Pyrolysis magnetization of low-rank coal and distribution characteristics of sulfur and heavy metals in char products
-
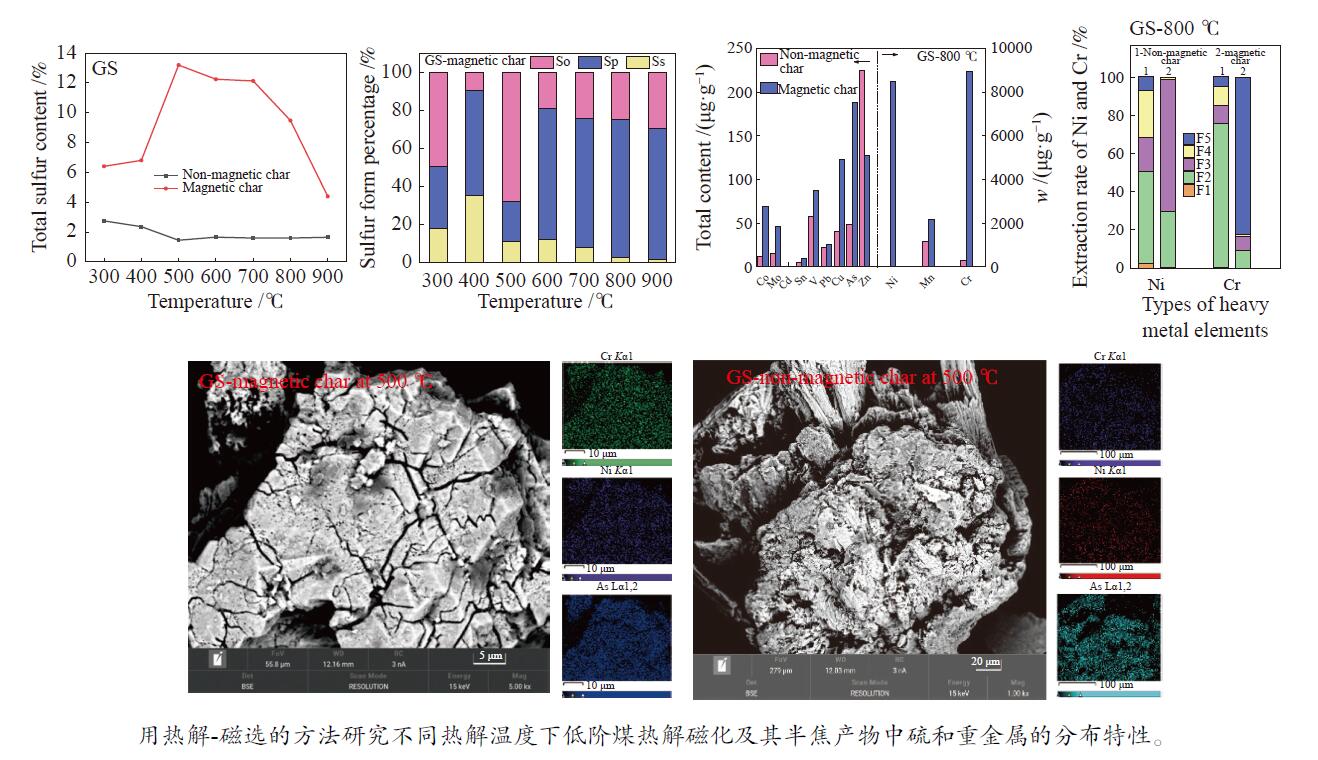
摘要: 用热解和磁选相结合的方法,研究了不同热解温度下甘肃褐煤和山西次烟煤热解磁化及其半焦产物中硫和重金属的分布特性。通过ICP-OES和ICP-MS分别对半焦中的硫和重金属元素含量进行分析测定,利用XRD和SEM-EDS对半焦的矿物组成和表观形貌进行了表征。结果表明,甘肃褐煤和山西次烟煤在最佳条件下的磁选脱硫率最高可以分别达到52.37%和17.54%;这与黄铁矿在热解过程中的相变行为有关。山西次烟煤半焦的磁选脱硫率低于甘肃褐煤半焦主要是由于其伴生矿物质的赋存包裹和有机质对黄铁矿在热解过程中的转化产生了影响。Ni和Cr与Fe-S矿物的亲和性较强,其随硫更多地富集到磁性半焦中;在800 ℃时,甘肃煤和山西煤磁性半焦中Cr含量分别比非磁性半焦中多8698.25和32327.47 µg/g。低阶煤热解磁化及其半焦产物中硫和重金属的分布特性为脱除煤中硫和重金属元素提供了数据支撑和新思路。Abstract: The distribution of sulfur and heavy metals in char of Gansu lignite and Shanxi subbituminous coal was studied by means of pyrolysis and magnetic separation at different pyrolysis temperatures. The contents of sulfur and heavy metal elements in char were analyzed and determined by ICP-OES and ICP-MS, and the mineral composition and apparent morphology of char were characterized by XRD and SEM-EDS. The results show that the highest desulfurization rates of Gansu lignite and Shanxi Subbituminous coal can reach 52.37% and 17.54% respectively under optimal conditions. This is related to the phase transition behavior of pyrite during pyrolysis. The desulphurization rate of Shanxi subbituminous char is lower than that of Gansu lignite char mainly because the occurrence and inclusion of associated minerals and the organic matter influence the transformation of pyrite during pyrolysis. Ni and Cr have a strong affinity with Fe–S minerals, which are enriched into magnetic char with sulfur. At 800 ℃, Cr content in magnetic char of Gansu coal and Shanxi coal is 8698.25 µg/g and 32327.47 µg/g higher than that in non-magnetic char, respectively. The pyrolytic magnetization of low-rank coal and the distribution of sulfur and heavy metals in its char products provide data support and a new idea for removal of sulfur and heavy metals from coal.
-
Key words:
- low-rank coal pyrolysis /
- char /
- magnetization /
- sulfur /
- heavy metals
-
表 1 GS和SX的工业分析、元素分析和硫形态分析
Table 1 Industrial analysis, elemental analysis and sulfur form analysis of GS and SX
Coal Industrial analysis w/% Elemental analysis w/% Sulfur form wad/% Mad Aad Vdaf FCdaf a Cdaf Hdaf Odaf a Ndaf St,ad Ss Sp Soa GS 9.69 22.96 46.68 53.32 70.02 5.78 19.68 2.01 1.69 0.45 0.23 1.01 SX 3.09 44.49 39.76 60.24 69.27 5.76 8.85 1.07 7.89 0.06 4.28 3.55 note: ad: air drying base; daf: dry without ash-based; Ss: Sulphate sulfur; Sp: Pyrite sulfur; So: Organic sulfur 表 2 煤样的灰分分析
Table 2 Ash analysis of coal samples
Coal Content/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO TiO2 SO3 K2O Na2O P2O5 Other GS 47.75 19.91 8.50 7.24 1.38 1.39 9.71 2.15 0.92 0.35 0.70 SX 41.42 35.24 18.92 0.23 0.08 3.40 0.14 0.21 0 0.22 0.13 表 3 不同热解温度下磁性和非磁性半焦中重金属元素含量的差值
Table 3 Difference between the content of heavy metal elements in magnetic and non-magnetic chars at different pyrolysis temperatures
Types of heavy metal AC /(µg·g−1) GS SX 400 ℃ 600 ℃ 800 ℃ 600 ℃ 800 ℃ Co 19.33 12.53 57.99 32.18 106.23 Mo 12.55 4.22 31.13 84.79 114.57 Cd 0.06 1.79 0.45 0.31 0.05 Sn 3.51 −12.42 3.53 6.52 4.13 V 17.23 0.28 30.50 74.78 104.11 Pb 20.76 65.18 3.76 58.09 18.68 Cu 33.34 28.53 82.67 105.73 170.16 As 210.42 159.01 139.64 54.05 59.16 Zn 24.81 60.05 −97.29 50.98 −66.68 Ni 1791.29 854.21 8459.47 2526.26 11608.49 Mn 1990.32 1784.11 1002.25 6472.12 −1105.22 Cr 3516.63 1282.53 8698.25 6728.40 32327.47 -
[1] U. S. Energy Information Administration. International energy outlook 2021[EB/OL]. www. eia. gov/outlooks/ieo, 2021. [2] 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2020年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020.National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. Statistical Communique of 2020 National Economic and Social Development of the People's Republic of China[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020. [3] 许洁. 典型煤灰与混合灰熔融特性及粘温特性研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2015.XU Jie. Melting and viscosity-temperature characteristics of typical coal ash and mixed ash[D]. Shanghai: East China University Science and Technology, 2015. [4] 李安. 浅析低阶煤提质技术现状及发展[J]. 石化技术,2018,25(2):281.LI An. The present situation and development of quality improvement technology of low-rank coal are analyzed[J]. Petrochem Ind Technol,2018,25(2):281. [5] 王顺庆. 我国的生态危险管理与生态保险[J]. 南京财经大学学报,2005,(1):55−59.WANG Shun-qing. Ecological danger management and ecological insurance in our country[J]. J Nanjing Univ Finance Economics,2005,(1):55−59. [6] SAIKIA J, SAIKIA P, BORUAH R, SAIKIA B. Ambient air quality and emission characteristics in and around a non-recovery type coke oven using high sulphur coal[J]. Sci Total Environ,2015,530−531:304−313. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.109 [7] 赵跃武, 邱宏伟, 洪涛. 煤中硫的迁移规律研究[J]. 中国新技术新产品,2012,(3):154.ZHAO Yue-wu, QIU Hong-wei, HONG Tao. Study on the transfer law of sulfur in coal[J]. China New Technol New Prod,2012,(3):154. [8] 孙成功, 李保庆, SNAPE COLIN E. 煤中有机硫形态结构和热解过程硫变迁特性的研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,1997,25(4):71−75.SUN Cheng-gong, LI Bao-qing, SNAPE COLIN E. Study on the morphological structure of organic sulfur in coal and the transition characteristics of sulfur during pyrolysis[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,1997,25(4):71−75. [9] 秦建华. 选煤是当前我国煤炭脱硫的首选方法[J]. 选煤技术,2000,(1):10−12.QIN Jian-hua. Coal preparation is the preferred method of coal desulphurization[J]. Coal Prep Technol,2000,(1):10−12. [10] 张鸿波, 边炳鑫, 康华. 当前我国煤炭脱硫方法的应用[J]. 国外金属矿选矿,2002,(8):20−22.ZHANG Hong-bo, BIAN Bing-xin, KANG Hua. The application of current coal desulphurization method[J]. Foreign Metal Ore Dress,2002,(8):20−22. [11] 马涛. 关于煤中脱硫法的探讨[J]. 内蒙古煤炭经济,2001,(1):85−88.MA Tao. Discussion on desulphurization in coal[J]. Inner Mongolia Coal Economy,2001,(1):85−88. [12] 莫海燕. 低阶煤高效清洁分质利用问题研究[J]. 化工设计通讯,2022,48(4):175−177.MO Hai-yan. Study on the high-efficiency, clean and quality utilization of low-rank coal[J]. Chem Eng Des Commun,2022,48(4):175−177. [13] SHEN Y, HU Y, WANG M, BAO W, CHANG L, XIE K. Speciation and thermal transformation of sulfur forms in high-sulfur coal and its utilization in coal-blending coking process: A review[J]. Chin J Chem Eng,2021,35:70−82. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2021.04.007 [14] CUI T, ZHOU Z, DAI Z, LI C, YU G, WANG F. Primary fragmentation characteristics of coal particles during rapid pyrolysis[J]. Energy Fuels,2015,29(10):6231−6241. [15] 李梅, 杨俊和, 夏红波, 常海洲, 孙慧. 典型炼焦高硫煤热解过程中硫迁移规律研究[J]. 煤炭转化,2013,36(4):41−45.LI Mei, YANG Jun-he, XIA Hong-bo, CHANG Hai-zhou, SUN Hui. Study on sulfur migration law during pyrolysis of typical coking high-sulfur coal[J]. Coal Convers,2013,36(4):41−45. [16] 李梅, 杨俊和, 张启锋, 夏红波, 常海洲, 孙慧. 高硫煤镜质组热解过程中结构变化及有机硫形态变迁规律研究[J]. 燃料化学学报.,2014,42(2):138−145.LI Mei, YANG Jun-he, ZHANG Qi-feng, XIA Hong-bo, CHANG Hai-zhou, SUN Hui. Structure change and organic sulfur forms transformation during pyrolysis of high-sulfur vitrinite[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2014,42(2):138−145. [17] 左伟, 骆振福, 吴万昌, 陈尚龙, 郭进, 刘小军, 籍永华. 高硫煤的干法分选技术[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用,2009,(6):17−21.ZUO Wei, LUO Zhen-fu, WU Wan-chang, CHEN Shang-long, GUO Jin, LIU Xiao-jun, JI Yong-hua. Dry separation technology of high sulfur coal[J]. Coal Process Compr Util,2009,(6):17−21. [18] 王东路, 李勇. 高梯度磁选脱硫试验研究[J]. 山东电力技术,2004,(3):7−11.WANG Dong-lu, LI Yong. Experimental study on desulfurization by high gradient magnetic separation[J]. Shandong Electric Power Technol,2004,(3):7−11. [19] M S CELIK, I Y. A new physical process for desulfurization of low-rank coals[J]. Fuel,2000,79:1665−1669. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(00)00013-2 [20] 刘振环. 低温干燥/热解预处理强化低阶煤干法磁选研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2016.LIU Zhen-huan. Study on enhancement of dry magnetic Separation of low rank coal by low temperature drying/pyrolysis pretreatment[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016. [21] RENDA D, ONAL G, MUSTAFAEV I. Consecutive thermomagnetic beneficiation of Turkish lignites[J]. Fuel,2001,80(5):641−644. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(00)00144-7 [22] 田冲. 煤中痕量元素与矿物关联性及其排放特性的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2014.TIAN Chong. Study on the correlation and emission characteristics of Trace elements and Minerals in coal[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2014. [23] 段飘飘. 西南地区高硫煤有害元素地球化学特征及其洗选分配规律[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017.DUAN Piao-piao. Geochemical characteristics and distribution rules of harmful elements in high sulfur coal in Southwest China[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017. [24] YANG Y, CHU M, GAO M, JIA C, ZHOU L, CHANG Z. The effect of strengthening thermal fragmentation by rotary kiln on sulfur distribution of fragmentation char with low-rank coal[J]. Fuel,2022,323:124444. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124444 [25] YAN J, BAI Z, ZHAO H, BAI J, LI W. Inappropriateness of the standard method in sulfur form analysis of char from coal pyrolysis[J]. Energy Fuels,2012,26(9):5837−5842. [26] 李沙. 煤粉燃前强磁选净化机理及试验研究[D]. 河南: 河南理工大学, 2011.LI Sha. Study on purification mechanism and experiment of pulverized coal by high intensity magnetic separation before burning[D]. Henan: Henan Polytechnic University, 2011. [27] GUO R, YANG J, LIU D, LIU Z. Transformation behavior of trace elements during coal pyrolysis[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2002,77:137−143. [28] 王丽. 超低排放机组中汞、砷和硒等重金属的迁移特性研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.WANG Li. Study on migration characteristics of heavy metals such as mercury, Arsenic and selenium in ultra-low emission units[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. [29] SPEARS D A. The determination of trace element distributions in coals using sequential chemical leaching—A new approach to an old method[J]. Fuel,2013,114:31−37. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.09.028 [30] 王灿, 焦红光, 陈清如, 李沙, 路阳. 低温热解强化煤粉磁选脱硫效果的实验研究[J]. 煤炭转化,2009,32(3):73−77.WANG Can, JIAO Hong-guang, CHEN Qing-ru, LI Sha, LU Yang. Experimental study on the effect of low temperature pyrolysis on desulfurization by magnetic separation of pulverized coal[J]. Coal Convers,2009,32(3):73−77. [31] ZHAO H, BAI Z, BAI J, GUO Z, KONG L, LI W. Effect of coal particle size on distribution and thermal behavior of pyrite during pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2015,148:145−151. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.01.104 [32] 杨晓杰, 丁述理. 京西煤系高岭石的铁占位[J]. 河北建筑科技学院学报(自然科学版),2005,22(3):73−75.YANG Xiao-jie, DING Shu-li. Study on the kaolin in coal measures of West Beijing by Mossbauer spectroscopy[J]. J Hebei Inst Architectural Sci Technol,2005,22(3):73−75. [33] XU F, CHU M, CHANG Z, GU Z, SUN X. Sulfur release and transformation during the pyrolysis of lignite with different particle sizes[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2021,156:105162. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105162 [34] GUO R, YANG J, LIU D, LIU Z. The fate of As, Pb, Cd, Cr and Mn in a coal during pyrolysis[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2003,70(2):555−562. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2370(03)00025-1 [35] FINKELMAN R B. Modes of occurrence of potentially hazardous elements in coal: Levels of confidence[J]. Fuel Process Technol,1994,39(1/3):21−34. doi: 10.1016/0378-3820(94)90169-4 [36] SEKINE Y, SAKAJIRI K, KIKUCHI E, MATSUKATA M. Release behavior of trace elements from coal during high-temperature processing[J]. Powder Technol,2008,180(1/2):210−215. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2007.03.012 [37] 李扬. 煤气化过程中微量元素的迁移转化及高温脱除的实验研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2011.LI Yang. Experimental study on migration, transformation and high-temperature removal of trace elements during coal gasification[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2011. -





 下载:
下载: