Desulfurization and denitrification of the marine diesel exhaust by non-thermal plasma method with the addition of monoethanolamine
-
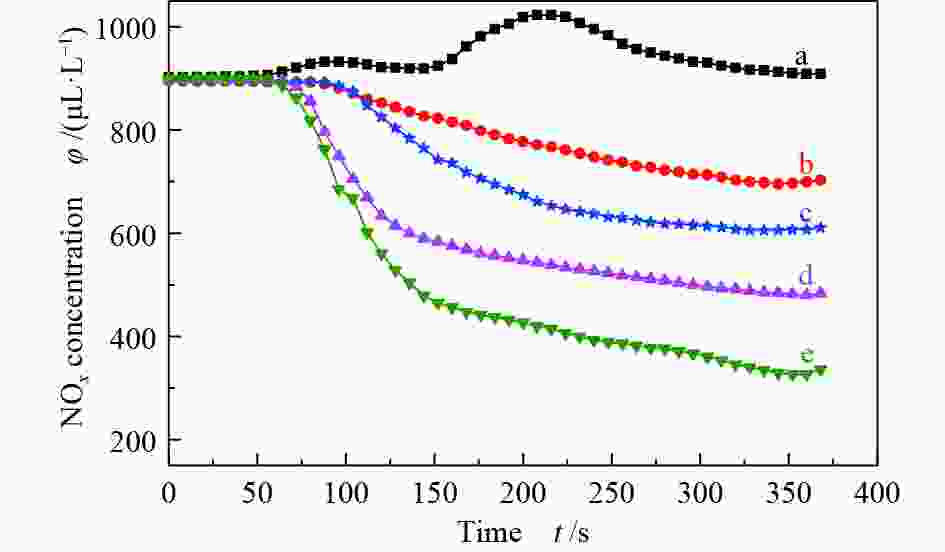
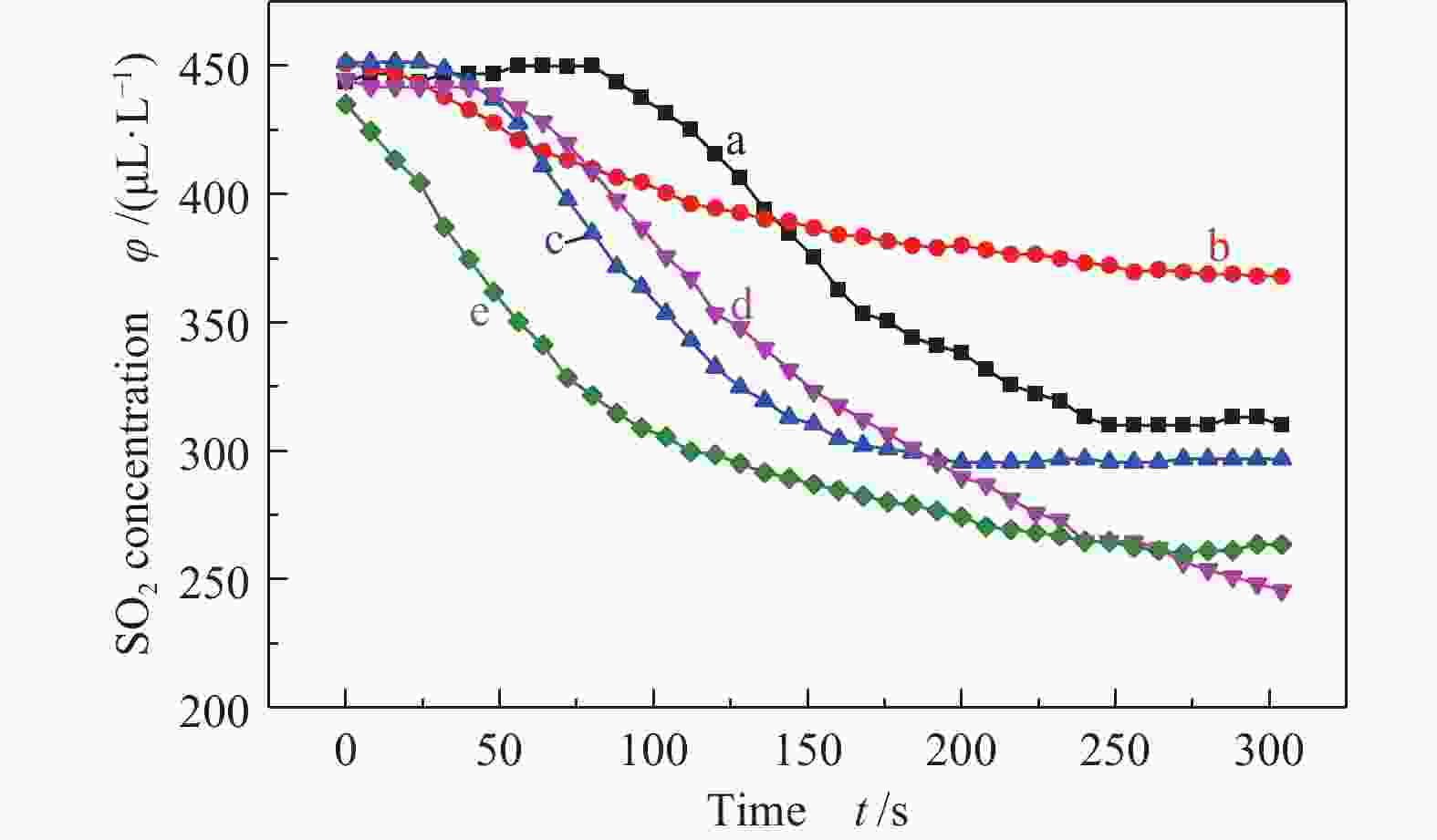
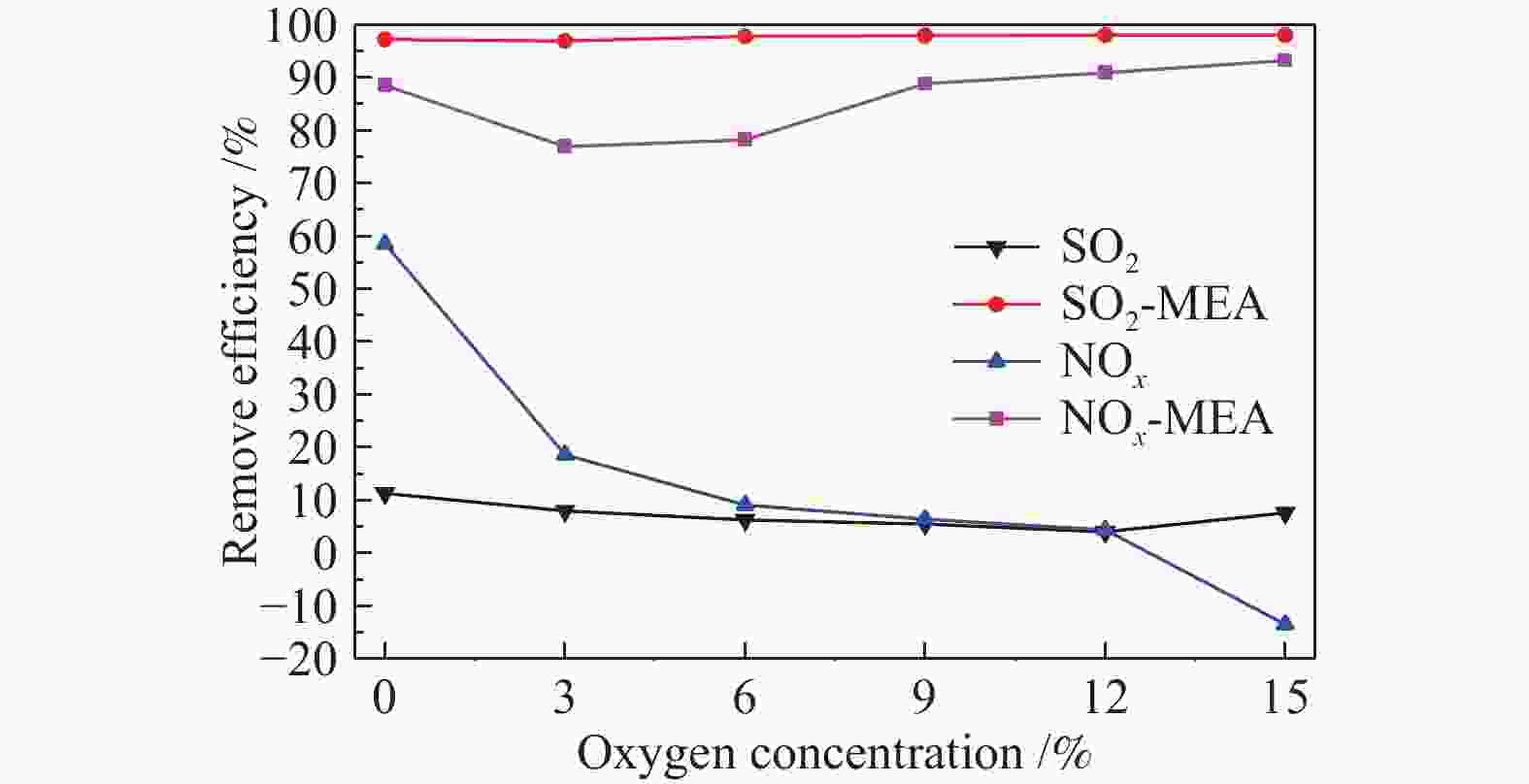
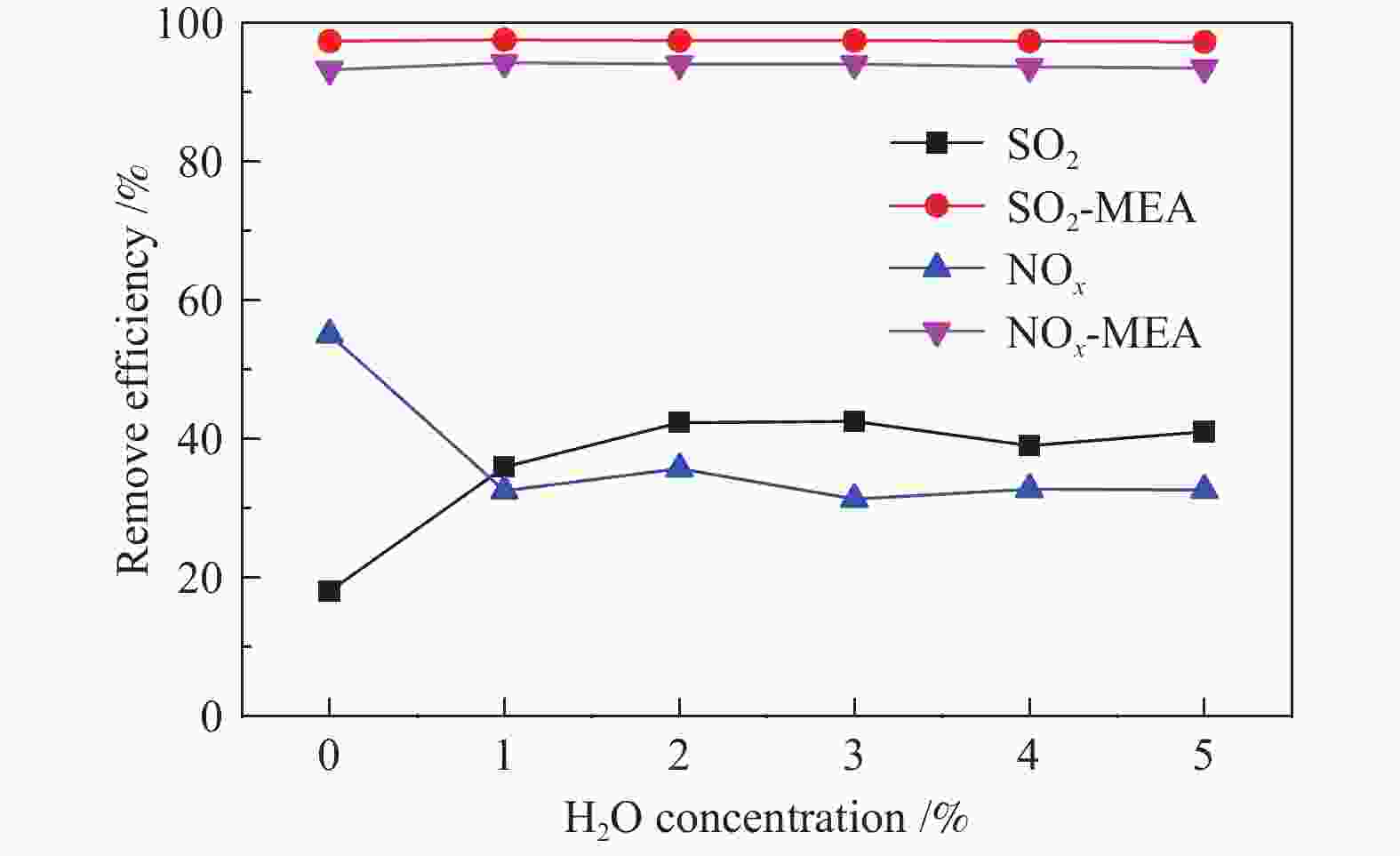
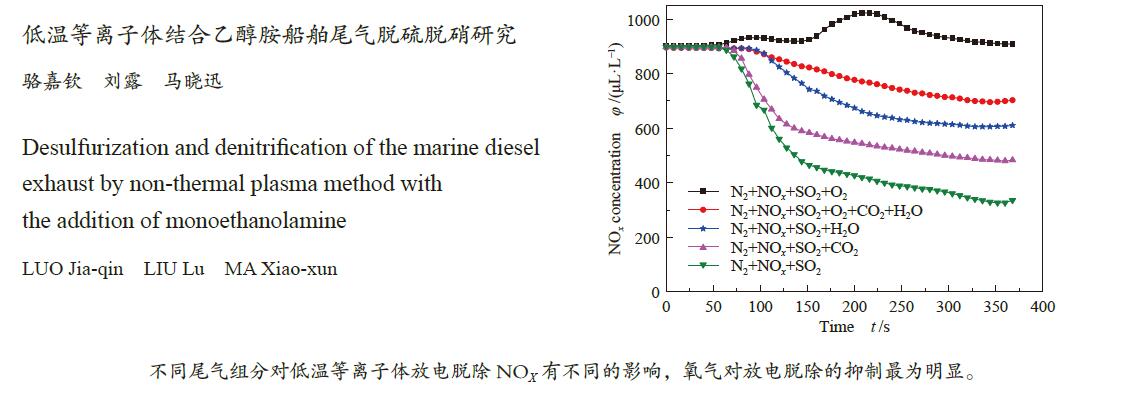
摘要: 采用自行设计的介质阻挡耦合电晕放电等离子体反应装置进行了模拟船舶尾气同时脱硫脱硝的研究。分别考察了尾气中各气体组分及乙醇胺用量、放电电流和气体流量等因素对NOx 和SO2脱除的影响,探究了放电脱除NOx 的机理。结果表明,在模拟船舶尾气(N2/O2/SO2/NOx /CO2/H2O)中,保持放电电流为1.67 A和气体总流量为650 mL/min,添加0.48%乙醇胺后可以有效减弱O2和H2O对等离子体放电脱除NOx 的抑制作用,同时乙醇胺会吸收进入体系中的部分CO2,减弱CO2对NOx 脱除的抑制,最终脱硝率达94%。添加乙醇胺后,由于其可高效吸收SO2,且不受尾气中O2、CO2和H2O等组分的影响,SO2脱除率可达97%。Abstract: Simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification of marine diesel exhaust was carried out by coupling the dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) with corona discharge pulse (CDP) to generate non-thermal plasma (NTP). The effect of various gas components in the exhaust gas and the amount of monoethanolamine, discharge current, gas flow rate and other factors on the desulfurization and denitrification were then investigated and the mechanism of denitrification by NTP was discussed. The results show that when the total gas flow rate is 650 mL/min, applying 1.67 A current discharge and adding 0.48% monoethanolamine to the simulated marine diesel exhaust (N2/O2/SO2/NOx/CO2/H2O) can weaken the negative effects of oxygen and water vapor on the denitrification. Besides, monoethanolamine can also weaken the negative effects of carbon dioxide by absorbing carbon dioxide from the exhaust and the final denitrification rate reaches 94%. Meanwhile, a high desulfurization rate (97%) is also achieved, as monoethanolamine can absorb sulfur dioxide rapidly, which is almost unaffected by any exhaust gas components.
-
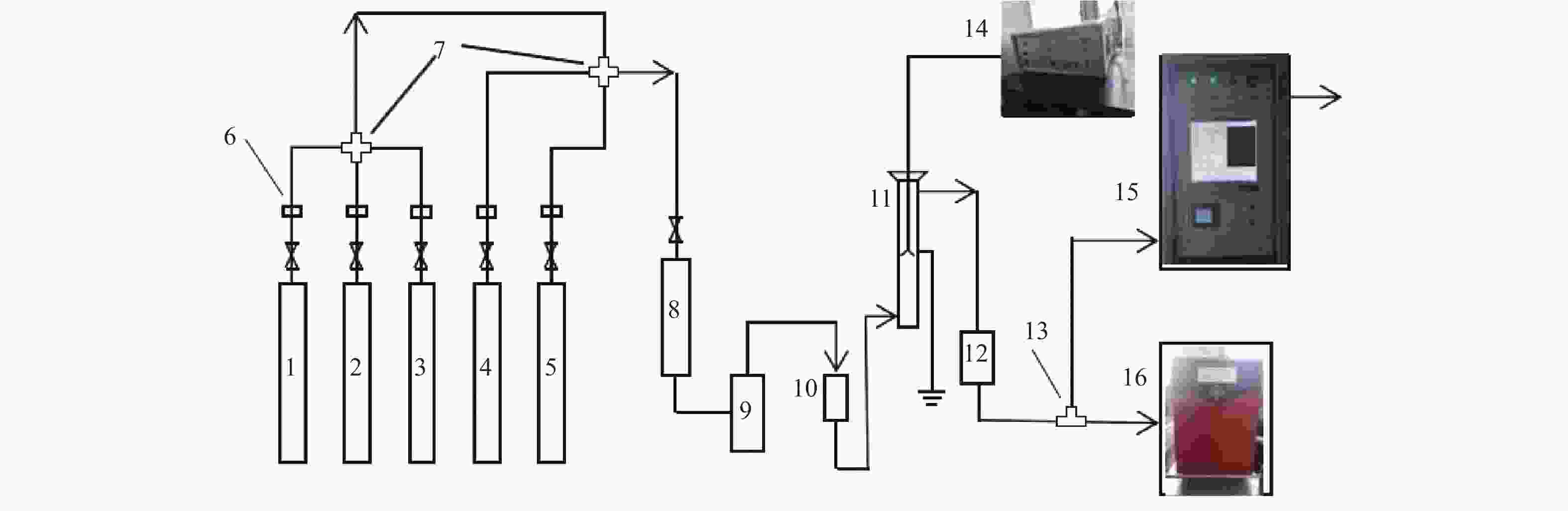
图 1 实验流程示意图
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the experimental setup
1:N2 gas cylinders;2:O2 gas cylinders;3:NO gas cylinders;4:SO2 gas cylinders;5:CO2 gas cylinders;6:mass flow controllers;7:check valves;8:buffer;9:water vapor generator;10:additives mixer;11:reactor;12:dehumidifier;13:check valve;14:high voltage power supply;15:gas analyzer;16:mass spectrometry
表 1 典型柴油机尾气与电厂烟气组分对比
Table 1 Comparison of typical diesel engine exhaust and power plant flue gas
-
[1] MERICO E, DONATEO A, GAMBARO A, CESARI D, GREGORIS E, BARBARO E. Influence of in-port ships emissions to gaseous atmospheric pollutants and to particulate matter of different sizes in a Mediterranean harbour in Italy[J]. Atmos Environ,2016,139:1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.05.024 [2] NI P, WANG X, LI H. A review on regulations, current status, effects and reduction strategies of emissions for marine diesel engines[J]. Fuel,2020,279:477−493. [3] BRUENING C. Transport impacts on atmosphere and climate: Aviation[J]. Atmos Environ,2010,44(37):4772−4816. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.01.002 [4] IMO. Fourth IMO greenhouse gas study[R]. Holland: IMO, 2020. [5] ZHAO Y, ZHANG L, CHEN Y, LIU X J, XU W, PAN Y P, DUAN L. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition to China: A model analysis on nitrogen budget and critical load exceedance[J]. Atmos Environ,2017,153:32−40. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.01.018 [6] ZUO X, KNOPS J M H. Effects of elevated CO2, increased nitrogen deposition, and plant diversity on aboveground litter and root decomposition[J]. Ecosphere,2018,9(2):e02111. doi: 10.1002/ecs2.2111 [7] LIU L, ZHANG X, XU W, LIU X J, ZHANG W T. Estimation of monthly bulk nitrate deposition in China based on satellite NO2 measurement by the Ozone Monitoring Instrument[J]. Remote Sens Environ,2017,199:93−106. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.07.005 [8] ZHOU M, FENG Z Y, ZI-YANG M A, JIANG, L. U, CHEN, N. Numerical Simulation of Marine Desulfurization Tower based on Cyclone Reaction[C]//2018 International Conference on Energy Development and Environmental Protection (EDEP 2018). 2018. [9] 付鹏睿, 范淑珍, 张帅, 戚科技. 低温等离子体协同催化降解废气污染物的研究进展[J]. 能源环境保护,2020,34(2):14−18.FU Peng-rui, FAN Shu-zhen, ZHANG Shuai, QI Ke-ji. Research progress of low-temperature plasma synergistic catalytic degradation of exhaust gas pollutants[J]. Energy Environ Prot,2020,34(2):14−18. [10] HONG L, CHEN D Z, YIN L J, CHEN H, WANG D, HU, Y. Hydrazine-enhanced NO conversion in a pulsed corona discharge plasma (PCDP) reactor: Behaviors and mechanism[J]. AIP Adv,2016,6(9):5−108. [11] YANG L, ZHANG X, KAN Q, ZHAO B, MA X. Effect of gas composition on nitric oxide removal from simulated flue gas with DBD-NPC method[J]. Chin J Chem Eng,2019,27(12):3017−3026. [12] 刘露, 骆嘉钦, 阚青, 马晓迅. 乙醇胺对介质阻挡耦合电晕放电同时脱除NO、SO2的影响[J]. 化工进展,2020,39(11):4685−4692.LIU Lu, LUO Jia-qin, KAN Qing, MA Xiao-xun. The effect of ethanolamine on the simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 by dielectric barrier coupled corona discharge[J]. Prog Chem Ind,2020,39(11):4685−4692. [13] 郝吉明, 王书肖. 燃煤二氧化硫污染控制技术手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2001.HAO Ji-ming, WANG Shu-xiao. Technical Manual of Coal-fired Sulfur Dioxide Pollution Control[M]. Beijing: Chem Ind Press, 2001. [14] 胡鹏怀, 沈春辉. 300 MW机组低氮燃烧改造后燃烧调整方式的优化[J]. 科学时代,2014,(18):239−240.HU Peng-huai, SHEN Chun-hui. Optimization of combustion adjustment mode after low-nitrogen combustion modification of 300 MW unit[J]. Sci Times,2014,(18):239−240. [15] 李斌. 船舶柴油机[M]. 大连: 大连海事大学出版社, 2008.LI Bin. Marine Diesel Engine[M]. Dalian: DMU Press, 2008. [16] LU W, ABBAS Y, MUSTAFA M F, PAN C, WANG H. A review on application of dielectric barrier discharge plasma technology on the abatement of volatile organic compounds[J]. Front Environ Sci Eng,2019,13(2). [17] PENETRANTE B M, BARDSLEY J N, HSIAO M C. Kinetic analysis of non-thermal plasmas used for pollution control[J]. Jpn J Appl Phys,1997,36(Part 1, No. 7B):5007−5017. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.36.5007 [18] ARITOSHI K, FUJIWARA M, ISHIDA M. Production and removal mechanisms of discharge NOx treatment in N2/O2 gas mixture[J]. Jpn J Appl Phys,2002,41(6 A):3936−3942. [19] GUI B Z, GARIKIPATI S V B J, HU X, ARGYLE M D, RADOSZ M. (2005). Effect of oxygen on nonthermal plasma reactions of nitrogen oxides in nitrogen[J]. AIChE J, 51(6): 1800-1812. [20] YU Q, WANG H, LIU T, XIAO L, JIANG X, ZHENG X. High-efficiency removal of NOx using a combined adsorption-discharge plasma catalytic process[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2012,46(4):2337−2344. doi: 10.1021/es203405c [21] 喻文烯. 等离子体脱硫脱硝及其用于船舶柴油机尾气处理的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉纺织大学, 2013.YU Wen-xi. Research on plasma desulfurization and denitrification and its use in marine diesel engine exhaust treatment[D]. Wuhan: WTU, 2013. [22] 张拿慧, 张磊, 李少林. 一种船舶内燃机尾气脱硫脱硝方法: 中国, 104437084 [P]. 2015-03-25.ZHANG Na-hui, ZHANG Lei, LI Shao-lin. A method for desulfurization and denitrification of marine internal combustion engine exhaust gas: CN, 104437084 [P]. 2015-03-25). [23] ABBOD M, BELECA R, PEIRCE D, GANIPPA L, BALACHANDRAN W. Power Controlled Microwave Reactor for the Removal of NOx and SOx from the Exhaust of Marine Diesel Engines[M]. Energy Environ. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2016. [24] BALACHANDRAN W, MANIVANNAN N, BELECA R, RADU. Nonthermal plasma system for marine diesel engine emission control[J]. IEEE Trans Ind Appl,2016,52(3):2496−2505. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2016.2518131 [25] 汪宗御. 低温等离子体辅助活性炭催化脱除船舶废气NOx研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2019.WANG Zong-yu. Low-temperature plasma assisted activated carbon for catalytic removal of NOx from ship exhaust[D]. Dalian: DMU 2019. [26] GUO X, XU Y, CHEN M, DU D F. Study on the Performance of NTP with Wood Fiber in NO Removal[J]. Plasma Chem Plasma Process,2020,40(6). [27] KHANI M R, POUR E B, RASHNOO S, TU X, GHOBADIAN B, SHOKRI B, KHADEM A, HOSSEINI S I. Real diesel engine exhaust emission control: indirect non-thermal plasma and comparison to direct plasma for NOX, THC, CO, and CO2[J]. J Environ Health Sci Eng,2020,(6):1−12. [28] BAI M, LENG B, MAO S, MAO S L, LI C Q. Flue gas desulfurization by dielectric barrier discharge[J]. Plasma Chem Plasma Process,2016,36(2):511−521. doi: 10.1007/s11090-015-9679-9 [29] LI R, LIU X. Main fundamental gas reactions in denitrification and desulfurization from flue gas by non-thermal plasmas[J]. Chem Eng Sci,2000,55(13):2491−2506. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2509(99)00505-9 [30] CHANG M B, BALBACH J H, ROOD M J, KUSHNER M J. Removal of SO2 from gas streams using a dielectric barrier discharge and combined plasma photolysis[J]. J Appl Phys,1991,69(8):4409−4417. doi: 10.1063/1.348367 [31] 代斌, 宫为民, 张秀玲, 张琳, 何仁. 冷等离子体作用下CO2-CO的转化[J]. 天然气化工,2000,(6):13−16.DAI Bin, GONG Wei-min, ZHANG Xiu-ling, ZHANG Lin, HE Ren. CO2-CO conversion under the action of cold plasma[J]. Nat Gas Chem Ind,2000,(6):13−16. [32] SEO J B, CHOI W J, KIM J W, CHOI B W, OH K J. The Simultaneous Absorption Rate of CO2/SO2NO2 from Flue Gas with Aqueous Alkanolamine Solutions[J]. Korean Chem Eng Res,2009,47(5):639−645. [33] SAIWAN C, CHANCHEY A, SUPAP T, IDEM R, TONTIWACHWUTHIKUL P. Ammonia emission kinetics of monoethanolamine (MEA) based CO2 absorption process[J]. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control,2013,12:333−340. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2012.10.015 [34] 胡学一, 罗敏敏, 方云, 李俊国, 孙洋, 李华山. 乙醇胺类原料形成亚硝胺的比较[J]. 应用化学,2019,36(9):1061−1068. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2019.09.190029HU Xue-yi, LUO Min-min, FANG Yun, LI Jun-guo, SUN Yang, LI Hua-shan. Comparison of the formation of nitrosamines from ethanolamine materials[J]. Appl Chem,2019,36(9):1061−1068. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2019.09.190029 [35] 张荣珍, 陈会欣, 张永贤. 乙醇胺为吸收液测定大气中二氧化硫的探讨[J]. 职业与健康,2003,19(8):56−57.ZHANG Rong-zhen, CHEN Hui-xin, ZHANG Yong-xian. Discussion on the determination of sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere with ethanolamine as an absorbent[J]. Occup Health,2003,19(8):56−57. [36] IGHIGEANU D, MARTIN D, ZISSULESCU E, MACARIE, R, IACOB N. SO2 and NOx removal by electron beam and electrical discharge induced non-thermal plasmas[J]. Vac,2005,77(4):493−500. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2004.09.009 [37] 李国锋, 唐本峰, 吴彦. 脉冲电晕放电过程中火花放电的研究[C]. 现代静电科学技术研究, 西安: 西安出版社, 1999, 58−60.LI Guo-feng, TANG Ben-feng, WU Yan. Research on spark discharge during pulse corona discharge[C]. Modern electrostatic science and technology research, Xi’an: Xi’an Publishing House, 1999, 58−60. [38] 杨岚. 基于氧化湿法与非平衡等离子体干法的高效烟气脱硫脱硝工艺研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019.YANG Lan. High efficiency flue gas desulfurization and denitrification technology based on wet oxidation and non-thermal plasma dry methods[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2019. [39] TANG X, ZHANG R, YI H, GAO F, ZHAO S, WANG J. Byproducts Generation Characteristics of Non-thermal Plasma for NO Conversion: Effect of Reaction Conditions[J]. Plasma Chem Plasma Process, 2020, 1−19. [40] PEDLEY J B, NAYLOR R D, KIRBY S P. Thermochemical Data of Organic Compounds[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Chapman and Hall, 1986. [41] 邵菊香, 程新路, 杨向东, 张芳沛, 葛素红. C-H, C-N, C-O, N-N的键离解能和键长的计算[J]. 原子与分子物理学报,2006,23(1):80−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0364.2006.01.016SHAO Ju-xiang, CHENG Xin-lu, YANG Xiang-dong, ZHANG Fang-pei, GE Su-hong. Calculation of bond dissociation energy and bond length of C-H, C-N, C-O, N-N[J]. J At Mol Phys,2006,23(1):80−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0364.2006.01.016 [42] SHEA J J. Handbook of bond dissociation energies in organic compounds[J]. IEEE Electr Insul Mag,2004,20(5):45−45. [43] YOUNG S M, INSIK N. Modeling of pulsed corona discharge process for the removal of nitric oxide and sulfur dioxide[J]. Chem Eng J,2002,85(1):87−97. doi: 10.1016/S1385-8947(01)00221-2 [44] CHMIELEWSKI A G, SUN Y X, LICKI J, BUŁKA S, KUBICA K, ZIMEK Z. NOx and PAHs removal from industrial flue gas by using electron beam technology with alcohol addition[J]. Radiat Phys Chem,2003,67:555−560. doi: 10.1016/S0969-806X(03)00105-1 [45] YAN Z C, LI C, LIN W H. Hydrogen generation by glow discharge plasma electrolysis of methanol solutions[J]. Inter J Hydrogen Energy,2009,34(1):48−55. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.09.099 [46] JUN H, KIM H, SAKAGUCHI Y, HONG Y. Reduction of NOx and SO2 in a non-thermal plasma reactor combined with catalyst and methanol[J]. J Phys D Appl Phys,2008,41(20):205−213. [47] 汪涛, 孙保民, 肖海平, 杜旭, 曾菊瑛, 段二朋, 饶甦. 介质阻挡放电中气体成分对NOx脱除的影响[J]. 化工学报,2012,63(11):3652−3659. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.11.040WANG Tao, SUN Bao-min, XIAO Hai-ping, DU Xu, ZENG Ju-ying, DUAN Er-peng, RAO Su. Effect of gas composition on NOx removal in dielectric barrier discharge reactor[J]. CIESC J,2012,63(11):3652−3659. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.11.040 [48] MARTIN A R, SHAWCROSS J T, WHITEHEAD J C. Modelling of non-thermal plasma aftertreatment of exhaust gas streams[J]. Soc Sci Electron Publish,2003,37(1):42. [49] 陈旺生, 叶威, 吴高明, 韩军, 伍德满. 甲醇对等离子体脱硫脱硝影响的实验研究[J]. 工业安全与环保,2012,38(5):1−3.CHEN Wang-sheng, YE Wei, WU Gao-ming, HAN Jun, WU De-man. Experimental study on the effect of methanol on plasma desulfurization and denitrification[J]. Ind Saf Environ Prot,2012,38(5):1−3. [50] 张俊杰, 任建兴, 李芳芹, 王海文, 朱锴锴. 介质阻挡放电低温等离子体脱硫脱硝过程的研究[J]. 应用化工,2018,47(1):109−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.01.027ZHANG Jun-jie, u Jian-xing, LI Fang-qin, WANG Hai-wen, ZHU Kai-kai. Research on low-temperature plasma desulfurization and denitration process with dielectric barrier discharge[J]. Appl Chem Ind,2018,47(1):109−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.01.027 [51] A T F, B Y A, C N Y, D M R. Removal of NO by DC corona reactor with water[J]. J Electrostat,2001,51(1):8−14. -





 下载:
下载: