Release properties of semi-volatile heavy metals in sewage sludge/coal co-incineration under O2/CO2 atmosphere
-
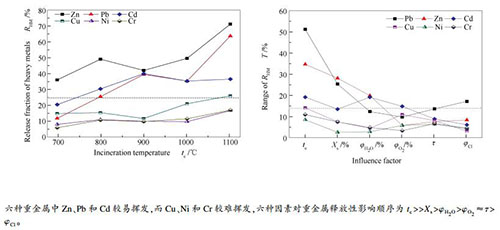
摘要: 在固定床焚烧实验装置上,采用正交实验法研究了焚烧温度(tc)、污泥掺混比(Xs)、O2体积分数(φO2)、初始含水率(φH2O)、焚烧时间(τ)和含氯量(φCl)六个因素对O2/CO2气氛下污泥/煤混燃中半挥发性重金属(Zn、Pb、Cd、Cu、Ni和Cr)释放特性的影响。结果表明,六种因素对重金属释放率影响程度排序为tc >> Xs > φH2O > φO2 ≈τ > φCl。相同焚烧工况下,Zn释放率最大,Pb和Cd次之,Cu、Ni和Cr较小。提高温度会促进重金属释放,且高温(1000-1100 ℃)对重金属释放的影响显著强于低温(700-900 ℃)。随着温度由700 ℃升高至1100 ℃,Zn和Pb释放率分别由36.1%和12.2%上升至70.9%和63.5%,Cd在900 ℃下达到40.0%的最大释放率,而Cu、Ni和Cr释放率大都维持在20.0%以下,温度对重金属释放率影响程度排序为Pb > Zn > Cd > Cu > Cr > Ni。重金属释放率随着污泥掺混比增加逐渐下降,却随着初始含水率增加呈现波浪式变化趋势,且在30%O2体积分数下重金属释放率取得最小值。焚烧时间和含氯量对Pb释放的影响程度显著强于其他五种重金属。O2/CO2气氛下污泥/煤混燃的最佳工况为:焚烧温度为900-1000 ℃、污泥掺混比为25%左右、O2体积分数为30%、初始含水率小于10%,并尽可能的缩短焚烧时间。Abstract: The effects of six factors involving incineration temperature (tc), sludge blending ratio (Xs), O2 concentration(φO2), initial moisture content (φH2O), incineration time (τ) and chlorine content (φCl) on the release properties of semi-volatile heavy metals (SVHMs) (such as Zn, Pb, Cd, Cu, Ni and Cr) in co-incineration of sewage sludge and coal under O2/CO2 atmosphere were investigated in a fixed-bed incinerator based on orthogonal experiment. The results indicate that the influence of six factors on the release fraction of SVHMs is ordered as tc >> Xs > φH2O > φO2 ≈ τ > φCl. The release fraction of Zn is the largest, followed by Pb and Cd, and the release fractions of Cu, Ni and Cr are the least at the same co-incineration condition. Increasing temperature is helpful for SVHMs release, and the promotion at high temperatures of 1000-1100 ℃ on SVHMs release is significantly stronger than that at the low temperature of 700-900 ℃. The release fractions of Zn and Pb increase remarkably from 36.1% and 12.2% to 70.9% and 63.5% with increasing tc from 700 to 1100 ℃, respectively, and the release fraction of Cd achieves the maximum of 40.0% at tc=900 ℃, however, the release fractions of Cu, Ni and Cr mostly keep below 20.0%. The influence of incineration temperature on the heavy metal release fraction is ordered as Pb > Zn > Cd > Cu > Cr > Ni. The release fractions of SVHMs decrease with increasing sludge blending ratio, but present a wave-like trend with increasing initial moisture content. The lower release fraction of SVHMs is achieved at φH2O=0 or 40%. O2 concentration has a certain influence on SVHMs release, and the lowest release fraction of SVHMs is achieved at φO2=30%. The influence of incineration time and chlorin content on the release of Pb is significantly stronger than that of other five SVHMs. The suggested optimal conditions of co-incineration of sludge and coal in O2/CO2 atmosphere are: the incineration temperature is 900-1000 ℃, the sludge blending ratio is about 25%, the O2 concentration is 30%, the initial moisture content is less than 10%, and the incineration time is reduced as far as possible.
-
Key words:
- sewage sludge /
- co-incineration /
- O2/CO2 /
- semi-volatile heavy metals /
- release properties /
- orthogonal experiment
-
图 1 固定床焚烧实验系统示意图
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the fixed-bed incinerator
1: O2; 2: CO2; 3: valve; 4: mass flow controller; 5: gas mixing container; 6: quartz glass rod; 7: quartz glass tube; 8: silica boat; 9: electric heating furnace; 10: temperature controller; 11: fly ash collector; 12: ice bath; 13: impingers
表 1 污泥与煤的工业分析、元素分析和热值的测定
Table 1 Proximate analysis, ultimate analysis and lower heating value of tested sludge and coal
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis w/% Qnet,d/(MJ·kg-1) Vd FCd Ad Cd Hd Od* Nd Sd SS 37.53 2.32 60.16 16.03 3.40 17.96 1.94 0.51 6.98 BC 23.33 55.87 20.80 64.42 3.87 9.12 0.23 1.56 24.96 *: by difference 表 2 污泥与煤的次量元素和痕量元素分析
Table 2 Results of minor elements and trace elements of sludge and coal(dry basis)
Sample Minor element w/% Trace element w/(μg·g-1) P Cl Si Fe K Na Ca Mg Al Zn Cd Pb Cu Ni Cr SS 1.93 1.29 12.04 2.99 0.17 0.06 2.00 0.58 1.12 723.2 18.7 86.0 158.9 41.9 178.0 BC 0.10 0.09 1.63 0.90 1.06 0.35 1.36 0.46 1.05 93.9 3.7 34.9 12.9 8.91 22.5 表 3 污泥/煤混燃正交实验方案
Table 3 Orthogonal experimental scheme for co-incineration of sludge and coal
Test no. tc/℃ φO2/% Xs/% φH2O/% τ/min φCl/% 1 1(700) 1(10) 1(0) 1(0) 1(3) 1(0) 2 1 2(20) 2(25) 2(10) 2(5) 2(1) 3 1 3(30) 3(50) 3(20) 3(10) 3(3) 4 1 4(40) 4(75) 4(40) 4(20) 4(5) 5 1 5(50) 5(100) 5(60) 5(40) 5(10) 6 2(800) 1 2 3 4 5 7 2 2 3 4 5 1 8 2 3 4 5 1 2 9 2 4 5 1 2 3 10 2 5 1 2 3 4 11 3(900) 1 3 5 2 4 12 3 2 4 1 3 5 13 3 3 5 2 4 1 14 3 4 1 3 5 2 15 3 5 2 4 1 3 16 4(1000) 1 4 2 5 3 17 4 2 5 3 1 4 18 4 3 1 4 2 5 19 4 4 2 5 3 1 20 4 5 3 1 4 2 21 5(1100) 1 5 4 3 2 22 5 2 1 5 4 3 23 5 3 2 1 5 4 24 5 4 3 2 1 5 25 5 5 4 3 2 1 -
[1] GAO N, KAMRAN K, QUAN C, WILLIAMS P T. Thermochemical conversion of sewage sludge:A critical review[J]. Prog Energy Combust Sci, 2020, 79:100843. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2020.100843 [2] 陈丹丹, 窦昱昊, 卢平, 黄亚继, 周军.污泥深度脱水技术研究进展[J].化工进展, 2019, 38(10):4722-4746. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgjz201910040CHEN Dan-dan, DOU Yu-hao, LU Ping, HUANG Ya-ji, ZHOU Jun. A review on sludge deep dewatering technology[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog, 2019, 38(10):4722-4746. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgjz201910040 [3] YANG G, ZHANG G, WANG H. Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China[J]. Water Res, 2015, 78(1):60-73. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=46ee7a26a1a090b67daa289c1608cea7 [4] KELESSIDIS A, STASINAKIS A S. Comparative study of the methods used for treatment and final disposal of sewage sludge in European countries[J]. Waste Manage, 2012, 32(6):1186-1195. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.01.012 [5] CHEN W, WANG F, KANHAR A H. Sludge acts as a catalyst for coal during the co-combustion process investigated by thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Energies, 2017, 10(12):1993. doi: 10.3390/en10121993 [6] 傅杰文, 刘敬勇, 孙水裕, 郭家宏, 黄绍松, 张耿崚, 孙健, 卓钟旭, 梁凯云.污泥与煤在CO2/O2及N2/O2气氛条件下的混燃特性分析[J].环境科学学报, 2017, 37(3):1021-1031. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjkxxb201703026FU Jie-wen, LIU Jing-yong, SUN Shui-yu, GUO Jia-hong, HUANG Shao-song, ZHANG Gen-lin, SUN Jian, ZHUO Zhan-xu, LIANG Kai-yun. Co combustion characteristic of sewage sludge and coal under CO2/O2 and N2/O2 atmosphere[J]. Acta Sci Circumst, 2017, 37(3):1021-1031. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjkxxb201703026 [7] 李国建, 胡艳军, 陈冠益, 钟英杰, 张雪梅.城市污水污泥与固体垃圾混烧过程中重金属迁移特性的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2011, 39(2):155-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2011.02.015LI Guo-jian, HU Yan-jun, CHEN Guan-yi, ZHONG Ying-jie, ZHANG Xue-mei. Transferring characteristics of heavy metals during co-incineration of municipal sewage sludge and solid waste[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2011, 39(2):155-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2011.02.015 [8] JANG H N, KIM J H, BACK S K, SUNG J H, YOO H M, CHOI H S, SEO Y C. Combustion characteristics of waste sludge at air and oxy-fuel combustion conditions in a circulating fluidized bed reactor[J]. Fuel, 2016, 170:92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.12.033 [9] MOŠKO J, POHOŘELY M, ZACH B, SVOBODA K, DURDA T, JEREMIÁŠ M, ŠYC M, VÁCLAVKOVÁ Š, SKOBLIA S, BEŇO Z, BRYNDA J. Fluidized bed incineration of sewage sludge in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 atmospheres[J]. Energy Fuels, 2018, 32(2):2355-2365. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b02908 [10] BU Y, DAI X, LU P. Release characteristics of semi-volatile heavy metals during co-combustion of sewage sludge and coal under the O2/CO2 atmosphere[J]. J Therm Anal Calorim, 2018, 133(2):1041-1047. doi: 10.1007/s10973-018-7170-6 [11] VEJAHATI F, XU Z, GUPTA R. Trace elements in coal:Associations with coal and minerals and their behavior during coal utilization-A review[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(4):904-911. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.06.013 [12] UDAYANGA W D C, VEKSHA A, GIANNIS A, LISAK G, CHANG V W C, LIM T T. Fate and distribution of heavy metals during thermal processing of sewage sludge[J]. Fuel, 2018, 226:721-744. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.04.045 [13] CHEN T, YAN B. Fixation and partitioning of heavy metals in slag after incineration of sewage sludge[J]. Waste Manage (Oxford), 2012, 32(5):957-964. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2011.12.003 [14] 张日旭, 蒋旭光, 池涌, 严建华.酸洗污泥与煤共燃烧过程中重金属的迁移分布研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(7):790-797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.07.003ZHANG Ri-xu, JIANG Xu-guang, CHI Yong, YAN Jian-hua. Migration and distribution of heavy metals during co-combustion of pickling sludge and coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(7):790-797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.07.003 [15] ZHANG R, JIANG X, CHI Y, YAN J. Experimental and thermodynamic study of the partition of Cr, Ni, Cu, Pb, and Mn during co-combustion of pickling sludge and bituminous coal[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30(1):690-697. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b02213 [16] 武宏香, 赵增立, 何方, 李海滨, 王杰.污泥与煤、木屑燃烧过程中重金属排放特性研究[J].环境工程学报, 2011, 5(11):195-201. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201111036WU Hong-xiang, ZHAO Zeng-li, HE Fang, LI Hai-bin, WANG Jie. Volatility of heavy metals in co-combustion of sludge with coal and wood[J]. Chin J Environ Eng, 2011, 5(11):195-201. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201111036 [17] 唐子君.污水处理厂污泥焚烧过程中重金属的迁移分布特性研究[D].北京: 中国环境科学研究院, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82405-1013315532.htmTANG Zi-jun. Study on the migration and distribution characteristics of heavy metals during sludge incineration of sewage treatment plants[D]. Beijing: Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82405-1013315532.htm [18] WANG R, ZHAO Z, YIN Q, LIU J. Mineral transformation and emission behaviors of Cd, Cr, Ni, Pb and Zn during the co-combustion of dried waste activated sludge and lignite[J]. Fuel, 2017, 199(1):578-586. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f3fc6d6a5ebba80be4f3550d5b8908c5 [19] 刘瑞江, 张业旺, 闻崇炜, 汤建.正交试验设计和分析方法研究[J].实验技术与管理, 2010, 27(9):52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4956.2010.09.016LIU Rui-jiang, ZHANG Ye-wang, WEN Chong-wei, TANG Jian. Study on the design and analysis methods of orthogonal experiment[J]. Exp Technol Manage, 2010, 27(9):52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4956.2010.09.016 [20] 张日旭.酸洗污泥与煤共燃烧过程中重金属的迁移分布规律研究[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 2016. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D01049767ZHANG Ri-xu. Study on migration and distribution of heavy metals during co-combustion of pickling sludge and coal[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D01049767 [21] 陈勇.垃圾焚烧中镉、铅迁移转化特性研究[D].北京: 清华大学, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10003-2009083558.htmCHEN Yong. Study on the partitioning and speciation of Cd and Pb during municipal solid waste incineration[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10003-2009083558.htm [22] CORELLA J, TOLEDO J M. Incineration of doped sludges in fluidized bed. Fate and partitioning of six targeted heavy metals. I. Pilot plant used and results[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2000, 80(1/3):81-105. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6b73bff3efb63ffbc03ed171b5f7c07f [23] MÉNARD Y, ASTHANA A, PATISSON F, SESSIECQ P, ABLITZER D. Thermodynamic study of heavy metals behaviour during municipal waste incineration[J]. Process Saf Environ Prot, 2006, 84(4):290-296. doi: 10.1205/psep.05166 [24] MENG A, LI Q, JIA J, ZHANG Y. Effect of moisture on partitioning of heavy metals in incineration of municipal solid waste[J]. Chin J Chem Eng, 2012, 20(5):1008-1015. doi: 10.1016/S1004-9541(12)60430-3 [25] LIU J, FU J, NING X, SUN S, WANG Y, XIE W, HUANG S, ZHONG S. An experimental and thermodynamic equilibrium investigation of the Pb, Zn, Cr, Cu, Mn and Ni partitioning during sewage sludge incineration[J]. J Environ Sci (China), 2015, 35:43-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2015.01.027 [26] YU J, SUN L, XIANG J, HU S, SU S, QIU J. Vaporization of heavy metals during thermal treatment of model solid waste in a fluidized bed incinerator[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 86(11):1122-1126. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.010 [27] 戴昕, 卢平, 祝秀明, 李珂, 王若琳, 布雨薇. O2/CO2气氛下污泥与煤混燃特性研究[J].工程热物理学报, 2015, 36(6):1376-1380. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcrwlxb201506044DAI Xin, LU Ping, ZHU Xiu-ming, LI Ke, WANG Ruo-lin, BU Yu-wei. Investigation on the co-combustion characteristics of sludge and coal under O2/CO2 atmospheres. J Eng Thermophys, 2015, 36(6):1376-1380. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcrwlxb201506044 [28] 张岩, 池涌, 李建新, 李晓东, 严建华, 岑可法.污泥焚烧过程中重金属排放特性试验研究[J].电站系统工程, 2005, 21(3):27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-006X.2005.03.012ZHANG Yan, CHI Yong, LI Jian-xin, LI Xiao-dong, YAN Jian-hua, CEN Ke-fa. An Experimental study on distribution of heavy metals in incineration of sludge[J]. Power Syst Eng, 2005, 21(3):27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-006X.2005.03.012 [29] 李建新, 严建华, 池涌, 张若冰, 倪明江, 岑可法.垃圾焚烧氯对重金属迀移特性的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2003, 31(6):579-583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2003.06.013LI Jian-xin, YAN Jian-hua, CHI Yong, ZHANG Ruo-bing, NI Ming-jiang, CEN Ke-fa. Effects of chlorine on the transfer of heavy metals in municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration process[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2003, 31(6):579-583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2003.06.013 -





 下载:
下载: