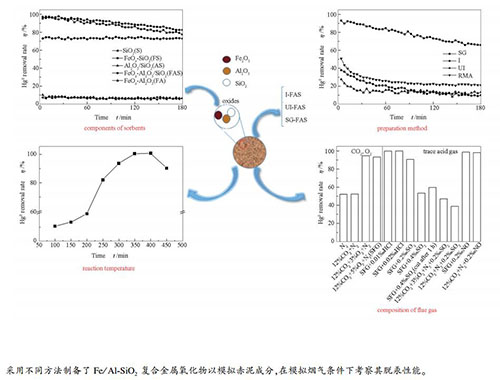
-
摘要: 采用不同方法制备了Fe/Al-SiO2复合金属氧化物以模拟赤泥成分,模拟烟气条件下考察其脱汞性能。结果表明,采用溶胶-凝胶法得到的复合金属氧化物在300-450 ℃具有优异的脱汞性能,其中,在350 ℃、3 h内平均脱汞率可达到94.8%。Fe2O3为Hg0的氧化提供了晶格氧和化学吸附氧;SiO2形成的硅溶胶则有利于活性组分Fe2O3的分散,增强了Hg0与活性位的接触。基本模拟烟气中存在微量HCl和NO时,Hg0脱除率接近100%;当烟气中存在0.2 mL/min、0.4 mL/min的SO2时,吸附剂的平均脱汞率分别降至90.7%、53.4%,这主要是由于SO2与Fe2O3反应生成Fe2(SO4)3,导致了Fe2O3的失活并抑制汞的脱除。
-
关键词:
- 吸附剂 /
- 元素汞 /
- 烟道气 /
- Fe/Al-SiO2
Abstract: The Fe/Al-SiO2 composite metal oxides were prepared by various methods to simulate the composition of red mud. A series of experiments were carried out to study the mercury removal performance from simulated flue gas. The results show that the composite metal oxide obtained by sol-gel method has an excellent mercury removal performance in a temperature range of 300-450 ℃. Among them, average mercury removal efficiency can reach 94.8% within 3 h at 350 ℃. Fe2O3 provides lattice oxygen and chemical adsorbed oxygen for the oxidation of Hg0, and SiO2 is conducive to the dispersion of the active component Fe2O3, which enhances the contact between Hg0 and the active sites. In the presence of trace HCl and NO in flue gas, the removal efficiency of Hg0 is close to 100%. However, the average mercury removal efficiency reduces to 90.7% and 53.4% respectively after adding 0.2 mL/min and 0.4 mL/min SO2, since the reaction of SO2 and Fe2O3 produces Fe2(SO4)3, leading to the deactivation of Fe2O3.-
Key words:
- sorbents /
- elemental mercury /
- flue gas /
- Fe/Al-SiO2
-
表 1 不同制备方法得到的样品比表面积和孔容
Table 1 Specific surface area and pore volume of samples prepared by different methods
Sample Specific surface area A /(m2·g-1) Pore volume v /(cm3·g-1) I-FAS 46 0.215 UI-FAS 32 0.078 SG-FS 403 0.672 SG-AS 370 0.861 SG-FAS 344 0.484 -
[1] UNEP. Global Mercury Assessment 2018 Review Draft: Sources, Emissions, Releases and Environmental Transport. Geneva: UNEP Chemicals Branch. 2018. [2] DB14/T1703, 燃煤电厂大气污染物排放标准[S].DB14/T1703, Standard emissions of atmospheric pollutants for coal-fired power plants[S]. [3] YANG J, YANG Q, SUN J, LIU Q C, ZHAO D, GAO W, LIU L. Effects of mercury oxidation on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst properties in NH3-SCR process[J]. Catal Commun, 2015, 59:78-82. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2014.09.049 [4] HSU C J, CHIOU H J, CHEN Y H, LIN K S, ROOD M J, HIS H C. Mercury adsorption and re-emission inhibition from actual WFGD wastewater using sulfur-containing activated carbon[J]. Environ Res, 2019, 168:319-328. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.10.017 [5] GRANITE E J, PENNLINE H W, HARGIS R A. Novel sorbents for mercury removal from flue gas[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2000, 39(4):1020-1029. doi: 10.1021/ie990758v [6] ZHAO S L, PUDASAINEE D, DUAN Y F, GUPTA R, LIU M. A review on mercury in coal combustion process:Content and occurrence forms in coal, transformation, sampling methods, emission and control technologies[J]. Prog Energy Combust, 2019, 73:26-64. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2019.02.001 [7] WANG P Y, SU S, XIANG J, CAO F, SUN L S, HU S, LEI S Y. Catalytic oxidation of Hg0 by CuO-MnO2-Fe2O3/γ-Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Chem Eng J, 2013, 225:68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.03.060 [8] 郝凯辉.改性赤泥基吸附剂用于燃煤烟气中汞的脱除[D].大连: 大连理工大学, 2017. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10141-1017823742.htmHAO Kai-hui. Removal of elemental mercury from flue gas over modified red mud based sorbents[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2017. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10141-1017823742.htm [9] CAO S T, MA H J, ZHANG Y, CHEN X F, ZHANG Y F. The phase transition in Bayer red mud from China in high caustic sodium aluminate solutions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 140:111-119. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.09.009 [10] KHAIRUL M A, ZANGANEH J, MOGHTADERI B. The composition, recycling and utilisation of Bayer red mud[J]. Resour Conserv Recycl, 2019, 141:483-498. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.11.006 [11] WANG X P, SUN T C, WU S C, CHEN C, KOU J, XU C Y. A novel utilization of Bayer red mud through co-reduction with a limonitic laterite ore to prepare ferronickel[J]. J Cleaner Prod, 2019, 216:33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.176 [12] SKODRAS G, DIAMANTOPOULOU I, SAKELLAROPOULOS G P. Role of activated carbon structural properties and surface chemistry in mercury adsorption[J]. Desalination, 2007, 210(1/3):281-286. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f781b1d179ff7b246f08f94ee79af493&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [13] KONG F H, QIU J R, LIU H, ZHAO R, AI Z H. Catalytic oxidation of gas-phase elemental mercury by nano-Fe2O3[J]. J Environ Sci (China), 2011, 23(4):699-704. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60438-X [14] ZHANG A C, ZHANG Z H, SHI J M, CHEN G Y, ZHOU C S, SUN L S. Effect of preparation methods on the performance of MnOx-TiO2 adsorbents for Hg0 removal and SO2 resistance[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(10):1258-1266. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(15)30038-4 [15] LIAO Y, XIONG S C, DANG H, XIAO X, YANG S J, WONG P K.The centralized control of elemental mercury emission from the flue gas by a magnetic rengenerable Fe-Ti-Mn spinel[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2015, 299:740-746. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.083 [16] LIU T, MAN C Y, GUO X, ZHENG C G. Experimental study on the mechanism of mercury removal with Fe2O3 in the presence of halogens:Role of HCl and HBr[J]. Fuel, 2016, 173:209-216. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.01.054 [17] KO K B, BYAN Y C, CHO M Y, NAMKUNG W, SHIN D N, KOH D J, KIM K T. Influence of HCl on oxidation of gaseous elemental mercury by dielectric barrier discharge process[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 71(9):1674-1682. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.01.015 [18] ZHANG A C, ZHENG W W, SONG J, HU S, LIU Z C, XIANG J. Cobalt manganese oxides modified titania catalysts for oxidation of elemental mercury at low flue gas temperature[J]. Chem Eng J, 2014, 236:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.060 [19] LIU W, XU H M, LIAO Y, QUAN Z W, LI S C, ZHAO S J, QU Z, YAN N Q. Recyclable CuS sorbent with large mercury adsorption capacity in the presence of SO2 from non-ferrous metal smelting flue gas[J]. Fuel, 2019, 235:847-854. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.08.062 [20] GUEDES A, VALENTIM B, PRIETO A C, SANZ A, FLORES D, NORONHA F. Characterization of fly ash from a power plant and surroundings by micro-Raman spectroscopy[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2008, 73(3/4):359-370. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=839549dab048935e88e06e3379ac5366 [21] DONG Y, REN X Y, QU R Y, LIU S J, ZHENG C H, GAO X. Designing SO2-resistant cerium-based catalyst by modifying with Fe2O3 for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Mol Catal, 2019, 462:10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.10.007 [22] XIANG J, WANG P Y, SU S, ZHANG L Q, CAO F, SUN Z J, XIAO X, SUN L S, H U S. Control of NO and Hg0 emissions by SCR catalysts from coal-fired boiler[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 135:168-173. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.12.044 [23] LIU J, GUO R T, GUAN Z Z, SUN X, PAN W G, LIU X Y, WANG Z Y, SHI X, QIN H, QIU Z Z, LIU S W. Simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 over Nb-modified MnTiOx catalyst[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(2):835-843. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.11.006 [24] KIM S C, NAHM S W, PARK Y K. Property and performance of red mud-based catalysts for the complete oxidation of volatile organic compounds[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2015, 300:104-113. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.059 [25] HE C, SHEN B X, LI F K. Effects of flue gas components on removal of elemental mercury over Ce-MnOx/Ti-PILCs[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2016, 304:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.044 [26] LI G L, SHEN B X, LI Y W, ZHAO B, WANG F M, HE C, WANG Y Y, ZHANG M. Removal of element mercury by medicine residue derived biochars in presence of various gas compositions[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2015, 298:162-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.05.031 [27] CHEN Y, GUO X, WU F, HUANG Y, YIN Z C. Mechanisms of mercury transformation over α-Fe2O3 (001) in the presence of HCl and/or H2S[J]. Fuel, 2018, 233:309-316. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.065 [28] JIANG S J, LIU X, LI H L, WANG J, YANG Z Q, PENG H Y, SHI K M. Synergistic effect of HCl and NO in elemental mercury catalytic oxidation over La2O3-TiO2 catalyst[J]. Fuel, 2018, 215:232-238 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.11.015 [29] ZHENG J M, SHAH K J, ZHOU J S, PAN S Y, CHIANG P C. Impact of HCl and O2 on removal of elemental mercury by heat-treated activated carbon:Integrated X-ray analysis[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2017, 167:11-17. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.06.017 [30] YANG Y J, LIU J, WANG Z, LIU F. Heterogeneous reaction kinetics of mercury oxidation by HCl over Fe2O3 surface[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2017, 159:266-271. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.01.035 -





 下载:
下载: