Migration and transformation law of potassium in the combustion of biomass blended coal
-
摘要: 通过将稻秆和褐煤混燃,研究了燃烧温度以及生物质掺混比例对于混燃过程中K的释放、灰样中K的赋存形式以及矿物质变化的影响。研究表明,燃烧温度对于混合燃料中K的释放影响显著。在600-750℃时,随着温度升高,水溶性K和醋酸铵溶性K大量释放到气相,使得K的释放速率较快;而当温度在750-850℃时,水溶性K和醋酸铵溶性K开始大量地转化为其他形式的K而被固定在灰样中,使得K的释放速率变得缓慢;当温度高于850℃时,随着温度升高,盐酸溶性K的分解导致K释放速率重新增大。通过XRD分析发现,灰样中水溶性K主要以KCl的形式存在,K2SO4的生成同时受到原料中K的含量和S/Cl比值两个因素的共同影响,原料中K的含量越高,且S/Cl比值越大,越会促进K2SO4的生成。同时也发现生物质和煤混燃时存在协同作用,煤中Al、Si等元素会和生物质中的K反应生成碱性硅铝酸盐,从而导致更多K留在灰烬中。Abstract: The effects of combustion temperature and biomass blending ratio on the release of K, the occurrence form of K in the ash and the change of mineral matter were studied. It is found that combustion temperature has a significant effect on the release of K. At 600-750℃, with an increase in temperature, water-soluble K and NH4Ac-soluble K are released to the gas phase, which makes the release ratio of K fast; while at 750-850℃, water-soluble K and NH4Ac-soluble K begin to convert into other forms of K and are fixed in the ash sample, which makes the release rate of K slow; when the temperature is higher than 850℃, as the temperature increases, the decomposition of HCl-soluble K causes the release rate of K increase again. Through XRD analysis, it is found that the water-soluble K in ash mainly exists in the form of KCl. The production of K2SO4 is affected by both the K content in the raw material and the S/Cl ratio, the higher the content of K in raw materials, and the greater the ratio of S/Cl, the more it will promote the formation of K2SO4. At the same time, it is also found that there is a synergistic effect between biomass and coal combustion. The elements such as Al, Si in coal may react with K in biomass to generate alkaline aluminosilicate, resulting in more K remaining in the ash.
-
Key words:
- biomass /
- coal /
- alkali metal /
- combustion
-
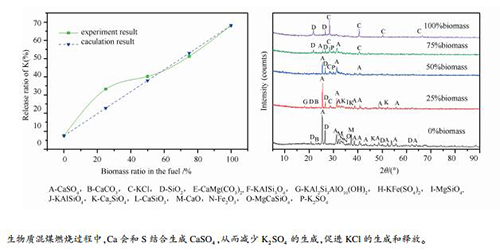
图 5 不同温度及生物质掺混比下灰样的XRD谱图
Figure 5 XRD patterns of ash at different temperatures and biomass blending ratios
(a): 25%biomass; (b): 800 ℃ A-CaSO4, B-CaCO3, C-KCl, D-SiO2, E-CaMg(CO3)2, F-KAlSi3O8, G-KAl2Si3AlO10(OH)2, H-KFe(SO4)2, I-MgSiO4, J-KAlSiO4, K-Ca2SiO4, L-CaSiO3, M-CaO, N-Fe2O3, O-MgCaSiO4, P-K2SO4
表 1 稻秆和褐煤的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of rice straw and lignite
Sample Ultimate analysis wad/% Proximate analysis wad/% C H O N S Cl M A V FC Straw 39.48 4.94 36.22 1.05 0.10 1.03 6.82 11.39 68.17 13.62 Lignite 46.56 3.72 17.90 1.38 1.46 0.05 13.90 15.08 39.53 31.49 表 2 稻秆和褐煤的灰分分析
Table 2 Ash composition of straw and lignite
Sample Content w/% K2O Na2O MgO CaO Fe2O3 SiO2 Al2O3 P2O5 Straw 29.44 2.93 2.13 2.54 0.34 43.58 4.11 1.58 Lignite 0.96 0.27 2.34 39.16 9.58 21.13 13.32 0.07 表 3 原料中K总含量及其赋存形式
Table 3 Total K content in raw materials and its occurrence form
Sample Total/(mg·kg-1) Water-soluble /% NH4Ac-soluble /% HCl-soluble /% Insoluble /% Straw 15966.52 86.52 4.90 2.31 6.27 Lignite 370.26 5.27 21.73 67.84 5.16 -
[1] ZHOU H, ZHANG H, LI L, ZHOU B. Ash deposit shedding during Co-combustion of coal and rice hull using a digital image technique in a pilot-scale furnace[J]. Energy Fuels, 2013, 27(11):7126-7137. doi: 10.1021/ef401814y [2] DE S, ASSADI M. Impact of cofiring biomass with coal in power plants-A techno-economic assessment[J]. Biomass Bioenergy, 2009, 33(2):283-293. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4baa2bc20721a81ee21b68c84ad2902e [3] NIU Y, TAN H, HUI S. Ash-related issues during biomass combustion:Alkali-induced slagging, silicate melt-induced slagging (ash fusion), agglomeration, corrosion, ash utilization, and related countermeasures[J]. Prog Energy Combust, 2016, 52:1-61. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2015.09.003 [4] 杨光.生物质燃烧过程中碱金属迁移研究[D].广州: 华南理工大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10561-1012452373.htmYANG Guang. Study on migration of alkali metals during biomass combustion[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10561-1012452373.htm [5] 叶家铭, 靳熹, 杨金鑫, 邓磊, 车得福.生物质热解和燃烧过程中钾的析出迁移特性研究[J].工程热物理学报, 2017, 38(9):2033-2037. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcrwlxb201709036YE Jia-ming, JIN Xi, YANG Jin-xin, DENG Lei, CHE De-fu. Study on the release and migration of potassium during biomass pyrolysis and combustion[J]. J Eng Thermophys, 2017, 38(9):2033-2037. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcrwlxb201709036 [6] NARAYAN V, JENSEN P A, HENRIKSEN U B, GLARBORG P, LIN W, NIELSEN R G. Defluidization in fluidized bed gasifiers using high-alkali content fuels[J]. Biomass Bioenergy, 2016, 91:160-174. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2016.05.009 [7] ROBINSON A L, JUNKER H, BAXTER L L. Pilot-scale investigation of the influence of coal-biomass cofiring on ash deposition[J]. Energy Fuels, 2002, 16(2):343-355. doi: 10.1021/ef010128h [8] XUE Z, ZHONG Z, ZHANG B, ZHANG J, XIE X. Potassium transfer characteristics during co-combustion of rice straw and coal[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2017, 124:1418-1424. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.06.116 [9] ABREU P, CASACA C, COSTA M. Ash deposition during the co-firing of bituminous coal with pine sawdust and olive stones in a laboratory furnace[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(12):4040-4048. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.04.012 [10] WU D, WANG Y, WANG Y, LI S, WEI X. Release of alkali metals during co-firing biomass and coal[J]. Renewable Energy, 2016, 96:91-97. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2016.04.047 [11] LIU Y, HE Y, WANG Z, XIA J, WAN K, WHIDDON R, CEN K. Characteristics of alkali species release from a burning coal/biomass blend[J]. Appl Energy, 2018, 215:523-531. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.02.015 [12] HÄRINEN V, HERNBERG R, AHO M. Demonstration of plasma excited atomic resonance line spectroscopy for on-line measurement of alkali metals in a 20kW bubbling fluidized bed[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(7):791-797. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5d8cd4e3c22371545175f723260490fd [13] JOHANSEN J M, JAKOBSEN J G, FRANDSEN F J, GLARBORG P. Release of K, Cl, and S during pyrolysis and combustion of high-chlorine biomass[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(11):4961-4971. doi: 10.1021/ef201098n [14] LIU Y, CHENG L, ZHAO Y, JI J, WANG Q, LUO Z, BAI Y. Transformation behavior of alkali metals in high-alkali coals[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2018, 169:288-294. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.09.013 [15] 刘颖祖.单颗粒煤及生物质燃烧过程中碱金属释放的激光测量及数值模拟[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10335-1019028599.htmLIU Ying-zu. Laser measurement and numerical simulation of alkali metal release during combustion of single particle coal and biomass[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10335-1019028599.htm [16] 谢兴运.生物质中碱金属的赋存形态及热释放的实验研究[D].北京: 华北电力大学, 2019. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10079-1019230461.htmXIE Xing-yun. Experimental study on the occurrence form and heat release of alkali metals in biomass[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2019. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10079-1019230461.htm [17] ZHANG J, HAN C L, YAN Z, LIU K L, XU Y Q, SHENG C D, PAN W P. The varying characterization of alkali metals (Na, K) from coal during the initial stage of coal combustion[J]. Energy Fuels, 2001, 15(4):786-793. doi: 10.1021/ef000140u [18] GUO D, WU S, LIU B, YIN X, YANG Q. Catalytic effects of NaOH and Na2CO3 additives on alkali lignin pyrolysis and gasification[J]. Appl Energy, 2012, 95:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.01.042 [19] DAYTON D C, BELLE-OUDRY D, NORDIN A. Effect of coal minerals on chlorine and alkali metals released during biomass/coal cofiring[J]. Energy Fuels, 1999, 13(6):1203-1211. doi: 10.1021/ef9900841 [20] ZHANG B, ZHONG Z, XUE Z, XUE J, XU Y. Release and transformation of potassium in co-combustion of coal and wheat straw in a BFB reactor[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2018, 144:1010-1016. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.09.021 [21] JURADO N, SIMMS N J, ANTHONY E J, OAKEY J E. Effect of co-firing coal and biomass blends on the gaseous environments and ash deposition during pilot-scale oxy-combustion trials[J]. Fuel, 2017, 197:145-158. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.01.111 [22] LI R, KAI X, YANG T, SUN Y, HE Y, SHEN S. Release and transformation of alkali metals during co-combustion of coal and sulfur-rich wheat straw[J]. Energy Convers Manage, 2014, 83:197-202. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2014.02.059 [23] SONG G, YANG S, SONG W, QI X. Release and transformation behaviors of sodium during combustion of high alkali residual carbon[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2017, 122:285-296. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.04.139 [24] LUPIÁÑEZ C, MAYORAL M C, GUEDEA I, ESPATOLERO S, DÍEZ L I, LAGUARTA S, ANDRÉS J M. Effect of co-firing on emissions and deposition during fluidized bed oxy-combustion[J]. Fuel, 2016, 184:261-268. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.07.027 [25] AHO M, FERRER E. Importance of coal ash composition in protecting the boiler against chlorine deposition during combustion of chlorine-rich biomass[J]. Fuel, 2005, 84(2):201-212. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=960b4ea9939f2275dfa8ba41c7bf10ac -





 下载:
下载: