Synthesis of mesoprous materials with Ce-Co/KIT-6 and its mercury removal performance
-
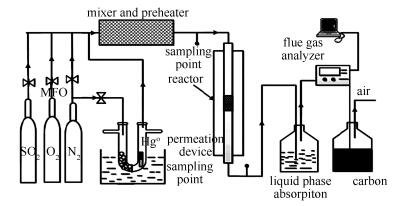
摘要: 以P123表面活性剂为模板,采用硬模板法制备了有序介孔材料KIT-6,以KIT-6为载体,Ce(NO3)2·6H2O和Co(NO3)2·6H2O为Ce和Co源,采用溶液浸渍法制备了负载型Ce-Co/KIT-6介孔材料。在模拟烟气条件下,利用固定床实验台架研究了Ce-Co/KIT-6材料对烟气中的单质汞(Hg0)的脱除性能。采用扫描电镜(SEM)、N2吸附-脱附(BET)、X射线衍射分析(XRD)、傅里叶红外光谱分析(FT-IR)、氢气程序升温还原(H2-TPR)以及热重分析(TGA)等方法对材料进行表征。结果表明,Ce和Co在KIT-6孔道内部高度分散,同时材料保持高度有序的孔道结构、比表面积高达495.2 m2/g,孔径4.6 nm。脱汞实验结果表明,Ce-Co/KIT-6对Hg0的氧化吸附去除效率很高,250 ℃下对Hg0的氧化吸附去除效率高达95%以上,在这个过程中,O2的存在明显促进了催化剂的脱汞能力。氧通过Ce-Co价态的变化进入金属结构中,再与汞发生反应是这个过程的主要机理。
-
关键词:
- Ce-Co/KIT-6 /
- KIT-6 /
- 单质汞 /
- 氧化吸附
Abstract: The oxidation activity of elemental mercury (Hg0) by transition metal modified KIT-6 was investigated using a simulated element mercury (Hg0) adsorption reactor. The physical and chemical propertied of the catalysts were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), N2 adsorption-desorption (BET), Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis, H2-Temperature programmed reduction (H2-TPR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The results show that Ce-Co/KIT-6 surface area and total pore volume of the catalysts decrease after the modification. However, the pore structure and distribution after modification have little variation. The mean pore size and BET surface area of mesoporous Ce-Co/KIT-6 are 4.6 nm and 495.2 m2/g, respectively. The Ce-Co/KIT-6 shows a high Hg0 adsorption efficiency without O2, the removal efficiency of Hg0 is about 50.67%; moreover, it has a high Hg0 removal efficiency of O2 above 95% for 250 ℃, the presence of O2 greatly contributes to mercury removal capacity of the catalyst. Oxygen enters the metal structure through changes in the valence state of Ce-Co and reacts with mercury, which may be the main mechanism of this process.-
Key words:
- Ce-Co/KIT-6 /
- KIT-6 /
- elemental mercury /
- oxidation and adsorption
-
表 1 催化剂的比表面积及孔容、孔径
Table 1 The specific area pore volume and pore diameter of the SCR catalysts

-
[1] LI P, FENG X B, QIU G L, SHANG L H, LIZG. Mercury pollution in Asia: A review of the contaminated sites[J]. J Hazrad Mater, 2009, 168(2/3): 591-601. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Zhonggen_Li/publication/24256386_Mercury_pollution_in_Asia_A_review_of_the_contaminated_sites/links/0a85e534161cb3cd12000000.pdf [2] PACYNA EG, PACYN JM, SUNDSETH K, MUNTHE J, KINDBOM K. Global emission of mercury to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in 2005 and projections to 2020[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2010, 44(20): 2487-2499. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.06.009 [3] ZHENG Liu-gen, LIU Gui-jian, Ql Cui-cui, CHEN Yi-wei, ZHANG Ying. Study on environment geochemistry of mercury in Chinese coals[J]. J Univer Sci Technol China, 2007, 37(8): 953-963. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJD200708021.htm [4] SLEMR F, SCHUSTER G, SEILER W. Distribution, speciation and budget of atmospheric mercury[J]. J Atmospheric Chem, 1985, 3(4): 407-434. doi: 10.1007/BF00053870 [5] QU Z, YAN N, LIU P, JIA J, YANG S. The role of iodine monochlorid, for the oxidation of elemental mercury[J]. J Hazardous Materials, 2010, 183(1/3): 132-137. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/45439057_The_role_of_iodine_monochloride_for_the_oxidation_of_elemental_mercury [6] HE C, SHEN B, CHEN J, CAI J. Adsorption and oxidation of elemental mercury over Ce-Mnx/Ti-PILCs[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2014, 48(14): 7891-7898. doi: 10.1021/es5007719 [7] ZHANG H R, WU H, LIU H, WANG M, YANG H. Performance and kinetics of mercury adsorption over Taixi activated coke[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(3): 1076-1083. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ201303042.htm [8] LI G, SHEN B, LI Y, ZHAO B, WANG F, HE C. Removal of element mercury by medicine residue derived biocharsin presence of various gas compositions[J]. J Hazardous Material, 2015, 298(15): 162-169. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389415004276 [9] SELVARAJ M, SINHAP K, LEE K, AHN I, PANDURANGAN A, LEE T G. Synthesis and characterization of Mn-MCM-41 and Zr-Mn-MCM-41[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2005, 78, 139-149. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2004.10.004 [10] O'SHEA V, ALVAREZ-GALVAN M C, FIERRO J L G, ARIAS P L. Influence of feed composition on the activity of Mn and PdMn/Al2O3 catalysts for combustion of formaldehyde/methanol[J]. Appl Catal B 2005, 57(3): 191-199. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2004.11.001 [11] XIE Xiao-wei, LI Yong, LIU Zhi-quan, MASATAKE H, SHEN Wen-jie. Low-temperature oxidation of CO catalysed by Co3O4 nanorods[J]. Nature, 2009, 458(7239): 746-749. doi: 10.1038/nature07877 [12] SCHUNK B S A, DEMUTH D G, SCHULZDOBRIK B, UNGER K K. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 78, 139. [13] KLEITZ F, CHOI S, RYOO R. Cubic Ia 3d large mesoporous silica: Synthesis and replication to platinum nanowires, carbannanorods and carbon nanotubes[J]. Korean J Chem Eng, 2009, 26(5): 2136-2137. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/13678168 [14] JERMY B R, KIM S Y, BINEESH K V, SELVARAJ M, PARK D W. Direct incorporation of vanadium into three-dimensional KIT-6:1. Optimization of synthesis conditions[J]. Korean J Chem Eng, 2009, 90: 55-63. doi: 10.1007/s11814-009-0199-2 [15] LAHA S C, RYOO R. Synthesis of thermally stable mesoporous cerium oxide with nanocrystalline frameworks using mesoporous silica templates[J]. Chem Soc, 2007, 129(21): 6698-6699. doi: 10.1021/ja070908q [16] LEE D, IHM S, LEE K. Mesostructure control using a titania-coated silica nanosphere framwork with extremely high thermal stability[J]. Korea J Chem Eng, 2009, 26(5): 1235-1240. doi: 10.1007/s11814-009-0199-2 [17] DING Z, LU G Q. Greenfeild. Role of the crystalltie phase of TiO2 in heterogeneous photocatalysis for phenol oxidation water[J]. Phys Chem B, 2000, 104: 4815-4821. doi: 10.1021/jp993819b [18] SONI K, RANA B S, SINHA A K, BHAUMIK A, NANDI M. 3-D ordered mesoporous KIT-6 support for effiective hydrodesulfurization catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ, 2009, 90: 55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.02.010 [19] YEE K K, REIMER N, LIU J, CHENG S Y, YIU S M. Effective mercury sorption by thiol-laced metal-organic frameworks: in strong acid and the vapor phase[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135(21): 7795-7798. doi: 10.1021/ja400212k [20] LEVI G, SENNECA O, CAUSÀ M, SALATINO P, LACOVIG P, LIZZIT S. Probing the chemical nature of surface oxides during coal char oxidation by high-resolution XPS[J]. Carbon, 2015, 90: 181-196. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.04.003 [21] ETTIREDDY P R, ETTIREDDY N, MAMEDOV S, BOOLCHAND P, SMIRNIOTIS P G. Surface characterization studies of TiO2 supported manganese oxide catalysts for low temperature SCR of NO with NH3[J]. Appl Catal B: Environmental, 2007, 76(1/2): 123-134. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092633730700152X [22] HAYKIRI-ACMA H, YAMAN S. Synergy in devolatilization characteristics of lignite and hazelnut shell during co-pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2007, 86(3): 373-380. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2006.07.005 [23] KAMATA H, UENOSI, NAITOT, YUKIMURA A. Mercury oxidation over the V2O5(WO3)/TiO2 commercial SCR catalyst[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2008, 47(21): 8136-8141. doi: 10.1021/ie800363g [24] YANG J, YANG Q, SUN J, LIU Q C, ZHAO D, GAO W, LIU L. Effects of mercury oxidation on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst properties in NH3-SCR process[J]. Catal Commun, 2015, 59: 78-82. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2014.09.049 [25] HONG H J, HAM S W, KIM M H, LEE S M, LEE J B. Characteristics of commercial selective catalytic reduction catalyst for the oxidation of gaseous elemental mercury with respect to reaction conditions[J]. Korean J Chem Eng, 2010, 27(4): 1117-1122. doi: 10.1007/s11814-010-0175-x [26] KONG F, QIU J, HAO L, RAN Z, ZENG H. Effect of NO/SO2 on elemental mercury adsorption by nano-Fe2O3[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2010, 30(35): 43-48. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC201035009.htm [27] LIU H, ZHANG H, YANG H. Photocatalytic removal of nitric oxide by multi-walled carbon nanotubes-supported TiO2[J]. Chin J Catal, 2014, 35(1): 66-77. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(12)60705-0 [28] HRDLICKA J A, SEAMES W S, MANN M D, MUGGLI D S, HORABIK C A. Mercury oxidation in flue gas using gold and palladium catalysts on fabric filters[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2008, 42(17): 6677-82. doi: 10.1021/es8001844 [29] CAO Y, CHENG C M, CHEN C W, LIU M, WANG C, PAN W P. Abatement of mercury emissions in the coal combustion process equipped with a fabric filter baghouse[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(15/16): 3322-3330. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236108002123 [30] HENDERSON MICHAEL A. An HREELS and TPD study of water on TiO2[J]. Surface Science, 1996, 355(1): 151-166. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0039602895013571 -





 下载:
下载: