庆艳, 陈刚.一种通过混合煤掺烧控制煤电厂污染物排放的方法: CN, 108459628A[P]. 2018-04-28.ZHANG C, XU H, YAO H, TAN P, HU H Y, FANG Q Y, CHEN G. A method to control pollutant emission of coal power plant by mixed coal combustion: CN, 108459628A[P]. 2018-04-28. [82] GULLETT B K, RAGHUNATHAN K. Reduction of coal-based metal emissions by furnace sorbent injection[J]. Energy Fuels, 1994, 8(5):1068-1076. https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?dirEntryId=129878 [83] 张军营, 任德贻, 钟秦, 徐复铭, 张衍国. CaO对煤中砷挥发性的抑制作用[J].燃料化学学报, 2000, 28(3):198-200. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RLHX200003001.htmZHANG Jun-ying, REN De-yi, ZHONG Qin, XU Fu-ming, ZHANG Yang-guo. Restraining of arsenic volatility using lime in coal combustion[J]. J Fuel Chemi Technol, 2000, 28(3):198-200. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RLHX200003001.htm [84] YAO H, NARUSE I. Using sorbents to control heavy metals and particulate matter emission during solid fuel combustion[J]. Particuology, 2009, 7(6):477-482. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1674200109000790 [85] WOUTERLOOD H, BOWLING K. Removal and recovery of arsenious oxide from flue gases[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1979, 13(1). doi: 10.1021/es60149a003 [86] LÓPEZ-ANTÓN M A, DÍAZ-SOMOANO M, FIERRO J L G, MARTÍNEZ-TARAZONA M R. Retention of arsenic and selenium compounds present in coal combustion and gasification flue gases using activated carbons[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2007, 88(8):799-805. [87] LÓPEZ-ANTÓN M A, DÍAZ-SOMOANO M, SPEARS D A, MARTÍNEZ-TARAZONA M R. Arsenic and selenium capture by fly ashes at low temperature[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2006, 40(12):3947-3951. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16830566 [88] LI S, GONG H, HU H, LIU H, HUANG Y, FU B, WANG L, YAO H. Re-using of coal-fired fly ash for arsenic vapors in-situ retention before SCR catalyst:Experiments and mechanisms[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 254:126700. [89] WANG J, ZHANG Y, WANG T, XU H, PAN W-P. Effect of modified fly ash injection on As, Se, and Pb emissions in coal-fired power plant[J]. Chem Eng J, 2020, 380. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1385894719319643 [90] 许豪, 张成, 袁昌乐, 余圣辉, 李权, 方庆艳, 陈刚.模拟烟气气氛下矿物元素组分对砷的吸附特性研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(7):876-883. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract29424.shtmlXU Hao, ZHANG Cheng, YUAN Chang-le, YU Sheng-hui, LI Quan, FANG Qing-yan, CHEN Gang. Study on arsenic adsorption characteristics by mineral elements in simulated flue gas atmosphere[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2019, 47(7):876-883. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract29424.shtml [91] 张月, 王春波, 刘慧敏, 孙喆, 李文瀚, 张永生, 潘伟平.金属氧化物吸附剂干法脱除气相As2O3实验研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(4):476-482. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18613.shtmlZHANG Yue, WANG Chun-bo, LIU Hui-min, SUN Zhe, LI Weng-han, ZHANG Yong-sheng, PAN Wei-ping. Removal of gas-phase As2O3 in dry process by metal oxide adsorbents[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(4):476-482. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18613.shtml [92] ZHANG Y, WANG C, LI W, LIU H, ZHANG Y, HACK P, PAN W. Removal of gas-phase As2O3 by metal oxide adsorbents:effects of experimental conditions and evaluation of adsorption mechanism[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(10):6578-6585. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236116303131 [93] CHEN D, HU H, XU Z, LIU H, CAO J, SHEN J, YAO H. Findings of proper temperatures for arsenic capture by CaO in the simulated flue gas with and without SO2[J]. Chem Eng J, 2015, 267:201-206. [94] HU H, CHEN D, LIU H, YANG Y, CAI H, SHEN J, YAO H. Adsorption and reaction mechanism of arsenic vapors over gamma-Al2O3 in the simulated flue gas containing acid gases[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 180:186-191. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045653517304897 [95] HUANG Y, YANG Y, HU H, XU M, LIU H, LI X, WANG X, YAO H. A deep insight into arsenic adsorption over γ-Al2O3 in the presence of SO2/NO[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2019, 37(3):2951-2957. [96] XING H, LIU H, ZHANG X, HUANG Y, LI H, HUANG B, HU H, YAO H. In-furnace control of arsenic vapor emissions using kaolinite during low-rank coal combustion:influence of gaseous sodium compounds[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2019, 53(20):12113-12120. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b03195 [97] GHOSH-DASTIDAR A, MAHULI S, AGNIHOTRI R, FAN L S. Selenium capture using sorbent powders:Mechanism of sorption by hydrated lime[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1996, 30(2):447-452. doi: 10.1021/es950129m [98] LI Y, TONG H, ZHUO Y, WANG S J, XU S C. Simultaneous removal of SO2 and trace SeO2 from flue gas:Effect of SO2 on selenium capture and kinetics study[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2006, 40(24):7919-7924. [99] FAN Y, ZHUO Y, LOU Y, ZHU Z, LI L. SeO2 adsorption on CaO surface:DFT study on the adsorption of a single SeO2 molecule[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 413:366-371. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169433217312771 [100] SCOTTO M V, UBEROI M, PETERSON T W, SHADMAN F, WENDT J O L. Metal capture by sorbents in combustion processes[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1994, 39(1/3):357-372. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0378382094901929 [101] YAO H, MKILAHA I S N, NARUSE I. Screening of sorbents and capture of lead and cadmium compounds during sewage sludge combustion[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(7/8):1001-1007. [102] WANG X, HUANG Y, PAN Z, WANG Y, LIU C. Theoretical investigation of lead vapor adsorption on kaolinite surfaces with DFT calculations[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2015, 295:43-54. [103] ZHAO S, DUAN Y, CHEN L, LI Y, YAO T, LIU S, LIU M, LU J. Study on emission of hazardous trace elements in a 350 MW coal-fired power plant. Part 2. arsenic, chromium, barium, manganese, lead[J]. Environ Pollut, 2017, 226:404-411. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0269749117303780 [104] CHENG C M, HACK P, CHU P, CHANG Y N, LIN T Y, KO C S, CHIANG P H, HE C C, LAI Y M, PAN W P. Partitioning of mercury, arsenic, selenium, boron, and chloride in a full-scale coal combustion process equipped with selective catalytic reduction, electrostatic precipitation, and flue gas desulfurization systems[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23(10):4805-4816. [105] CHANG L, YANG J, ZHAO Y, LIU H, ZHANG J, ZHENG C. Behavior and fate of As, Se, and Cd in an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant[J]. J Clean Prod, 2019, 209:722-730. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652618332979 [106] WANG J, ZHANG Y, LIU Z, GU Y, NORRIS P, XU H, PAN W-P. Coeffect of air pollution control devices on trace element emissions in an ultralow emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Energy Fuels, 2018, 33(1):248-256. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b03549 [107] ZHAO S, DUAN Y, WANG C, LIU M, LU J, TAN H, WANG X, WU L. Migration behavior of trace elements at a coal-fired power plant with different boiler loads[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 31(1):747-754. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02393 [108] 华伟, 孙和泰, 祁建民, 黄治军, 石志鹏, 段伦博.燃煤电厂超低排放机组重金属铅, 砷排放特性[J].热力发电, 2019, 48(10):65-70. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rlfd201910011HUA W, SUN H T, QI J M, HUANG Z J, SHI Z P, DUAN L B. Emission characteristics of Pb and As from an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Therm Power Gener, 2019, 48(10):65-70. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rlfd201910011 [109] MEIJ R, TE WINKEL H. The emissions of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from modern coal-fired power stations[J]. Atmos Environ, 2007, 41(40):9262-9272. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1352231007003937 [110] 张凯华, 张锴, 潘伟平. 300MW燃煤电站砷, 汞排放特征研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(7):839-844. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18219.shtmlZHANG Kai-hua, ZHANG Kai, PAN Wei-ping. Emission characteristics of arsenic and mercury from a 300 MW coal-fired power plant[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(7):839-844. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18219.shtml [111] BREKKE D W, BOTROS P E, ERICKSON T A, MUDD M J. Comparison of hazardous air pollutants from advanced and conventional power systems[Z]. 12th Annual International Pittsburgh Coal Conference, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, 1995. [112] 王春波, 史燕红, 吴华成, 张月, 康玺.电袋复合除尘器和湿法脱硫装置对电厂燃煤重金属排放协同控制[J].煤炭学报, 2016, 41(7):1833-1840. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201607031WANG Chun-bo, SHI Yan-hong, WU Hua-cheng, ZHANG Yue, KANG Xi. Research on collaborative control of heavy metals discharge from coal combustion by hybrid particulate collector and wet flue gas desulphurization[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2016, 41(7):1833-1840. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201607031 [113] 李兵, 王宏亮, 许月阳, 薛建明, 管一明.燃煤电厂湿法脱硫设施对烟气中微量元素的减排特性[J].煤炭学报, 2015, 40(10):2479-2483.LI Bing, WANG Hong-liang, XU Yue-yang, XUE Jian-ming, GUAN Yi-ming. l.Reduction of trace elements in flue gas by wet desulphurization facilities in coal-fired power plants[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(10):2479-2483. [114] WANG C, LIU X, LI D, SI J, ZHAO B, XU M. Measurement of particulate matter and trace elements from a coal-fired power plant with electrostatic precipitators equipped the low temperature economizer[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2015, 35(3):2793-2800. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1540748914003149 [115] JUAN A. GALLEGO-JUÁREZ, ENRIQUE RIERA-FRANCO DE SARABIA, GERMAN RODRÍGUEZ-CORRAL, THOMAS L. HOFFMANN, JUAN C. GÁLVEZ-MORALEDA, JESUS J. RODRÍGUEZ-MAROTO, FRANCISCO J. GÓMEZ-MORENO, ALBERTO BAHILLO-RUIZ, MANUEL MARTÍN-ESPIGARES, MIGUEL ACHA. Application of acoustic agglomeration to reduce fine particle emissions from coal combustion plants[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1999, 33, 21:3843-3849. [116] 赵爽, 骆仲泱, 王鹏, 徐飞, 岑可法.燃煤锅炉烟气中小颗粒的电凝并脱除[J].能源工程, 2006, (3):38-40, 43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NYGC200603015.htmZHAO Shuang, LUO Zhong-yang, WANG Peng, XU Fei, CEN Ke-fa. Removal of fine particles of flue gas by electric agglomeration[J]. Energy Eng, 2006, (3):38-40, 43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NYGC200603015.htm [117] 赵永椿, 张军营, 魏凤, 陈俊, 郑楚光.燃煤超细颗粒物团聚促进机制的实验研究[J].化工学报, 2007, 58:2876-2881. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb200711032ZHAO Yong-chun, ZHANG Jun-ying, WEI Feng, CHEN Jun, ZHENG Chu-guan. Experimental study on agglomeration of submicron particles from coal combustion[J]. J Chem Ind Eng (China), 2007, 58:2876-2881. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb200711032 -





 下载:
下载: