Preparation of La-Ce oxide-modified platinum-cobalt nano-bimetallic catalysts with perovskite-type composite oxides as precursors and their performance in CO oxidation
-
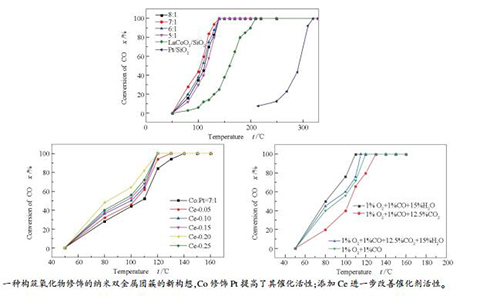
摘要: 利用钙钛矿型复合氧化物(PTO)可以将多种金属离子限域并均匀混合于钙钛矿晶格中的特点,提出了一种构筑氧化物修饰的纳米双金属催化剂团簇的新构想。以担载于大比表面积SiO2上的钙钛矿型复合氧化物La1-yCeyCo0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2作为前驱体,将La、Ce、Co和Pt多种金属离子均匀混合并限域于PTO晶粒中,还原后得到Pt-Co/La-Ce-O/SiO2催化剂;通过氮气吸附-脱附、XRD、H2-TPR和TEM等手段对Pt-Co/La-Ce-O/SiO2催化剂进行了表征,考察了其对CO氧化的催化性能,研究了构效关系。结果发现,La-Ce-O-Pt-Co构成了纳米团簇,担载于SiO2表面,形成了Pt-Co纳米双金属颗粒;Co修饰Pt提高了其催化活性,而添加Ce进一步改善了其催化性能。当Ce含量(y)为0.2时,催化剂La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2的活性最佳,在120℃下即可实现CO完全转化,且在含体积分数15% H2O及12.5% CO2的气氛中仍具有较好的催化性能。稳定性测试表明,所制得的Pt-Co/La-Ce-O/SiO2催化剂具有良好的稳定性和抗烧结性能。Abstract: A new scheme for constructing composite catalyst composed of oxide-modified bimetallic nanoparticles was proposed, where perovskite-type oxide (PTO) is utilized to confine multifold metal ions in the perovskite crystal lattice. With a perovskite-type oxide (PTO) of La1-yCeyCo0.87Pt0.13O3 loaded on large surface area SiO2 as the precursor, where the La, Ce, Co and Pt ions were uniformly mixed and confined in the PTO crystallites, a series of Pt-Co/La-Ce-O/SiO2 catalysts were prepared through reduction. The Pt-Co/La-Ce-O/SiO2 catalysts were characterized by nitrogen physisorption, XRD, H2-TPR and TEM; their catalytic performance in CO oxidation was investigated. The results indicate that La-Ce-O-Pt-Co clusters are constructed on the SiO2 surface, forming platinum-cobalt nano-bimetallic particles after reduction; the modification of Pt with Co can enhance the catalytic activity and the addition of Ce can further improve the catalytic performance in CO oxidation. The La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2 catalyst with y=0.2 (representing the Ce content) exhibits high activity in CO oxidation; over it, a complete conversion of CO can be achieved at 120℃. The La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2 catalyst performs well for CO oxidation even in the presence of 15% (volume ratio) H2O and 12.5% (volume ratio) CO2. Moreover, the oxide-modified platinum-cobalt nano-bimetallic catalysts display excellent stability with high resistance against sintering.
-
Key words:
- nano-bimetal catalyst /
- perovskite-type oxide /
- CO oxidation /
- oxide promoter /
- rare earth metal
-
图 2 不同Ce掺杂量(a)负载型催化剂前驱体La1-yCeyCo0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2和(b)非负载型催化剂La1-yCeyCo0.87Pt0.13O3, 及其(c)局部放大的XRD谱图
Figure 2 XRD patterns of (a) the supported La1-yCeyCo0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2 catalyst precursors; (b) and (c) unsupported La1-yCeyCo0.87Pt0.13O3 precursorsand
a: La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3; b: La0.85Ce0.15Co0.87Pt0.13O3; c: La0.9Ce0.1Co0.87Pt0.13O3; d: La0.95Ce0.05Co0.87Pt0.13O3; e: LaCoO3
图 4 600℃还原后的La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2的La、Ce、Co、Pt的STEM-EDS照片和线扫描
Figure 4 STEM-EDS mapping images of La, Ce, Co, Pt and line scanning results for the used La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2 catalyst at 600℃: surface scan area (a); distribution of the La (b), Ce (c), Co (d), and Pt (e) elements; distribution of a combination of four elements (f); sweep path (g); elemental distribution curves along the sweep path (h)
图 5 600℃还原后的((a), (b)) La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2, ((c), (d)) LaCo0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2及煅烧后未还原的((e), (f))La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2的TEM照片
Figure 5 TEM images of the catalysts after reduction at 600℃ ((a) and (b)) La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2, ((c) and (d)) LaCo0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2 and fresh ((e) and (f))La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2
表 1 SiO2和La1-yCeyCo0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2的物理性质
Table 1 Textural properties of SiO2 and the supported La1-yCeyCo0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2 catalyst precursors
Sample ABET/
(m2·g-1)dpore
/nmvpore/
(cm3·g-1)SiO2 368.5 9.3 0.87 Co:Pt=7:1 167.5 4.8 0.46 Ce-0.05 182.3 4.9 0.36 Ce-0.10 216.4 4.9 0.41 Ce-0.15 220.0 4.8 0.42 Ce-0.20 229.1 4.9 0.38 表 2 样品理论耗氢与实验耗氢对比
Table 2 Experimental and theoretical H2 consumption values of the supported La1-yCeyCo0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2 catalyst precursors in H2-TPR
Sample Experimental H2 consumptiona /(μmol·g-1) Theoretical H2 consumption /(μmol·g-1) low temp. high temp. Pt2+→Pt0 Co3+→Co2+ Co2+→Co0 LaCoO3 10.1 23.0 - 11.0 21.9 Ce-0.05 11.9 19.1 2.6 9.0 17.9 Ce-0.1 11.0 18.2 2.6 9.0 17.9 Ce-0.15 10.0 18.9 2.6 9.0 17.9 Ce-0.2 8.2 22.4 2.6 9.0 17.9 a:experimental H2 consumptions calculated using CuO 表 3 近些年制备的具有代表性的催化活性良好的催化剂, 用以与本文所制备的在常压下CO氧化反应中使用的催化剂作对比
Table 3 A comparison of current La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2 catalyst with the representative catalysts reported in recent years in their performance for CO oxidation
Catalyst Stability performance Ref. WHSV/
(mL·g-1·h-1)t/
℃time
t/h1%Pt-ZrO2 30000 90 40 [31] 5.0%Pt/γ-Al2O3 25000 160 112 [32] 1%Pt/Fe2O3 96000 25 2.2 [33] 3.32%Co/1.44%
Pt/TiO222000 45 2 [34] 1%Pt/Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 16800 60 50a [35] Leached 4%
Pt-0.3%Fe/CB30000 25 11 [36] 1%Pt-Co/La2O3-
CeO2/SiO2b24000 400 250 this
worka: the CO conversion was maintained at 80%; b: the catalyst was obtained by reducing La0.8Ce0.2Co0.87Pt0.13O3/SiO2 at 600℃ -
[1] SCHUBERT M M, HACKENBERG S, VEEN A C V, MUHLER M, PLZAK V, BEHM R J. CO oxidation over supported gold catalysts-"Inert" and "active" support materials and their role for the oxygen supply during reaction[J]. J Catal, 2001, 197(1):113-122. doi: 10.1006/jcat.2000.3069 [2] EINAGA H, NASU Y, ODA M, SAITO H. Catalytic performances of perovskite oxides for CO oxidation under microwave irradiation[J]. Chem Eng J, 2016, 283:97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.07.051 [3] NURIA L, NØRSKOV J K. Catalytic CO oxidation by a gold nanoparticle:A density functional study[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2002, 124(38):11262-11263. doi: 10.1021/ja026998a [4] IMBIHL R, COX M P, ERTL G, MÜLLER H, BRENIG W. Kinetic oscillations in the catalytic CO oxidation on Pt(100):Theory[J]. J Chem Phys, 1987, 87(1):742-749. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.21.2381 [5] CAIXIA X, JIXIN S, XIAOHONG X, PENGPENG L, HONGJUAN Z, FANG T, YI D. Low temperature CO oxidation over unsupported nanoporous gold[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129(1):42-43. doi: 10.1021/ja0675503 [6] KUNG H H, KUNG M C, COSTELLO C K. Supported Au catalysts for low temperature CO oxidation[J]. J Catal, 2003, 216(1/2):425-432. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_219cebef5929c1aa6cc35d6a2921a6d8 [7] BOTAO Q, AIQIN W, XIAOFENG Y, ALLARD L F, ZHENG J, YITAO C, JINGYUE L, JUN L, TAO Z. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx[J]. Nat Chem, 2011, 3(8):634-641. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1095 [8] HENDRIKSEN B L M, FRENKEN J W M. CO oxidation on Pt(110):Scanning tunneling microscopy inside a high-pressure flow reactor[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 89(4):046101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.046101 [9] WANG C, LI B, LIN H, YUAN Y. Carbon nanotube-supported Pt-Co bimetallic catalysts for preferential oxidation of CO in a H2-rich stream with CO2 and H2O vapor[J]. J Power Sources, 2012, 202:200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.11.044 [10] XU H, FU Q, GUO X, BAO X. Architecture of Pt-Co bimetallic catalysts for catalytic CO oxidation[J]. ChemCatChem, 2012, 4(10):1645-1652. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201200255 [11] SNYTNIKOV P V, YUSENKO K V, KORENEV S V, SHUBIN Y V, SOBYANIN V A. Co-Pt bimetallic catalysts for the selective oxidation of carbon monoxide in hydrogen-containing mixtures[J]. Kinet Catal, 2007, 48(2):276-281. doi: 10.1134/S0023158407020127 [12] BERA P, GAYEN A, HEGDE M S, LALLA N P, ARENA F. Promoting effect of CeO2 in combustion synthesized Pt/CeO2 catalyst for CO oxidation[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2003, 107(25):6122-6130. doi: 10.1021/jp022132f [13] AVAKYAN L A, KOLPACHEVA N A, PARAMONOVA E V, SINGH J, HARTFELDER U, BOKHOVEN J A V, BUGAEV L A. Evolution of the atomic structure of ceria-supported platinum nanocatalysts:Formation of single layer platinum oxide and Pt-O-Ce and Pt-Ce linkages[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2016, 120(49):28057-28066. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b09824 [14] SURENDAR M, SAGAR T V, RAVEENDRA G, ASHWANI KUMAR M, LINGAIAH N, RAMA RAO K S, SAI PRASAD P S. Pt doped LaCoO3 perovskite:A precursor for a highly efficient catalyst for hydrogen production from glycerol[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(4):2285-2297. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.12.075 [15] ZHAO L, HAN T, WANG H, ZHANG L, LIU Y. Ni-Co alloy catalyst from LaNi1-xCoxO3 perovskite supported on zirconia for steam reforming of ethanol[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2016, 187:19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.01.007 [16] GONG D, LI S, GUO S, TANG H, WANG H, LIU Y. Lanthanum and cerium co-modified Ni/SiO2 catalyst for CO methanation from syngas[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 434:351-364. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.179 [17] SUN S, YANG L I, PANG G, FENG S. Surface properties of Mg doped LaCoO3 particles with large surface areas and their enhanced catalytic activity for CO oxidation[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2011, 401(1/2):199-203. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1571118299214e235b1ad528e2f66701 [18] LI S, TANG H, GONG D, MA Z, LIU Y. Loading Ni/La2O3 on SiO2 for CO methanation from syngas[J]. Catal Today, 2017, 297:298-307. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.06.014 [19] THOMMES M, KANEKO K, NEIMARK A V, OLIVIER J P, RODRIGUEZ-REINOSO F, ROUQUEROL J, SING K S W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report)[J]. Pure Appl Chem, 2015, 87(9/10):1051-1069. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=90760a340a671ebad24fef1d6782ecab&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] LEOFANTI G, PADOVAN M, TOZZOLA G, VENTURELLI B. Surface area and pore texture of catalysts[J]. Catal Today, 1998, 41(1):207-219. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5b77958bb4f3d40165a0ac0a0fc7ec0e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [21] SONG Z, SHI X, NING H, LIU G, ZHONG H, YUAN L. Loading clusters composed of nanoparticles on ZrO2 support via a perovskite-type oxide of La0.95Ce0.05Co0.7Cu0.3O3 for ethanol synthesis from syngas and its structure variation with reaction time[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 405:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.003 [22] BENJARA M, REDDY M, KATTA L, THRIMURTHULU G. Novel nanocrystalline Ce1-xLaxO2-δ(x=0.2) solid solutions:Structural characteristics and catalytic performance[J]. Chem Mater, 2010, 22(2):467-475. doi: 10.1021/cm100735n [23] JOB N, PEREIRA M F R, LAMBERT S, CABIAC A, DELAHAY G, COLOMER J F, MARIEN J, FIGUEIREDO J L, PIRARD J P. Highly dispersed platinum catalysts prepared by impregnation of texture-tailored carbon xerogels[J]. J Catal, 2006, 240(2):160-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2006.03.016 [24] JERMWONGRATANACHAI T, JACOBS G, MA W, SHAFER W D, GNANAMANI M K, PEI G, KITIYANAN B, DAVIS B H, KLETTLINGER J L S, YEN C H. Fischer-tropsch synthesis:Comparisons between Pt and Ag promoted Co/Al2O3 catalysts for reducibility, local atomic structure, catalytic activity, and oxidation-reduction (OR) cycles[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2013, 464(6):165-180. [25] FANG C, ZHONG H, WEI Y, WANG J, ZHANG S, ZHANG L, LIU Y. Highly dispersed Pt species with excellent stability and catalytic performance by reducing a perovskite-type oxide precursor for CO oxidation[J]. Trans Tianjin Univ, 2018, 24(6):547-554. doi: 10.1007/s12209-018-0175-1 [26] GONG D D, LI S S, GUO S X, TANG H G, WANG H, LIU Y. Lanthanum and cerium co-modified Ni/SiO2 catalyst for CO methanation from syngas[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 434:351-364. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.179 [27] WANG T, XING J Y, ZHU L, JIA A P, WANG Y J, LU J Q, LUO M F. CO oxidation over supported Pt/CrxFe2-xO3 catalysts and their good tolerance to CO2 and H2O[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2019, 245:314-324. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.054 [28] DENG Y, WANG T, ZHU L, JIA A P, LU J Q, LUO M F. Enhanced performance of CO oxidation over Pt/CuCrOx catalyst in the presence of CO2 and H2O[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 442:613-621. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.099 [29] WANG H F, KAVANAGH R, GUO Y L, GUO Y, LU G Z, HU P. Structural origin:Water deactivates metal oxides to CO oxidation and promotes low-temperature CO oxidation with metals[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2012, 51(27):6657-6661. doi: 10.1002/anie.201108981 [30] JIN Y, SUN G, XIONG F, DING L, HUANG W. Water-activated lattice oxygen in FeO(111) islands for low-temperature oxidation of CO at Pt-FeO interface[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2016, 120(18):9845-9851. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b02256 [31] SINGHANIA A, GUPTA S M. Nanocrystalline ZrO2 and Pt-doped ZrO2 catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation[J]. Beilstein J Nanotechnol, 2017, 8(1):264-271. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.8.29 [32] AVGOUROPOULOS G, IOANNIDES T, PAPADOPOULOU C, BATISTA J, HOCEVAR S, MATRALIS H K. A comparative study of Pt/γ-Al2O3, Au/α-Fe2O3 and CuO-CeO2 catalysts for the selective oxidation of carbon monoxide in excess hydrogen[J]. Catal Today, 2002, 75(1/4):157-167. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(02)00058-5 [33] LI S, LIU G, LIAN H, JIA M, ZHAO G, JIANG D, ZHANG W. Low-temperature CO oxidation over supported Pt catalysts prepared by colloid-deposition method[J]. Catal Commun, 2008, 9(6):1045-1049. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2007.10.016 [34] EPLING W S, CHEEKATAMARLA P K, LANE A M. Reaction and surface characterization studies of titania-supported Co, Pt and Co/Pt catalysts for the selective oxidation of CO in H2 -containing streams[J]. Chem Eng J, 2003, 93(1):61-68. doi: 10.1016/S1385-8947(02)00109-2 [35] ROH H S, POTDAR H S, JUN K W, HAN S Y, KIM J W. Low temperature selective CO oxidation in excess of H2 over Pt/Ce-ZrO2 catalysts[J]. Catal Lett, 2004, 93(3):203-207. doi: 10.1023/b:catl.0000017077.38760.1f [36] XU H, FU Q, YAO Y, BAO X. Highly active Pt-Fe bicomponent catalysts for CO oxidation in the presence and absence of H2[J]. Energy Environ Sci, 2012, 5(4):6313-6320. doi: 10.1039/C1EE02393D -





 下载:
下载: