Electrocatalyst hydrogenation of lignol-derived compounds: Conversion regularity and product selectivity
-
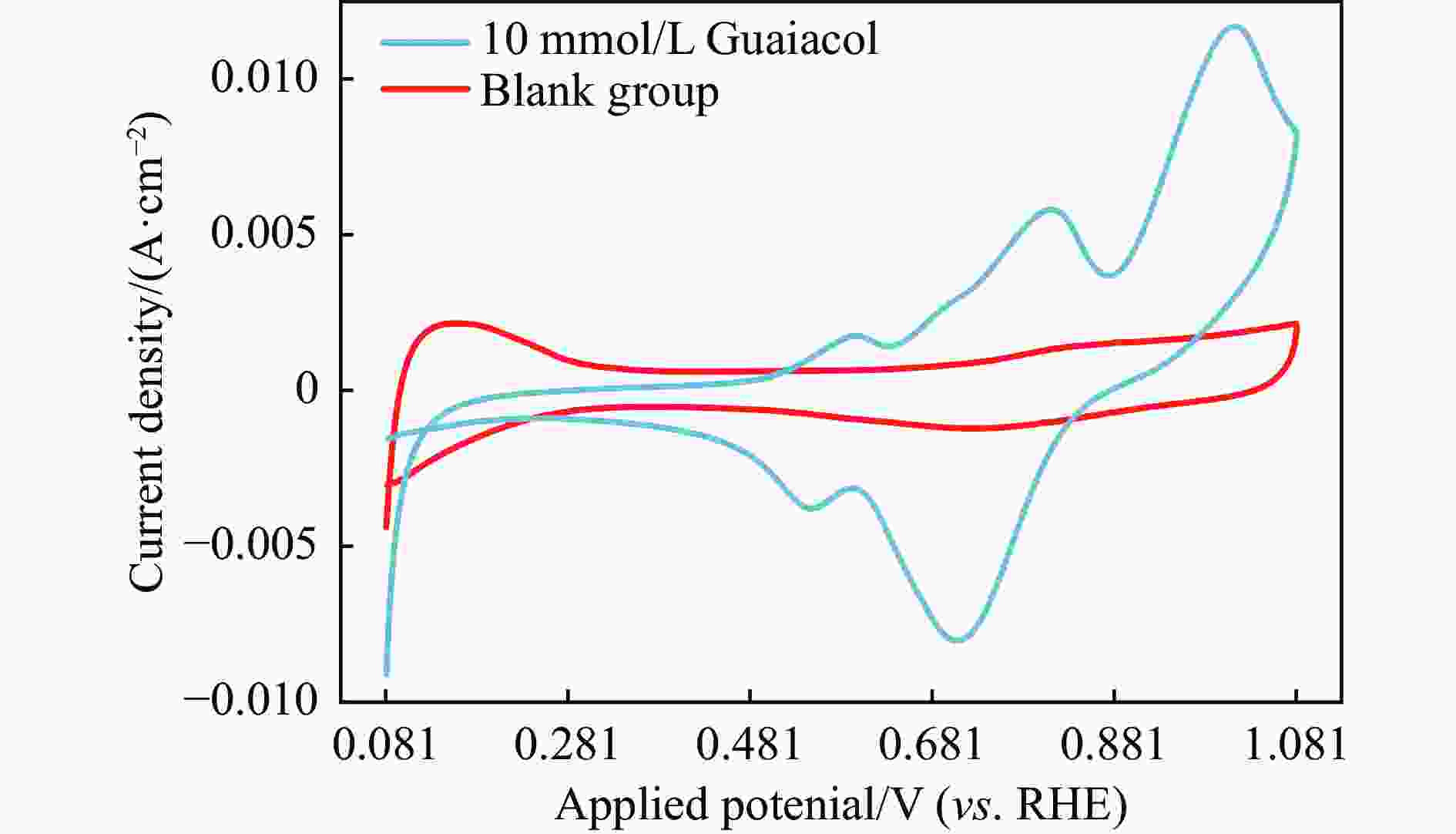
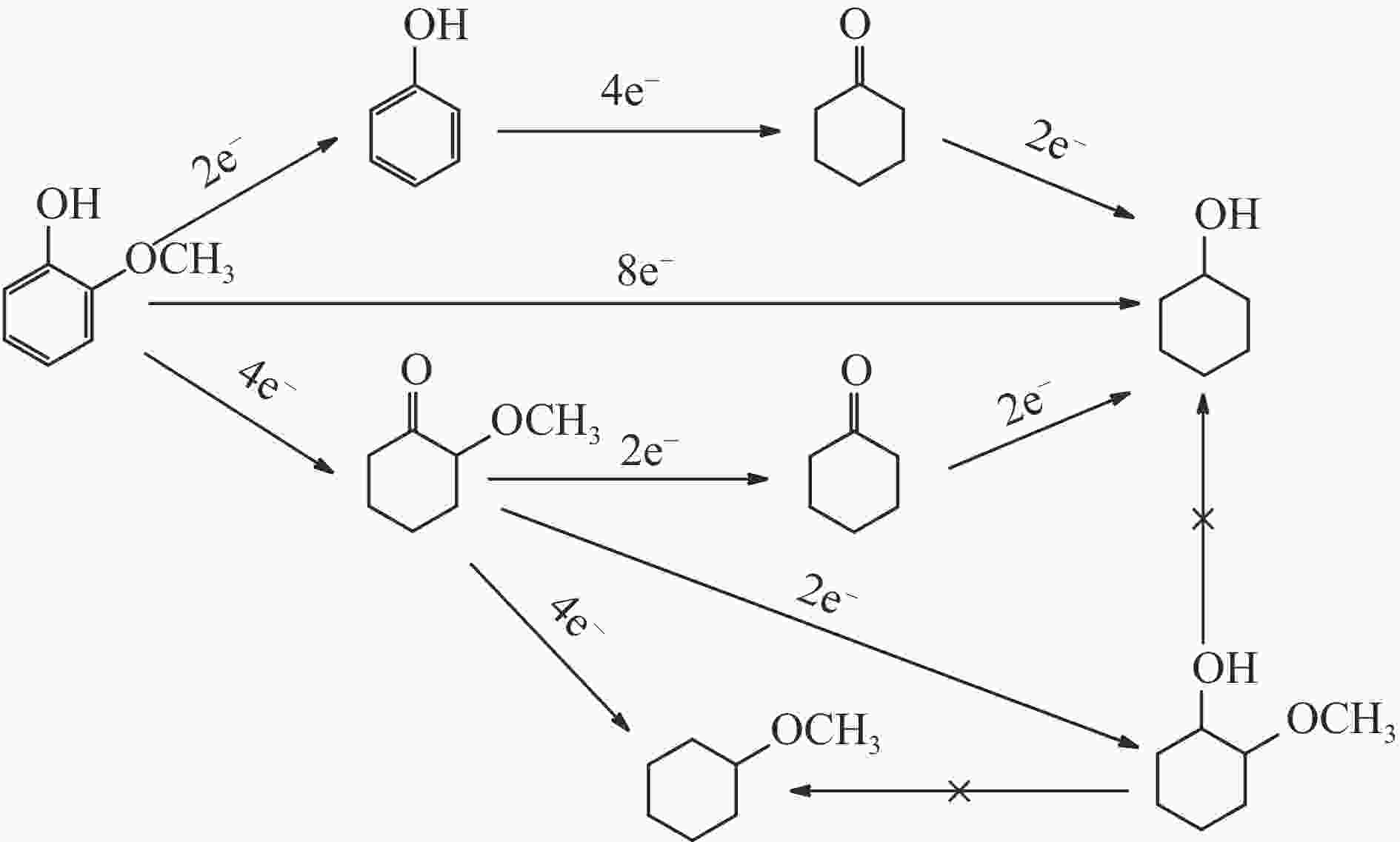
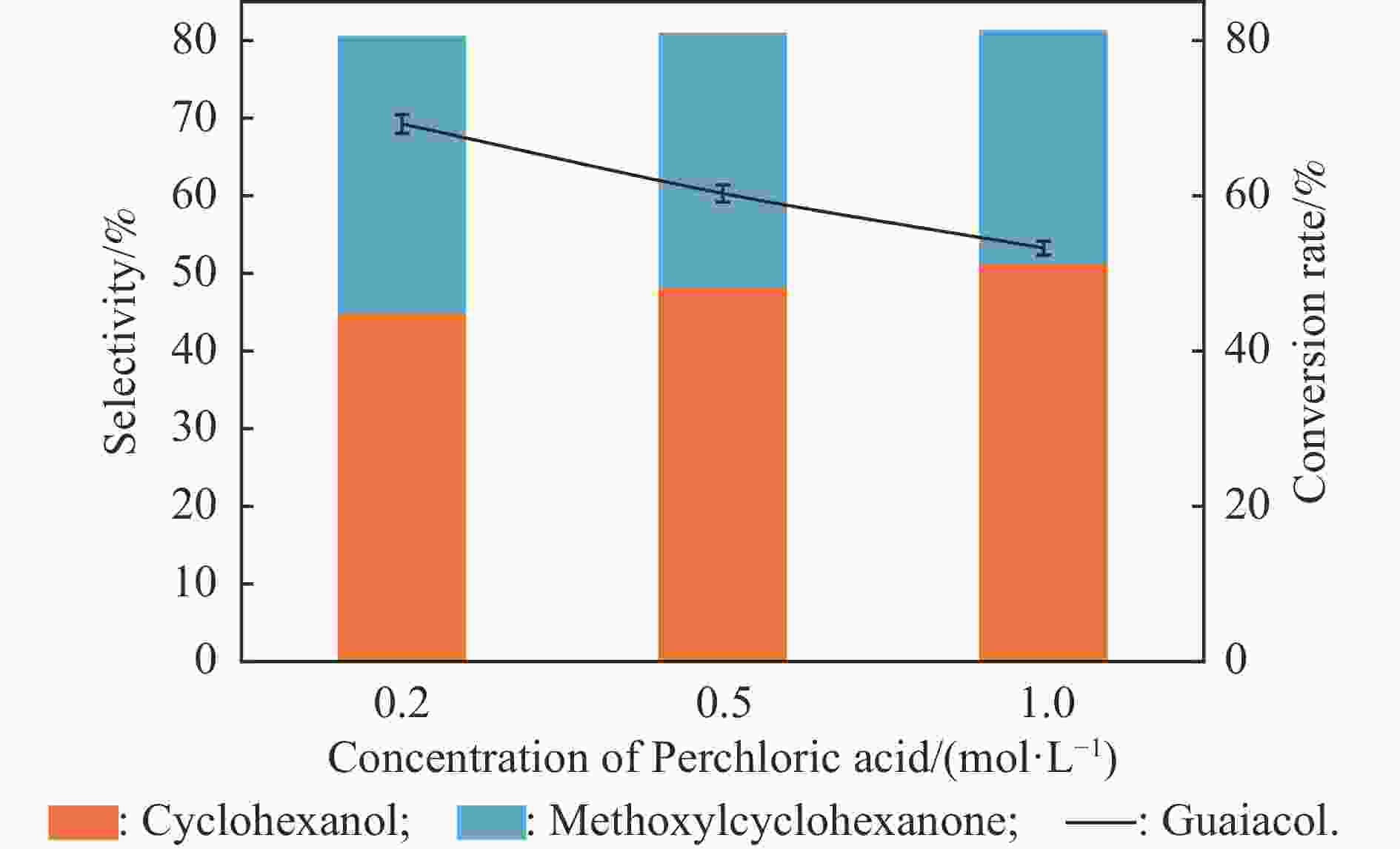
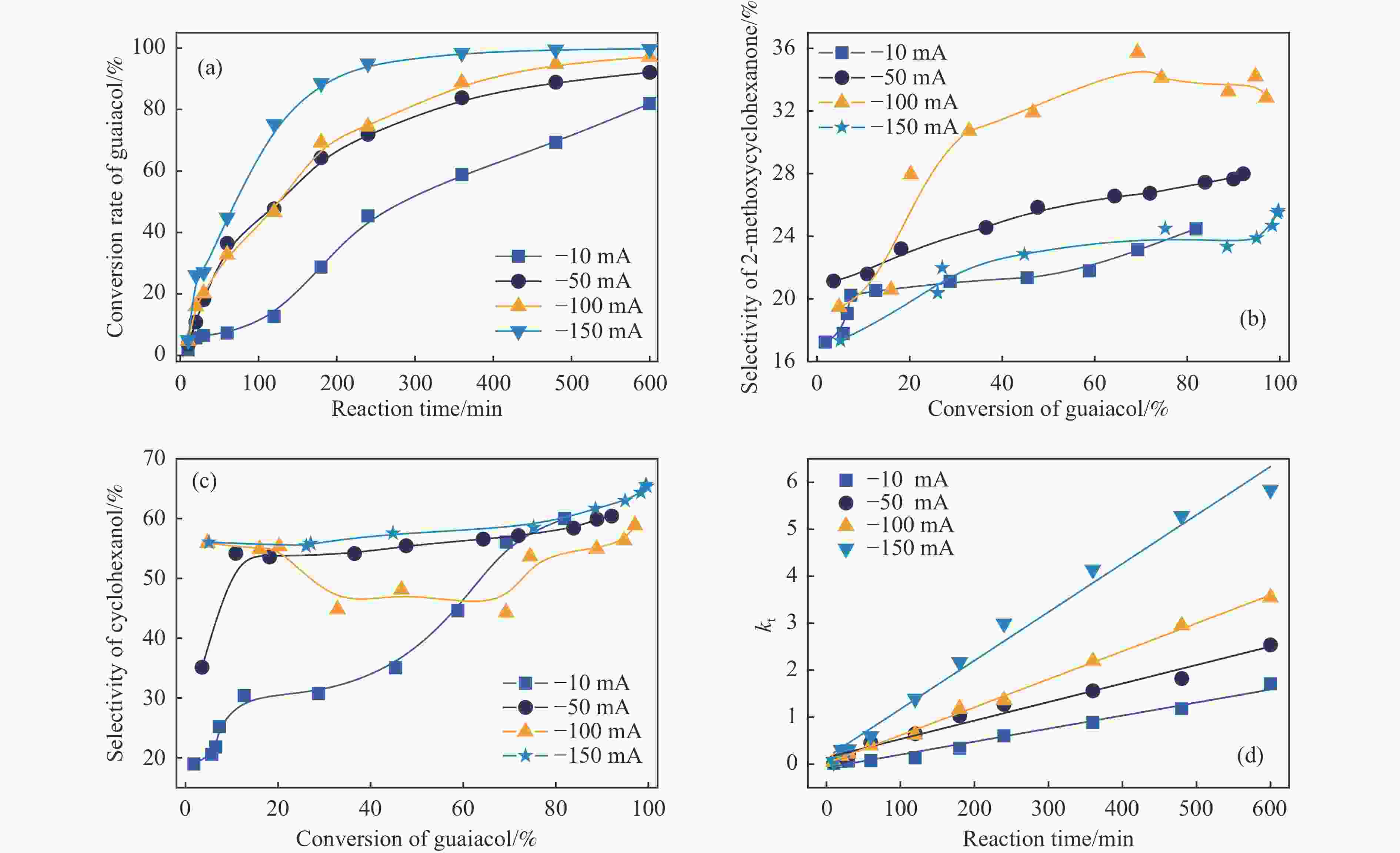
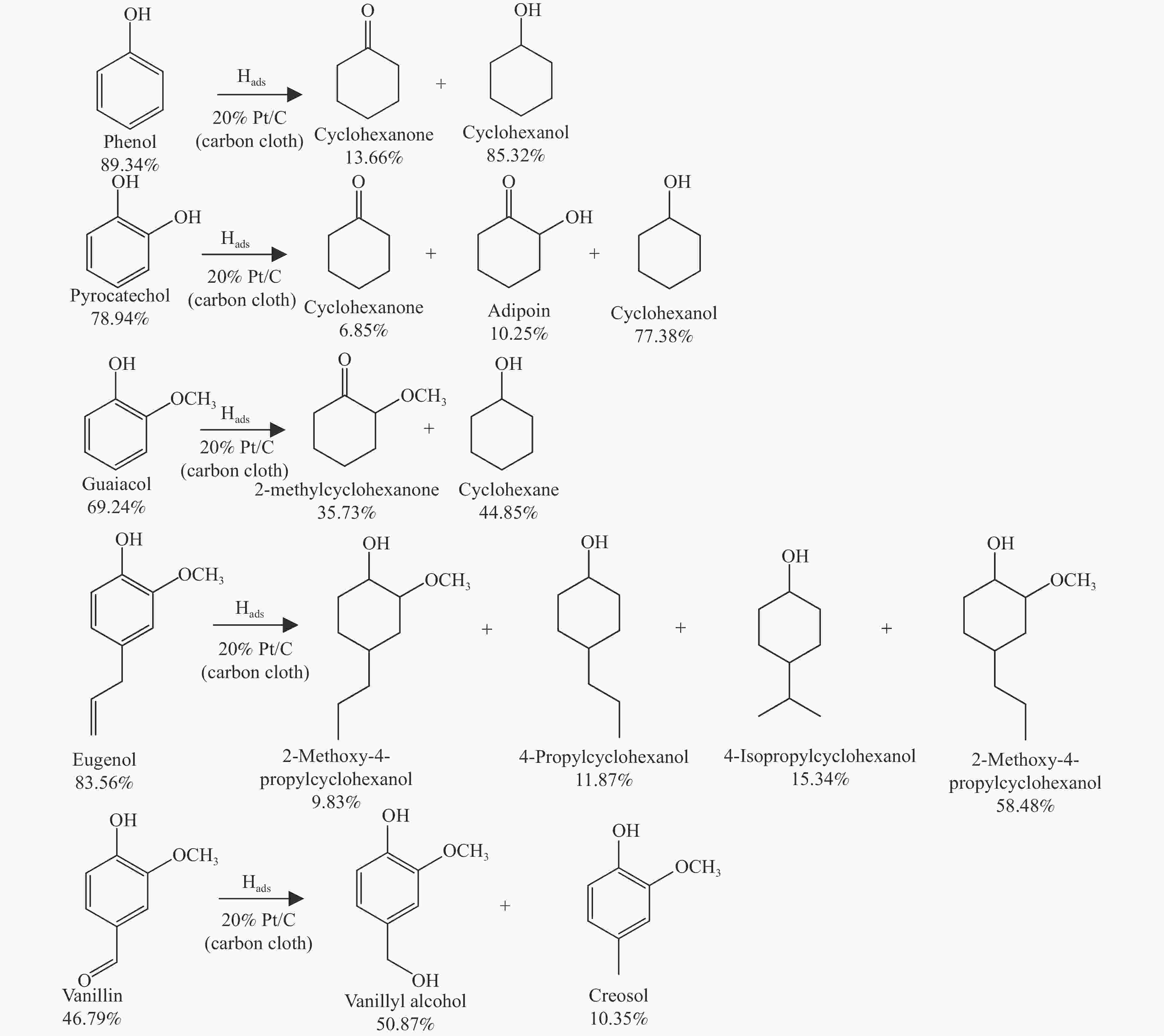
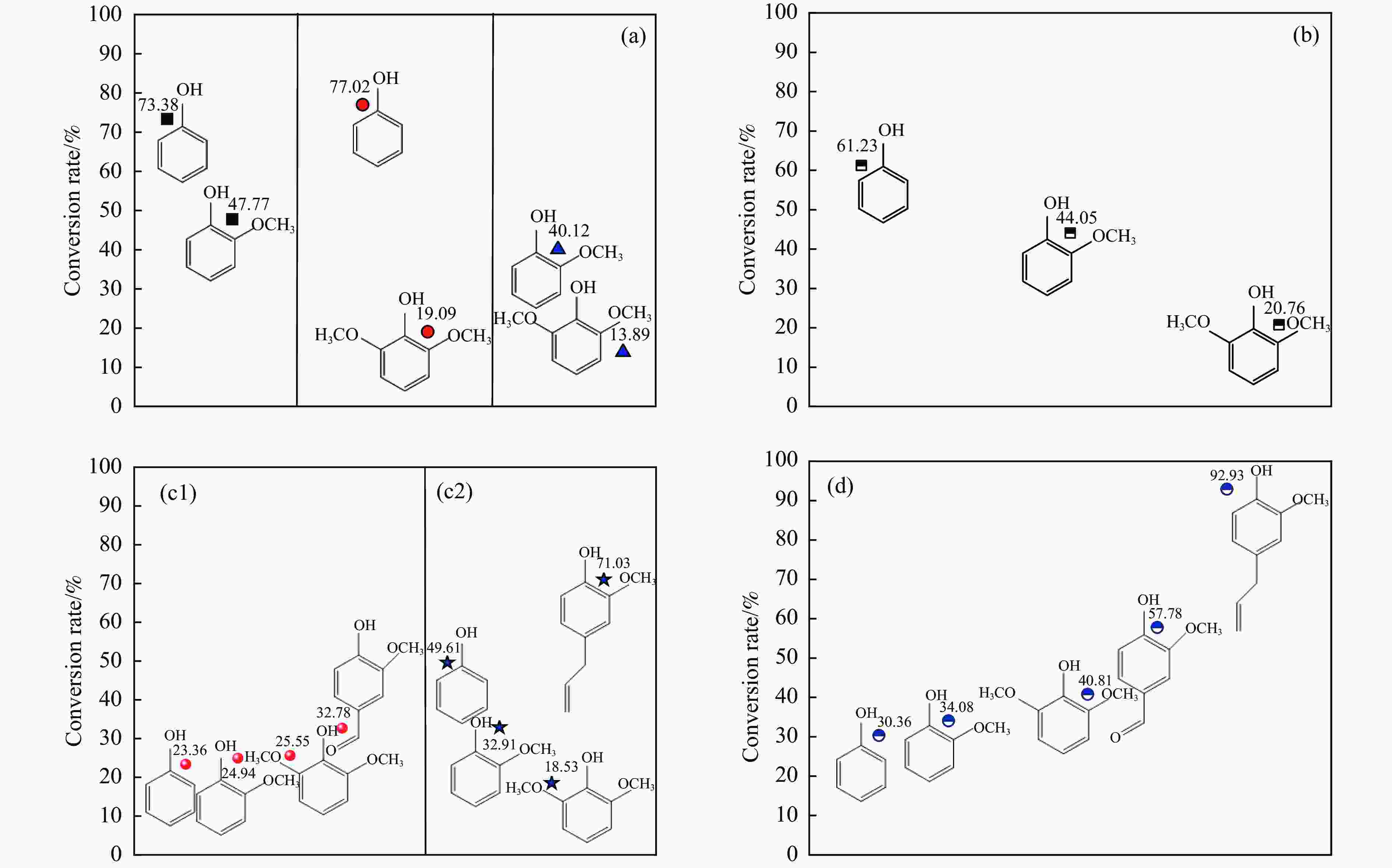
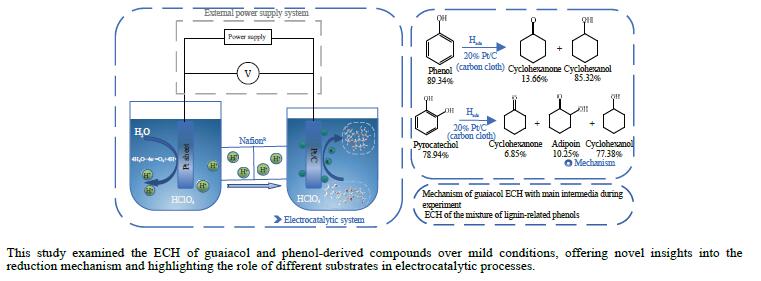
摘要: 酚类衍生物是生物油的关键组分,对其电催化加氢(ECH)性质的深入理解对于高效利用生物油至关重要。基于此种考量,本工作研究了生物油中代表性物质愈创木酚的电催化加氢性能,探讨了其电催化加氢的反应机制、转化率和产品选择性在不同反应条件下(温度:40−80 °C,高氯酸浓度:0.2–1.0 mol/L,电流强度:(–10)–(–150) mA)的变化。同时,也探索了愈创木酚中间产物(2-甲氧基环己酮和环己酮)等对其电催化加氢的影响。结果表明,愈创木酚的ECH转化率随温度和电流强度的提高而增加,但高氯酸浓度的增加则对转化率具有相反的影响。同时发现,中间产物的存在增强了愈创木酚的电催化加氢转化率,尤其是2-甲氧基环己酮,其效果更为显著。在此基础上,对其他种酚类衍生物(包括苯酚、邻苯二酚、愈创木酚、丁香酚和香草醛)及其混合物的电催化加氢机制的进一步研究中发现,模型化合物的电催化转化率与苯环上官能团的复杂程度成反比。在其中结构最简单的苯酚具有最高的转化率(89.34%),而由于结构更复杂,香草醛的转化率最低,仅为46.79%。同时,在多组分混合物的电催化加氢研究中发现,模型化合物的协同和竞争机制将显著影响各自的转化率。Abstract: Phenolic derivatives, crucial components of bio-oil, require thorough understanding of their electrocatalytic hydrogenation (ECH) properties for efficient bio-oil utilization. This study investigated guaiacol, a representative phenolic derivative in bio-oil, focusing on its ECH mechanism, conversion, and product selectivity under varied conditions (temperature: 40−80 °C, perchloric acid concentration: 0.2−1.0 mol/L, current intensity: ((−10)−(−150) mA). Additionally, this study also explored the influence of intermediate products (2-methoxycyclohexanone and cyclohexanone) on both the conversion rate and the selectivity of the products. The experiment had revealed that guaiacol's ECH conversion rate improved with higher temperature and current intensity, whereas an increase in perchloric acid concentration negatively affected the conversion. Significantly, the presence of intermediate products, especially 2-methoxycyclohexanone, markedly enhanced the ECH conversion of guaiacol. Investigating further into the ECH mechanism of other phenolic derivatives, including phenol, pyrocatechol, guaiacol eugenol, and vanillin, as well as their combination, revealed a trend where conversion rates inversely correlated with the complexity of the functional groups on the benzene ring. Specifically, phenol, with its simpler structure, showed the highest conversion rate at 89.34%, in stark contrast to vanillin which, owing to its more complex structure, exhibited the lowest at 46.79%. In our multi-component mixture studies, it was observed that synergistic and competitive interactions significantly alter ECH conversion rates, with some mixtures showing enhanced conversion rate indicative of synergistic effects.
-
Table 1 The effect on ECH conversion exerted by blending of 2-methoxycyclohexanone and cyclohexanone
Time/min Conversion rate of the blank groupa/% Conversion rate of the blank group with 2-methoxycyclohexanonea/% Conversion rate of blank group with cyclohexanonea/% 10 4.74 22.88 8.21 20 15.99 29.48 18.65 30 20.23 32.00 21.49 60 32.83 41.94 40.21 120 46.66 66.19 58.08 180 69.24 68.36 67.35 240 74.46 74.93 80.79 360 88.85 83.43 87.62 480 94.79 87.90 91.92 600 97.12 89.04 94.40 a: Reaction condition: t= 60 °C, c(guaiacol)= 10 mmol/L, c(HClO4) = 0.2 mol/L, Iw= −100 mA. -
[1] DAI L, WANG Y, LIU Y, et al. A review on selective production of value-added chemicals via catalytic pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass[J]. Sci Total Environ,2020,749:142386. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142386 [2] FAKAYODE O A, WAHIA H, ZHANG L, et al. State-of-the-art co-pyrolysis of lignocellulosic and macroalgae biomass feedstocks for improved bio-oil production-A review[J]. Fuel,2023,332:126071. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126071 [3] SÁNCHEZ-BORREGO F J, ALVAREZ-MATEOS P, GARCÍA-MARTÍN J F. Biodiesel and other value-added products from bio-oil obtained from agrifood waste[J]. Processes,2021,9:797. doi: 10.3390/pr9050797 [4] CHEN C, WEI D, ZHAO J, et al. Study on co-pyrolysis and products of Chlorella vulgaris and rice straw catalyzed by activated carbon/HZSM-5 additives[J]. Bioresour Technol,2022,360:127594. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127594 [5] WEI D, CHEN C, HUANG X, et al. Products and pathway analysis of rice straw and chlorella vulgaris by microwave-assisted co-pyrolysis[J]. J Energy Inst,2023,107:101182. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2023.101182 [6] ZACHER A H, OLARTE M V, SANTOSA D M, et al. A review and perspective of recent bio-oil hydrotreating research[J]. Green Chem,2014,16:491−515. doi: 10.1039/C3GC41382A [7] KUMAR R, STREZOV V. Thermochemical production of bio-oil: A review of downstream processing technologies for bio-oil upgrading, production of hydrogen and high value-added products[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev,2021,135:110152. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.110152 [8] WANG X, WU P, WANG Z, et al. Chlorine-Modified Ru/TiO2 catalyst for selective guaiacol hydrodeoxygenation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng,2021,9:3083−3094. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07292 [9] LAM C H, LOWE C B, LI, et al. Electrocatalytic upgrading of model lignin monomers with earth abundant metal electrodes[J]. Green Chem,2015,17:601−609. doi: 10.1039/c4gc01632g [10] WIJAYA Y P, PUTRA R D, SMITH K J, et al. Guaiacol hydrogenation in methanesulfonic acid using a stirred slurry electrocatalytic reactor: Mass transport and reaction kinetics aspects[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng,2021,9:13164−13175. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c03332 [11] GAREDEW M, LIN F, SONG B, et al. Greener routes to biomass waste valorization: Lignin transformation through electrocatalysis for renewable chemicals and fuels production[J]. ChemSusChem,2020,13:4214−4237. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202000987 [12] LI Z, KELKAR S, RAYCRAFT L, et al. A mild approach for bio-oil stabilization and upgrading: Electrocatalytic hydrogenation using ruthenium supported on activated carbon cloth[J]. Green Chem,2014,16:844−852. doi: 10.1039/C3GC42303D [13] LAZZARI E, SCHENA T, MARCELO M C A, et al. Classification of biomass through their pyrolytic bio-oil composition using FTIR and PCA analysis[J]. Ind Crops Prod,2018,111:856−864. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.11.005 [14] XIAO Y, RAMANATHAN A, SUBRAMANIAM B, et al. Guaiacol hydrodeoxygenation and hydrogenation over bimetallic Pt-M (Nb, W, Zr)/KIT-6 catalysts with tunable acidity[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng,2022,10:4831−4838. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c07071 [15] TRAN Q K, LY H V, KWON B, et al. Catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of guaiacol as a model compound of woody bio-oil over Fe/AC and Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalysts[J]. Renewable Energy,2021,173:886−895. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.03.138 [16] PARRILLA-LAHOZ S, JIN W, PASTOR-PÉREZ L, et al. Guaiacol hydrodeoxygenation in hydrothermal conditions using N-doped reduced graphene oxide (RGO) supported Pt and Ni catalysts: Seeking for economically viable biomass upgrading alternatives[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2021,611:117977. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117977 [17] MORTEO-FLORES F, ROLDAN A. Mechanisms and trends of guaiacol hydrodeoxygenation on transition metal catalysts[J]. Front Catal.,2022,2:861364. doi: 10.3389/fctls.2022.86136425 [18] BROGLIA F, RIMOLDI L, MERONI D, et al. Guaiacol hydrodeoxygenation as a model for lignin upgrading. Role of the support surface features on Ni-based alumina-silica catalysts[J]. Fuel (Lond),2019,243:501−508. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.01.157 [19] DEEPA AK, DHEPE P L. Function of metals and supports on the hydrodeoxygenation of phenolic compounds[J]. ChemPlusChem,2014,79:1573−1583. doi: 10.1002/cplu.201402145 [20] CHEN G, LIANG L, LI N, et al. Upgrading of bio-oil model compounds and bio-crude into biofuel by electrocatalysis: A review[J]. ChemSusChem,2021,14:1037−1052. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202002063 [21] WU Y, GUO Z, SUN C, et al. High-efficiency electrochemical hydrogenation of biomass-derived benzaldehyde compounds via a durable and versatile dendritic-like Pd/Cu-CF electrocatalyst[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2022,237:107436. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2022.107436 [22] ANDREWS E, LOPEZ-RUIZ J A, EGBERT J D, et al. Performance of base and noble metals for electrocatalytic hydrogenation of bio-oil-derived oxygenated compounds[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng,2020,8:4407−4418. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b07041 [23] WIJAYA YP, SMITH K J, KIM C S, et al. Synergistic effects between electrocatalyst and electrolyte in the electrocatalytic reduction of lignin model compounds in a stirred slurry reactor[J]. J Appl Electrochem,2021,51:51−63. doi: 10.1007/s10800-020-01429-w [24] WIJAYA Y P, GROSSMANN-NEUHAEUSLER T, DHEWANGGA PUTRA R D, et al. Electrocatalytic hydrogenation of Guaiacol in diverse electrolytes using a stirred slurry reactor[J]. ChemSusChem,2020,13:629−639. [25] MCCAFFERTY E. Introduction to Corrosion Science[M]. BerlinL: Springer Science & Business Media, 2010. [26] SONG Y, CHIA S H, SANYAL U, et al. Integrated catalytic and electrocatalytic conversion of substituted phenols and diaryl ethers[J]. J Catal,2016,344:263−272. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2016.09.030 [27] ZHAO C, HE J, LEMONIDOU A A, et al. Aqueous-phase hydrodeoxygenation of bio-derived phenols to cycloalkanes[J]. J Catal,2011,280:8−16. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2011.02.001 [28] BEHROUZI L, ZAND Z, FOTUHI M, et al. Water oxidation couples to electrocatalytic hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds and unsaturated carbon–carbon bonds by nickel[J]. Sci Rep,2022,12:19968. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23777-7 -




 下载:
下载: