Hydrothermal dewatering of lignite to improve the slurry-ability, rheology, and stability of coal-water slurry
-
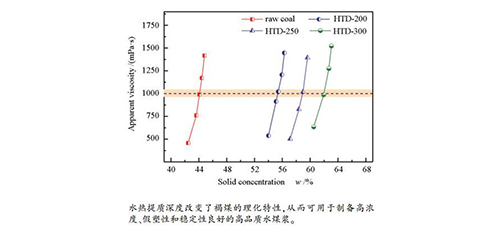
摘要: 采用水热法对小龙潭褐煤进行提质处理,从煤质特性、含氧基团、表面亲水性和粒度分布等因素,探究了水热提质对褐煤水煤浆成浆浓度、流变特性以及稳定性的影响。结果表明,水热提质脱除了褐煤中的水分,氧含量降低,煤阶升高。水热提质脱除了褐煤中含氧基团,煤水表面接触角增大,褐煤表面亲水性得到改善。小龙潭褐煤颗粒粒度呈现双峰分布,水热提质后褐煤颗粒粒径减小且趋于规则。水热提质改善了水煤浆的成浆性能,成浆浓度由提质前的44.09%,最高可提升到61.94%。在相近的表观黏度下,水热提质后水煤浆的稠度系数K减小,流变指数n增大,水热提质在降低浆体黏度的同时,仍保持假塑性流体特征。水热提质降低水煤浆的析水率,延缓了浆体出现硬沉淀的时间,改善浆体的稳定性。水热提质从理化特性对褐煤进行深度改性,从而获得高浓度,假塑性以及稳定性良好的符合工业应用的水煤浆。Abstract: Xiaolongtan lignite was upgraded by hydrothermal dewatering (HTD). The main factors affecting slurry-ability of the lignite including coal property, oxygen functional groups, surface hydrophilicity, and particle size distribution were analyzed. The effect of HTD on solid concentration, rheology, and stability of the upgraded coal was also investigated. The results show that a substantial amount of moisture was removed, oxygen content decreased, and the coal rank was enhanced by HTD upgrading. The contact angle between coal and water increased after removal of oxygen functional groups by HTD, thereby improving surface property of the upgraded lignite. A typical bimodal distribution of the lignite particle size was observed. The mean particle diameter of lignite decreased and the lignite particles became more regular after HTD. HTD upgrading significantly improved slurry-ability of the lignite. The solid concentration of raw coal was 44.09%, while that of the upgraded coal after HTD increased to 61.94%. The consistency coefficient K decreased, while the rheological index n increased for the CWS prepared from the upgraded coals. HTD upgrading decreased the apparent viscosity, and maintained the shear-thinning behavior of pseudo-plastic fluid. Moreover, as the water separation ratio decreased and formation of hard sedimentation was delayed, stability of the CWS was enhanced after HTD upgrading. Overall, the physico-chemical properties of Xiaolongtan lignite were significantly modified after HTD, thus a high-quality slurry fuel with high solid concentration, superior pseudo-plastic behavior, and good stability could be achieved.
-
Key words:
- hydrothermal dewatering /
- lignite /
- coal-water slurry /
- slurry-ability /
- rheology
-
表 1 原煤和水热提质煤的煤质分析
Table 1 Coal property analyses of raw coal and hydrothermally dewatered coals
Sample Proximate analysis wad/% Qb, ad
/(MJ·kg-1)Ultimate analysis wd/% O/C
atomic ratioM A V FC C H N O St Raw coal 16.44 12.12 39.09 32.35 18.15 56.00 3.64 1.49 22.05 2.32 29.5 HTD-200 11.26 13.70 38.24 36.80 20.59 59.05 3.76 1.71 17.76 2.28 22.6 HTD-250 9.30 14.60 36.48 39.62 21.98 60.83 3.84 1.78 15.19 2.26 18.7 HTD-300 6.21 15.65 34.83 43.31 23.28 63.96 4.14 1.86 11.14 2.21 13.1 表 2 原煤与水热提质煤的官能团相对百分含量
Table 2 Relative contents of different functional groups in raw and upgraded coals
Sample Content w/% C-C/C-H C-O C=O O=C- O 284.8 eV 286.1 eV 287.5 eV 289.0 eV Raw coal 64.52 25.26 6.37 3.85 HTD-200 67.88 22.37 6.29 3.26 HTD-250 71.30 20.84 5.61 2.25 HTD-300 76.95 16.53 4.64 1.88 表 3 原煤及水热提质煤的粒径参数
Table 3 Parameters of particle diameter in raw and hydrothermally dewatered coals
Sample Parameters of particle diameter /μm Dmean D10 D50 D90 Raw coal 50.57 5.28 38.25 116.8 HTD-200 39.84 4.07 27.61 95.82 HTD-250 33.20 3.68 23.00 78.54 HTD-300 30.07 3.42 20.93 68.90 表 4 水热提质前后褐煤的定黏浓度
Table 4 Fixed-viscosity concentration of coal water slurry before and after HTD upgrading
Sample Raw coal HTD-200 HTD-250 HTD-300 Fixed-viscosity
concentration/%44.09 55.42 58.96 61.94 表 5 水热提质前后褐煤水煤浆的流变特性参数
Table 5 Parameters of rheological property for coal water slurry before and after HTD upgrading
Sample ηc/(mPa·s) K/(Pa·s) n R2 Raw coal 990.5 7.05 0.568 0.999 HTD-200 1022.0 4.25 0.675 0.993 HTD-250 1019.0 3.80 0.716 0.987 HTD-300 987.1 2.59 0.803 0.994 -
[1] 白向飞.中国褐煤及低阶烟煤利用与提质技术开发[J].煤质技术, 2010, (6):9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7677.2010.06.003BAI Xiang-fei. Discussion on utilization and development of improving quality technology of lignite and low rank bituminous coal in China[J]. Coal Qual Technol, 2010, (6):9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7677.2010.06.003 [2] WILLSON W G, WALSH D A N, IRWINC W. Overview of low-rank coal (LRC) drying[J]. Coal Prep, 1997, 18(1/2):1-15. doi: 10.1080/07349349708905135 [3] 虞育杰, 刘建忠, 王传成, 胡亚轩, 周俊虎, 岑可法.低阶煤脱水提质技术发展现状[J].热力发电, 2011, 40(9):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2011.09.001YU Yu-jie, LIU Jian-zhong, WANG Chuan-cheng, HU Ya-xuan, ZHOU Jun-hu, CEN Ke-fa. Status quo of development in dewatering for upgrading low rank coal[J]. Therm Power Gener, 2011, 40(9):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2011.09.001 [4] 张大洲, 卢文新, 陈风敬, 夏吴, 左静, 王志刚, 商宽祥.褐煤干燥水分回收利用及其研究进展[J].化工进展, 2016, 35(2):472-478. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgjz201602021ZHANG Da-zhou, LU Wen-xin, CHEN Feng-jing, XIA Wu, ZUO Jing, WANG Zhi-gang, SHANG Kuan-xiang. Recent developments in recovery and utilization of water and heat from lignite dewatering[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog, 2016, 35(2):472-478. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgjz201602021 [5] YU J, TAHMASEBI A, HAN Y, YIN F, LI X. A review on water in low rank coals:The existence, interaction with coal structure and effects on coal utilization[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2013, 106:9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2012.09.051 [6] 王传成, 刘建忠, 虞育杰, 罗炉林, 程军, 周俊虎, 岑可法.内蒙古褐煤的成浆特性[J].中国电机工程学报, 2010, 30(S1):85-90. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2507859WANG Chuan-cheng, LIU Jian-zhong, YU Yu-jie, LUO Lu-lin, CHENG Jun, ZHOU Jun-hu, CEN Ke-fa. Slurryability of coal water slurry prepared by Inner Mongolia brown coal[J]. Proc CSEE, 2010, 30(S1):85-90. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2507859 [7] WU J, LIU J, YUAN S, ZHANG X, LIU Y, WANG Z, ZHOU J. Sulfur transformation during hydrothermal dewatering of low rank coal[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(10):6586-6592. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b01258 [8] YU Y, LIU J, CEN K. Properties of coal water slurry prepared with the solid and liquid products of hydrothermal dewatering of brown coal[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2014, 53(11):4511-4517. doi: 10.1021/ie5000592 [9] MORIMOTO M, NAKAGAWA H, MIURA K. Low rank coal upgrading in a flow of hot water[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23(9):4533-4539. doi: 10.1021/ef9004412 [10] NONAKA M, HIRAJIMA T, SASAKI K. Upgrading of low rank coal and woody biomass mixture by hydrothermal treatment[J]. Fuel, 2011, 90(8):2578-2584. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.03.028 [11] LIU J, WU J, ZHU J, WANG Z, ZHOU J, CEN K. Removal of oxygen functional groups in lignite by hydrothermal dewatering:An experimental and DFT study[J]. Fuel, 2016, 178:85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.03.045 [12] UMAR D F, SANTOSO B, USUI H. The effect of upgrading processes on combustion characteristics of berau coal[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(6):3385-3387. doi: 10.1021/ef070061j [13] LIU M, LI J, DUAN Y. Effects of solvent thermal treatment on the functional groups transformation and pyrolysis kinetics of Indonesian lignite[J]. Energy Convers Manage, 2015, 103:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2015.06.047 [14] 葛立超, 张彦威, 应芝, 王智化, 周俊虎, 岑可法.水热处理对我国典型褐煤气化特性的影响[J].中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(32):14-20. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb201332018GE Li-chao, ZHANG Yan-wei, YING Zhi, WANG Zhi-hua, ZHOU Jun-hu, CEN Ke-fa. Influence of the hydrothermal dewatering on the gasification characteristics of typical Chinese lignite[J]. Proc CSEE, 2013, 33(32):14-20. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb201332018 [15] GE L, ZHANG Y, XU C, WANG Z, ZHOU J, CEN K. Influence of the hydrothermal dewatering on the combustion characteristics of Chinese low-rank coals[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2015, 90:174-181. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.07.015 [16] 宋成建, 曲建林, 杨志远, 汪广恒, 杨伏生, 周安宁.分散剂与神府煤成浆性的匹配规律[J].化工学报, 2016, 67(9):3965-3971. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201609055SONG Cheng-jian, QU Jian-lin, YANG Zhi-yuan, WANG Guang-heng, YANG Fu-sheng, ZHOU An-ning. Matching rules between dispersants and Shenfu coal slurryability[J]. J Chem Ind Eng, 2016, 67(9):3965-3971. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201609055 [17] 尉迟唯, 李保庆, 李文, 陈皓侃.中国不同变质程度煤制备水煤浆性质研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2005, 33(2):155-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2005.02.006YU Chi-wei, LI Bao-qing, LI Wen, CHEN Hao-kan. Study on the properties of coal water slurry prepared with different coal ranks[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2005, 33(2):155-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2005.02.006 [18] GENG W, KUMABE Y, NAKAJIMA T, TAKANASHI H, OHKI A. Analysis of hydrothermally-treated and weathered coals by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(4):644-649. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.09.025 [19] KADIOGLU Y, VARAMAZ M. The effect of moisture content and air-drying on spontaneous combustion characteristics of two Turkish lignites[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(13):1685-1693. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00402-7 [20] 刘猛, 陈良勇, 段钰锋.煤浆浓度和颗粒分布对煤浆黏度预测的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2009, 37(3):266-270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2009.03.003LIU Meng, CHEN Liang-yong, DUAN Yu-feng. Influence of concentration and particle size distribution on viscosity prediction of coal slurry[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2009, 37(3):266-270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2009.03.003 [21] 高志芳, 朱书全, 吴晓华.褐煤提质改性对水煤浆特性的影响[J].煤炭科学技术, 2010, 38(9):112-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtkxjs201009030GAO Zhi-fang, ZHU Shu-quan, WU Xiao-hua. Lignite upgrading modification affected to features of coal water mixture[J]. Coal Sci Technol, 2010, 38(9):112-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtkxjs201009030 [22] 刘煜, 李伟东, 刘海峰.污泥干燥预处理后与神府煤共成浆性的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2010, 38(6):656-659. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2010.06.004LIU Yu, LI Wei-dong, LIU Hai-feng. Co-slurry ability of dried sewage sludge and Shenfu coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2010, 38(6):656-659. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2010.06.004 [23] 刘明强, 刘建忠, 王睿坤, 周俊虎, 岑可法.热解温度对褐煤半焦成浆特性影响的实验研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(8):36-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb201308006LIU Ming-qiang, LIU Jian-zhong, WANG Rui-kun, ZHOU Jun-hu, CEN Ke-fa. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on slurry ability of lignite semi-coke[J]. Proc CSEE, 2013, 33(8):36-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb201308006 [24] ROH N S, SHIN D H, KIM D C, KIM J D. Rheological behavior of coal-water mixtures.1. Effects of coal type, loading and particle-size[J]. Fuel, 1995, 74(8):1220-1225. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(95)00041-3 [25] WU J H, LIU J Z, YU Y J, WANG R K, ZHOU J H, CEN K F. Improving slurryability, rheology, and stability of slurry fuel from blending petroleum coke with lignite[J]. Pet Sci, 2015, 12(1):157-169. doi: 10.1007/s12182-014-0008-3 [26] 刘猛, 段钰锋, 李华锋, 马修元.改性污泥与石油焦的共成浆性及流变性分析[J].中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32(35):59-65. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb201235009LIU Meng, DUAN Yu-feng, LI Hua-feng, MA Xiu-yuan. Analysis on co-slurryability and rheology of modified sludge and petroleum coke[J]. Proc CSEE, 2012, 32(35):59-65. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb201235009 -





 下载:
下载: