Effect of silicon oxide additive on the transformation characteristics of sodium and sulfur in Zhundong coal ash under atmospheric and elevated pressure
-
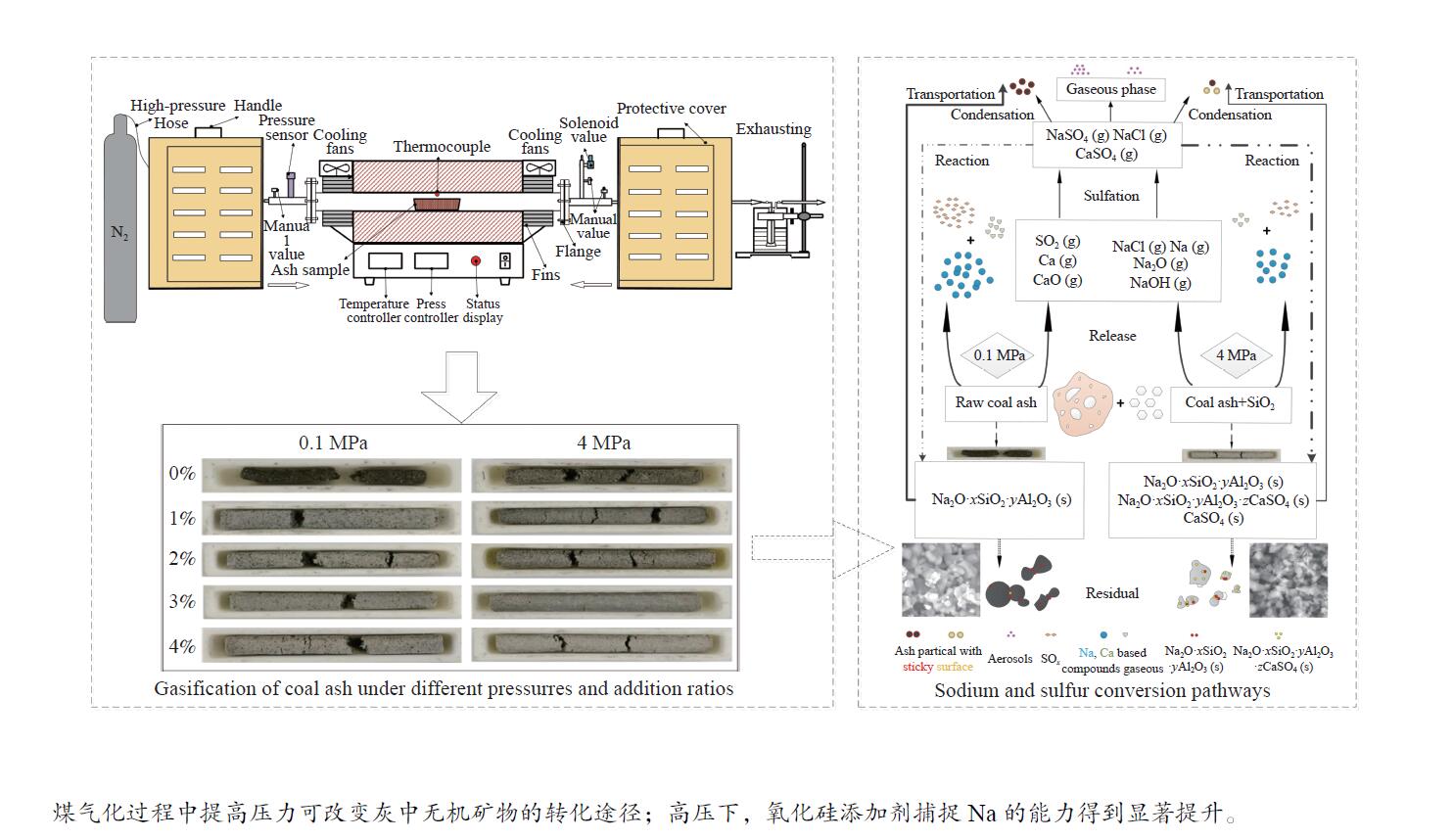
摘要: 本实验研究了常压和加压条件下氧化硅添加剂对准东煤灰中钠和硫转化特性的影响。结果表明,氧化硅添加剂在高压下对钠的释放具有更强的抑制作用。0.1 MPa下,添加比为4%时,灰中钠含量比无添加剂时高3.5%。而4 MPa、添加比例为0和4%时,灰中钠含量比0.1 MPa、无添加剂时分别高5.4%和6.9%。在0.1 MPa时,钠主要以NaAlSiO4 和 NaAlSi3O8的形式存在。随添加比的升高灰中NaAlSiO4的含量增加,这有效地减弱了灰的团聚。在4 MPa时,添加剂含量的增加,抑制了低熔点矿物CaSO4的分解,并且显著促进了NaAlSiO4与CaSO4反应生成Na6Ca2Al6Si6O24(SO4)2的反应。本实验提出了高压下氧化硅抑制煤灰中钠和硫释放的机理。Abstract: The effects of silicon oxide additive on the transformation characteristics of sodium and sulfur in coal ash under atmospheric and elevated pressure were investigated in this study. The results indicated that silicon oxide additive significantly inhibited the release of sodium under high pressure. The sodium content in ash with 4% of silicon oxide additive was 3.5% at 0.1 MPa, which was higher than that without additive. However, the sodium content increased to 5.4% without additive and 6.9% with 4% additive at 4 MPa, respectively. The sodium mainly existed in the forms of NaAlSiO4 and NaAlSi3O8 at 0.1 MPa, and the content of NaAlSiO4 increased with increasing additive dosage, which weakened the agglomeration of ash. The decomposition of low melting point mineral CaSO4 was inhibited at 4 MPa, and the formation of Na6Ca2Al6Si6O24(SO4)2 from NaAlSiO4 and CaSO4 was promoted significantly with increasing additive dosage. Furthermore, the inhibition mechanism of sodium and sulfur released from coal ash by silicon oxide under high pressure was proposed.
-
Key words:
- Zhundong coal ash /
- elevated pressure /
- silicon oxide additive /
- sodium /
- sulfur
-
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of HSQ coal
Sample Proximate analysis wad/% Ultimate analysis wad/% M A V FC C H O N S HSQ 14.18 4.06 24.60 57.16 63.19 2.90 15.34 0.51 0.39 Table 2 Ash compositions of HSQ coal sample
Composition Na2O Al2O3 Fe2O3 MgO TiO2 SiO2 SO3 K2O CaO P2O5 Content/% 6.41 4.58 8.28 11.09 0.20 0.28 27.72 0.31 40.46 0.07 Table 3 Ash-500 mass with different addition ratios
Addition ratios w/% 0 1 2 3 4 Mass /g 0.2500±0.0005 0.3500±0.0005 0.4000±0.0005 0.4500±0.0005 0.5000±0.0005 Table 4 Element contents of Ash-1000 with different addition ratios by EDS under 0.1 and 4 MPa
Element w/% O Na Ca Al Si Fe S Mg 0 0.1MPa Area-A 36.82 4.48 17.31 9.98 14.95 11.29 − 5.18 4MPa Area-B 36.79 4.73 17.11 12.76 14.19 9.08 − 5.34 0.1MPa Spot-a 44.70 16.61 − 15.52 20.53 − − 2.64 4MPa Spot-b 49.07 8.97 9.49 14.24 13.59 − 1.78 2.86 4% 0.1MPa Area-C 40.82 4.57 10.91 12.92 19.19 6.32 − 5.28 4MPa Area-D 35.81 3.81 13.52 10.75 19.41 10.94 1.10 4.67 0.1MPa Spot-c 42.86 4.59 11.21 13.94 19.09 5.30 − 3.02 4MPa Spot-d 53.30 8.44 7.72 13.54 15.24 − 2.84 1.92 4MPa Spot-e 23.80 − 43.40 2.01 2.57 2.95 24.41 0.873 “−”: indicates that no relevant crystalline phase was detected -
[1] BLOCH H, RAFIQ S, SALIM R. Economic growth with coal, oil and renewable energy consumption in China: Prospects for fuel substitution[J]. Econ Model,2015,44:104−115. doi: 10.1016/j.econmod.2014.09.017 [2] LIN J, FRIDLEY D, LU H, PRICE L, ZHOU N. Has coal use peaked in China: Near-term trends in China's coal consumption[J]. Energy Policy,2018,123:208−214. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2018.08.058 [3] ZHOU J, ZHUANG X, ALASTUEY A, LI. Geochemistry and mineralogy of coal in the recently explored Zhundong large coal field in the Junggar basin, Xinjiang province, China[J]. Int J Coal Geol,2010,82(1/2):51−67. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2009.12.015 [4] HE C, BAI J, LI W, KONG L, BAI Z, LI W. Iron transformation behavior in coal ash slag in the entrained flow gasifier and the application for Yanzhou coal[J]. Fuel,2019,237:851−859. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.09.134 [5] LI X, LI J, WU G, BAI Z, LI, W. Clean and efficient utilization of sodium-rich Zhundong coals in China: Behaviors of sodium species during thermal conversion processes[J]. Fuel,2018,218:162−173. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.01.027 [6] QIAO H, CHEN S, DONG X, DONG K. Has China's coal consumption actually reached its peak? National and regional analysis considering cross-sectional dependence and heterogeneity[J]. Energy Economics,2019,84:104509. doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2019.104509 [7] SONG G, YANG S, QI X, YANG Z. Occurrence and transformation characteristics of recoverable soluble sodium in high alkali, high carbon fly ash during Zhundong coal gasification in a circulating fluidized bed[J]. Energy Fuels,2018,32(4):4617−4627. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b03410 [8] XU J, YU D, FAN B, ZENG X, CHEN J. Characterization of ash particles from co-combustion with a Zhundong coal for understanding ash deposition behavior[J]. Energy Fuels,2013,28(1):678−684. [9] LI J, ZHU M, ZHANG K, SHEN G, ZHANG D. The mineralogy, morphology and sintering characteristics of ash deposits on a probe at different temperatures during combustion of blends of Zhundong lignite and a bituminous coal in a drop tube furnace[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2016,149:176−186. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.04.021 [10] QI X, SONG G, SONG W, LU Q. Influence of sodium-based materials on the slagging characteristics of Zhundong coal[J]. J Energy Inst,2017,90(6):914−922. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2016.08.003 [11] WEI B, WANG X, TAN H, WANG Y, WANG Z. Effect of silicon-aluminum additives on ash fusion and ash mineral conversion of Xinjiang high-sodium coal[J]. Fuel,2016,181:1224−1229. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.02.072 [12] SHI H, WU Y, ZHANG M, ZHANG Y, LYU J. Ash deposition of Zhundong coal in a 350 MW pulverized coal furnace: Influence of sulfation[J]. Fuel,2020,260:116317. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116317 [13] YANG S, SONG G, NA Y, YANG Z. Alkali metal transformation and ash deposition performance of high alkali content Zhundong coal and its gasification fly ash under circulating fluidized bed combustion[J]. Appl Therm Eng,2018,141:29−41. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.113 [14] LIU Y, GUAN Y, ZHANG K. CO2 gasification performance and alkali/alkaline earth metals catalytic mechanism of Zhundong coal char[J]. Korean J Chem Eng,2018,35(4):859−866. doi: 10.1007/s11814-017-0357-x [15] TAO Y, WANG X, TAN H, WEI B, ZHANG L. Existence and release of sodium in Zhundong coal: Effects of treating temperature and silica additives[J]. Int J Oil Gas Coal Technol,2016,11(1):63−74. doi: 10.1504/IJOGCT.2016.073774 [16] DING L, GAO Y, LI X, WANG W, XUE Y, ZHU X, XU K, LUO G, YAN H. A novel CO2-water leaching method for AAEM removal from Zhundong coal[J]. Fuel,2019,237:786−792. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.084 [17] FAN Y, LYU Q, ZHU Z, ZHANG H. The impact of additives upon the slagging and fouling during Zhundong coal gasification[J]. J Energy Inst,2020,93(4):1651−1665. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2020.02.003 [18] HUI A, LV Y, NIU Y, LI S, LEI Y, LI P. Effects of leaching and additives on the formation of deposits on the heating surface during high-Na/Ca Zhundong coal combustion[J]. J Energy Inst,2021,94:319−328. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2020.09.016 [19] LI G, LI S, HUANG Q, YAO Q. Fine particulate formation and ash deposition during pulverized coal combustion of high-sodium lignite in a down-fired furnace[J]. Fuel,2015,143:430−437. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.11.067 [20] WANG C, ZHAO L, SUN R, HU Y, CHEN W, DU Y, CHE D. Effects of silicon-aluminum additives on ash mineralogy, morphology, and transformation of sodium, calcium, and iron during oxy-fuel combustion of zhundong high-alkali coal[J]. Int J Greenh Gas Con,2019,91:102832. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2019.102832 [21] DENG S, TAN H, WEI B, WANG X, YANG F, XIONG X. Investigation on combustion performance and ash fusion characteristics of Zhundong coal co-combustion with coal gangue[J]. Fuel,2021,294:120555. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120555 [22] WANG X, XU Z, WEI B, ZHANG L, TAN H, YANG T, DUIC N. The ash deposition mechanism in boilers burning Zhundong coal with high contents of sodium and calcium: A study from ash evaporating to condensing[J]. Appl Therm Eng,2015,80:150−159. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.01.051 [23] ZHANG L, LI Z, HE W, ZHU J, ZHAO L, ZHANG X. Study on the change of organic sulfur forms in coal during low-temperature oxidation process[J]. Fuel,2018,222:350−361. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.02.157 [24] SONG G, SONG W, QI X, LU Q. Transformation characteristics of sodium of zhundong coal combustion/gasification in circulating fluidized bed[J]. Energy Fuels,2016,30(4):3473−3478. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00028 [25] YANG H, JIN J, LIU D, WANG Y, ZHAO B. The influence of vermiculite on the ash deposition formation process of Zhundong coal[J]. Fuel,2018,230:89−97. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.05.049 [26] DUAN W, YU Q, LIU J, WU T, YANG F, QIN Q. Experimental and kinetic study of steam gasification of low-rank coal in molten blast furnace slag[J]. Energy,2016,111:859−868. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.06.052 [27] LIANG C, LYU Q, NA Y, WANG X. Gasification of preheated coal: Experiment and thermodynamic equilibrium calculation[J]. J Energy Inst,2019,92(4):1005−1013. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2018.07.006 [28] WALL T, LIU G, WU H, GUPTA S, LUCAS J, HARRIS D. The effects of pressure on coal reactions during pulverised coal combustion and gasification[J]. Prog Energy Combust Sci,2002,28(5):405−433. doi: 10.1016/S0360-1285(02)00007-2 [29] WANG J, WEI B, ABUDOUREHEMAN M, LI X, TAN H, LI G. Effect of pressure on the transformation characteristics of inorganic minerals Na/S in Zhundong coal ash[J]. J Energy Inst,2021,98:161−171. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2021.06.007 [30] BARROSO J, BALLESTER J, FERRER L. M, JIMENEZ S. Study of coal ash deposition in an entrained flow reactor: Influence of coal type, blend composition and operating conditions[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2006,87(8):737−752. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2006.02.004 [31] LIU H, LUO C, KATO S, UEMIYA S, KOJIMA T, TOMINAGA H. Mineral reaction and morphology change during gasification of coal in CO2 at elevated temperatures[J]. Fuel,2003,82(5):523−530. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00292-2 [32] FERMOSO J, STEVANOV C, PEVIDA C, RUBIERA F, PIS J. High-pressure gasification reactivity of biomass chars produced at different temperatures[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2009,85(1/2):287−293. [33] SATHE C, HAYASHI J, LI C, CHIBA T. Release of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during rapid pyrolysis of a Victorian brown coal at elevated pressures[J]. Fuel,2003,82(12):1491−1497. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(03)00070-X [34] JING N, CHENG L, LUO Z, CEN K, ZHANG D. Effect of temperature and pressure on the mineralogical and fusion characteristics of Jincheng coal ash in simulated combustion and gasification environments[J]. Fuel,2013,104:647−655. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.05.040 [35] SHAKRAVARTY S, MOHANTY A, TRIPATHY R, MANDAL G K, RAVIATHUL BASARIYA M, SHARMA M. Composition, mineral matter characteristics and ash fusion behavior of some Indian coals[J]. Fuel,2015,150:96−101. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.02.015 [36] NIU Y, SONG Y, ZHANG X, LIANG Y, WANG D, HUI S. Effects of leaching and additives on the ash fusion characteristics of high-Na/Ca Zhundong coal[J]. J Energy Inst,2019,92(4):1115−1122. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2018.06.006 [37] WANG Y, JIN J, LIU D, YANG H, LI S. Understanding ash deposition for the combustion of Zhundong coal: Focusing on fifferent additives effects[J]. Energy Fuels,2018,32(6):7103−7111. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b00384 [38] XU L, LIU J, KANG Y, MIAO Y, REN W, WANG T. Safely burning high alkali coal with kaolin additive in a pulverized fuel boiler[J]. Energy Fuels,2014,28(9):5640−5648. doi: 10.1021/ef501160f [39] LIU D, LI W, LI S, SONG W, LIU D, KONG R. Transformation characteristics of sodium, chlorine and sulfur of Zhundong coal during O2/CO2 combustion in circulating fluidized bed[J]. Energy,2019,185:254−261. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.07.043 [40] ZAHNG X, ZHANG H, NA Y. Transformation of sodium during the ashing of Zhundong coal[J]. Proc Eng,2015,102:305−314. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.01.147 [41] WANG C, FAN G, WANG C, CHENG W, CHE D. Effects of coal blending on transformation of alkali and alkaline-earth metals and iron during oxy-fuel co-combustion of Zhundong coal and high-Si/Al coal[J]. J Energy Inst,2021,94:96−106. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2020.11.002 [42] WANG C, ZHAO L, HAN T, CHEN W, YAN Y, XI J, CEH D. Release and transformation behaviors of sodium, calcium, and iron during oxy-fuel combustion of Zhundong coals[J]. Energy Fuels,2018,32(2):1242−1254. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b03200 [43] SONG G, YANG S, SONG W, QI X. Release and transformation behaviors of sodium during combustion of high alkali residual carbon[J]. Appl Therm Eng,2017,122:285−296. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.04.139 [44] ZHANG L, DONG X, HU Z, YANG X, DUAN C. The effect of additive on sodium transformation and existing forms during zhundong coal combustion[J]. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng,2018,394:042039. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/394/4/042039 [45] LIU X, YU G, XU J, LIANG Q, LIU H. Viscosity fluctuation behaviors of coal ash slags with high content of calcium and low content of silicon[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2017,158:115−122. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.12.013 [46] WU H, BRYANT G, WALL T. The effect of pressure on ash formation during pulverized coal combustion[J]. Energy Fuels,2000,14(4):745−750. doi: 10.1021/ef990080w -





 下载:
下载: