Insight into the correlation between the effective adsorption sites and adsorption desulfurization performance of CuNaY zeolite
-
摘要: 以液相离子交换法制备了一系列不同Cu负载量的CuNaY分子筛;采用XRD及N2吸附-脱附表征分子筛的微观结构和织构性质,采用动态吸附法考察其对噻吩模拟油的吸附脱硫性能,结合NH3-TPD和Py-FTIR方法对CuNaY分子筛的酸量和有效Cu+物种进行定量分析,研究了CuNaY分子筛的表面酸性和铜物种形态结构对其吸附脱硫性能的影响机制。结果表明,通过改变铜负载量可有效调控改性Y分子筛的表面酸性以及铜物种化学形态;适量铜物种的引入可以最大限度的形成有效吸附位,从而获得最优吸附脱硫性能,而过量的Cu物种会在Y分子筛笼内形成多核铜物种结构,导致有效吸附位点的减少,影响其对噻吩的吸附能力。Abstract: A series of CuNaY zeolites with different Cu loadings were prepared from NaY by liquid-phase ion exchange (LPIE) method. The microstructure and textural properties of CuNaY zeolites were characterized by XRD and N2 sorption and their adsorption desulfurization performance were evaluated with a model oil containing thiophene by the dynamic adsorption method. Combined with the Py-FTIR and NH3-TPD methods, the amounts of surface acid sites and effective Cu+ species were determined quantitatively and a correlation between the effective adsorption sites and adsorption desulfurization performance of CuNaY zeolite towards thiophene was then established. The results revealed that the surface acidity and the active copper species in Y zeolite can be regulated effectively by controlling the copper loading; an adsorbent provided with abundant effective adsorption sites and excellent adsorption desulfurization performance can be obtained by loading appropriate amount of copper. On the contrary, an excessively high copper loading may promote the formation of polymeric copper species in the cavity of Y zeolite, which leads to a decrease in the number of effective adsorption sites as well as a decrease in the adsorption capacity of CuNaY zeolite towards thiophene.
-
Key words:
- CuNaY zeolite /
- adsorption site /
- copper loading /
- adsorption desulfurization
-
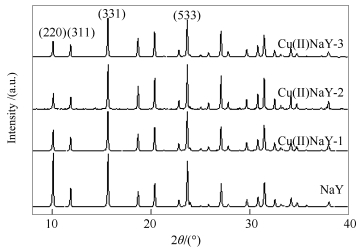
表 1 不同铜负载量Cu(Ⅱ)NaY分子筛的结构与组成
Table 1 Structure and composition of Cu(Ⅱ)NaY zeolites with different copper loadings
Sample w(Na2O)/% w(CuO)/% Nactual Lattice parameter d/nm Relative crystallinity/% NaY 12.73 0 0.0 2.464 100 CuNa(Ⅱ)Y-1 11.40 1.18 3.4 2.463 96.2 CuNa(Ⅱ)Y-2 5.31 9.39 15.2 2.462 83.1 CuNa(Ⅱ)Y-3 4.02 10.89 17.7 2.460 70.6 note: Nactual: Cu2+ number per unit cell 表 2 不同铜负载量Cu(Ⅰ)NaY分子筛的孔结构参数
Table 2 Textural properties of Cu(Ⅰ)NaY zeolites with different copper loadings
Sample Surface area
A/(m2·g-1)Mesoporous
surface area A/(m2·g-1 )Micropore volume
v/(cm3·g-1)Mesoporous volume
v/(cm3·g-1)NaY 585.3 38.2 0.28 0.029 Cu(Ⅰ)NaY-1 602.7 86.8 0.31 0.074 Cu(Ⅰ)NaY-2 601.0 65.0 0.28 0.060 Cu(Ⅰ)NaY-3 597.8 65.1 0.28 0.055 表 3 Cu(Ⅰ)NaY分子筛的酸量和具有络合能力Cu(Ⅰ)物种的含量
Table 3 Distribution of acid sites and complex Cu(Ⅰ) species in the Cu(Ⅰ)NaY zeolites
Sample Acid strength distribution /(μmol·g-1) μt/μ0 Mediate strong acid
amounts /(μmol·g-1)Neffective 100-250 ℃ 250-500 ℃ NaY 126.0(100%) 0 0 0 0 Cu(Ⅰ)NaY-1 213.9(52.6%) 193.1(47.4%) 1 64.37 3.4 Cu(Ⅰ)NaY-2 58.3(7%) 733.6 (93%) 4.01 237.77 13.58 Cu(Ⅰ)NaY-3 23.6 (4%) 626.9(96%) 3.84 189.86 10.02 note: μ0 is the mediate strong acid amounts of Cu(Ⅰ)NaY-1; μt is the mediate strong acid amounts of NaY, Cu(Ⅰ)NaY-2 and Cu(Ⅰ)NaY-3; Neffective represents the number of Cu+ with complexing capability per unit cell -
[1] LI B, XU D, JIANG Z Y, ZHANG X F, LIU W P, DONG X. Pervaporation performance of PDMS-Ni2+Y zeolite hybrid membranes in the desulfurization of gasoline[J]. J Membrane Sci, 2008, 322(2):293-301. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2008.06.015 [2] AVIDAN A, CULLEN M. Sulphco-desulfurization via selective oxidation-pilot plant results and commercialization plans[M]. National Petrochemical Refiners Association, 2001. [3] FUNAKOSHI I, AIDA T. Process for recovering organic sulfur compounds from fuel oil US, 5753102[P]. 1998. [4] 唐克, 宋丽娟, 段林海, 李秀奇, 桂建舟, 孙兆林.杂原子Y分子筛的二次合成及其吸附脱硫性能[J].物理化学学报, 2006, 22(9):1116-1120. http://www.whxb.pku.edu.cn/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=25954TANG Ke, SONG Li-juan, DUAN Lin-hai, Li Xiu-qi, GUI Jian-zhou, SUN Zhao-lin. Deep desulfurization by selective adsorption on heteroatom zeolite prepared by secondary synthesis[J]. Acta Phys Chim Sin, 2006, 22(9):1116-1120. http://www.whxb.pku.edu.cn/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=25954 [5] MEI H, MEI B W, YEN T F. A new method for obtaining ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel via ultrasound assisted oxidative desulfurization[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(4):405-414. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00318-6 [6] LANSBARKIS J R, WILSONS T, ZINNEN H A. Zeolitic capillary columas for gas chromatography: US, 5719322[P]. 1998. [7] YANG R T, HERNANDEZ-MALDONADO A J, YANG F H. Desulfurization of transportation fuels with zeolites under ambient conditions[J]. Science, 2003, 301(5629):79-81. doi: 10.1126/science.1085088 [8] HERNÁNDEZ-MALDONADO A J, YANG R T. Desulfurization of diesel fuels by adsorption via π-complexation with vapor-phase exchanged Cu(Ⅰ)-Y zeolites[J]. J Amer Chem Soc, 2004, 126(4):992-993. doi: 10.1021/ja039304m [9] HERNÁNDEZ-MALDONADO A J, YANG F H, QI G, YANG R T. Desulfurization of transportation fuels by π-complexation sorbents:Cu (I)-, Ni (Ⅱ)-, and Zn (Ⅱ)-zeolites[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2005, 56(1/2):111-126. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092633730400503X [10] 范闽光, 李斌, 张飞跃, 李望良, 邢建民, 刘自力.铜离子在CuLaHY分子筛中的分布与吸附脱硫性能[J].物理化学学报, 2009, 25(3):495-501. http://www.whxb.pku.edu.cn/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=21436FAN Min-guang, LI Bin, ZHANG Fei-yue, LI Wang-liang, XING Jian-min, LIU Zi-li. Distribution of copper ions in a CuLaHY zeolite and its performance in adsorption desulfurization[J]. Acta Phys Chim Sin, 2009, 25(3):495-501. http://www.whxb.pku.edu.cn/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=21436 [11] JIANG M, NG F T T. Adsorption of benzothiophene on Y zeolites investigated by infrared spectroscopy and flow calorimetry[J]. Catal Today, 2006, 116(4):530-536. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2006.06.034 [12] 秦玉才, 高雄厚, 裴婷婷, 郑兰歌, 王琳, 莫周胜, 宋丽娟.噻吩在稀土离子改性Y型分子筛上吸附与催化转化研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(7):889-896. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18233.shtmlQIN Yu-cai, GAO Xiong-hou, PEI Ting-ting, ZHENG Lan-ge, WANG lin, MO Zhou-sheng, SONG Li-juan. Adsorption and catalytic conversion of thiophene on Y-type zeolites modified with rare-earth metal ions[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(7):889-896. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18233.shtml [13] 王旺银, 潘明雪, 秦玉才, 王凌涛, 宋丽娟. Cu(Ⅰ)Y分子筛表面酸性对其吸附脱硫性能的影响[J].物理化学学报, 2011, 27(5):1176-1180. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlhxxb201105027WANG Wang-yin, PAN Ming-xue, QIN Yu-cai, WANG Ling-tao, SONG Li-juan. Effects of surface acidity on the adsorption desulfurization of Cu(Ⅰ)Y zeolites[J]. Acta Phys Chim Sin, 2011, 27(5):1176-1180. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlhxxb201105027 [14] PETERSON A A, ABILD-PEDERSEN F, STUDT F, ROSSMEISL J, NØRSKOV J K. How copper catalyzes the electroreduction of carbon dioxide into hydrocarbon fuels[J]. Energy Environ Sci, 2010, 3(9):1311-1315. doi: 10.1039/c0ee00071j [15] STUDT F, SHARAFUTDINOV I, ABILD-PEDERSEN F, ELKJÆR C F, HUMMELSHØJ J S, DAHL S, NØRSKOV, J K. Discovery of a Ni-Ga catalyst for carbon dioxide reduction to methanol[J]. Nat Chem, 2014, 6(4):320-324. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1873 [16] 贾未鸣, 秦玉才, 张乐, 莫周胜, 宋丽娟, 孙兆林. Ce改性对Y型分子筛酸中心可接近性及催化活性的影响[J].石油炼制与化工, 2017, 48(6):14-19. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=sylh201706005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQJIA Wei-ming, QIN Yu-cai, ZHANG Le, MO Zhou-sheng, SONG Li-juan, SUN Zhao-lin. Study on accessibility and catalytic activity of Y zeolite modified by Ce-species[J]. Pet Process Petrochem, 2017, 48(6):14-19. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=sylh201706005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [17] SHERRY H S. The ion-exchange properties of zeolites. I. Univalent ion exchange in synthetic faujasite[J]. J Phys Chem C, 1966, 70(4):1158-1168. doi: 10.1021/j100876a031 [18] 祖运, 秦玉才, 高雄厚, 莫周胜, 张磊, 张晓彤, 宋丽娟.催化裂化条件下噻吩与改性Y分子筛的作用机制[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(7):862-869. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18664.shtmlZU Yun, QIN Yu-cai, GAO Xiong-hou, MO Zhou-sheng, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Xiao-tong, SONG Li-juan. Mechanisms of thiophene conversion over the modified Y zeolites under catalytic cracking conditions[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(7):862-869. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18664.shtml [19] ZU Y, QIN Y C, GAO X H, LIU H H, ZHANG X T, ZHANG J D, SONG L J. Insight into the correlation between the adsorption-transformation behaviors of methylthiophenes and the active sites of zeolites Y[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2017, 203:96-107. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.008 [20] FOWKES A J, IBBERSON R M, ROSSEINSKY M J. Structural characterization of the redox behavior in copper-exchanged sodium zeolite Y by high-resolution powder neutron diffraction[J]. Chem Mater, 2002, 14(2):590-602. doi: 10.1021/cm010504b [21] KVHL G H. The coordination of aluminum and silicon in zeolites as studied by X-ray spectrometry[J]. J Phys Chem Solids, 1977, 38(11):1259-1263. doi: 10.1016/0022-3697(77)90025-7 [22] AMANO F, TANAKA T, FUNABIKI T. Auto-reduction of Cu(Ⅱ) species supported on Al2O3 to Cu(Ⅰ) by thermovacuum treatment[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2004, 221(1):89-95. http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/631671468261575153/SFG1110-IPP-P148527-Urumqi-SA-Box391461B-PUBLIC-Disclosed-5-19-2015.docx [23] SUN P, YU D, FU K, GU M, WANG Y, HUANG H, YING H. Potassium modified NaY:A selective and durable catalyst for dehydration of lactic acid to acrylic acid[J]. Catal Commun, 2009, 10(9):1345-1349. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2009.02.019 -





 下载:
下载: