Production of hydrogen and carbon nanofibers by methane decomposition over the Ni/SiO2 catalyst
-
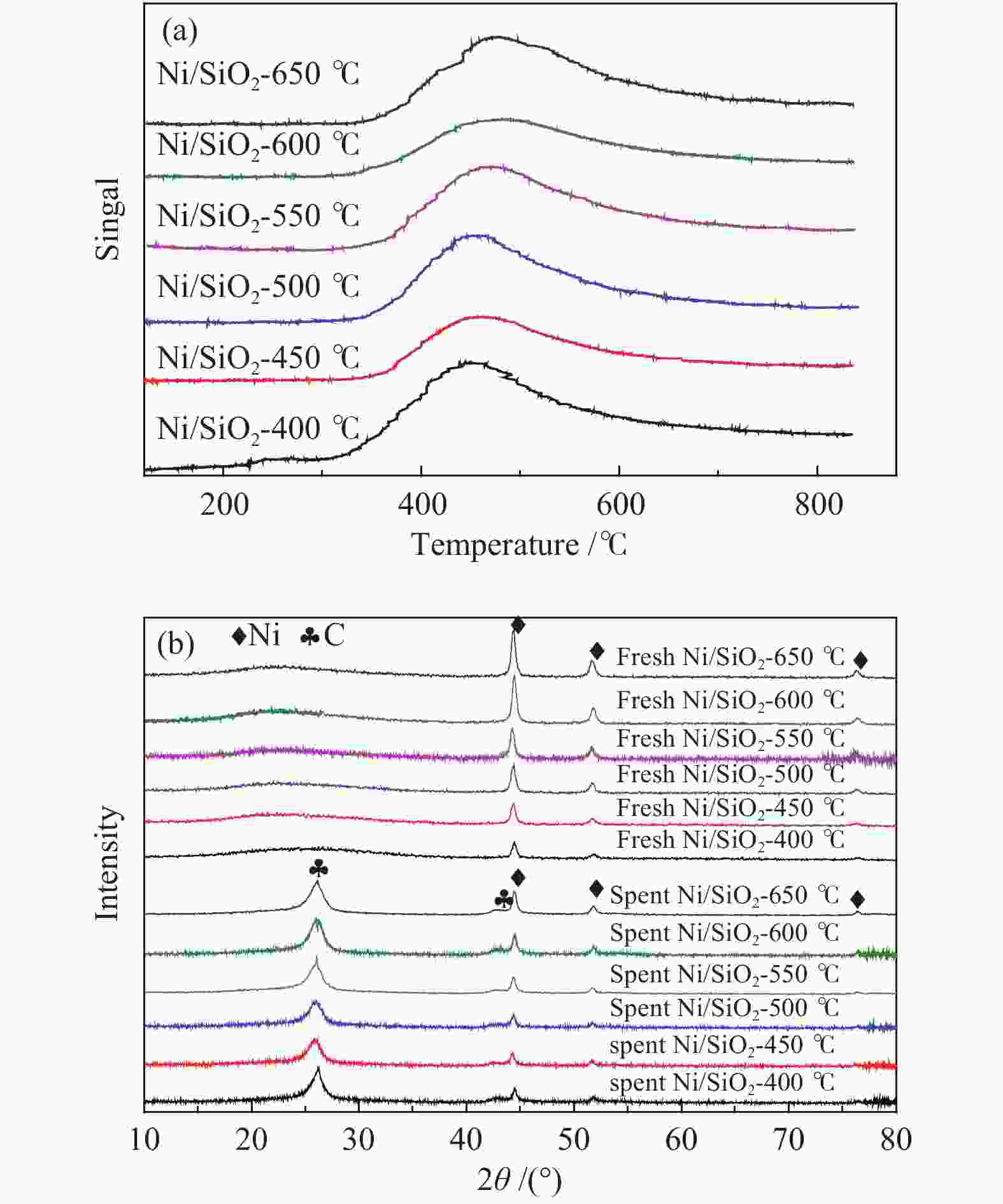
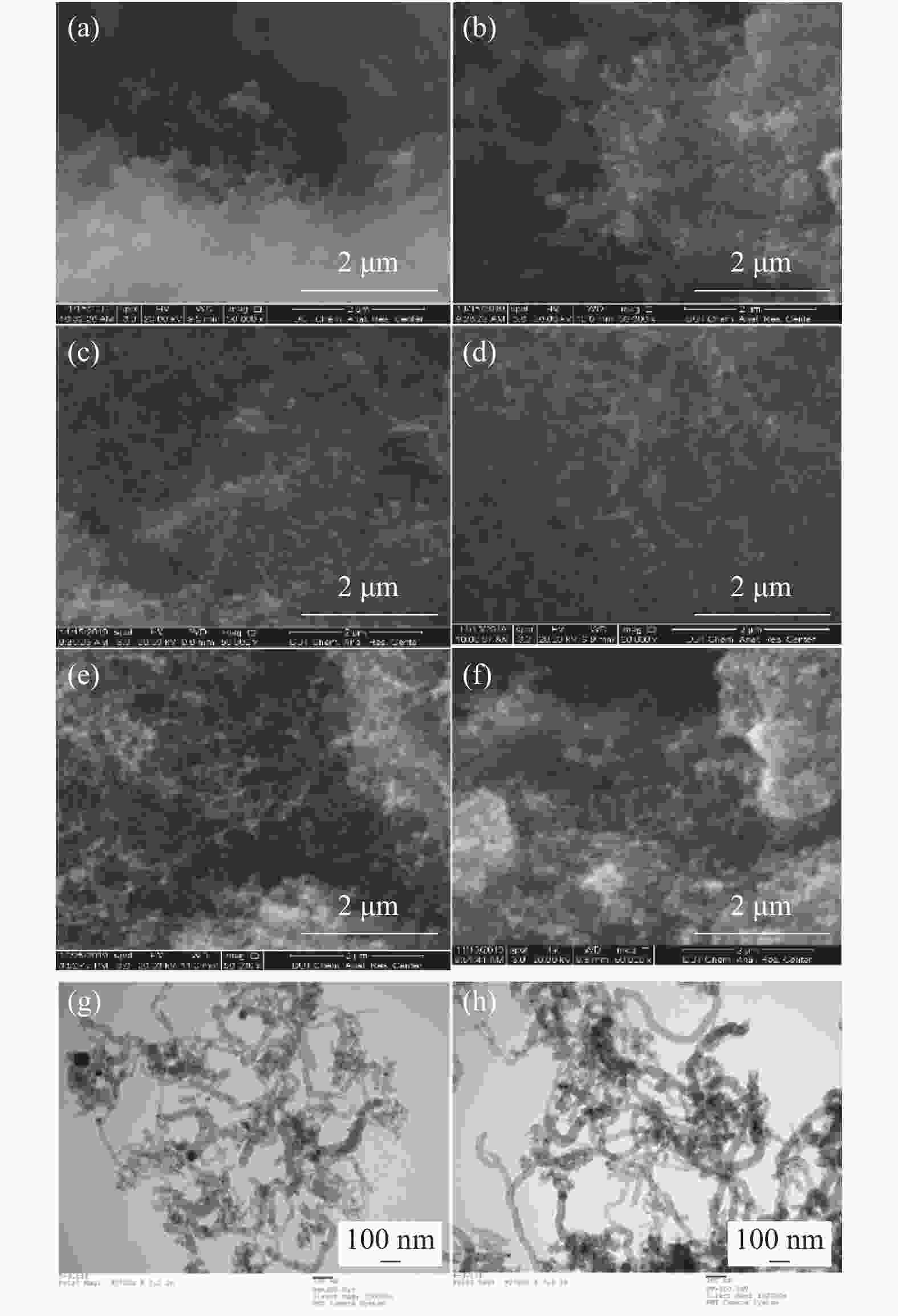
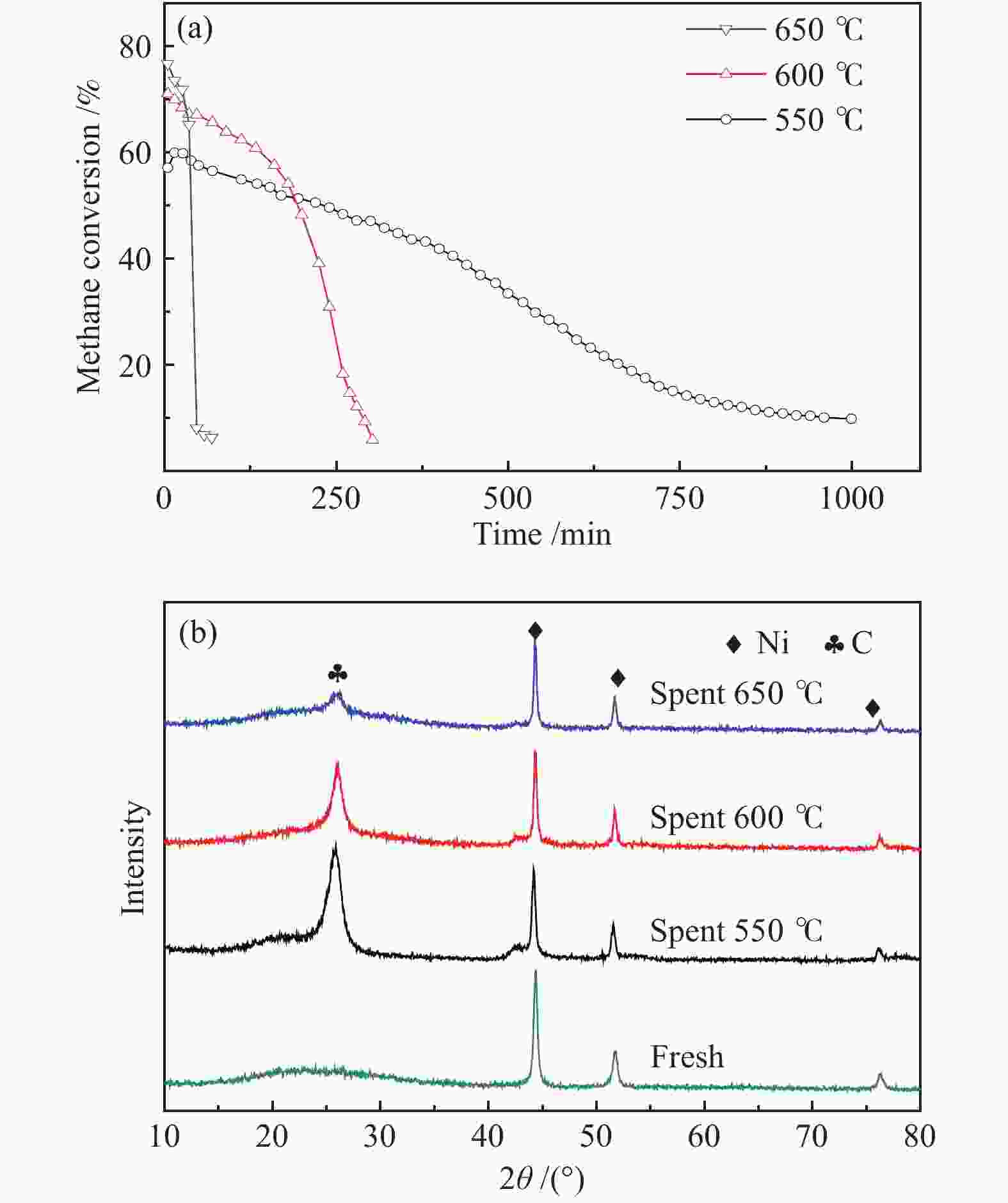
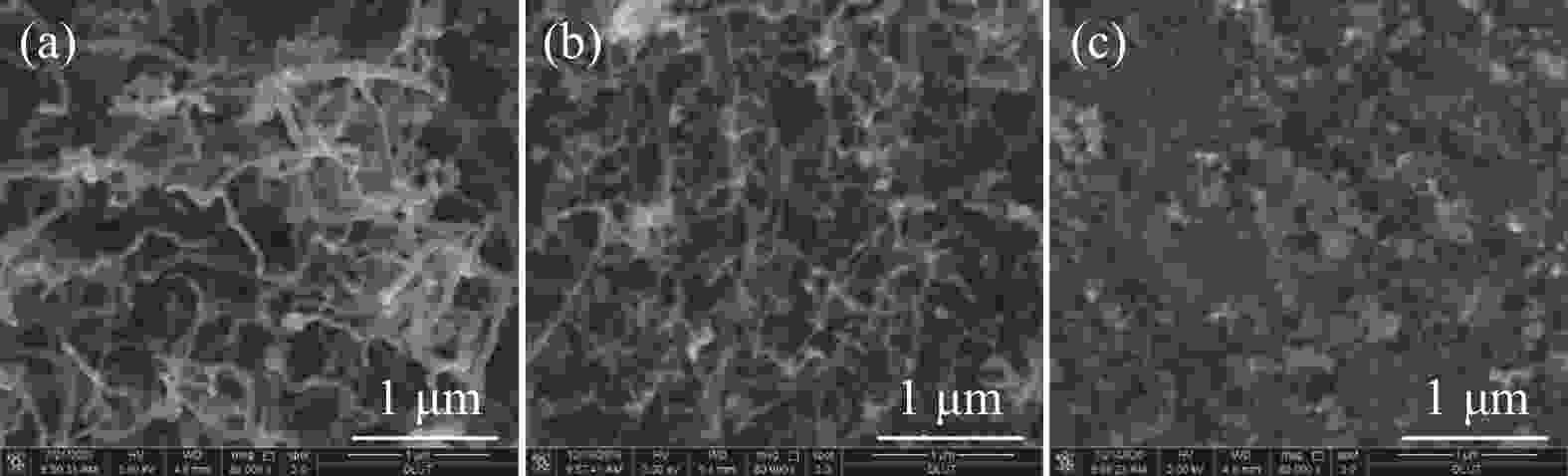
摘要: 甲烷催化裂解制氢具有过程简单、产物易分离、无COx产生等优点,是一种潜在的制氢工艺。本工作采用浸渍法制备Ni/SiO2介孔催化剂,通过N2吸附-脱附、X射线衍射、程序升温还原、扫描电子显微镜和透射电子显微镜对反应前后的催化剂结构及生成炭的形貌进行表征,研究了焙烧温度、金属负载量和反应温度对其甲烷催化裂解性能的影响。结果表明,所制备的Ni/SiO2催化剂具有较好的介孔结构,焙烧温度对催化剂的结构性质和催化性能影响较小,但会改变Ni晶粒在催化剂表面团聚程度。随着金属负载量的增加,催化剂的活性呈现先增加后降低的趋势,其中30% Ni/SiO2催化剂的催化活性最佳。反应温度会显著影响催化剂的活性、稳定性以及生成炭的形态;较高反应温度导致催化剂的稳定性降低和包覆炭的形成。在30% Ni/SiO2催化剂上、550 °C下反应1000 min,甲烷转化率为9.8%,纤维炭产率约为650 °C下的7.2倍。Abstract: Catalytic decomposition of methane is a promising route for hydrogen production owing to simple operation, easy separation of the products and no COx emission. In this work, a mesoporous Ni/SiO2 catalyst was prepared by impregnation method and used in methane decomposition; the fresh and spent catalysts and the morphology of deposited carbon were characterized by N2 adsorption-desorption, X-ray diffraction, hydrogen temperature programmed reduction, scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The effects of calcination temperature, metal loading and reaction temperature on the catalytic performance of Ni/SiO2 in methane decomposition were investigated. The results show that the Ni/SiO2 catalyst exhibits mesoporous structure. The calcination temperature has a slight effect on the textural properties and catalytic performances of Ni/SiO2, but a significant influence on the agglomeration degree of Ni particles on the catalyst surface. The catalytic activity of Ni/SiO2 increases first with increasing the metal loading up to 30% and then declines with a further increase of metal loading. Meanwhile, the reaction temperature has a remarkable influence on the catalytic activity and stability and the state of the deposited carbon; a high temperature results in the decrease of the catalytic stability and the formation of encapsulated carbon. In particular, for the methane decomposition over the 30% Ni/SiO2 catalyst, the methane conversion of about 9.8% was obtained at 500 °C after reaction for 1000 min; the yield of carbon nanofiber at 500 °C is about 7.2 times higher than that at 650 °C.
-
Key words:
- methane decomposition /
- Ni/SiO2 /
- hydrogen /
- carbon nanofiber
-
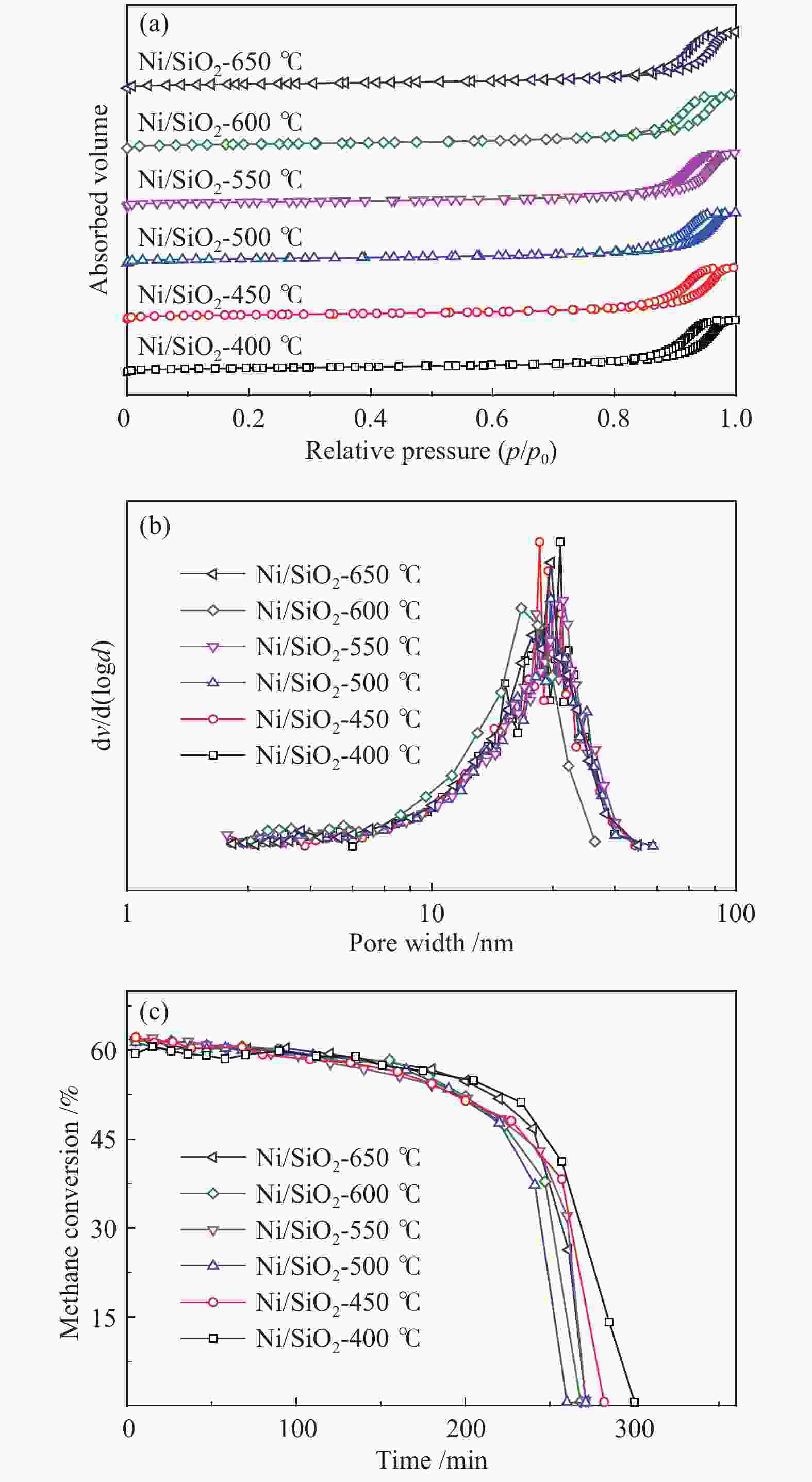
表 1 不同焙烧温度制备催化剂的结构性质
Table 1 Textural properties of the catalysts prepared under different calcination temperatures
Sample SBET/(m2·g−1) vt/(cm3·g−1) dave/ nm SiO2 196.3 0.60 12.5 Ni/SiO2-400 170.2 0.88 16.9 Ni/SiO2-450 170.4 0.87 17.2 Ni/SiO2-500 160.4 0.85 17.1 Ni/SiO2-550 166.3 0.90 17.1 Ni/SiO2-600 162.7 0.90 15.4 Ni/SiO2-650 162.5 0.95 18.1 表 2 不同焙烧温度所制备催化剂反应前后镍颗粒平均粒径
Table 2 Average particle size of nickel particles before and after reaction of catalyst prepared under different calcination temperatures
Sample Particle size d/nm 400 ℃ 450 ℃ 500 ℃ 550 ℃ 600 ℃ 650 ℃ Fresh 16.9 17.8 18.8 18.9 19.2 19.6 Spent 17.0 18.2 18.9 19.1 19.9 20.9 表 3 不同镍负载量所制备催化剂的结构性质
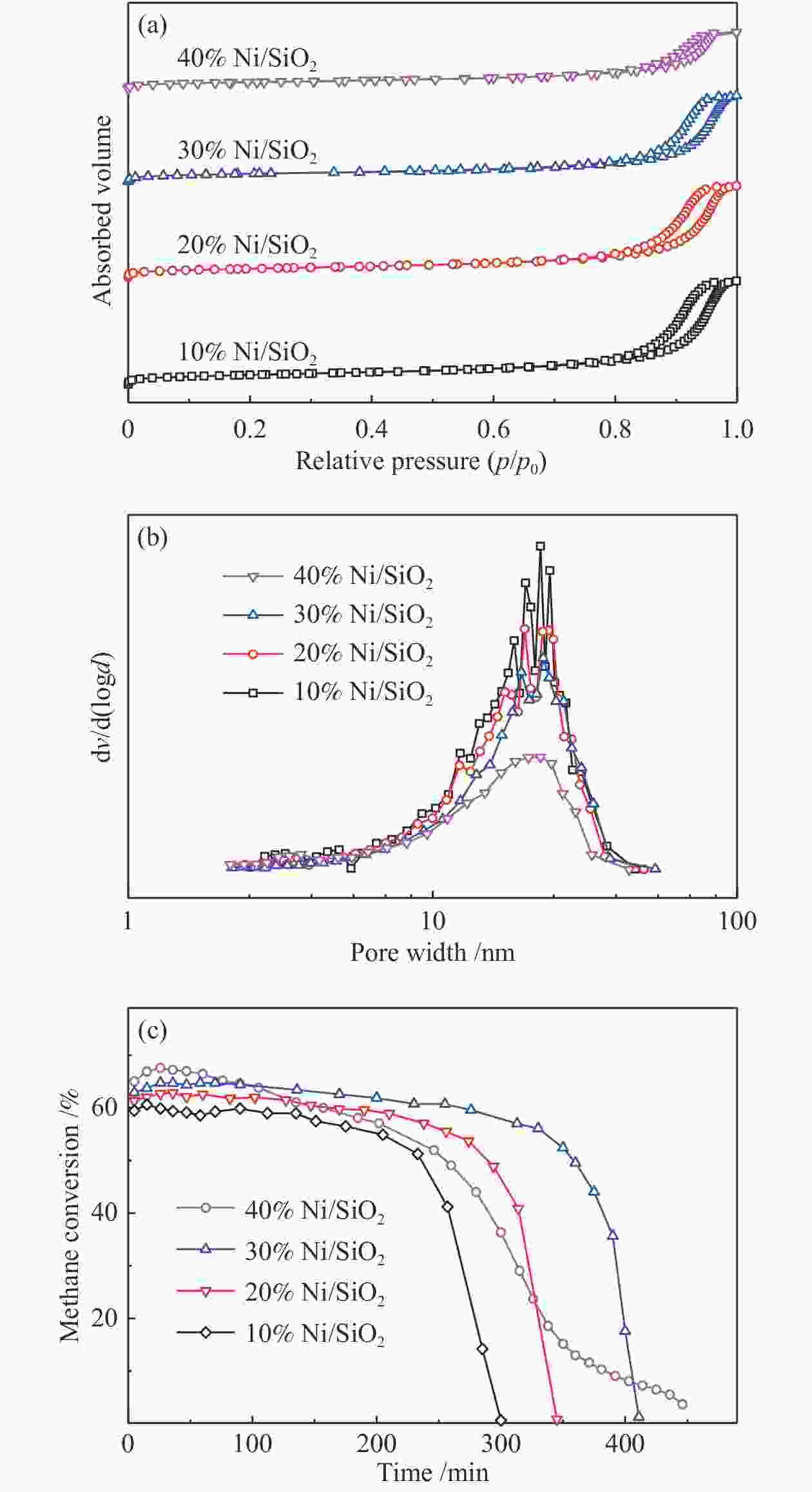
Table 3 Textural properties of the catalysts prepared under different Ni contents
Sample SBET/ (m2·g−1) vt/ (cm3·g−1) dave/ nm 10% Ni/SiO2 170.2 0.88 16.9 20% Ni/SiO2 161.8 0.78 15.9 30% Ni/SiO2 149.7 0.73 17.5 40% Ni/SiO2 128.8 0.48 13.5 表 4 不同负载量所制备催化剂反应前后镍颗粒平均粒径
Table 4 Average particle size of nickel particles before and after reaction of catalyst prepared under different Ni contents
Sample Particle size d/nm 10% 20% 30% 40% Fresh 16.9 21.5 23.7 25.0 Spent 17.0 22.9 24.5 27.6 -
[1] ABBAS H F, DAUD W M A W. Hydrogen production by methane decomposition: A review[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2010,35(3):1160−1190. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.11.036 [2] IBRAHIM A A, FAKEEHA A H, AL-FATWSH A S. Enhancing hydrogen production by dry reforming process with strontium promoter[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2014,39(4):1680−1687. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.11.050 [3] AMIN A, CROISET E, EPLING W. Review of methane catalytic cracking for hydrogen production[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(4): 2904-2935. [4] 刘攀, 陆继长, 陈定凯, 刘峰, 刘江平, 余杰, 刘珂臻, 罗永明. 碳质与金属催化剂热催化裂解甲烷产氢研究进展[J]. 分子催化,2016,30(5):480−495.LIU Pan, LU Ji-chang, CHEN Ding-kai, LIU Feng, LIU Jiang-ping, YU Jie, LIU Ke-zhen, LUO Yong-ming. Research progress on hydrogen production from methane catalyzed decomposition with carbonaceous and metal catalysts[J]. J Mol Catal,2016,30(5):480−495. [5] ASHIK U P M, WAN DAUD W M A, ABBAS H. Production of greenhouse gas free hydrogen by thermocatalytic decomposition of methane – A review[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev,2015,44:221−256. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.12.025 [6] YABE T, SEKINE Y. Methane conversion using carbon dioxide as an oxidizing agent: A review[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2018,181:187−198. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.09.014 [7] MARINHO A L A, RABELO-NETO R C, EPRON F, BION N, TONIOLO F S, NORONHA F B. Embedded Ni nanoparticles in CeZrO2 as stable catalyst for dry reforming of methane[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2020,268:118387. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118387 [8] DE VASCONCELOS B R, MINH D P, LYCZKO N, PHAN T S, SHARROCKT P J, NZIHOUL A. Upgrading greenhouse gases (methane and carbon dioxide) into syngas using nickel-based catalysts[J]. Fuel,2018,226(15):195−203. [9] CHO E, YU Y J, KIM Y, PHAN T N, PARKT D, KO C H. Egg-shell-type Ni supported on MgAl2O4 pellets as catalyst for steam methane reforming: Enhanced coke-resistance and pellet stability[J]. Catal Today,2020,352:157−165. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.11.013 [10] IGLESIAS I, FORTI M, BARONETTI G, MARINO F. Zr-enhanced stability of ceria based supports for methane steam reforming at severe reaction conditions[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2019,.44(16):8121−8132. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.02.070 [11] ENGER B C, LØDENG R, HOLMEN A. A review of catalytic partial oxidation of methane to synthesis gas with emphasis on reaction mechanisms over transition metal catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2008,346(1/2):1−27. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2008.05.018 [12] LI Y, LI D, WANG G. Methane decomposition to COx-free hydrogen and nano-carbon material on group 8–10 base metal catalysts: A review[J]. Catal Today,2011,162(1):1−48. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.12.042 [13] LAZARO M J, ECHEGOYEN Y, SUELVES I, PALACIOS J M, MOLINER R. Decomposition of methane over Ni-SiO2 and Ni-Cu-SiO2 catalysts: Effect of catalyst preparation method[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2007,.329:22−29. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2007.06.014 [14] IBRAHIM A A, FAKEEHA A H, AL-FATESH A S, ABASAEED A E, KHAN W U. Methane decomposition over iron catalyst for hydrogen production[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2015,40(24):7593−7600. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.10.058 [15] LI Y, CHEN J, QIN Y, CHANG L. Simultaneous production of hydrogen and nanocarbon from decomposition of methane on a nickel-based catalyst[J]. Energy Fuels,2012,14(6):1188−1194. [16] SHINKAREV V V, GLUSHENKOV A M, KUVSHINOV D G, KUVSHINOV G G. Nanofibrous carbon with herringbone structure as an effective catalyst of the H2S selective oxidation[J]. Carbon,2010,48(7):2004−2012. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2010.02.008 [17] WANG W, WANG H, YANG Y, JIANG S. Ni-SiO2 and Ni-Fe-SiO2 catalysts for methane decomposition to prepare hydrogen and carbon filaments[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2012,37(11):9058−9066. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.03.003 [18] JIN L, SI H, ZHANG J, LIN P, HU Z, QIU B, HU H. Preparation of activated carbon supported Fe-Al2O3 catalyst and its application for hydrogen production by catalytic methane decomposition[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2013,38(25):10373−10380. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.06.023 [19] SUELVES I, PINILLA J L, LAZARO M J, MOLINER R. Carbonaceous materials as catalysts for decomposition of methane[J]. Chem Eng J,2008,140(1/3):432−438. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2007.11.014 [20] ZHANG J, LI X, CHEN H, QI M, ZHANG G, HU H. Hydrogen production by catalytic methane decomposition: Carbon materials as catalysts or catalyst supports[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2017,42(31):19755−19775. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.06.197 [21] ZHANG Y, SMITH K J. Carbon formation thresholds and catalyst deactivation during CH4 decomposition on supported Co and Ni catalysts[J]. Catal Lett,2004,95(1/2):7−12. [22] AVDEEVA L B, RESHETENKO T V, ISMAGILOV Z R, LIKHOLOBOV V A. Iron-containing catalysts of methane decomposition: accumulation of filamentous carbon[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2002,228(1):53−63. [23] LI J, ZHAO L, HE J, DONG L, XIONG L, DU Y, YANG Y, WANG H, PENG S. Methane decomposition over high-loaded Ni-Cu-SiO2 catalysts[J]. Fusion Eng Des,2016,113:279−287. doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2016.06.046 [24] URDIANA G, VALDEZ R, LASTRA G, VALENZUELA M A, OLIVAS A. Production of hydrogen and carbon nanomaterials using transition metal catalysts through methane decomposition[J]. Mater Lett,2018,217(15):9−12. [25] TAKENAKA S, OGIHARA H, YAMANAKA I, OTSUKA K. Decomposition of methane over supported-Ni catalysts: effects of the supports on the catalytic lifetime[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2001,217(1):101−110. [26] TAKENAKA S, KOBAYASHI S, OGIHARA H, OTSUKA K. Ni/SiO2 catalyst effective for methane decomposition into hydrogen and carbon nanofiber[J]. J Catal,2003,217(1):79−87. [27] ERMAKOVA M A, ERMAKOV D Y. Ni/SiO2 and Fe/SiO2 catalysts for production of hydrogen and filamentous carbon via methane decomposition[J]. Catal Today,2002,77(3):225−235. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(02)00248-1 [28] ASHIK U P M, DAUD W A M W. Probing the differential methane decomposition behaviors of n-Ni/SiO2, n-Fe/SiO2 and n-Co/SiO2 catalysts prepared by co-precipitation cum modified Stober method[J]. RSC Adv,2015,5:67227−67241. doi: 10.1039/C5RA10997C [29] 蔡诚, 张志杰, 胡涛, 戴丽娜, 王浩宇, 吴崇刚, 龚兴厚. 二氧化硅负载铂催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工新型材料,2020,48(10):201−205.CAI Cheng, ZHANG Zhi-jie, HU Tao, DAI Li-na, WANG Hao-yu, WU Chong-gang, GONG Xing-hou. Preparation and property of SiO2 supported Pt catalyst[J]. New Chem Mater,2020,48(10):201−205. [30] LI J, GONG Y, CHEN C, HOU J, YUE L, FU X, ZHAO L, CHEN H, WANG H, PENG S. Evolution of the Ni-Cu-SiO2 catalyst for methane decomposition to prepare hydrogen[J]. Fusion Eng Des,2017,125:593−602. doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2017.05.040 [31] RASTEGARPANAH A, REZAEI M, MESHKANI F, ZHANG K, ZHAO X, PEI W, LIU Y, DENG J, ARANDIYAN H, DAI H. Influence of group VIB metals on activity of the Ni/MgO catalysts for methane decomposition[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2019,248:515−525. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.067 [32] LI J, DONG L, XIONG L, YANG Y, DU Y, ZHAO L, WANG, H, PENG S. High-loaded Ni-Cu-SiO2 catalysts for methane decomposition to prepare hydrogen and carbon filaments[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2016,41(28):12038−12048. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.05.137 [33] CHEN J, LI Y, LI Z, ZHANG X. Production of COx-free hydrogen and nanocarbon by direct decomposition of undiluted methane on Ni-Cu-alumina catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2004,269(1/2):179−186. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2004.04.016 [34] DONG L, DU Y, LI J, WANG H, YANG Y, LI S, TAN Z. The effect of CH4 decomposition temperature on the property of deposited carbon over Ni/SiO2 catalyst[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2015,40(31):9670−9676. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.06.005 -




 下载:
下载: