Application of nano-Fe3O4 catalyst in the viscosity reduction of heavy oil by hydrothermal cracking
-
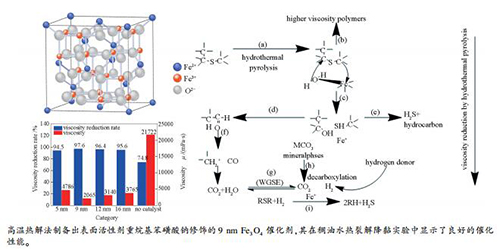
摘要: 通过高温热解法和低温双相回流法制备了四种不同尺寸的纳米Fe3O4催化剂,并将其应用于辽河油田稠油水热裂解降黏实验中。结果表明,制备过程中加入重烷基苯磺酸钠(HABS)表面活性剂能够有效提高Fe3O4催化剂在稠油水热裂解体系中的分散性,以高温热解法制备出的HABS修饰的9 nm Fe3O4催化剂降黏效果最佳。当稠油量为250 g时,按m(稠油):m(催化剂):m(油层水)质量比为100:0.3:30加入催化剂和油层水,加入0.75 g正作为己烷供氢体,在240℃下反应24 h,辽河油田稠油黏度从86200 mPa·s下降到2065 mPa·s,降黏率高达到97.6%。反应机理分析显示,纳米Fe3O4催化剂攻击稠油长链上键能最低C-S键,使其断键,重组分转化为轻组分。Abstract: Four nano-Fe3O4 catalysts with different particle sizes were prepared by high temperature pyrolysis and low temperature two-phase reflux method; their performance in the hydrothermal cracking and viscosity reduction of Liaohe oil-field heavy oil was investigated. The results indicate that the addition of sodium sulfonate (HABS) surfactant in the preparation process can effectively improve the dispersion of Fe3O4 catalyst in heavy oil for hydrothermal cracking; the HABS-modified 9 nm Fe3O4 catalyst prepared by high temperature pyrolysis exhibits the best viscosity reduction performance. In a reaction system with 250 g heavy oil and 0.75 g n-hexane as hydrogen donor, where the mass ratio of heavy oil:catalyst:reservoir water is 100:0.3:30, the viscosity of heavy oil can be reduced from 86200 to 2065 mPa·s after reaction at 240℃ for 24 h; the viscosity reduction rate is as high as 97.6%. Analysis on the reaction mechanism suggests that the nano-Fe3O4 catalyst attacks the C-S bond on the long-chain heavy oil, breaks the bond and converts the heavy component into light component.
-
Key words:
- hydrothermal cracking /
- heavy oil /
- nano Fe3O4 /
- catalytic viscosity reduction /
- viscosity
-
表 1 稠油性质
Table 1 Properties of Liaohe oilfield heavy oil
Property Elemental analysis w/% Group analysis w/% ρ20/(g·cm-3) μ50/(mPa·s) C H S N O saturates aromatics resins asphaltenes 0.956 86200 85.16 11.72 0.66 1.64 0.82 25.2 28.3 39.6 6.9 ρ20, density at 20℃; μ50, viscosity at 50℃ 表 2 稠油四组分反应前后变化表
Table 2 Variance in the four-component composition of heavy oil during the viscosity reduction process
Saturates /% Aromatics /% Resins /% Asphaltenes /% Before reaction 25.2 28.3 39.6 6.9 After reaction(5 nm) 30.1 30.6 33.4 5.9 After reaction(9 nm) 33.2 32.2 29.3 5.3 After reaction(12 nm) 32.6 31.3 30.6 5.5 After reaction(16 nm) 32.1 31.1 31.2 5.6 -
[1] ZOU C, ZHAI G, ZHANG G, WANG H, ZHANG G, LI J, WANG Z, WEN Z, MA F, LIANG Y, YANG Z, LI X, LIANG K. Formation, distribution, potential and prediction of global conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon resources[J]. Petrol Explor Dev, 2015, 42(1):14-28. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(15)60002-7 [2] NIU J, HU J. Formation and distribution of heavy oil and tar sands in China[J]. Mar Petrol Geol, 1999, 16(1):0-95. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4dce9e49deaa214fd5a2d28addc0ae15&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] PANG Z, LYU X, ZHANG F, WU T, GAO Z, GENG Z, LUO C. The macroscopic and microscopic analysis on the performance of steam foams during thermal recovery in heavy oil reservoirs[J]. Fuel, 2018, 233:166-176. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.048 [4] 王鹏, 徐海霞, 陈兰, 刘敏, 姜许健, 钟婷, 刘迎斌, 张博.高温稠油掺稀降黏开采辅助降黏剂的研究与应用[J].钻采工艺, 2018, 41(1):95-98. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2018.01.29WANG Peng, XU Hai-xia, CHEN Lan, LIU Min, JIANG Xu-jian, ZHONG Ting, LIU Ying-bin, ZHANG Bo. Development of viscosity reducer for thinning production of high temperature heavy oil[J]. Drill Prod Technol, 2018, 41(1):95-98. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2018.01.29 [5] SHI L, MA D, LIU P, LI X, XI C, WANG C. Experimental and numerical simulation studies on effects of viscosity reducers for steam assisted gravity drainage performances in extra-heavy oil reservoirs[J]. J Petrol Sci Eng, 2018. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7b93f664f8c504517c502ed06cc9142b [6] WANG Y, REN S, ZHANG L. Mechanistic simulation study of air injection assisted cyclic steam stimulation through horizontal wells for ultra heavy oil reservoirs[J]. J Pet Sci Eng, 2019, 172:209-216. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.09.060 [7] LI X, SHI L, LI H, LIU P, LUO J, YUAN Z. Experimental study on viscosity reducers for SAGD in developing extra-heavy oil reservoirs[J]. J Pet Sci Eng, 2018, 166:25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.03.022 [8] WANG Y, REN S, ZHANG L. Mechanistic simulation study of air injection assisted cyclic steam stimulation through horizontal wells for ultra heavy oil reservoirs[J]. J Pet Sci Eng, 2019, 172:209-216. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.09.060 [9] ZHOU W, DONG M, CHEN S. Investigation of initial water mobility and its effects on SAGD performance in bitumen reservoirs and oil sands[J]. J Pet Sci Eng, 2015, 135:39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.08.013 [10] PANG Z, WU Z, ZHAO M. A novel method to calculate consumption of non-condensate gas during steam assistant gravity drainage in heavy oil reservoirs[J]. J Pet Sci Eng, 2017, 130:76-85. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c6fb9a38aea1c602c2acdfa8b2a51ff3 [11] HART A, OMAJALI J B, MURRAY A J, MACASKIE L E, GREAVES M, WOOD J. Comparison of the effects of dispersed noble metal (Pd) biomass supported catalysts with typical hydrogenation (Pd/C, Pd/Al2O3) and hydrotreatment catalysts (CoMo/Al2O3) for In-situ heavy oil upgrading with toe-to-heel air injection (THAI)[J]. Fuel, 2016, 180:367-376. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.04.064 [12] HART A, WOOD J, GREAVES M. In situ catalytic upgrading of heavy oil using a pelletized Ni-Mo/Al2O3, catalyst in the THAI process[J]. J Pet Sci Eng, 2017, 156:958-965. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.06.067 [13] LV W, DING B, FENG X, WANG Q. A highly efficient UV-emitting Mg3Y2Ge3O12:Bi3+, crystal as a fluorescent irradiation source for use in heavy oil viscosity reduction[J]. J Mater Sci:Mater Electron, 2019, 30(7):7095-7102. doi: 10.1007/s10854-019-01026-4 [14] SHI C, YANG W, CHEN J, SUN X, CHEN W, AN H, DUO Y, PEI M. Application and mechanism of ultrasonic static mixer in heavy oil viscosity reduction[J]. Ultrason Sonochem, 2017, 37:648-653. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.02.027 [15] CHEN Q, ZHU Y, WANG M, REN G, LIU Q, XÜ Z, SUN D. Viscosity reduction of extra-heavy oil using toluene in water emulsions[J].Colloid Surface A, 2019, 560:252-259. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.10.025 [16] 鹿剑, 盛剑平, 骆建敏, 宿新泰.油溶性纳米Fe3O4催化稠油水热裂解降黏[J].广东化工, 2017, 44(6):56-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2017.06.025LU Jian, SHENG Jian-ping, LUO Jian-min, SU Xin-tai. Viscosity reduction of heavy oil by aquathermolysis with oil-soluble Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Guangdong Chem Ind, 2017, 44(6):56-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2017.06.025 [17] AKHMADIYAROV A A, RAKIPOV I T, KHACHATRIAN A A, PETROV A A, SITNOV S A, GERASIMOV A V, OSIN Y N, VARFOLOMEEV M A. Thermocatalytic upgrading of heavy oil by iron oxides nanoparticles synthesized by oil-soluble precursors[J]. J Petrol Sci Eng, 2018, 169:200-204. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.04.066 [18] NGUYEN M T, NGUYEN N T, CHO J, PARK C, PARK S, JUNG J, LEE C W. A review on the oil-soluble dispersed catalyst for slurry-phase hydrocracking of heavy oil[J]. J Ind Eng Chem, 2016, 43:1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2016.07.057 [19] 陈刚, 赵巍, 宁阳, 张洁, 李永飞, 宋华.水溶性有机钴(Ⅱ)盐催化的稠油低温清洁水热裂解[J].化学研究, 2016, 27(3):307-311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2016.03.005CHEN Gang, ZHAO Wei, NING Yang, ZHANG Jie, LI Yong-fei, SONG Hua. Aquathermolysis of heavy oil at relatively low temperature catalyzed by water-soluble organic Co(Ⅱ)salt[J]. Chem Res, 2016, 27(3):307-311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2016.03.005 [20] RAFFA P, BROEKHUIS A A, PICCHIONI F. Amphiphilic copolymers based on PEG-acrylate as surface active water viscosifiers:Towards new potential systems for enhanced oil recovery[J]. J Appl Polym Sci, 2016, 133(42):44100. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f544d618ff280a04556063f342f41c3d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [21] RUIZ M P, FARIA J, SHEN M, DREXLER S, PRASOMSRI T, RESASCO D E. Nanostructured carbon-metal oxide hybrids as amphiphilic emulsion catalysts[J]. ChemSusChem, 2011, 4(7):964-974. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201000322 [22] 李晨.改性SO42-/ZrO2-TiO2固体超强酸在稠油催化降黏中的应用研究[D].开封: 河南大学, 2016.LI Chen. Preparation of modified SO42-/ZrO2-TiO2 solid superacid and their catalytic performance in heavy oil reduction[D]. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2016. [23] EZZAT A O, ATTA A M, AL-LOHEDAN H A, HASHEM A L. Synthesis and application of new surface active poly (ionic liquids) based on 1, 3-dialkylimidazolium as demulsifiers for heavy petroleum crude oil emulsions[J]. J Mol Liq, 2018, 251:201-211. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2017.12.081 [24] BERA A, BELHAJ H. Ionic liquids as alternatives of surfactants in enhanced oil recovery-a state-of-the-art review[J]. J Mol Liq, 2016, 224:177-188. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.09.105 [25] 赵法军, 刘灏亮, 张新宇, 安毅, 田哲熙.稠油水热裂解中的金属纳米粒子催化剂研究进展[J].油田化学, 2017, 34(3):567-570. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ythx201703036ZHAO Fa-jun, LIU Hao-liang, ZHANG Xin-yu, AN Yi, TIAN Zhe-xi. Catalysts of metal nano-particles for aquathermolysis of heavy crude oil[J]. Oilfield Chem, 2017, 34(3):567-570. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ythx201703036 [26] LI H, CUI K, JIN L, WANG L, YU B. Experimental study on the viscosity reduction of heavy oil with nano-catalyst by microwave heating under low reaction temperature[J]. J Pet Sci Eng, 2018, 170:374-382. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.06.078 [27] ALAEI M, BAZMI M, RASHIDI A, RAHIMI A. Heavy crude oil upgrading using homogenous nanocatalyst[J]. J Pet Sci Eng, 2017, 158:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.08.031 [28] DEHKORDI J A, JAFARI A, SABET S A, KARAMI F. Kinetic studies on extra heavy crude oil upgrading using nanocatalysts by applying CFD techniques[J]. Chin J Chem Eng, 2018, 26:343-355. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2017.07.001 [29] LAM-MALDONADO M, MELO-BANDA J A, MACIAS-FERRER D, PORTALES-MARTINEZ B, DOMINGUEZ J M, SILVA-RODRIGO R, PARAMO-GARCIA U, MATA-PADILLA J M. Transition metal nanocatalysts by modified inverse microemulsion for the heavy crude oil upgrading at reservoir[J]. Catal Today, 2018:S0920586118306722. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/David_Macias_Ferrer/publication/325387463_Transition_Metal_Nanocatalysts_by_Modified_Inverse_Microemulsion_for_the_Heavy_Crude_Oil_Upgrading_at_Reservoir/links/5b0d4d920f7e9b1ed7fd7d8e/Transition-Metal-Nanocatalysts-by-Modified-Inverse-Microemulsion-for-the-Heavy-Crude-Oil-Upgrading-at-Reservoir.pdf [30] LAM-MALDONADO M, MELO-BANDA J A, MACIAS-FERRER D, SCHACHT P, MATA-PADILLA J M, REYES DE LA TORRE A I, MERAZ MELO M A, DOMINGUEZ J M. NiFe nanocatalysts for the hydrocracking heavy crude oil[J]. Catal Today, 2018, in press. [31] 宋景杨, 何勇.纳米级金属粒子对稠油或沥青降黏的研究[J].化工设计通讯, 2018, 44(1):76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2018.01.067SONG Jing-yang, HE Yong. Research on the viscosity of heavy oil or asphalt by nano-grade metal[J]. Chem Eng Des Commun, 2018, 44(1):76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2018.01.067 [32] 蔡可迎, 周颖梅, 陶伟, 周磊.四氧化三铁制备及其催化水合肼还原硝基苯活性[J].无机盐工业, 2017, 49(12):65-68. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjygy201712017CAI Ke-ying, ZHOU Ying-mei, TAO Wei, ZHOU Lei. Preparation of Fe3O4 particles and their activity in reduction of nitrobenzene with hydrazine hydrate[J]. Inorg Chem Ind, 2017, 49(12):65-68. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjygy201712017 [33] 杨兆中, 朱静怡, 李小刚, 罗丹.纳米材料用于提高稠油采收率的研究进展[J].应用化工, 2016, 45(5):949-952. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sxhg201605037YAO Zhao-zhong, ZHU Jing-yi, LI Xiao-gang, LUO Dan. Research progress on nano-materials application for heavy oil recovery enhancement[J]. Appl Chem Ind, 2016, 45(5):949-952. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sxhg201605037 [34] LI Y, MA F, SU X, SHI L.Ultra-large-scale synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their application for direct coal liquefaction[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2014, 53(16):6718-6722. doi: 10.1021/ie500216c [35] 赵法军, 刘永建, 赵田红, 闻守斌, 赵国.利用供氢体对稠油进行水热裂解催化改质的研究进展[J].油田化学, 2006, 23(4):89-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4092.2006.04.022ZHAO Fa-jun, LIU Yong-jian, ZHAO Tian-hong, WEN Shou-bin, ZHAO Guo. Advance in catalytically upgrading heavy oil by aquathermolysis using hydrogen donor[J]. Oilfield Chem, 2006, 23(4):379-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4092.2006.04.022 [36] 张博, 刘永建, 赵法军, 胡绍彬.注蒸汽条件下稠油催化改质降黏实验研究[J].新疆石油地质, 2011, 28(5):167-171. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ythx201102013ZHANG Bo, LIU Yong-Jian, ZHAO Fa-jun, HU Shao-bin. Catalytic upgrading heavy oil for viscosity reduction in steam injection[J]. Oilfield Chem, 2011, 28(2):167-171. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ythx201102013 [37] 杨翠定.石油化工分析方法:RIPP试验方法[M].北京:科学出版社, 1990.YANG Cui-ding. Petrochemical Analysis Method:RIPP Test Method[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1990. [38] GAWANDE M B, BRANCO P S, VARMA R S. Nano-magnetite (Fe3O4) as a support for recyclable catalysts in the development of sustainable methodologies[J]. ChemInform, 2013, 42(8):3371-3393. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cd623868ba5a90a3acf571b6cb60b2f8 [39] 朱路平.微纳米结构磁性材料的设计、制备及磁性能研究[D].北京: 中国科学院研究生院(理化技术研究所), 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80030-2008126129.htmZHU Lu-ping. Design, preparation and magnetic properties of micro/nanostructured magnetic materials[D]. Beijing: Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry CAS, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80030-2008126129.htm [40] 沈彬, 王永安, 王志飞, 张玲.超顺磁性介孔纳米颗粒嫁接肟Pd环络合物对Heck反应的催化活性[J].物理化学学报, 2010, 26(7):1860-1866. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB20100707SHEN Bin, WANG Yong-an, WANG Zhi-fei, ZHANG Ling. Catalytic activity of an oxime carbapalladacycle complex grafted onto superparamagnetically mesoporous nanoparticles for the heck reaction[J]. Acta Phys-Chim Sin, 2010, 26(7):1860-1866. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB20100707 [41] 张立德.纳米材料和纳米结构[J].中国科学院院刊, 2001, 16(6):444-445. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjclxb201409001ZHANG Li-de. Nanomaterials and nanostructures[J].B Chinese Acad Sci, 2001, 16(6):444-445. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjclxb201409001 [42] XU Z, SHEN C, HOU Y, GAO H, SUN S. Oleylamine as both reducing agent and stabilizer in a facile synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles[J]. Chem Mater, 2009, 21(9):1778-1780. doi: 10.1021/cm802978z [43] 韩晓强, 李爱军, 刘琼.稠油含水对粘度影响探讨[J].新疆石油科技, 2010, 20(4):48-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsykj201004012HAN Xiao-qiang, LI Ai-jun, LIU Qiong. Study of the effect of the water in heavy oil on viscosity[J]. Xinjiang Pet Sci Technol, 2010, 20(4):48-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsykj201004012 [44] 李恩田, 王树立, 赵会军, 申龙涉, 王为民.含水超稠油表观粘度的试验与研究[J].油气储运, 2007, 26(11):52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8241-D.2007.11.015LI En-tian, WANG Shu-li, ZHAO Hui-jun, SHEN Long-she, WANG Wei-min. Experimental study on apparent viscosity of water cut super-heavy oils[J]. Oil Gas Storage Transp, 2007, 26(11):52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8241-D.2007.11.015 [45] BELGRAVE J D M, MOORE R G, URSENBACH M G. Comprehensive kinetic models. for the aquathermolysis of heavy oils[J]. J Can Pet Technol, 1997, 36(4):38-44. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=134363a78642d01c1cc82c369c4894a1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn -





 下载:
下载: