Effects of K+, Ca2+ and Fe3+ on the distribution, structure and quality of the pyrolysis products of Hefeng coal
-
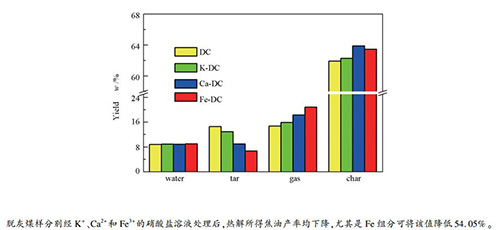
摘要: 将K+、Ca2+、Fe3+的硝酸盐用于处理脱灰和丰煤样(K-DC、Ca-DC和Fe-DC),在热重分析仪中考察了处理煤样的失重特征和气体逸出规律。结果表明,处理煤样的总失重率减少,CO2和H2的浓度较原煤(DC)的高。通过固定床研究了处理煤样热解过程中产物的分配规律,采用元素分析、FT-IR、模拟蒸馏和GC-MS等分析了半焦的结构特征和焦油的组成与品质。结果表明,与DC相比,处理煤样的半焦和气体产率增加,焦油产率降低,相应半焦的不饱和度和缩合程度降低。在各金属组分的作用下,焦油中的轻质组分分率增加,其中,Fe3+的作用最为显著,其值增加了22.4%。GCMS结果表明,长链烷烃含量高达70%,是焦油组分重的主要原因,K和Fe组分可促进其分解。Abstract: The nitrate solution of K+, Ca2+ and Fe3+ was used to treat Hefeng demineralized coal (DC) separately. The weight loss and gas evolution of coal samples were studied by thermogravimetric analyzer. It is found that the total weight loss of treated coal samples decreases, while the concentration of CO2 and H2 increases for treated samples. Then the distribution variation of products during the pyrolysis process of treated coal samples were investigated in a fixed bed reactor together with the analyses of elemental analysis, FT-IR, simulated distillation and GC-MS. The results indicate that the char and gas yields of treated coal samples rise, while the tar yields decline. The unsaturation and condensation of corresponded char samples exhibit a decreasing tendency. Under the action of these metal components, the percentage of light component in the tar increases, especially by 22.4% due to the effect of iron species. GC-MS analysis exhibits that long chain alkanes occupy about 70% of the total relatively, leading to the high content of heavy component in tar, which can be catalytically cracked by K and Fe species.
-
Key words:
- demineralized coal /
- metal ion /
- catalytic pyrolysis /
- char structure /
- tar quality
-
表 1 煤样分析
Table 1 Analyses of coal samples
Coal sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% H/C Ad Vdaf FCdaf* C H O* N S Raw coal 15.14 45.42 54.58 77.08 6.29 15.09 1.27 0.27 0.98 DC 1.69 43.56 56.44 71.84 5.64 20.79 1.50 0.23 0.94 *:by difference 表 2 半焦的元素分析
Table 2 Ultimate analysis of char samples
Sample Ultimate analysis w/% H/C (molar ratio) Degree of unsaturation Ω C H N O* S DC-char 83.34 2.49 2.08 11.85 0.24 0.359 11.53 K-DC-char 81.02 2.49 2.10 14.16 0.23 0.369 11.16 Ca-DC-char 79.86 2.66 2.14 15.14 0.20 0.400 10.80 Fe-DC-char 82.37 2.50 2.46 12.41 0.26 0.364 11.00 *: by difference 表 3 半焦Raman光谱分峰面积比
Table 3 Curve fitting peak area ratio of char samples
Sample Peak area ratio/% IG/ ID3 ID1/ Iall ID2/ Iall ID3/ Iall ID4/ Iall IG/ Iall DC-char 65.52 5.13 7.01 2.16 20.17 2.88 K-DC-char 63.12 4.16 11.34 2.88 18.49 1.63 Ca-DC-char 65.46 3.87 8.58 3.27 18.82 2.19 Fe-DC-char 66.84 4.15 9.25 2.17 17.59 1.90 表 4 焦油的模拟蒸馏分析
Table 4 Simulating distillate fractions of tar samples
Sample Fraction w/% light oil(< 170 ℃) phenol oil(170-210 ℃) naphthalene oil(210-230 ℃) wash oil(230-280 ℃) anthracene oil(280-360 ℃) pitch(> 360 ℃) DC 1.8 8.6 5.5 13.8 21.1 49.2 K-DC 1.0 10.0 6.0 15.1 22.2 45.7 Ca-DC 1.6 9.4 6.2 16.0 22.7 44.1 Fe-DC 2.8 12.4 6.9 16.1 23.6 38.2 表 5 焦油中各主要组分的GC-MS谱图鉴定
Table 5 Identification of major peaks in GC-MS spectrum of tar
Peak Compound Peak Compound 1 heptane 44, 69 1-tetradecene 2 2, 6-dimethyl-2, 4-heptdiene 45, 48 1-methyl-naphthalene 3 ethylbenzene 46 tridecane 4 1, 1-dimethyl-2-pentayl-cyclopropane 47 7- hexadecene 5, 7 o-xylene 49 [3-(2-cyclohexylethyl)-6-cyclopentylhexyl]-benzene 6 1-nonene 50 heptyl-benzene 8 nonane 51, 57 1-pentadecene 9 4-nonene 52 3-tetradecene 10 2-methyl-1-octanol 53 tetradecane 11 3-ethyl-2-methyl-1-heptane 54 5-tetradecene 12 4, 5-dimethyl-octane 55 1, 2-dimethyl-naphthalene 13 propylbenzene 56, 68 heneicosane 14 1-ethyl-3-methyl-benzene 58 pentadecane 15 5-methyl-undecane 59 1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydro-5, 6, 7, 8-tetramethyl-naphthalene 16, 19, 23 1, 3, 5-trimethyl-benzene 60, 63 1-heptadecene 17 1-ethyl-2-methyl-benzene 61 hexadecane 18 1-decene 62 hexadecamethyl-cyclooctasiloxane 20 2, 4, 6-trimethyl-octane 64 heptadecane 21 1- ethyl-2-phenyl-cyclopropane 65 1-octadecene 22 2-dodecene 66 octadecane 24 1-ethyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-benzene 67 1-heneicosanol 25 indane 70, 78 n-tetracosanol-1 26 butyl-benzene 71 tetracosane 27 2-methyl-phenol 72, 74, 83 1-heptacosanol 28 1-methyl-4-propyl-benzene 73, 77 pentacosane 29 3-methyl-phenol 75 hexacosane 30 nonyl-cyclopropane 76, 85 1-octacosanol 31 undecane 79 octacosane 32 1-hexyl-2-propyl-cis-cyclopropane 80 carbonic acid, ethyl octadecyl ester 33 3-phenyl-2-propenal 81 1-octacosanol 34 2-ethyl-phenol 82 nonacotane 35 1H-indene 84, 89 triacontane 37 1-methylindene 86 hentriacontane 38 3, 4-dimethyl-phenol 87 dotriacontane 39 naphthalene 88 1-hentetracontanol 40 nonyl-cyclopropane 90 tetracontane 41 dodecane 91 diploptene 42 5-tetradecene 92 acetate lupan-3-ol 43 2, 5-dimethyl-undecane 93, 94 15-isobutyl-(13.alpha.H)-isocopalane 表 6 各处理煤样热解焦油的成分分析
Table 6 Compositions of pyrolysis tar from treated coal samples
Component Relative content w/% DC K-DC Ca-DC Fe-DC Aliphatic hydrocarbons 69.00 70.44 70.00 69.99 b.p. above 300 ℃ 46.80 33.07 40.42 35.98 Aromatic hydrocarbons: 16.22 20.40 13.96 20.04 Benzenes 7.21 11.83 7.27 11.08 Phenols 5.67 4.86 1.77 4.79 Naphthalenes 1.92 2.27 3.58 2.35 Indenes 1.42 1.44 1.07 1.82 Oxygen containing compounds beyond phenol derivatives 14.78 9.16 16.04 9.97 -
[1] WANG W S, HUANG S D, ZOU J L. The present situation and policy suggestion of clean coal technology in China[J]. Adv Mater Res, 2013, 616/618:1120-1123. [2] SHI L, LIU Q Y, GUO X J, WU W Z, LIU Z Y. Pyrolysis behavior and bonding information of coal-A TGA study[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2013, 108(6):125-132. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0228907559 [3] BARUAH B P, KHARE P. Pyrolysis of high sulfur Indian coals[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(6):3346-3352. doi: 10.1021/ef070005i [4] LUO K, ZHANG C, ZHU S, BAI Y H, LI F. Tar formation during coal pyrolysis under N2, and CO2, atmospheres at elevated pressures[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2016, 118:130-135. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2016.01.009 [5] LI C S, SUZUKI K. Resources, properties and utilization of tar[J]. Res Cons Recycl, 2010, 54(11):905-915. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.01.009 [6] QU X, LIANG P, WANG Z, ZHANG R, SUN D, GONG X, GAN Z, BI J. Pilot development of polygeneration process of circulating fluidized bed combustion combined with coal pyrolysis[J]. Chem Eng Technol, 2011, 34(1):61-68. doi: 10.1002/ceat.v34.1 [7] GONG X M, WANG Z, LI S G, SONG W L, LIN W G. Coal pyrolysis in a laboratory-scale two-stage reactor:Catalytic upgrading of pyrolytic vapors[J]. Chem Eng Technol, 2015, 37(12):2135-2142. [8] 赵洪宇, 李玉环, 宋强, 吕俊鑫, 舒元锋, 王子民, 阎杰, 曾鸣, 舒新前.外加铁矿石对哈密低阶煤热解特性影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2016, 44(2):154-161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2016.02.004ZHAO Hong-yu, LI Yu-huan, SONG Qiang, LÜ Jun-xin, SHU Yuan-feng, WANG Zi-min, YAN Jie, ZENG Ming, SHU Xin-qian. Effect of additive iron ore on pyrolysis characteristics of a low rank coal from Hami[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2016, 44(2):154-161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2016.02.004 [9] FU Y, GUO Y H, ZHANG K X. Effect of three different catalysts (KCl, CaO and Fe2O3) on the reactivity and mechanism of low-rank coal pyrolysis[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30:2428-2433. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b02720 [10] ZHU T Y, ZHANG S Y, HUANG J J, WANG Y. Effect of calcium oxide on pyrolysis of coal in a fluidized bed[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 64(1):271-284. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rlhxxb200001008 [11] FENG J, XUE X Y, LI X H, LI W J, GUO X F, LIU K. Products analysis of Shendong long-flame coal hydropyrolysis with iron-based catalysts[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 130:96-100. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.09.035 [12] HE L, HUI H L, LI S G, LI W G. Production of light aromatic hydrocarbons by catalytic cracking of coal pyrolysis vapors over natural iron ores[J]. Fuel, 2018, 216:227-232. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.12.005 [13] ÖZTASN A, YÜRÜM Y. Pyrolysis of Turkish Zonguldak bituminous coal. Part 1. Effect of mineral matter[J]. Fuel, 2000, 79(10):1221-1227. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(99)00255-0 [14] DING L, ZHOU Z J, GUO Q H, HUO W, YU G S. Catalytic effects of Na2CO3, additive on coal pyrolysis and gasification[J]. Fuel, 2015, 142:134-144. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.11.010 [15] LI F, CHANG L P, WEN P, XIE K C. Simulated distillation of coal tar[J]. Energy Sources, 2001, 23(2):189-199. doi: 10.1080/00908310151092416 [16] MIN Z H, YIMSIRI P, ASADULLAH M, ZHANG S, LI C Z. Catalytic reforming of tar during gasification. Part Ⅱ. Char as a catalyst or as a catalyst support for tar reforming[J]. Fuel, 2011, 90(7):2545-2552. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.03.027 [17] PORADA S. The influence of elevated pressure on the kinetics of evolution of selected gaseous products during coal pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(7):1071-1078. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ024994232 [18] 赵洪宇, 任善普, 贾晋炜, 付兴民, 李子君, 梁新星, 阎杰, 曾鸣, 舒新前.钙、镍离子3种不同负载方式对褐煤热解-气化特性影响[J].煤炭学报, 2015, 40(7):1660-1669. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201507029ZHAO Hong-yu, REN Shan-pu, JIA Jin-wei, FU Xing-min, LI Zi-jun, LIANG Xin-xing, YAN Jie, ZENG Ming, SHU Xin-qian. Effects of calcium and nickel ions by three different load methods on pyrolysis and gasification characteristics of lignite[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2015, 40(7):1660-1669. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201507029 [19] ZENG X, WANG Y, YU J, WU S S, ZHONG M, XU S P, XU G W. Coal pyrolysis in a fluidized bed for adapting to a two-stage gasification process[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(3):1092-1098. doi: 10.1021/ef101441j [20] 曾昭琼.有机化学参考资料[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 1989.ZENG Zhao-qiong. Reference Materials for Organic Chemistry[M]. Beijing:Higher Education Press, 1989. [21] 朱廷钰, 刘丽鹏, 王洋, 黄戒介.氧化钙催化煤温和气化研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2000, 28(1):36-39. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb200001007ZHU Ting-yu, LIU Li-peng, WANG Yang, HUANG Jie-jie. Study on coal mild gasification with CaO catalyst[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2000, 28(1):36-39. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb200001007 [22] WIKTORSSON L P, WANZL W. Kinetic parameters for coal pyrolysis at low and high heating rates-a comparison of data from different laboratory equipment[J]. Fuel, 2000, 79(6):701-716. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(99)00138-6 [23] 王桂茹.催化剂与催化作用[M]. 4版.大连:大连理工大学出版社, 2015.WANG Gui-ru. Catalyst and Catalysis[M].4th ed. Dalian:Dalian University of Technology Press, 2015. [24] XU S Q, ZHOU Z J, XIONG J, YU G S, WANG F C. Effects of alkaline metal on coal gasification at pyrolysis and gasification phases[J]. Fuel, 2011, 90(5):1723-1730. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.01.033 [25] SHENG C D. Char structure characterised by Raman spectroscopy and its correlations with combustion reactivity[J]. Fuel, 2007, 86(15):2316-2324. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2007.01.029 [26] SADEZKY A, MUCKENHUBER H, GROTHE H, NIESSNER R, POSCHL U. Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials:Spectral analysis and structural information[J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(8):1731-1742. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.02.018 [27] DANIEL M K, LI X J, JUNICHIRO H, LI C Z. Characterization of the structural features of char from the pyrolysis of cane trash using fourier Transform-Raman spectroscopy[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(3):1816-1821. doi: 10.1021/ef070049r [28] OMAE I. Agostic bonds in cyclometalation[J]. J Organometallic Chem, 2011, 96(6):1128-1145 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0221647433 [29] 齐学军, 郭欣, 罗重奎, 郑楚光.热解过程中铁对神府褐煤焦结构的影响[J].工程热物理学报, 2014, 35(4):796-800. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gcrb201404040&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQQI Xue-jun, GUO Xin, LUO Zhong-kui, ZHENG Chu-guang. Effect of iron on the structure of shenfu brown coal char during pyrolysis[J]. J Eng Thermophysics, 2014, 35(4):796-800. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gcrb201404040&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [30] 武建军, 周国莉, 高志远, 乔军, 祖静如.半焦制铸造型焦的碳微晶结构X-衍射分析[J].煤炭学报, 2009, 34(12):1693-1696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.12.020WU Jian-jun, ZHOU Guo-li, GAO Zhi-yuan, QIAO Jun, ZU Jing-ru.The X-ray diffraction analysis of carbon micro-crystal structure of the foundry formed coke prepared by semi-coke[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2009, 34(12):1693-1696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.12.020 [31] MUEAKAMI K, SHIRATO H, OZAKI J I, NISHIYAMA Y. Effects of metal ions on the thermal decomposition of brown coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1996, 46(3):183-194. doi: 10.1016/0378-3820(95)00056-9 -





 下载:
下载: