Preparation of Au/β-Mo2C catalyst with high thermal stability and its performance in the reverse water-gas shift
-
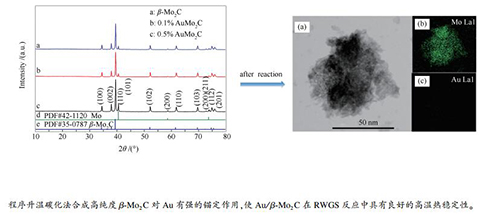
摘要: 以程序升温碳化法合成β-Mo2C载体,采用原位沉淀法制备负载量不同的Au/β-Mo2C催化剂,利用XRD、STEM和氮气吸附-脱附等手段对Au在载体表面的分散性、微观形貌及孔结构等进行表征,并在逆水煤气变换(RWGS)反应中对其高温热稳定性进行了研究。XRD表征结果表明,在34.44°、38.02°、39.44°、52.12°、61.53°、69.62°和74.65°处出现了β-Mo2C对应的(100)、(002)、(101)、(102)、(110)、(103)和(200)晶面的X射线特征衍射峰;同时,未出现Au物种的特征吸收峰,说明Au负载量较低的0.1%和0.5%的催化剂上Au纳米粒子的分散性较好。STEM表征结果也显示,当负载量较低(0.5%、1.0%和2.0%)时,金纳米粒子以2 nm左右的原子簇形式均匀分散并锚定在β-Mo2C载体上。氮气吸附-脱附表征结果表明,催化剂具有良好的介孔结构。反应评价结果表明,0.2% Au/β-Mo2C催化剂在RWGS反应中具有较好的催化活性和较高的CO选择性,且反应后孔结构良好,Au纳米粒子仍然均匀分散,说明Au/β-Mo2C催化剂在此反应中具有较高的催化性能和高温热稳定性。Abstract: β-Mo2C support was first prepared by the temperature-programmed carbonization and the Au/β-Mo2C catalysts with different Au loadings were then obtained by using the in -situ precipitation method. The Au/β-Mo2C catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) and nitrogen physisorption; their performance, the thermal stability at the high temperature in particular was then investigated in the reverse water-gas shift (RWGS). The XRD results reveal that the diffraction peaks appeared at 34.44°, 38.02°, 39.44°, 52.12°, 61.53°, 69.62° and 74.65° correspond to the (100), (002), (101), (102), (110), (103) and (200) planes of β-Mo2C, respectively, whereas no characteristic peak of Au species is detected, suggesting the high dispersion of Au nanoparticles on the Au/β-Mo2C catalysts with a low Au loading (0.1%-0.5%). The STEM results illustrate that for the Au/β-Mo2C catalysts with an Au loading of 0.5%-2.0%, gold nanoparticles in the form of atom clusters (about 2 nm) are anchored and uniformly dispersed on the β-Mo2C surface. The nitrogen physisorption results demonstrate that the Au/β-Mo2C catalysts have plenty of mesopores. The catalytic evaluation results indicate that the 0.2%Au/β-Mo2C catalyst exhibits high activity and high selectivity to CO for the RWGS reaction; moreover, after the reaction, the Au nanoparticles are still evenly dispersed and the pore structure remain intact, suggesting that the Au/β-Mo2C catalyst owns excellent performance and high thermal stability in the he reverse water-gas shift at high temperature.
-
Key words:
- in-situ precipitation /
- lattice orientation /
- RWGS reaction /
- thermal stability /
- catalyst
-
表 1 不同负载量催化剂Au/Mo2C反应前后的孔性质
Table 1 Textural properties of the Au/Mo2C catalysts with different Au loadings, fresh and spent ones after reaction
Catalyst ABET/(m2·g-1) vpore/(m3·g-1) dmean /nm fresh used fresh used fresh used Mo2C 29.00 - 0.051 - 6.81 - 0.2%Au/Mo2C 37.44 32.27 0.079 0.088 8.28 10.33 2.0%Au/Mo2C 40.80 33.21 0.090 0.100 8.80 12.35 -
[1] LI F J, DONG S C, LI S T, LI Z H, LI Y. Measurement and scenario simulation of effect of urbanization on region CO2 emission based on UES-SD model:A case study in Liaoning Province, China[J]. Chin Geogr Sci, 2015, 25(3):350-360. doi: 10.1007/s11769-014-0729-7 [2] WANG X X, JIANG D B, LANG X M. Climatechange of 4℃ global warming above pre-industrial levels[J]. Adv Atmos Sci, 2018, 35(7):757-770. doi: 10.1007/s00376-018-7160-4 [3] KEDIA S. Approaches to low carbon development in China and India[J]. Adv Clim Change Res, 2016, 7:213-221. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2016.11.001 [4] SU X, YANG X L, ZHAO B, HUANG Y Q. Designing of highly selective and high-temperature endurable RWGS heterogeneous catalysts:Recent advances and the future directions[J]. J Energy Chem, 2017, 26:854-867. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2017.07.006 [5] POROSOFF M D, YANG X F, BOSCOBOINIK J A, CHEN J G G. Molybdenum carbide as alternative catalysts to precious metals for highly selective reduction of CO2 to CO[J]. Angew, 2014, 53(26):6705-6709. doi: 10.1002/anie.201404109 [6] SAGAWA T. Conversion of CO2 to useful substances with composite iron, nickel, and copper catalysts[J]. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci A, 2018, 19(1):80-85. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1700056 [7] ÁLVAREZ GALVÁN C, SCHUMANN J, BEHRENS, M, FIERRO J L G, SCHLÖGL R, FREI E. Reverse water-gas shift reaction at the Cu/ZnO interface:Influence of the Cu/Zn ratio on structure-activity correlations[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2016, 195:104-111. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.05.007 [8] DUKE A S, XIE K, BRANDT A J, MADDUMAPATABANDI T D, AMMAL S C, HEYDEN A, MONNIER J R, CHEN D A. Understanding active sites in the water-gas shift reaction for Pt-Re catalysts on titania[J]. ACS Catal, 2017, 7(4):2597-2606. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b00086 [9] KATTEL S, YAN B H, CHEN J G G, LIU P. CO2 hydrogenation on Pt, Pt/SiO2 and Pt/TiO2:Importance of synergy between Pt and oxide support[J]. J Catal, 2016, 343:115-126 doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.12.019 [10] CHEN X D, SU X, LIANG B L, YANG X L, REN X Y, DUAN H M, HUANG Y Q, ZHANG T. Identification of relevant active sites and a mechanism study for reverse water gas shift reaction over Pt/CeO2 catalysts[J]. J Energy Chem, 2016, 25:1051-1057. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2016.11.011 [11] ZHU X B, QU X, LI X S, LIU J L, LIU J H, ZHU B, SHI C. Selective reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide over Au/CeO2 catalyst and identification of reaction intermediate[J]. Chin J Catal, 2016, 12(37):2053-2058. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cuihuaxb201612002 [12] HE S N, SHAO Z J, SHU Y J, SHI Z P, CAO X M, GAO Q S, HU P J, TANG Y. Enhancing metal-support interactions by molybdenum carbide:an efficient strategy toward the chemoselective hydrogenation of α, β-unsaturated Aldehydes[J]. Chem-Eur J, 2016, 16(22):5698-5704. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/296690859_Enhancing_Metal-Support_Interactions_by_Molybdenum_Carbide_An_Efficient_Strategy_toward_the_Chemoselective_Hydrogenation_of_ab-Unsaturated_Aldehydes [13] 赵立红, 闫捷, 房克功, 魏灵朝, 蒋元力, 孙予罕. K含量对纳米K/Fe/β-Mo2C催化剂CO加氢反应性能的影响[J].天然气化工(C1化学与化工), 2014, 39(3):25-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9219.2014.03.006ZHAO Li-hong, YAN Jie, FANG Ke-gong, WEI Ling-chao, JIANG Yuan-li, SUN Yu-han. Influence of K content on performance of nano-structured K/Fe/β-Mo2C catalysts in CO hydrogenation[J]. Nat Gas Ind, 2014, 39(3):25-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9219.2014.03.006 [14] POROSOFF M D, BALDWIN J W, PENG X, MPOURMPAKIS G, WILLAUER H D. Potassium promoted molybdenum carbide as a highly active and selective catalyst for CO2 conversion to CO[J]. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10(11):2408-2415. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201700412 [15] 耿文浩, 刘飞, 韩寒, 肖林飞, 吴伟. N, P掺杂型C@Mo2C催化剂的制备及其催化CO2加氢反应研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(4):458-467. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.04.010GENG Wen-hao, LIU Fei, HAN Han, XIAO Lin-fen, WU Wei. Synthesis of N, P-doped C@Mo2C catalyst and its application in CO2 hydrogenation[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(4):458-467. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.04.010 [16] 胡瑞珏, 赵娜娜, 李佳佳, 张幔娣, 李建立, 苏海全, 谷晓俊.不同方法制备的Ni修饰介孔碳负载的β-Mo2C催化CO加氢反应制备混合醇[J].石油学报(石油加工), 2018, 34(4):201-210. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb-syjg201804025HU Rui-jue, ZHAO Na-na, LI Jia-jia, ZHANG Man-di, LI Jian-li, SU Hai-quan, GU Xiao-jun.β-Mo2C catalysts supported on Ni modified mesoporous carbon prepared by different methods and their application in CO hydrogenation to synthesize mixed alcohol[J]. Acta Pet Sin (Pet Process Sect), 2018, 34(4):201-210. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb-syjg201804025 [17] 赵立红, 闫捷, 魏灵朝, 蒋元力, 房克功, 孙予罕. K改性Ni/β-Mo2C催化剂用于CO加氢反应研究[J].天然气化工(C1化学与化工), 2015, 40(4):23-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqhg201504005ZHAO Li-hong, YAN Jie, WEI Ling-chao, JIANG Yuan-li, FANG Ke-gong, SUN Yu-han. Preparation of K doped Ni/β-Mo2C and its performance for CO hydrogenation[J]. Nat Gas Ind, 2015, 40(4):23-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqhg201504005 [18] PERRET N, WANG X D, DELANNOY L, POTVIN C, LOUIS C, KEANE M A. Enhanced selective nitroarene hydrogenation over Au supported on β-Mo2C and β-Mo2C/Al2O3[J]. J Catal, 2012, 286:172-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2011.10.026 [19] CHENG C, ZHANG X L, FU Z M, YANG Z X. Strong metal-support interactions impart activity in the oxygen reduction reaction:Au monolayer on Mo2C (MXene)[J]. J Phys-Condens Mater, 2018, 30(47):112403-112429. doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/aae7ab [20] ROOHI P, ALIZADEH R, FATEHIFAR E. Thermodynamic study and methanothermal temperature-programmed reaction synthesis of molybdenum carbide[J]. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2016. 23(3):339-347. doi: 10.1007/s12613-016-1243-y [21] KOIZUMI R, OZDEN S, SAMANTA A, ALVES A P P, MISHRA A, YE G, SILVA G G, VAJTAI R, SINGH A K, TIWARY C S, AJAYAN P M. Origami-inspired 3D interconnected molybdenum carbide nanoflakes[J]. Adv Mater Interfaces, 2018, 5(6):1701113-1701120. doi: 10.1002/admi.201701113 [22] BADDOUR F G, ROBERTS E J, TO A T, WANG L, HABAS S E, RUDDY D A, BEDFORD N M, WRIGHT J, NASH C P, SCHAIDLE J A, BRUTCHEY R L, MALMSTADT N. An exceptionally mild and scalable solution-phase synthesis of molybdenum carbide nanoparticles for thermocatalytic CO2 hydrogenation[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2020, 142(2):1010-1019. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b11238 [23] DHAS N A, GEDANKEN A. Sonochemical synthesis of molybdenum oxide- and molybdenum carbide-silica nanocomposites[J]. Chem Mater, 1997, 9(12):3144-3154. doi: 10.1021/cm9704488 [24] LL X Y, MA D, CHEN LM, AO X H. Fabrication of molybdenum carbide catalysts over multi-walled carbon nanotubes by carbothermal hydrogen reduction[J]. Catal Lett, 2007, 116:63-69 doi: 10.1007/s10562-007-9093-x [25] WANG T, WANG J, CHEN W, ZHENG X, WANG E. A reusable N-doped-carbon-coated Mo2C composite counter electrode for high-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells[J]. Chem-Eur J, 2017, 23(68):17311-17317. doi: 10.1002/chem.201703519 [26] MA D. Strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) effect between metal catalysts and carbide supports[J]. Acta Phys-Chim Sin, 2019, 35(8):794-795. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlhxxb201908003 [27] DUAN X P, TIAN X L, KE J H, YIN YN, ZHENG J W, CHEN J, CAO Zh M, XIE Z X, YUAN YO Z. Size controllable redispersion of sintered Au nanoparticles by using iodohydrocarbon and its implications[J]. Chem Sci, 2016, 5:3181-3187. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=22c8c4009639f102690cb76cb06fe881 [28] CHEN X D, SU X, DUAN H M, LIANG B L, HUANG Y Q, ZHANG T. Catalytic performance of the Pt/TiO2 catalysts in reverse water gas shift reaction:Controlled product selectivity and a mechanism study[J]. Catal Today, 2017, 281:312-318. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.03.020 -





 下载:
下载: