Steam reforming of phenol for producing hydrogen over nickel support on MgO prepared by different methods
-
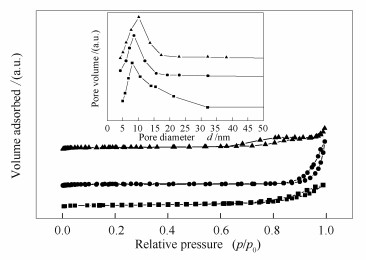
摘要: 利用浸渍法和水热共沉淀法两种方法,制备了介孔Ni/MgO催化剂,用于水蒸气重整生物质油模型物苯酚制取氢气;利用XRD、N2吸附/脱附、H2-TPR、TEM以及TG等手段对催化剂进行了表征。结果表明,以介孔MgO为载体,采用浸渍法制备的介孔NiO/MgO固溶体,具有较高的比表面积(60.6 m2/g)以及较大的孔径(10.1 nm)。与水热共沉淀法制备的催化剂相比,浸渍法制备的NiO/MgO前驱体经还原后的所得到介孔Ni/MgO催化剂Ni颗粒较小(5.0-6.0 nm),分布均匀,具有较高的分散度(19.44%)。较大的比表面积能有效地促进活性金属颗粒的分散,而介孔有利于反应物和产物在催化剂孔道中的扩散。因此,该Ni/MgO催化剂在水蒸气重整苯酚制氢反应中具有较高的催化活性、稳定性和优异的抗积炭能力。Abstract: MgO-supported nickel catalysts were prepared by impregnation and hydrothermal coprecipitation methods; they were characterized by XRD, N2 sorption, H2-TPR, TEM and TG and used in the steam reforming of biomass oil model compound-phenol for hydrogen production. The results indicated that the NiO/MgO solid solution prepared by the impregnation method displays higher surface area (60.6 m2/g) and larger pore diameter (10.1 nm), in comparison with that prepared by hydrothermal coprecipitation. After reduction, the mesoporous Ni/MgO catalyst obtained from impregnation exhibits small and uniform Ni nanoparticles (5.0-6.0 nm) with high dispersion (19.44%). As high surface area is favorable for the dispersion of Ni nanoparticles and mesoporous structure can promote the mass transfer of reactants and products, the Ni/MgO catalyst exhibits high activity as well as excellent coke resistance ability and long-term stability in the steam reforming of phenol.
-
Key words:
- mesoporous MgO /
- Ni/MgO catalyst /
- steam reforming /
- phenol /
- hydrogen
-
图 5 Ni/Mm催化剂和Ni-Mm催化剂的苯酚转化率、H2产率以及H2选择性
Figure 5 Phenol conversion (○, ●), H2 yield (■, □), H2 selectivity (△, ▲) vs.reaction time over the Ni/Mm catalyst (solid symbols) and Ni-Mm catalyst (hollow symbols) reaction conditions: 0.3 g catalyst, 450 ℃, N2 flow rate=45 mL/min, liquid flow rate=5.2 mL/h, S/C (mol ratio)=20
表 1 不同方法制备的催化剂的物理性质
Table 1 Physical properties of the catalysts prepared by different methods
Catalyst BET surface areaa A/(m2·g-1) Pore sizeb d/nm Pore volumeb v/(cm3·g-1) Mm 66.4 8.5 0.30 NiO/Mm 60.6 10.1 0.26 NiO-Mm 49.5 8.0 0.25 a: surface areas were obtained from nitrogen adsorption data by BET method;
b: total pore volume and average pore size were calculated from desorption branch isotherm by BJH method表 2 Ni基MgO催化剂的物理化学性质
Table 2 Physical and chemical properties of MgO supported Ni-based catalysts
Catalyst Ni loading
w/%Ni reducibilitya
/%Ni size d/nm Ni dispersiond
/%Ni surface aread
/(m2·(g-Ni)-1)by TEMb by XRDc Ni/Mm 10.98 12.29 5.42 5.17 19.44 16.02 Ni-Mm 10.98 13.32 6.93 6.79 14.84 14.81 a: Ni reducibility was calculated from H2-TPR profiles;
b: Ni particle size was calculated by using weighted average from the TEM results;
c: Ni particle size was determined by XRD;
d: Ni dispersion and Ni surface area were calculated according to literature[15]表 3 不同催化剂的苯酚转化率、氢气产率和产物选择性
Table 3 Phenol conversion, H2 yield and product selectivity for phenol steam-reforming over various catalysts
Catalyst xphenol /% wH2 /% Selectivity s/% H2 CO CO2 CH4 Ni/Mm 83.1 49.9 85.2 2.5 12.3 - Ni-Mm 72.7 45.2 77.1 4.9 18.0 - reaction conditions: 0.3 g catalyst, 450 ℃, N2 flow rate=45 mL/min, liquid flow rate=5.2 mL/h, S/C (mol ratio)=20, TOS=6 h -
[1] AZADI P, SYED K M, FARNOOD R. Catalytic gasification of biomass model compound in near-critical water[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen, 2009, 358(1): 65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.01.041 [2] VAN ROSSUM G, KERSTEN S R A, VAN SWAAIJ W P M. Catalytic and noncatalytic gasification of pyrolysis oil[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2007, 46(12): 3959-3967. doi: 10.1021/ie061337y [3] ARMAROLI N, BALZANI V. The hydrogen issue[J]. ChemSusChem, 2011, 4(1): 21-36. doi: 10.1002/cssc.v4.1 [4] LI C, SUZUKI K. Tar property, analysis, reforming mechanism and model for biomass gasification-An overview[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev, 2009, 13(3): 594-604. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2008.01.009 [5] 谢登印, 张素平, 陈志远, 陈振奇, 许庆利. Ni/Al2O3改性催化剂催化重整生物油模拟物制氢研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(3): 302-308. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18588.shtmlXIE Deng-yin, ZHANG Su-ping, CHEN Zhi-yuan, CHEN Zhen-qi, XU Qing-li. Co and Cu modified Ni/Al2O3 steam reforming catalysts for hydrogen production from model bio-oil[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(3): 302-308. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18588.shtml [6] 王一双, 陈明强, 刘少敏, 杨忠连, 沈朝萍, 刘珂.负载NiO-Fe2O3的凹凸棒石对生物油模型物催化重整制氢性能的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(12): 1470-1475. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18746.shtmlWANG Yi-shuang, CHEN Ming-qiang, LIU Shao-min, YANG Zhong-lian, SHEN Chao-ping, LIU Ke. Hydrogen production via catalytic steam reforming of bio-oil model compounds over NiO-Fe2O3-loaded palygouskite[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(12): 1470-1475. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18746.shtml [7] YANG X, WANG Y, WANG Y. Significantly improved catalytic performance of Ni-based MgO catalyst in steam reforming of phenol by inducing mesostructure[J]. Catalysts, 2015, 5(4): 1721-1736. doi: 10.3390/catal5041721 [8] CHEN L, JAENICKE S, CHUAH G K. Thermal and hydrothermal stability of framework-substituted MCM-41 mesoporous materials[J]. Microporous Mater, 1997, 12(4): 323-330. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248292039_Thermal_and_Hydrothermal_Stability_of_Framework-Substituted_MCM-41_Mesoporous_Materials [9] JEONG H J, AN K H, LIM S C, PARK M, CHANG J, PARK S, EUM S J, YANG C W, PARK C, LEE Y H. Narrow diameter distribution of singlewalled carbon nanotubes grown on Ni-MgO by thermal chemical vapor deposition[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2003, 380(3/4): 263-268. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Young_Lee22/publication/222697551_Narrow_diameter_distribution_of_singlewalled_carbon_nanotubes_grown_on_Ni-MgO_by_thermal_chemical_vapor_deposition/links/02e7e52416ffc09b0f000000.pdf [10] ROGGENBUCK J, TIEMANN M. Ordered mesoporous magnesium oxide with high thermal stability synthesized by exotemplating using CMK-3 carbon[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127(4): 1096-1097. doi: 10.1021/ja043605u [11] YANG X, WANG Y, LI M, SUN B, LI Y, WANG Y. Enhanced hydrogen production by steam reforming of acetic acid over a Ni catalyst supported on mesoporous MgO[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30(3): 2198-2203. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b02615 [12] WEI Y, WANG Y, ZHU J, WU Z. In-situ coating of SBA-15 with MgO: Direct synthesis of mesoporous solid bases from strong acidic systems[J]. Adv Mater, 2003, 15(22): 1943-1945. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095 [13] WANG N, YU X, SHEN K, CHU W, QIAN W. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance of MgO-coated Ni/SBA-15 catalysts for methane dry reforming to syngas and hydrogen[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(23): 9718-9731. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.05.097 [14] LING Z, ZHENG M, DU Q, WANG Y, SONG J, DAI W, ZHANG L, JI G, CAO J. Synthesis of mesoporous MgO nanoplate by an easy solvothermal-annealing method[J]. Solid State Sci, 2011, 13(12): 2073-2079. doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2010.01.013 [15] BI Q, DU X, LIU Y, CAO Y, HE H, FAN K. Efficient subnanometric gold-catalyzed hydrogen generation via formic acid decomposition under ambient conditions[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134(21): 8926-8933. doi: 10.1021/ja301696e [16] ZHONG L, HU J, WAN L, SONG W. Facile synthesis of nanoporous anatase spheres and their environmental applications[J]. Chem Commun, 2008, (10): 1184-1186. doi: 10.1039/b718300c [17] YU C, ZHANG L, SHI J, ZHAO J, GAO J, YAN D. A simple template-free strategy to synthesize nanoporous manganese and nickel oxides with narrow pore size distribution, and their electrochemical properties[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2008, 18(10): 1544-1554. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1616-3028 [18] LIU D, QUEK X, WAH H H A, ZENG G, LI Y, YANG Y. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane over nickel-grafted SBA-15 and MCM-41 catalysts[J]. Catal Today, 2009, 148(3/4): 243-250. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229122941_Carbon_dioxide_reforming_of_methane_over_nickel-grafted_SBA-15_and_MCM-41_catalysts [19] ZHANG L, PAN L, NI C, SUN T, ZHAO S, WANG S, WANG A, HU Y. CeO2-ZrO2-promoted CuO/ZnO catalyst for methanol steam reforming[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2003, 38: 4397-4406. [20] CAO L, MAN T, KRUK M. Synthesis of ultra-large-pore SBA-15 silica with two-dimensional hexagonal structure using triisopropylbenzene as micelle expander[J]. Chem Mater, 2009, 21(6): 1144-1153. doi: 10.1021/cm8012733 [21] YU M, ZHU K, LIU Z, XIAO H, DENG W, ZHOU X. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane over promoted NixMg1-xO (111) platelet catalyst derived from solvothermal synthesis[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ, 2014, 148-149: 177-190. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.10.046 [22] BENGAARD H S, NØRSKOV J K, SEHESTED J, CLAUSEN B S, NIELSEN L P, MOLENBROEK A M, NIELSEN J R R. Steam reforming and graphite formation on Ni catalysts[J]. J Catal, 2002, 209(2): 365-384. doi: 10.1006/jcat.2002.3579 -





 下载:
下载: