Microwave-assisted catalytic oxidative desulfurization of gasoil fuel using synthesized CuO-ZnO nanocomposites
-
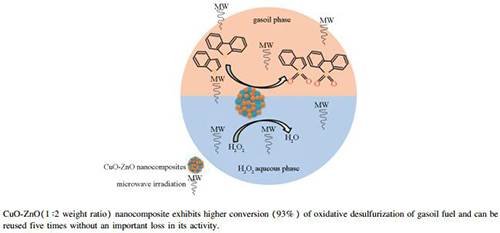
Abstract: Recently, organosulfur removal from liquid petroleum fuels is very significant aspect of environment protecting and fuel cell requests. Therefore, improved approaches to remove sulfur are still essential. In the present work, a simple catalytic oxidative desulfurization (CODS) system for Iraqi gasoil fraction has been successfully developed using CuO-ZnO nanocomposites as catalysts, and H2O2 as oxidant under microwave irradiation. The main reaction parameters influencing sulfur conversion including microwave power, irradiation time, catalyst dosage and H2O2 to gasoil volume ratio have been investigated. The CuO-ZnO nanocomposites was synthesized with different weight ratios and characterized by XRD, FE-SEM, AFM and BET surface area methods. The results reveal that, high sulfur conversion (93%) has been achieved under suitable conditions of microwave CODS as follows:microwave power of 540 W, irradiation time of 15 min, catalyst dosage of 8 g/L (0.4 g), and H2O2:gasoil volume ratio of 0.3. The catalyst reusability shows that the synthesized catalyst can be reused five times without an important loss in its activity.
-
Key words:
- microwave /
- oxidative desulfurization /
- nanocomposites /
- catalyst /
- gasoil
-
Table 1 General characteristics of light gasoil fraction
Property Value Sulfur w/% 1.01 SG @ 15.6℃ 0.826 Flash point t/℃ 68 Distillation t/℃ IBP 184 5% 216 10% 230 20% 250 30% 262 40% 272 50% 280 60% 286 70% 294 80% 302 90% 310 95% 316 FBP 330 Table 2 Surface area values for prepared catalyst samples
Catalyst sample BET specific surface area A/(cm2·g-1) vP /(cm3·g-1) dp /nm ZnO 16.93 0.0712 46.52 CuO 13.48 0.0481 67.1 CuO-ZnO (1:2) 26.52 0.0722 76.77 CuO-ZnO (1:1) 23.35 0.0653 75.2 CuO-ZnO (2:1) 19.44 0.0369 74.56 -
[1] ZHU W, LI H, JIANG X, YAN Y, LU J, HE L, XIA J. Commercially available molybdic compound-catalyzed ultra-deep desulfurization of fuels in ionic liquids[J]. Green Chem, 2008, 10(6):641-646. doi: 10.1039/b801185k [2] CHEN X, SONG D, ASUMANA C, YU G. Deep oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuels by Lewis acidic ionic liquids based on 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium metal chloride[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2012, 359:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2012.03.014 [3] SEEBERGER A, JESS A. Desulfurization of diesel oil by selective oxidation and extraction of sulfur compounds by ionic liquids-a contribution to a competitive process design[J]. Green Chem, 2010, 12:602-608. doi: 10.1039/b918724c [4] EβER J, WASSERSCHEID P, JESS A. Deep desulfurization of oil by extraction with ionic liquids[J]. Green Chem, 2004, 6:316-322. doi: 10.1039/B407028C [5] AGARWAL P, SHARMA D K. Comparative studies on the bio-desulfurization of crude oil with other desulfurization techniques and deep desulfurization through integrated processes[J]. Energy Fuels, 2010, 24(1):518-524. doi: 10.1021/ef900876j [6] LIU S, WANG B, CUI B, SUN L. Deep desulfurization of diesel oil oxidized by Fe (Ⅵ) systems[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(3):422-428. [7] ZHANG J, WANG A, LI X, MA X. Oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene and diesel over[Bmim]3PMo12O40[J]. J Catal, 2011, 279(2):269-275. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=85306610c42e2e43818aae01b2f5cdd9 [8] SUN B, YU X, WANG L, FENG L J, LI C H. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization by BiOBr-graphene composite[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2016, 44(9):1074-1081. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(16)30049-4 [9] ZENG A X, XIAO X, LI Y, CHEN J, WANG H. Deep desulfurization of liquid fuels with molecular oxygen through graphene photocatalytic oxidation[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2017, 209:98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.02.077 [10] CHICA A, CORMA A, DÓMINE M E. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization (ODS) of diesel fuel on a continuous fixed-bed reactor[J]. J Catal, 2006, 242(2):299-308. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8ef00c0f3475d50127d1773297df801f [11] GAO Y, GAO R, ZHANG G, ZHENG Y, ZHAO J. Oxidative desulfurization of model fuel in the presence of molecular oxygen over polyoxometalate based catalysts supported on carbon nanotubes[J]. Fuel, 2018, 224:261-270. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.03.034 [12] SARAVANAN R, KARTHIKEYAN S, GUPTA V K, SEKARAN G, NARAYANAN V, STEPHEN A. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO/CuO nanocomposite for the degradation of textile dye on visible light illumination[J]. Mater Sci Eng C, 2013, 33(1):91-98. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5d117220749789d199ef1551ca18d974 [13] ZHU L, LI H, LIU Z, XIA P, XIE Y, XIONG D. Synthesis of 0D/3D CuO/ZnO heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity synthesis of 0D/3D CuO/ZnO heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. J Phys Chem, 2018, 122(17):9513-9539. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a230cd9ef4187cc6e0d3a3d4625b9337 [14] CHEN C, LIU P, LU C. Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized ZnO powders by direct precipitation method[J]. Chem Eng J, 2008, 144(3):509-513. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6b77297cf5567985b00f05b26746d9e7 [15] PHIWDANG K, SUPHANKIJ S, MEKPRASART W. Synthesis of CuO nanoparticles by precipitation method using different precursors[J]. Energy Procedia, 2013, 34:740-745. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.808 [16] LI B, WANG Y. Superlattices and microstructures facile synthesis and photocatalytic activity of ZnO-CuO nanocomposite[J]. Superlattices Microstruct, 2010, 47(5):615-623. doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2010.02.005 [17] KHAN M F, ANSARI A H, HAMMEEDULLAH M, AHMAD E, HUSAIN F M, ZIA Q, BAIG U, ZAHEER M R, ALAM M M, KHAN A H, ALOTHMAN Z A, AHMAD I, ASHRAF G N, ALIEV G. Sol-gel synthesis of thorn-like ZnO nanoparticles endorsing mechanical stirring effect and their antimicrobial activities:Potential role as nano-antibiotics[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 27689. [18] KUMARI R, SAHAI A, GOSWAMI N. Effect of nitrogen doping on structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int, 2015, 25(4):300-309. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2015.08.003 [19] MOEZZI A, MCDONAGH A M, CORTIE M B. Zinc oxide particles:Synthesis, properties and applications[J]. Chem Eng J, 2012, 185/186:1-22. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/clkxjsxb-e200804003 [20] SATHISHKUMAR P, SWEENA R, WU J J, ANANDAN S. Synthesis of CuO-ZnO nanophotocatalyst for visible light assisted degradation of a textile dye in aqueous solution[J]. Chem Eng J, 2011, 171(1):136-140. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3a49ee19357c171968d5575f4a2675ee [21] MUTYALA S, FAIRBRIDGE C, PARÉ J R J, BÉLANGER J M R, NG S, HAWKINS R. Microwave applications to oil sands and petroleum:A review[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2010, 91(2):127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.09.009 [22] MIADONYE A, SNOW S, IRWIN D J G, KHAN M R, BRITTEN A J. Desulfurization of heavy crude oil by microwave irradiation[J]. 2009, 63: 455-465. [23] MESDOUR S, LEKBIR C, DOUMANDJI L, HAMADA B. Microwave-assisted extractive catalytic-oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel via a VO (acac)2/ionic liquid system with H2O2 and H2SO4 as oxidizing agents[J]. J Sulfur Chem, 2017, 38(4):421-439. doi: 10.1080/17415993.2017.1304550 [24] SHANG H, ZHANG H, DU W, LIU Z. Development of microwave assisted oxidative desulfurization of petroleum oils:A review[J]. J Ind Eng Chem, 2013, 19(5):1426-1432. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2013.01.015 -





 下载:
下载: