-
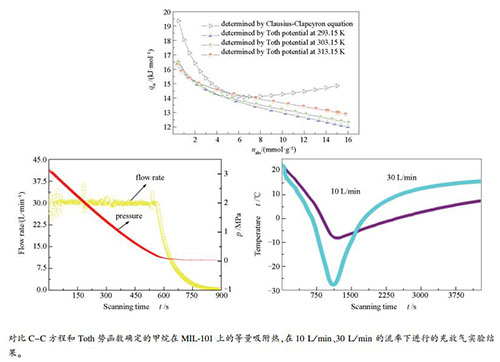
摘要: 为研制吸附储存天然气(ANG)用的金属有机框架物(MOFs),选择MIL-101(Cr)试样进行甲烷的吸附平衡与充放气实验。试样由溶剂热法合成,经测试77.15 K氮吸附数据作表征结构后,在温度293-313 K、压力0-100 kPa和0-7 MPa条件下测试甲烷吸附平衡数据,运用亨利定律标绘和Toth方程确定甲烷在试样上的极限吸附热和绝对吸附量,比较了Clausius-Clapeyron(C-C)方程和Toth势函数计算的等量吸附热。最后,在工程应用对应的流率10-30 L/min,对装填940 g试样、容积为3.2 L的适型储罐吸附床进行甲烷充放气实验。结果表明,甲烷在试样上的平均极限吸附热为23.89 kJ/mol,测试范围内Toth方程预测的平均相对误差为1.06%,由C-C方程和Toth势函数确定的平均等量吸附热分别为15.51和13.56 kJ/mol;在有效充放气时间内,储罐在10和30 L/min流率时的总充/放气量分别为347 L/338 L和341 L/318 L,放气率为98.3%和94.1%。工程应用应选用C-C方程确定的等量吸附热,并采取慢充/放以增大充/放气量和提高吸附床脱气率。Abstract: For developing metal organic frameworks (MOFs) suitable for the storage of nature gas by adsorption, the MIL-101 (Cr) sample was synthesized by solvothermal method, with which the characterization by adsorption of nitrogen at 77.15 K and the adsorption equilibrium and charge/discharge of methane were conducted. The adsorption equilibrium data of methane on the sample were measured volumetrically at temperature range of 293-313 K within a pressure range of 0-100 kPa and 0-7 MPa, respectively. The limit isosteric heat of adsorption was determined by employing the Henry's law using the adsorption data at very low pressure region, and the absolute adsorption amounts of methane on the sample were determined via nonlinear fit of the adsorption data at high pressure range by using Toth's equation. Isosteric heats of methane adsorption were then calculated through Clausius-Clapeyron equation and Toth's potential function. The charge and discharge tests of methane were performed at a flow rate range of 10-30 L/min on a 3.2 L conformable vessel packed with samples about 940 g. The results show that the mean limit isosteric heat is 23.89 kJ/mol, and the average relative error of the result predicted by the Toth equation is about 1.06%. The mean isosteric heat of adsorption determined by Clausius-Clapeyron equation and Toth's potential function is about 15.51 kJ/mol and 13.56 kJ/mol, respectively. The results also reveal that the total amount of charge/discharge at the flow rate of 10 L/min and 30 L/min is about 347 L/338 L and 341 L/318 L, respectively, which are in correspondence with the ratios of discharge about 98.3% and 94.1%. It suggests that the isosteric heat of methane adsorption determined by Clausius-Clapeyron equation is more reasonable for practical applications, and slower charging/discharging with a smaller flow rate is beneficial to increasing the total amount of charge/discharge and the discharging of the adsorbent bed.
-
Key words:
- MIL-101 /
- methane /
- adsorption equilibrium /
- charge and discharge
-
表 1 极低压力下甲烷在MIL-101样品上的热力学参数
Table 1 Thermodynamic parameters of methane adsorption on MIL-101 sample at very low pressure
T/K HP/(mmol· Pa-1·g-1) qst0/ (kJ·mol-1) Qadv/ (kJ·mol-1) 293.15 5.74×10-6 23.81 303.15 4.27×10-6 23.89 23.89 313.15 3.28×10-6 23.98 -
[1] ZHANG H D, DERIA P, FARHA O K, HUPP J T, SNURR, R Q. A thermodynamic tank model for studying the effect of higher hydrocarbons on natural gas storage in metal-organic frameworks[J]. Energy Environ Sci, 2015, 8(5):1501-1510. doi: 10.1039/C5EE00808E [2] KAYAL S, SUN B, CHAKRABORTY A. Study of metal-organic framework MIL-101(Cr) for natural gas (methane) storage and compare with other MOFs (metal-organic frameworks)[J]. Energy, 2015, 91:772-781. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2015.08.096 [3] WU Y, TANG D, VERPLOEGH R J, XI H X, SHOLL D S. Impacts of gas impurities from pipeline natural gas on methane storage in metal-organic frameworks during long term cycling[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2017, 121(29):15735-15745. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b03459 [4] KUMAR K V, PRESUU K, TITIRICI M M, RODRIGUEZ-RRINOSO F. Nanoporous materials for the onboard storage of natural gas[J]. Chem Rev, 2017, 117(3):1796-1825. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00505 [5] KONDO M, YOSHITOMI T, MATSUZAKA H, MATSUZAKA H, KITAGAWA S. Three-dimensional framework with channeling cavities for small molecules:{[M2(4, 4'-bpy)3(NO3)4]·xH2O}n(M=Co, Ni, Zn)[J]. Angew Chem (Int Ed Engl), 1997, 36(16):1725-1727. doi: 10.1002/anie.199717251 [6] MA S, ZHOU H C. A metal-organic framework with entatic metal centers exhibiting high gas-adsorption affinity[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(36):11734-11735. doi: 10.1021/ja063538z [7] DÜREN T, SARKISOV L, YAGHI O M, SNURR R Q. Design of new materials for methane storage[J]. Langmuir, 2004, 20(7):2683-2689. doi: 10.1021/la0355500 [8] LIANG C, SHI Z, HE C T, TAN J, ZHOU H D, ZHOU H L, LEE Y J, ZHANG Y B. Engineering of pore geometry for ultrahigh capacity methane storage in mesoporous metal-organic frameworks[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139(38):13300-13303. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b08347 [9] FEREY C, MELLOT-DRAZNIEKS C, SERRE C, MILLANGE F, DUTOUR, J SURBLE, S, MARGIOLAKI I. A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area[J]. Science, 2005, 309(5743):2040-2042. doi: 10.1126/science.1116275 [10] BIMBO N, PHYSICK J A, NOGUERA-DIAZ A, PUGSLEY A, HOLYFIELD L T, TING V P, MAYS, T J. High volumetric and energy densities of methane stored in nanoporous materials at ambient temperatures and moderate pressures[J]. Chem Eng J, 2015, 272:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.088 [11] THORNTON A W, SIMON C M, KIM J, KWON O, DEEG K S, KONSTAS K, PAS S J, HILL M R, WINKLER D A, HARANCZYK M, SMIT B. Materials genome in action:Identifying the performance limits of physical hydrogen storage[J]. Chem Mater, 2017, 29(7):2844-2854. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b04933 [12] WILMER C E, LEAF M, LEE C Y, FARHA O K, HAUSER B G, HUPP J T, SNURR R Q. Large-scale screening of hypothetical metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nat Chem, 2011, 4(2):83-89. [13] CHUNG Y G, CAMP J, HARANCZYK M, SIKORA B J, BURY W, KRUNGLEVICIUTE V, YILDIRIM T, FARHA, O K, SHOLL D S, SNURR R Q. Experimental metal-organic frameworks:A tool to enable high-throughput screening of nanoporous crystals[J]. Chem Mater, 2014, 26(21):6185-6192. doi: 10.1021/cm502594j [14] RAHMAN K A, LOH W S, CHAKRABORTYA, BIDYUT B S, WON G C, KIM C N. Thermal enhancement of charge and discharge cycles for adsorbed natural gas storage[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2011, 31(10):1630-1639. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2011.02.002 [15] LIU S, SUN L, XU F, ZHANG J, JIAO C L, LI F, LI Z B, WANG S, WANG Z Q, JIANG X, ZHOU H Y, YANG L N, SCHICK C. Nanosized Cu-MOFs induced by graphene oxide and enhanced gas storage capacity[J]. Energy Environ Sci, 2013, 6(3):818-823. doi: 10.1039/c3ee23421e [16] SZCZESNIAK B, CHOMA J, JARONIEC M. Development of activated graphene-MOF composites for H2 and CH4 adsorption[J]. Adsorpt, 2019, 25(3):521-528. doi: 10.1007/s10450-019-00024-6 [17] RAHMAN K A, LOH W S, CHAKRABORTY A, SAHA B B, CHUN W G, NG K C. Thermal enhancement of charge and discharge cycles for adsorbed natural gas storage[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2011, 31(10):1630-1639. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2011.02.002 [18] ZHENG Q R, ZHU Z W, WANG X H. Experimental studies of storage by adsorption of domestically used natural gas on activated carbon[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2015, 77:134-141. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.12.022 [19] ZHOU Y P, WANG Y X, CHEN H H, ZHOU L. Methane storage in wet activated carbon:Studies on the charging/discharging process[J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(9):2007-2012. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.03.017 [20] PROSNIEWSKI M J, RASH T A, KNIGHT E W, GILLESPIE A K, STALLA D, SCHULZ C J, PFEIFER P. Controlled charge and discharge of a 40-L monolithic adsorbed natural gas tank[J]. Adsorpt, 2018, 24(6):541-550. doi: 10.1007/s10450-018-9961-2 [21] 朱子文. MOFs储氢应用于船舶燃料电池电力推进系统的研究[D].厦门: 集美大学, 2019.ZHU Zi-wen. Research on the application of MOFs as hydrogen storage materials in fuel cell electric propulsion system for ships[D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2019. [22] 曹达鹏, 高广图, 汪文川.巨正则系综Monte Carlo方法模拟甲烷在活性炭孔中的吸附存储[J].化工学报, 2000, 51(1):23-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-1157.2000.01.005CAO Da-peng, GAO Guang-tu, WANG Wen-chuan. Grand canonical ensemble monte carlo simulation of adsorption storage of methane inslit micropores[J]. CIESC J, 2000, 51(1):23-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-1157.2000.01.005 [23] CLARK A. The Theory of Adsorption and Catalysis[M]. New York:Academic Press, 1970. [24] ZHENG Q R, ZHU Z W, FENG Y L, WANG X H. Development of composite adsorbents and storage vessels for domestically used adsorbed natural gas[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2016, 98:778-785. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.12.127 [25] 骆婉珍.船用混合燃料发动机燃烧过程数值模拟[D].厦门: 集美大学, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10390-1015350378.htmLUO Wan-zhen. Numerical simulation of combustion process of an engine powered by mixing fuel[D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10390-1015350378.htm [26] MEEKS O R, RYBOLT T R. Correlations of adsorption energies with physical and structural properties of adsorbate molecules[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1997, 196(1):103-109. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1997.5198 [27] MENON P G. Adsorption at high pressures[J]. Chem Rev, 1968, 68(3):277-294. doi: 10.1021/cr60253a002 [28] BIMBO N, XU W, SHARPE J E, TING V P, MAYS T J. High-pressure adsorptive storage of hydrogen in MIL-101(Cr) and AX-21 for mobile applications:Cryocharging and cryokinetics[J]. Mater Des, 2016, 89:1086-1094. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.069 [29] SOAVE G. Equilibrium constants from a modified redlich-kwong equation of state[J]. Chem Eng Sci, 1972, 27(6):1197-1203. doi: 10.1016/0009-2509(72)80096-4 [30] 张维东, 郑青榕, 王泽浩, 张轩.甲烷在层状石墨烯和活性炭上的吸附平衡[J].燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(8):1008-1015. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2019.08.015ZHANG Wei-dong, ZHENG Qing-rong, WANG Ze-hao, ZHANG Xuan. Adsorption e quilibrium of me thane on laye re dgraphe ne she e ts and activate d carbon[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2019, 47(8):1008-1015. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2019.08.015 [31] 高帅, 郑青榕.甲烷在活性炭上吸附平衡模型的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(3):380-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2013.03.019GAO Shuai, ZHENG Qing-rong. Comparisons of adsorption mode ls forme thane adsorption e quilibrium on activate d carbon[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(3):380-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2013.03.019 [32] KLOUTSE A F, ZACHARIA R, COSSEMENT D, CHAHINE R, BALDERAS-XICOHTENCATL R, OH, H, STREPPEL B, SCHLICHTENMAYER M, HIRSCHER M. Isosteric heat of hydrogen adsorption on MOFs:Comparison between adsorption calorimetry, sorption isosteric method, and analytical models[J]. Appl Phys A, 2015, 121(4):1417-1424. doi: 10.1007/s00339-015-9484-6 [33] 王泽浩.甲烷在典型吸附材料上的吸附平衡研究[D].厦门: 集美大学, 2018. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10390-1018186254.htmWANG Ze-hao. Studies of adsorption equilibrium of methane on typical materials[D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2018. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10390-1018186254.htm -





 下载:
下载: