-
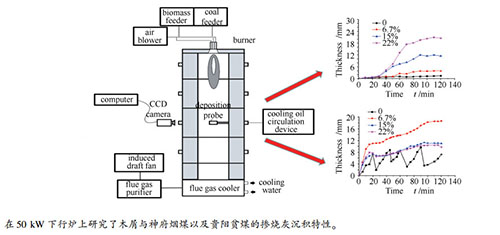
摘要: 利用CCD相机和沉积探针组成的在线监测系统,在50 kW下行炉上研究了木屑与神府烟煤以及贵阳贫煤的掺烧灰沉积特性。灰渣沉积过程可分为三个阶段:缓慢增长阶段、快速增长阶段和稳定阶段。烟煤掺烧灰沉积厚度随着木屑掺烧比例的增加而增加,贫煤掺烧灰沉积厚度则随着木屑掺烧比例增加而减小。烟煤中掺烧木屑比例为0、6.7%、15%和22%时,渣层稳定厚度分别为1.37、3.85、11.50、20.56 mm,稳定相对热流密度分别为0.44、0.41、0.30、0.26。贫煤掺烧木屑比例为6.7%、15%和22%时,稳定厚度分别为18.65、10.97和9.78 mm,稳定相对热流密度分别为0.29、0.31、0.33。掺烧木屑之后,灰渣初始层中Ca、K元素显著增加。在相同温度下,随着木屑掺烧比例的增加,灰中熔融相比例增加,因为木屑灰分中含有较多的Na2O、K2O等碱金属氧化物,而Al2O3、SiO2等含量较少,降低了灰的熔融温度。Abstract: The ash deposition characteristics during co-combustion of coal and sawdust was studied in a 50 kW furnace with an online monitoring system composed of CCD camera and ash deposition probe. The deposition process can be divided into three stages: slow growth stage, rapid and stable stage. The stable thickness of bituminous coal increases with increasing proportion of sawdust, while that of lean coal is opposite. The stable thickness of bituminous coal are 1.37, 3.85, 11.50, 20.56 mm and the stable relative heat flux are 0.44, 0.41, 0.30, 0.26 when blending ratio of sawdust are 0, 6.7%, 15%, 22% respectively. The stable slags thickness of lean coal are 18.65, 10.97, 9.78 mm and the stable relative heat flux densities are 0.29, 0.31, 0.33 when blending ratio of sawdust are 6.7%, 15% and 22%. Ca and K in the initial layer of deposition significantly increases in the co-combustion. The melting fraction calculated by FactSage software shows that at the same tem-perature, the melting fraction of ash increases as the sawdust is increased. Because the wood ash contains more alkali metal oxides such as Na2O and K2O, while the content of Al2O3 and SiO2 is less, which lowers the melting temperature of ash.
-
Key words:
- biomass /
- slagging /
- heat flux /
- on-line monitoring
-
图 3 数字图像处理方法;原始图像(左)和边缘图像(右)[13]
Figure 3 Method of digital image processing; the original image (left) and the edge image (right)
表 1 烟煤、贫煤与木头的燃料特性
Table 1 Fuel characteristics of bituminous coal, lean coal and sawdust
Proximate analysis wad/% Ultimate analysis w/% Ash fusion temperature t/℃ M V FC A C H N S O DT ST HT FT SF 8.77 26.96 48.96 15.32 77.94 4.47 1.42 0.34 15.83 1234 1257 1275 1302 GY 1.66 9.00 50.69 38.66 87.23 3.48 1.08 3.23 4.98 1204 1234 1257 1301 Sawdust 6.42 78.21 14.73 0.64 50.40 5.95 0.73 0.04 42.88 1420 >1450 >1450 >1450 Ash composition w/% Higher heating value Q/(MJ·kg-1) Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 SO3 K2O CaO TiO2 Fe2O3 SF 0.05 1.13 27.95 55.19 0.34 1.06 0.25 6.34 0.78 6.92 22.57 GY 0.15 1.10 26.58 51.66 0.30 1.58 4.31 3.85 1.41 9.07 19.93 Sawdust 0.12 3.22 11.80 40.32 1.57 5.34 2.20 31.35 0.50 3.57 18.07 表 2 实验工况
Table 2 Operating test parameters
Fuel SF bituminous coal, GY lean coal, sawdust Excess air ratio 1.1 Power /kW 50 Velocity of flue gas /(m·s-1) ~2.0 Furnace temperature t/℃ 1200 Oxygen concentration in flue gas /% 4 Thermal oil temperature t/℃ 230 Deposition time t/min 120 Case1 SF Case2 SF+6.7%sawdust Case3 SF+15%sawdust Case4 SF+22%sawdust Case5 GY Case6 GY+6.7%sawdust Case7 GY+15%sawdust Case8 GY+22%sawdust 表 3 实验结果汇总
Table 3 Test results of different cases
Case Final stable thickness /mm Final relative heat flux(q/q0) SF 1.37 0.44 SF+6.7%sawdust 3.58 0.41 SF+15%sawdust 11.50 0.30 SF+22%sawdust 20.56 0.26 GY - - GY+6.7%sawdust 18.65 0.29 GY+15%sawdust 10.97 0.31 GY+22%sawdust 9.78 0.33 表 4 灰渣初始层中的元素分布
Table 4 Elemental composition in the initial layer of deposition
w/% Na Mg Al Si P S K Ca Ti Fe SF 1.34 1.77 13.32 47.26 0.82 4.03 2.09 12.05 1.26 16.06 SF+6.7%sawdust 1.35 1.36 11.12 46.80 - 3.79 3.33 13.59 1.01 17.66 SF+15%sawdust 1.12 1.55 11.12 42.78 - 6.77 3.26 21.08 1.39 10.83 SF+22%sawdust 1.60 1.54 12.08 38.11 0.68 5.50 2.12 22.43 0.91 15.02 GY 0.42 0.95 16.61 50.56 0 2.65 1.41 6.99 1.44 18.96 GY+6.7%sawdust 0.33 0.58 15.48 52.30 0.58 2.99 2.23 7.88 1.31 16.32 GY+15%sawdust 0.64 0.80 16.65 51.16 0 2.45 3.71 8.88 0 15.28 GY+22%sawdust 0.56 0.81 17.51 48.52 0.50 2.65 3.93 9.00 2.17 14.35 表 5 各工况下的灰成分
Table 5 Chemical composition of the ash
w/% SF SF+6.7%sawdust SF+15%sawdust SF+22%sawdust GY GY+6.7%sawdust GY+15%sawdust GY+22%sawdust Na2O 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.07 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.14 MgO 1.13 1.27 1.44 1.59 1.10 1.24 1.42 1.57 Al2O3 27.95 26.87 25.53 24.40 26.58 25.59 24.36 23.33 SiO2 55.19 54.19 52.96 51.92 51.66 50.90 49.96 49.16 P2O5 0.34 0.42 0.52 0.61 0.30 0.38 0.49 0.58 SO3 1.06 1.34 1.70 2.00 1.58 1.83 2.14 2.41 K2O 0.25 0.38 0.55 0.68 4.31 4.17 3.99 3.84 CaO 6.34 8.02 10.09 11.84 3.85 5.69 7.97 9.90 TiO2 0.78 0.76 0.74 0.72 1.41 1.35 1.27 1.21 Fe2O3 6.92 6.69 6.42 6.18 9.07 8.70 8.25 7.86 表 6 灰沉积指数标准[16]
Table 6 Slagging standard
Slagging index Ash deposition tendency slight moderate serious 1 silicon ratio >78.8 66.1-78.8 <66.1 2 silica-alumina ratio <1.87 1.87-2.65 >2.65 3 acid-base ratio <0.2 0.2-0.4 >0.4 4 iron-calcium ratio <0.3 or>3 0.3-3 ≈1 表 7 各灰沉积指数对比
Table 7 Slagging index of different cases
Case Silicon ratio Silica-alumina ratio Acid-base ratio Iron-calcium ratio SF 79.32 1.97 0.18 1.09 slight moderate slight serious SF+6.7%sawdust 77.23 2.02 0.20 0.84 moderate moderate slight moderate SF+15%sawdust 74.69 2.07 0.23 0.64 moderate moderate moderate moderate SF+22%sawdust 72.58 2.13 0.26 0.52 moderate moderate moderate moderate GY 78.66 1.94 0.23 2.36 moderate moderate moderate moderate GY+6.7%sawdust 76.50 1.99 0.26 1.53 moderate moderate moderate moderate GY+15%sawdust 73.91 2.05 0.29 1.03 moderate moderate moderate serious GY+22%sawdust 71.78 2.11 0.32 0.79 moderate moderate moderate moderate -
[1] ZHOU W, SWANSON L, MOYEDA D, XU G. Process evaluation of biomass cofiring and reburning in utility boilers[J]. Energy Fuels, 2010, 24(8):4510-4517. doi: 10.1021/ef1005379 [2] 宁新宇, 李诗媛, 吕清刚.秸秆类生物质与石煤在流化床中的混烧与黏结机制[J].中国电机工程学报, 2008, 28(29):105-110. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGDC200829021.htmNING Xin-yu, LI Shi-yuan, LÜ Qing-gang. Study on co-firing and agglomeration mechanism of stalk biomass and stone coal in fluidized bed[J]. Proc CSEE, 2008, 28(29):105-110. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGDC200829021.htm [3] BARTOLOMÉ C, GIL A. Ash deposition and fouling tendency of two energy crops (cynara and poplar) and a forest residue (pine chips) co-fired with coal in a pulverized fuel pilot plant[J]. Energy Fuels, 2013, 27(10):5878-5889. doi: 10.1021/ef401420j [4] DEMIRBAS A. Combustion characteristics of different biomass fuels[J]. Prog Energy Combust Sci, 2004, 30(2):219-223. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2003.10.004 [5] NAGANUMA H, IKEDA N, KAWAI T, TAKUWA T, ITO T, IGARASHI Y, YOSHIIE R, NARUSE I. Control of ash deposition in pulverized coal fired boiler[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2009, 32(2):2709-2716. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2008.06.001 [6] VAMVUKA D, MISTAKIDOU E, DRAKONAKI S, FOSCOLOS A, KAVOURIDIS K. Ash quality of a beneficiated lignite from ptolemais basin, northern greece[J]. Energy Fuels, 2001, 15(5):1181-1185. doi: 10.1021/ef0100193 [7] ZHIMIN Z, HUI W, YONGTIE C, XING W, SHAOHUA W. A novel method used to study growth of ash deposition and in situ measurement of effective thermal conductivity of ash deposit[J]. Heat Transf Res, 2018, 47(2):271-285. doi: 10.1002/htj.21302 [8] ABREU P, CASACA C, COSTA M. Ash deposition during the co-firing of bituminous coal with pine sawdust and olive stones in a laboratory furnace[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(12):4040-4048. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.04.012 [9] WANG X, XU Z, WEI B, ZHANG L, TAN H, YANG T, MIKULI H, DUI N. The ash deposition mechanism in boilers burning Zhundong coal with high contents of sodium and calcium:A study from ash evaporating to condensing[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2015, 80:150-159. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.01.051 [10] NORDGREN D, HEDMAN H, PADBAN N, BOSTRÖM D, ÖHMAN M. Ash transformations in pulverised fuel co-combustion of straw and woody biomass[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2013, 105:52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.05.027 [11] WIGLEY F, WILLIAMSON J, MALMGREN A, RILEY G. Ash deposition at higher levels of coal replacement by biomass[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2007, 88(11/12):1148-1154. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5e312ef31cd6d1e1c6e9d9a204445752 [12] ZHOU HAO, ZHANG JIAKAI, ZHANG KUN. Investigation of the deposition characteristics of ammonium bisulfate and fly ash blend using an on-line digital image technique:Effect of deposition surface temperature[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2018, 179:359-368. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.07.030 [13] ZHOU H, ZHOU B, LI L, ZHANG H. Experimental measurement of the effective thermal conductivity of ash deposit for high sodium coal (Zhun Dong Coal) in a 300 KW test furnace[J]. Energy Fuels, 2013, 27(11):7008-7022. doi: 10.1021/ef4012017 [14] ZHOU H, ZHOU B, ZHANG H, LI L. Behavior of fouling deposits formed on a probe with different surface temperatures[J]. Energy Fuels, 2014, 28(12):7701-7711. doi: 10.1021/ef502141x [15] LI G, LI S, HUANG Q, YAO Q. Fine particulate formation and ash deposition during pulverized coal combustion of high-sodium lignite in a down-fired furnace[J]. Fuel, 2015, 143:430-437 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.11.067 [16] 潘攀.煤的灰沉积特性研究[D].保定: 华北电力大学(保定), 2007.PAN Pan. Research on ash deposition characteristics of coal[D]. Baoding: North China Electric Power University (Baoding), 2007. -





 下载:
下载: