-
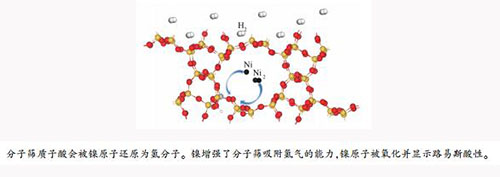
摘要: 分子筛被用作工业催化剂时常需要过渡金属改性,镍是制备加氢/脱氢催化剂常用的过渡金属,本研究采用密度泛函理论研究镍改性的ZSM-12分子筛的结构和酸性。结果表明,分子筛的B酸质子可以被镍原子还原成氢分子,而Ni2的团簇不能将B酸质子还原生成氢气分子。镍原子在分子筛内会被氧化,并形成Lewis酸性位,这会导致分子筛骨架铝的Lewis酸性变弱,镍改性后,分子筛吸附氢气的能力变强,被吸附的氢分子解离为氢原子,并带负电荷,不再具有B酸的功能。从计算的氨分子的吸附能来判断,由于吸附的氢会从镍原子得到电子,吸附的氢分子会增强镍原子的Lewis酸性。Abstract: The catalytic performance of zeolites in industry can often be enhanced by modification with transition metals and Ni is one of the most widely used transition metals for the hydrogenation and dehydrogenation catalysts. In this work, the structure and acid properties of Ni-modified HAl-ZSM-12 zeolites were investigated by the dispersion corrected periodic density functional theory. The results indicate that single Ni atoms can reduce the H atoms in the zeolites into H2 molecule, whereas the Ni clusters like Ni2 cannot. The quantity of Brønsted acid sites may decrease after the modification with single Ni atoms; the Ni atoms in the zeolites are oxidized and work as strong Lewis acid sites, which may weaken the Lewis acidity of Al3+. After modification with Ni, the Ni-modified ZSM-12 displays greater ability to adsorb hydrogen molecules. The adsorbed hydrogen molecules are dissociated to negatively charged H atoms, which do not function as Brønsted acid sites. Due to the transfer of electron from the Ni atoms to the pre-adsorbed H atoms, as revealed by the adsorption energy of NH3, the pre-adsorption of hydrogen on the Ni-modified ZSM-12 zeolites can enhance the Lewis acidity.
-
Key words:
- Ni /
- ZSM-12 zeolite /
- acidity /
- density functional theory /
- adsorption energy /
- hydrogen
-
Figure 1 Structure model of p(1×2×2) cell of pure silica ZSM-12 (a) and local structure (b) of H-form ZSM-12 zeolite all T sites of the zeolites are indexed with numbers (1-7) following the international zeolite association [http://asia.iza-structure.org]; the O atoms are indexed with letters (a-k), H, O, Al and Si atoms are shown in small white, red, gray, and yellow balls, respectively
Figure 3 Structures for the HAl-ZSM-12 zeolites modified with Ni monomer and dimer, the T and O sites of the zeolites are indexed with numbers and letters in accordance with Figure 1; bond distances, Bader charges and total adsorption energies are shown in nm, e, and kJ/mol, respectively; O, Si, Al, Ni and H atoms are shown in red, yellow, gray, black and small white balls, respectively
Figure 4 Structures for H2 adsorption in the Ni-modified HAl-ZSM-12 zeolites the T and O sites of the zeolites are indexed with numbers and letters in accordance with Figure 1; bond distances, Bader charges and the adsorption energies are shown in nm, e, and kJ/mol, respectively; O, Si, Al, Ni and H atoms are shown in red, yellow, gray, black and small white balls, respectively
Figure 5 Structures for the adsorption of NH3 in the Ni-modified HAl-ZSM-12 zeolites the T and O sites of the zeolites are indexed with numbers and letters in accordance with Figure 1; Bond distances, Bader charges and the adsorption energies are shown in nm, e, and kJ/mol, respectively; N, O, Si, Al, Ni and H atoms are shown in blue, red, yellow, gray, black and small white balls, respectively
Figure 6 Structures for adsorption of NH3 in the hydrogen pre-covered Ni-modified HAl-ZSM-12 zeolites the T and O sites of the zeolites are indexed with numbers and letters in accordance with Figure 1; Bond distances, Bader charges and the adsorption energies are shown in nm, e, and kJ/mol, respectively; N, O, Si, Al, Ni and H atoms are shown in blue, red, yellow, gray, black and small white balls, respectively
-
[1] DEDECEK J, SOBALIK Z, WICHTERLOVA B. Siting and distribution of framework aluminium atoms in silicon-rich zeolites and impact on catalysis[J]. Catal Rev, 2012, 54(2):135-223. doi: 10.1080/01614940.2012.632662 [2] CUNDY C S, COX P A. The hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites:History and development from the earliest days to the present time[J]. Chem Rev, 2003, 103(3):663-702. doi: 10.1021/cr020060i [3] GIL B, MOKRZYCKI L, SULIKOWSKI B, OLEJNICZAK Z, WALAS S. Desilication of ZSM-5 and ZSM-12 zeolites:Impact on textural, acidic and catalytic properties[J]. Catal Today, 2010, 152(1/4):24-32. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920586110000787 [4] DEMUTH T, HAFNER J, BENCO L, TOULHOAT H. Structural and acidic properties of mordenite:An ab initio density-functional study[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2000, 104(19):4593-4607. doi: 10.1021/jp993843p [5] CHEN F, ZHANG L, FENG G, WANG X, ZHANG R, LIU J. Trivalent ions modification for high-silica mordenite:A first principles study[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 433(1):627-638. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5ada4a01516504c4346618e9793c8b10&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [6] GAO W, AMOO C C, ZHANG G, JAVED M, MAZONDE B, LU C, YANG R, XING C, TSUBAKI N. Insight into solvent-free synthesis of MOR zeolite and its laboratory scale production[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2019, 280:187-194. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.01.041 [7] STANCIAKOVA K, ENSING B, GOLTL F, BULO R, EWECKHUYSEN B M. Cooperative role of water molecules during the Initial stage of water-induced zeolite dealumination[J]. ACS Catal, 2019, 9(6):5119-5135. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b00307 [8] MARTÍNEZ C, CCORMA A. Inorganic molecular sieves:Preparation, modification and industrial application in catalytic processes[J]. Coordin Chem Rev, 2011, 255(13):1558-1580. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3e53b825bb7de377adcdeb8990828ad3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [9] LIU Z, WANG Y, XIE Z. Thoughts on the future development of zeolitic catalysts from an industrial point of view[J]. Chin J Catal, 2012, 33(1):22-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cuihuaxb201201004 [10] ZANG Y, DONG X, PING D, GENG J, DANG H. Green routes for the synthesis of hierarchical HZSM-5 zeolites with low SiO2/Al2O3 ratios for enhanced catalytic performance[J]. Catal Commun, 2018, 113:51-54. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2018.05.018 [11] VAN LAAK A N C, SAGALA S L, ZECEVIC J, FRIEDRICH H, DE JONGH P E, DE JONG K P. Mesoporous mordenites obtained by sequential acid and alkaline treatments-catalysts for cumene production with enhanced accessibility[J]. J Catal, 2010, 276(1):170-180. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f6c7eed03bc73b3250d1d2c6c5f8f782 [12] CARVALHO K T G, URQUIETA-GONZALEZ E A. Microporous-mesoporous ZSM-12 zeolites:Synthesis by using a soft template and textural, acid and catalytic properties[J]. Catal Today, 2015, 243:92-102. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.09.025 [13] LAPIERRE R B, ROHRMAN A C, SCHLENKER J L, WOOD J D, RUBIN M, KROHRBAUGH W J. The framework topology of ZSM-12:A high-silica zeolite[J]. Zeolites, 1985, 5(6):346-348. doi: 10.1016/0144-2449(85)90121-6 [14] KAMIMURA Y, ITABASHI K, OKUBO T. Seed-assisted, OSDA-free synthesis of MTW-type zeolite and "Green MTW" from sodium aluminosilicate gel systems[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2012, 147(1):149-156. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.05.038 [15] AKYALCIN S, AKYALCIN L, BJØRGEN M. Optimization of desilication parameters of low-silica ZSM-12 by Taguchi method[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2019, 273:256-264. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.07.014 [16] DIMITROV L, MIHAYLOV M, HADJIIVANOV K, MAVRODINOVA V. Catalytic properties and acidity of ZSM-12 zeolite with different textures[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2011, 143(2/3):291-301. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4909da8a0dd7f13615036b5a3e97e15e [17] WANG Q, CUI Z M, CAO C Y, SONG W G. 0.3 angstrom makes the difference:Dramatic changes in methanol-to-olefin activities between H-ZSM-12 and H-ZSM-22 zeolites[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2011, 115(50):24987-24992. doi: 10.1021/jp209182u [18] MOKRZYCKI Ł, SULIKOWSKI B, OLEJNICZAK Z. Properties of desilicated ZSM-5, ZSM-12, MCM-22 and ZSM-12/MCM-41 derivatives in isomerization of α-pinene[J]. Catal Lett, 2008, 127(3/4):296-303. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e2788003e91d61af647aea4ab5459d7a [19] LI C, LI L F, WU W, WANG D S, TOKTAREV A V, KIKHTYANIN O V, ECHEVSKII G V. Highly selective synthesis of 2, 6-dimethylnaphthalene over alkaline treated ZSM-12 zeolite[J]. Proc Eng, 2011, 18:200-205. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.032 [20] BAI X, SUN K, WU W, YAN P, YANG J. Methylation of naphthalene to prepare 2, 6-dimethylnaphthalene over acid-dealuminated HZSM-12 zeolites[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2009, 314(1/2):81-87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f45fbf5712c52d5ae80256d15d213bae [21] MILLINI R, FRIGERIO F, BELLUSSI G, PAZZUCONI G, PEREGO C, POLLESEL P, ROMANO U. A priori selection of shape-selective zeolite catalysts for the synthesis of 2, 6-dimethylnaphthalene[J]. J Catal, 2003, 217(2):298-309. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d0aca38738442417359a7077612c8976 [22] FELLAH M F. Adsorption of hydrogen sulfide as initial step of H2S removal:A DFT study on metal exchanged ZSM-12 clusters[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2016, 144:191-196. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.01.003 [23] FELLAH M F. Hydrogen adsorption on M-ZSM-12 zeolite clusters (M=K, Na and Li):A density functional theory study[J]. J Porous Mater, 2014, 21(5):883-888. doi: 10.1007/s10934-014-9838-z [24] POCKAJ M, MEDEN A, LOGAR N Z, RANGUS M, MALI G, LEZCANO-GONZALEZ I, BEALE A, MGOLOBIC A. Structural investigations in pure-silica and Al-ZSM-12 with MTEA or TEA cations[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2018, 263:236-242. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.12.015 [25] SANHOOB M A, MURAZA O, AL-MUTAIRI E M, ULLAH N. Role of crystal growth modifiers in the synthesis of ZSM-12 zeolite[J]. Adv Powder Technol, 2015, 26(1):188-192. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7cbaa428e2451f397c9c062f9648fabc [26] YOO K, KASHFI R, GOPAL S, SMIRNIOTIS P G, GANGODA M, BOSE R N. TEABr directed synthesis of ZSM-12 and its NMR characterization[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2003, 60(1/3):57-68. [27] ZHANG W, BURCKLE E, CSMIRNIOTIS P G. Characterization of the acidity of ultrastable Y, mordenite, and ZSM-12 via NH3-stepwise temperature programmed desorption and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 1999, 33(1):173-185. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1387181199001365 [28] NGUYEN C M, REYNIERS M-F, MARIN G B. Adsorption thermodynamics of C1-4 alcohols in H-FAU, H-MOR, H-ZSM-5, and H-ZSM-22[J]. J Catal, 2015, 322:91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2014.11.013 [29] NING W, YANG X, ZHENG J, SUN X, PAN M, LI R. An environmentally friendly route to prepare hierarchical ZSM-12 using waste liquor as partial nutrients[J]. Mater Chem Phys, 2019, 223:299-305. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.10.069 [30] JEGATHEESWARAN S, CHENG C M, CHENG C H. Effects of adding alcohols on ZSM-12 synthesis[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2015, 201:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.09.008 [31] FENG G, YANG D Q, KONG D J, LIU J W, LU Z H. A comparative computational study on the synthesis prescriptions, structures and acid properties of B-, Al-and Ga-incorporated MTW-type zeolites[J]. RSC Adv, 2014, 4(89):47906-47920. doi: 10.1039/C4RA06114D [32] SANHOOB M A, MURAZA O, YOSHIOKA M, QAMARUDDIN M, YOKOI T. Lanthanum, cerium, and boron incorporated ZSM-12 zeolites for catalytic cracking of n-hexane[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2018, 129:231-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2017.11.007 [33] DE BAERDEMAEKER T, MVLLER U, YILMAZ B. Alkali-free synthesis of Al-MTW using 4-cyclohexyl-1, 1-dimethylpiperazinium hydroxide as structure directing agent[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2011, 143(2/3):477-481. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1387181111001259 [34] FENG G, LU Z H, YANG D, KONG D, LIU J. A first principle study on Fe incorporated MTW-type zeolite[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2014, 199:83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.08.009 [35] MOUDRAKOVSKI I L, SAYARI A, RATCLIFFE C I, RIPMEESTER J A, PRESTON K F. Vanadium-modified zeolite with the structure of ZSM-12:EPR and NMR studies[J]. J Phys Chem, 1994, 98(42):10895-10900. doi: 10.1021/j100093a035 [36] MAL N K, BHAUMIK A, KUMAR R R, AMASWAMY A V. Sn-ZSM-12, a new, large pore MTW type tin-silicate molecular sieve:Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties in oxidation reactions[J]. Catal Lett, 1995, 33(3):387-394. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=190f49985afd3e8c8ec1511ff0d81d8f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [37] SANTOS M R F D, PEDROSA A M G, SOUZA M J B D. Oxidative desulfurization of thiophene on TiO2/ZSM-12 zeolite[J]. Mater Res-ibero-am J Mater, 2016, 19(1):24-30. https://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1516-14392016000100024 [38] FENG G, LIAN Y Y, YANG D, LIU J, KONG D. Distribution of Al and adsorption of NH3 and pyridine in ZSM-12:A computational study[J]. Can J Chem, 2013, 91(10):925-934. doi: 10.1139/cjc-2013-0135 [39] VILHENA F D S. SERRA R M, BOIX A V. DFT study of Li+ and Na+ positions in mordenites and hydration stability[J]. Comput Theor Chem, 2016, 1091:115-121. doi: 10.1016/j.comptc.2016.07.017 [40] ZHANG W M, SMIRNIOTIS P G, GANGODA M, BOSE R N. Bronsted and lewis acid sites in dealuminated ZSM-12 and beta zeolites characterized by NH3-STPD, FT-IR, and MAS NMR spectroscopy[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2000, 104(17):4122-4129. doi: 10.1021/jp993072p [41] FENG G, YANG J, WANG C, LU K, ZHOU J, LIU J, WANG X, ZHANG R, ZHANG N. A first-principles study on Pd modified ZSM-12 zeolites[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2018, 260:227-234. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.10.009 [42] KRESSE G, FURTHMVLLER J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set[J]. Comp Mater Sci, 1996, 6(1):15-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=aa3c3f32846d39a6fe452417035cf9ed [43] KRESSE G, FURTHMVLLER J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set[J]. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54(16):11169-11186. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169 [44] PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Perdew, burke, and ernzerhof reply[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 80(4):891-891. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.891 [45] TANG W, SANVILLE E, HENKELMAN G. A grid-based bader analysis algorithm without lattice bias[J]. J Phys-Condens Matter, 2009, 21(8):084204. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/21/8/084204 [46] SANVILLE E, KENNY S D, SMITH R. Improved grid-based algorithm for Bader charge allocation[J]. J Comput Chem, 2007, 28(5):899-908. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e45059d0e490aba5df34f0fe78a2246b [47] HENKELMAN G, ARNALDSSON A, JÓNSSON H. A fast and robust algorithm for bader decomposition of charge density[J]. Comp Mater Sci, 2006, 36(3):354-360. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8b349feb49fca205cfb22ce02f8e04cf [48] VANOVA SHOR E A, NASLUZOV V A, SHOR A M. Reverse hydrogen spillover onto zeolite-supported metal clusters:An embedded cluster density functional study of models M6(M=Rh, Ir, or Au)[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111(33):12340-12351. doi: 10.1021/jp0711287 -





 下载:
下载: