Effect of Mg content in Ni/MgAl2O4 catalysts on catalytic performance during methane dry reforming reaction
-
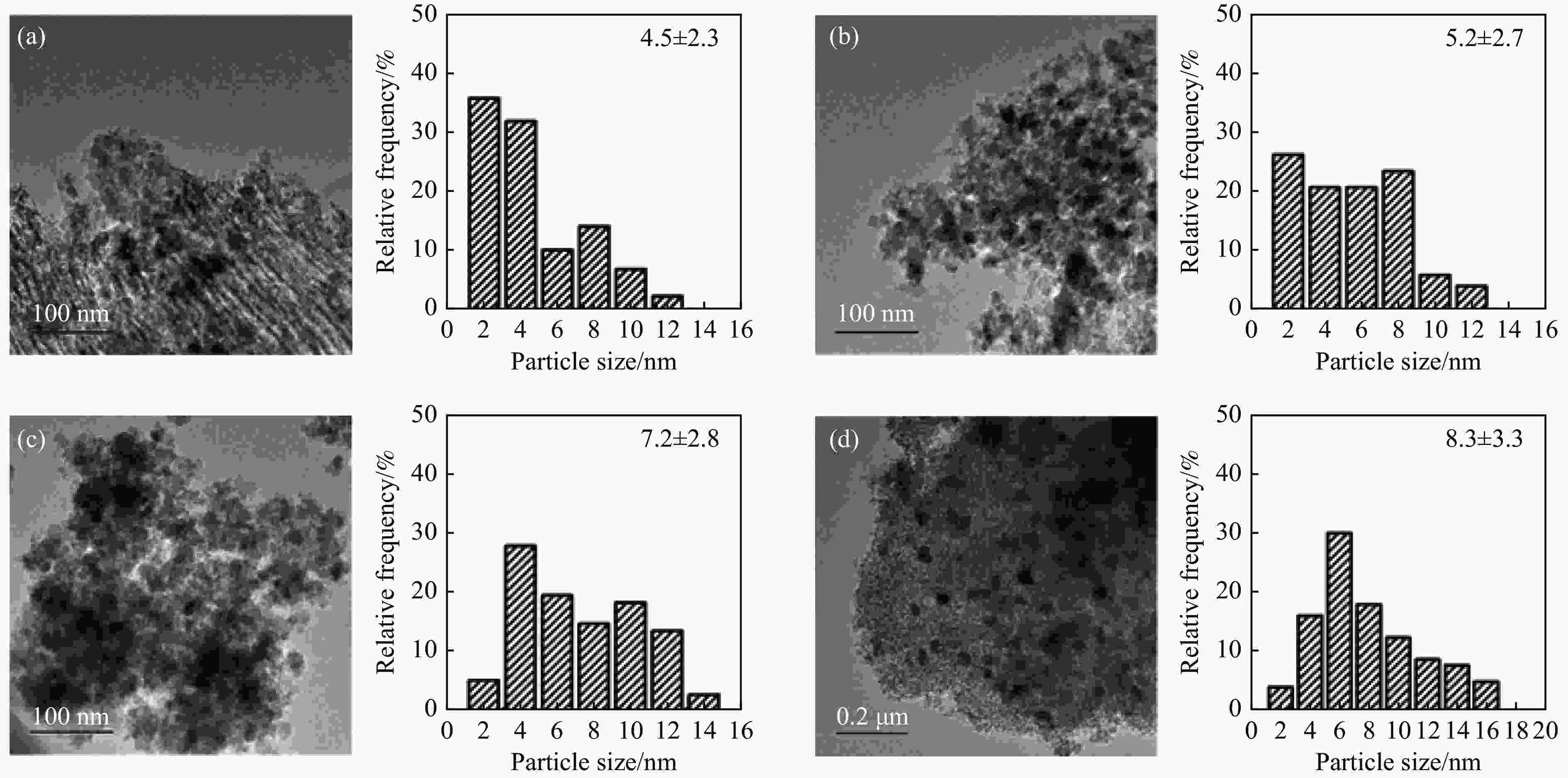
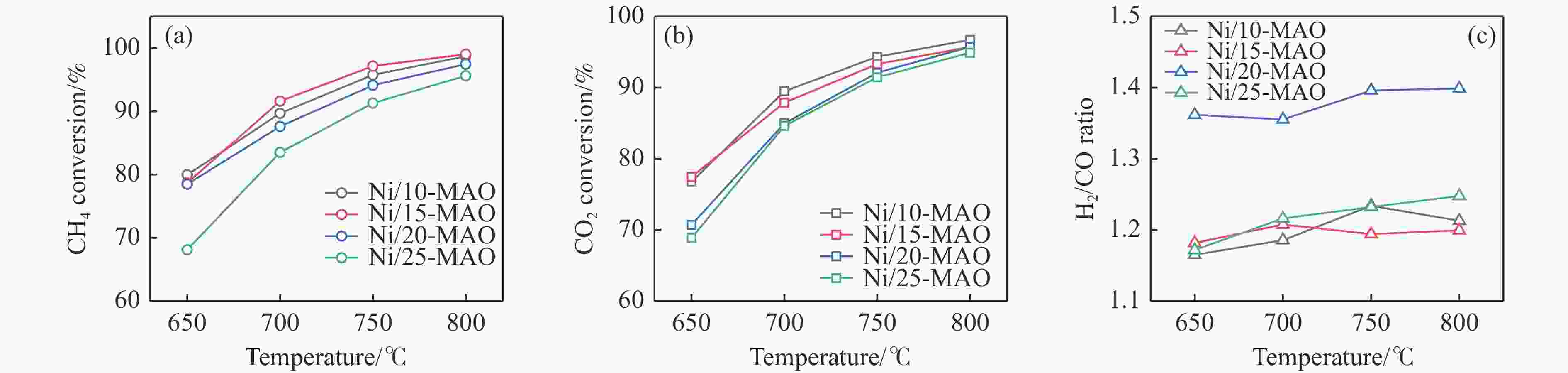
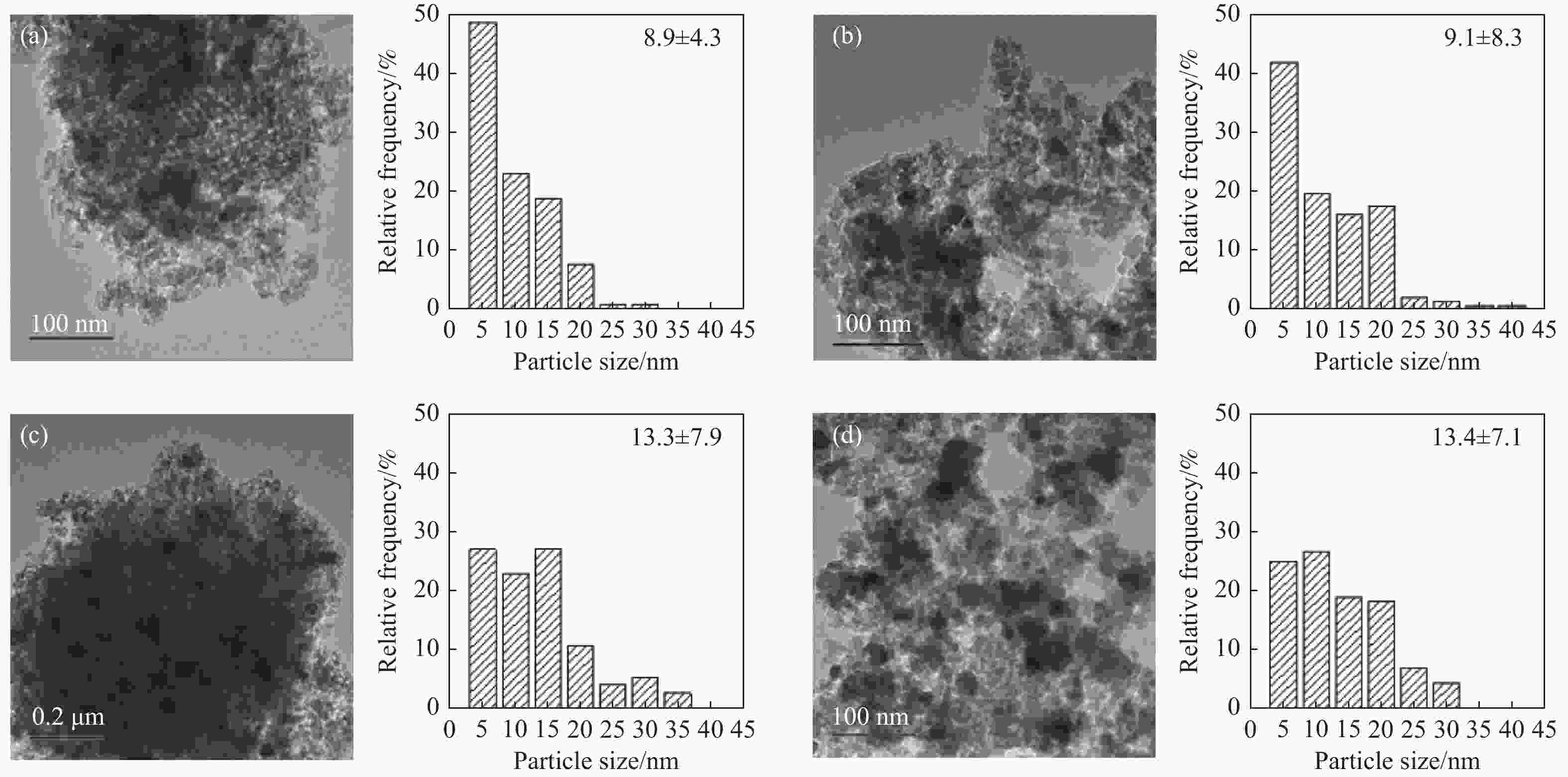
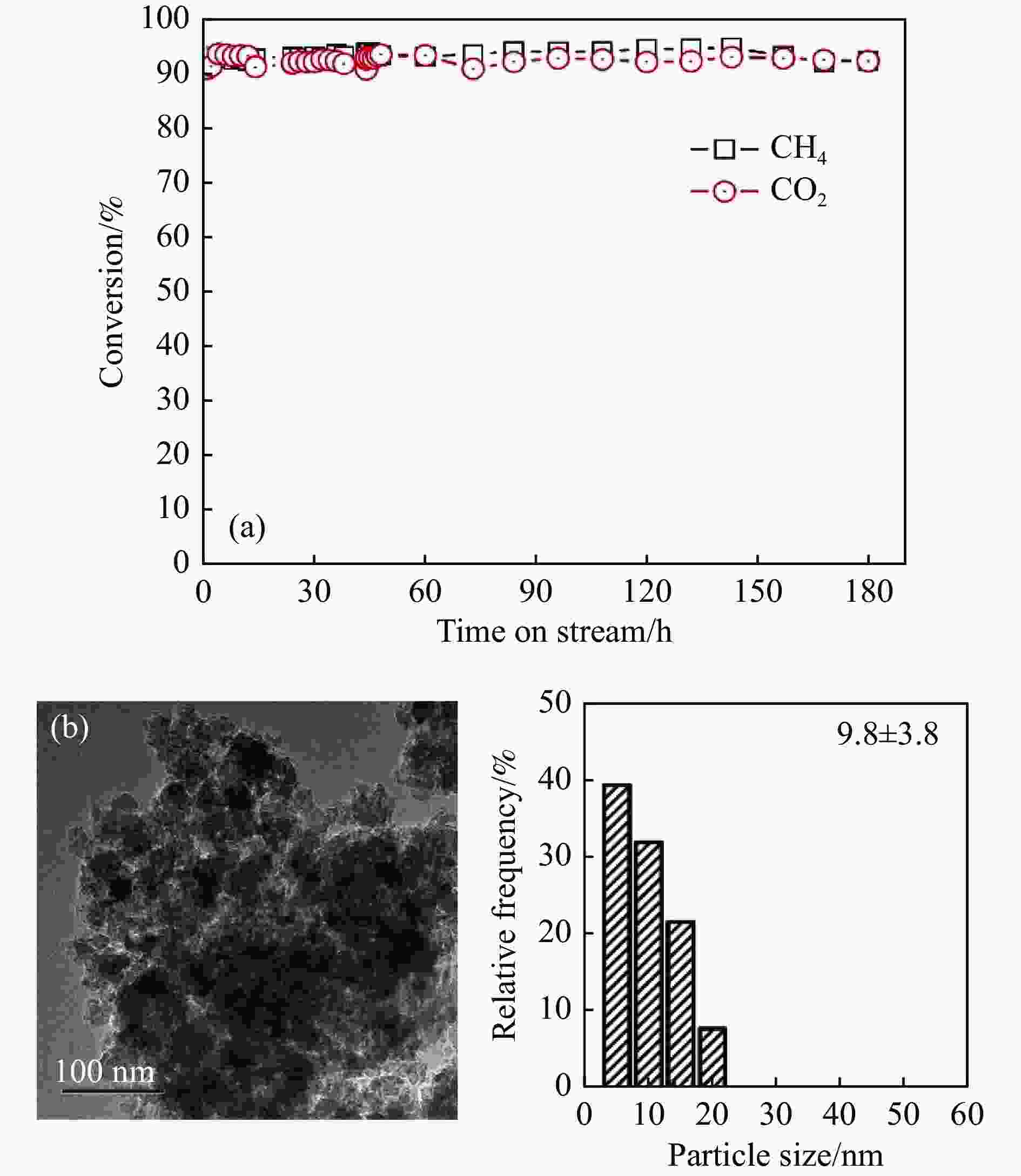
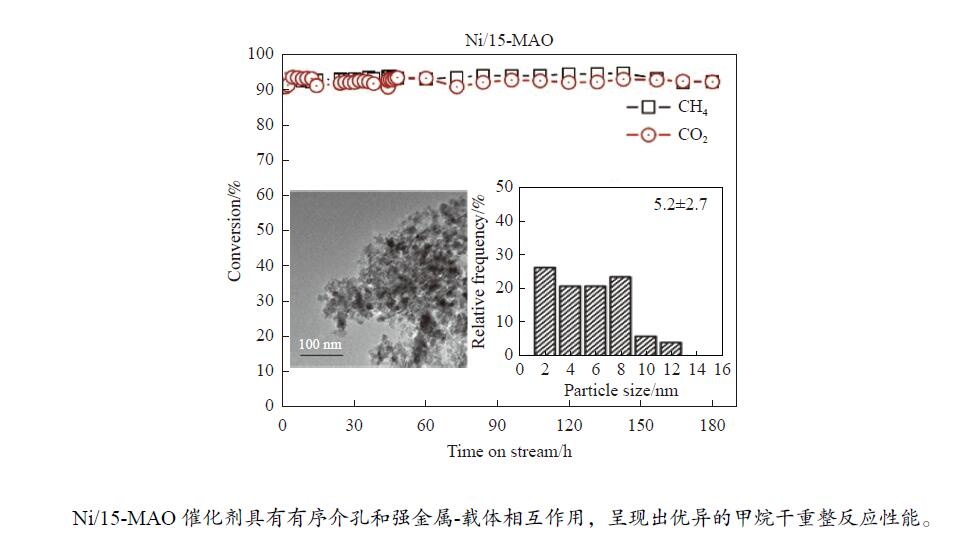
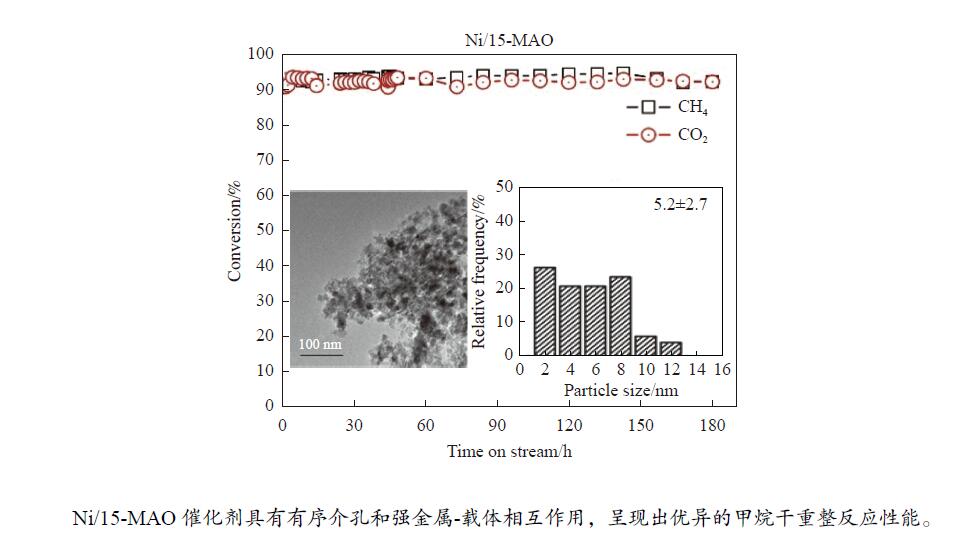
摘要: 本研究采用溶剂蒸发自组装法制备了不同Mg含量的镁铝尖晶石(MgAl2O4)载体,随后负载了金属Ni,并将该催化剂(Ni/x-MAO)应用于甲烷干重整制合成气反应。结合X射线衍射、氮气物理吸附-脱附和透射电镜等表征对催化剂的结构性质进行了分析,发现适量Mg的加入(10%−15%)有利于提高载体的比表面积,并形成耐高温的有序介孔结构。该结构可以将Ni颗粒限域在孔道内,有利于形成高分散、小晶粒的活性物种,其在高温反应下不易烧结。同时,H2-TPR和XPS结果表明,10%−15%的Mg含量有利于增强Ni与MgAl2O4的金属-载体相互作用,有效抑制Ni烧结,且其表面的活性氧物种有效抑制了积炭生成。在性能评价中,10%−15%Mg含量的Ni/MgAl2O4催化剂呈现出优异的CH4和CO2转化率,在180 h的长周期活性评价期间,Ni/15-MAO催化剂的CH4和CO2转化率分别保持在92.6%和92.5%左右,同时积炭量仅为0.89%,且反应后的Ni颗粒尺寸变化不大。
-
关键词:
- 甲烷干重整反应 /
- 有序介孔MgAl2O4 /
- 镍基催化剂
Abstract: Methane dry reforming reaction is a promising route for the valorization of both CO2 and CH4. However, the catalysts usually suffered from the coking deactivation and the sintering of active phase under the harsh reaction conditions. In this paper, the Mg-Al spinel support with different Mg content prepared by the solvent evaporation-induced self-assembly method was investigated. With this support, Ni/MgAl2O4 was used as the catalyst for methane dry reforming to syngas. XRD, BET and TEM results showed that the addition of appropriate amount of magnesium (10%−15%) was beneficial to the formation of highly stable ordered mesoporous magnesia spinel support with large specific surface area, which can confine the Ni particles in the pore structure and thus enhance the nickel dispersion and improve the resistance of coke formation under high temperature. H2-TPR and XPS analysis indicated the addition of 10%−15% magnesium can promote the interaction between Ni and MgAl2O4, inhibiting the agglomeration of Ni and the coke formation with the active surface-adsorbed oxygen species. Detailed activity tests showed that Ni/MgAl2O4 catalysts with 10%−15% magnesium content has high CH4 and CO2 conversion. During the long-term test for 180 h, the Ni/15-MAO catalyst exihibited the CH4 and CO2 conversions of 92.6% and 92.5%, respectively. The coke deposition percentage was only 0.89% and the grain size of Ni was maintained after reaction.1) # 共同第一作者 -
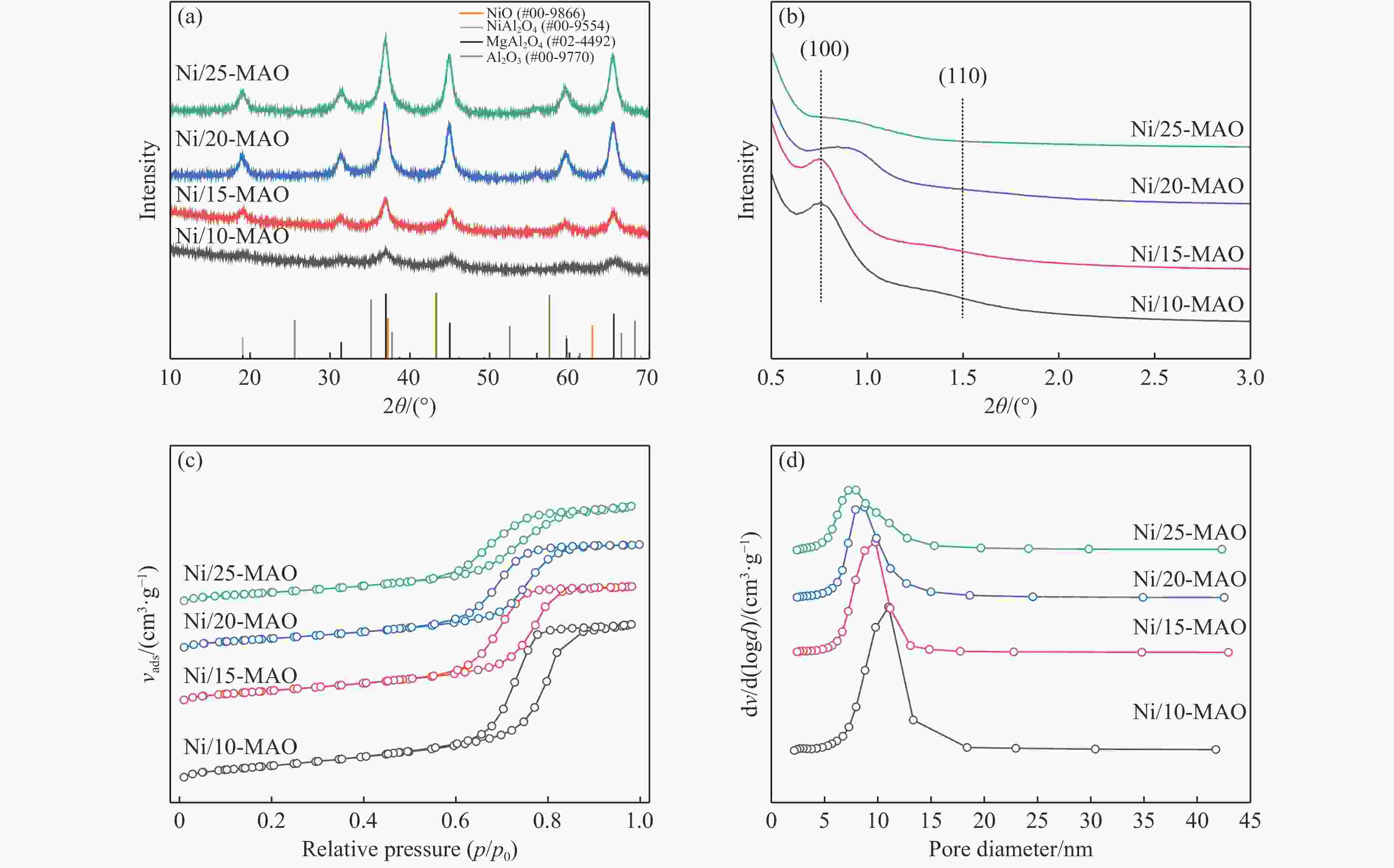
表 1 新鲜催化剂的孔结构参数
Table 1 Pore structure parameters of the fresh catalysts
Catalyst BET surface area S/(m2·g−1) Total pore volume v/(cm3·g−1) Average pore size d/nm Ni/10-MAO 247.3 0.628 10.2 Ni/15-MAO 203.1 0.471 9.3 Ni/20-MAO 181.2 0.424 9.4 Ni/25-MAO 177.1 0.394 8.9 表 2 还原催化剂的XPS分析
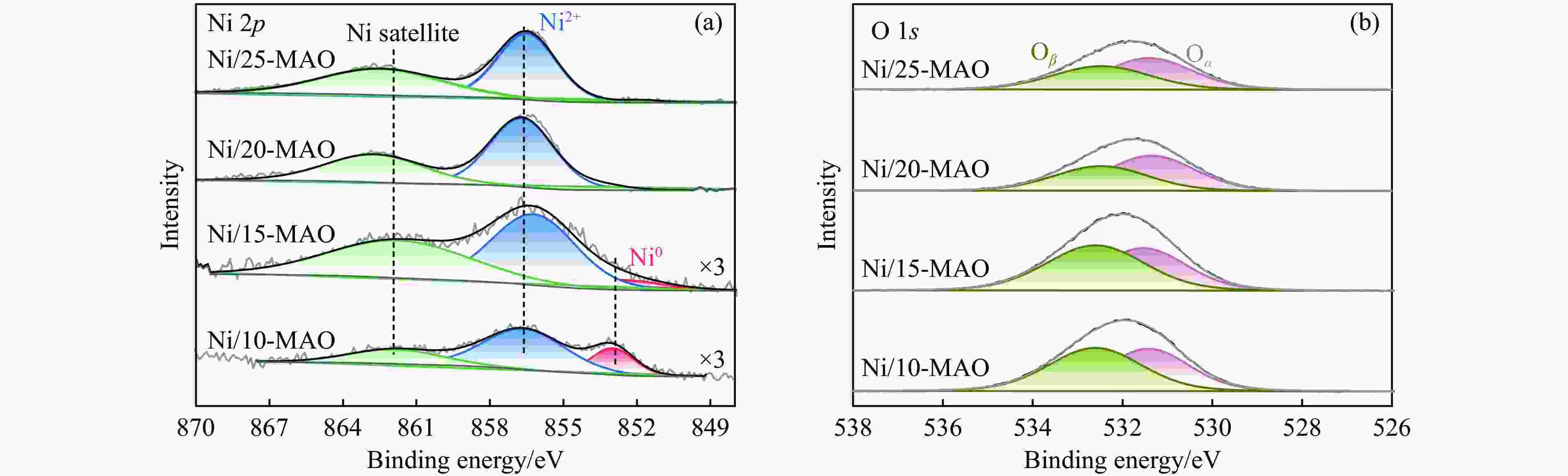
Table 2 XPS analysis results of the reduced catalysts
Catalyst Ni 2p/% O 1s/% Ni contenta Ni0/(Ni0+Ni2+) Oα Oβ Ni/10-MAO 1.56 19.6 46.5 53.5 Ni/15-MAO 1.80 13.1 45.3 54.8 Ni/20-MAO 5.44 N.D. 56.9 43.1 Ni/25-MAO 5.73 N.D. 54.5 45.5 a: Ni content on the surface of catalysts. -
[1] ABDULRASHEED A, JALIL A A, GAMBO Y, et al. A review on catalyst development for dry reforming of methane to syngas: Recent advances[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev,2019,108:175−193. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.03.054 [2] USMAN M, WAN DAUD W, ABBAS H F. Dry reforming of methane: Influence of process parameters-A review[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev,2015,45:710−744. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.02.026 [3] PAKHARE D, SPIVEY J. A review of dry (CO2) reforming of methane over noble metal catalysts[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2014,43(22):7813−7837. doi: 10.1039/C3CS60395D [4] JANG W-J, SHIM J-O, KIM H-M, et al. A review on dry reforming of methane in aspect of catalytic properties[J]. Catal Today,2019,324:15−26. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.07.032 [5] 李嘉卿, 徐彬, 王文博, 等. 等离子体催化甲烷干重整实验研究[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文),2021,49(8):1161−1172. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60070-1LI Jiaqing, XU Bin, WANG Wenbo, et al. Experimental study on dry reforming of methane by a plasma catalytic hybrid system[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol.,2021,49(8):1161−1172. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60070-1 [6] WANG C, SUN N, ZHAO N, et al. Coking and deactivation of a mesoporous Ni-CaO-ZrO2 catalyst in dry reforming of methane: A study under different feeding compositions[J]. Fuel,2015,143:527−535. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.11.097 [7] BOUKHA Z, JIMÉNEZ-GONZÁLEZ C, RIVAS B de, et al. Synthesis, characterisation and performance evaluation of spinel-derived Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for various methane reforming reactions[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2014,158−159:190−201. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.014 [8] ALABI W O, SULAIMAN K O, WANG H, et al. Effect of spinel inversion and metal-support interaction on the site activity of Mg-Al-Ox supported Co catalyst for CO2 reforming of CH4[J]. J CO2 Util,2020,37:180−187. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2019.12.006 [9] LI S, ZHANG G, WANG J, et al. Enhanced activity of Co catalysts supported on tungsten carbide-activated carbon for CO2 reforming of CH4 to produce syngas[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2021,46(56):28613−28625. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.06.085 [10] ALABI W O, SULAIMAN K O, WANG H. Sensitivity of the properties and performance of Co catalyst to the nature of support for CO2 reforming of CH4[J]. Chem Eng J,2020,390:124486. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124486 [11] THEOFANIDIS S A, GALVITA V V, POELMAN H, et al. Enhanced carbon-resistant dry reforming Fe-Ni catalyst: Role of Fe[J]. ACS Catal,2015,5(5):3028−3039. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b00357 [12] BRADFORD M C, VANNICE M. CO2 reforming of CH4 over supported Ru catalysts[J]. J Catal,1999,183(1):69−75. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1999.2385 [13] MARK M F, MAIER W F. CO2-reforming of methane on Supported Rh and Ir catalysts[J]. J Catal,1996,164(1):122−130. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1996.0368 [14] MUNERA J, IRUSTA S, CORNAGLIA L, et al. Kinetics and reaction pathway of the CO2 reforming of methane on Rh supported on lanthanum-based solid[J]. J Catal,2007,245(1):25−34. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2006.09.008 [15] WANG H, RUCKENSTEIN E. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane to synthesis gas over supported rhodium catalysts: The effect of support[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2000,204(1):143−152. doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00547-0 [16] O’CONNOR A M, SCHUURMAN Y, ROSS J R, et al. Transient studies of carbon dioxide reforming of methane over Pt/ZrO2 and Pt/Al2O3[J]. Catal Today,2006,115(1/4):191−198. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2006.02.051 [17] YU M, ZHU Y-A, LU Y, et al. The promoting role of Ag in Ni-CeO2 catalyzed CH4-CO2 dry reforming reaction[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2015,165:43−56. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.09.066 [18] SHINDE V M, MADRAS G. Catalytic performance of highly dispersed Ni/TiO2 for dry and steam reforming of methane[J]. RSC Adv,2014,4(10):4817. doi: 10.1039/c3ra45961f [19] ZHAO Q, WANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Steam reforming of CH4 at low temperature on Ni/ZrO2 catalyst: Effect of H2O/CH4 ratio on carbon deposition[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2020,45(28):14281−14292. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.03.112 [20] CHENG Z X, ZHAO X G, LI J L, et al. Role of support in CO2 reforming of CH4 over a Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2001,205(1/2):31−36. doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00560-3 [21] CUI Y, ZHANG H, XU H, et al. Kinetic study of the catalytic reforming of CH4 with CO2 to syngas over Ni/α-Al2O3 catalyst: The effect of temperature on the reforming mechanism[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2007,318:79−88. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2006.10.044 [22] GUO Y, FENG J, LI W. Effect of the Ni size on CH4/CO2 reforming over Ni/MgO catalyst: A DFT study[J]. Chin J Chem Eng,2017,25(10):1442−1448. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2017.03.024 [23] LA PAROLA V, LIOTTA L F, PANTALEO G, et al. CO2 reforming of CH4 over Ni supported on SiO2 modified by TiO2 and ZrO2: Effect of the support synthesis procedure[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2022,642:118704. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2022.118704 [24] PEREÑIGUEZ R, GONZALEZ-DELACRUZ V M, CABALLERO A, et al. LaNiO3 as a precursor of Ni/La2O3 for CO2 reforming of CH4: Effect of the presence of an amorphous NiO phase[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2012,123-124:324−332. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.044 [25] BAHARUDIN L, RAHMAT N, OTHMAN N H, et al. Formation, control, and elimination of carbon on Ni-based catalyst during CO2 and CH4 conversion via dry reforming process: A review[J]. J CO2 Util,2022,61:102050. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2022.102050 [26] GHOLIZADEH F, IZADBAKHSH A, HUANG J, et al. Catalytic performance of cubic ordered mesoporous alumina supported nickel catalysts in dry reforming of methane[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2021,310:110616. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110616 [27] XU L, ZHAO H, SONG H, et al. Ordered mesoporous alumina supported nickel based catalysts for carbon dioxide reforming of methane[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2012,37(9):7497−7511. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.01.105 [28] HORIUCHI T, SAKUMA K, FUKUI T, et al. Suppression of carbon deposition in the CO2-reforming of CH4 by adding basic metal oxides to a Ni/Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,1996,144(1/2):111−120. doi: 10.1016/0926-860X(96)00100-7 [29] LU Y, KANG L, GUO D, et al. Double-site doping of a V promoter on Nix-V-MgAl catalysts for the DRM reaction: Simultaneous effect on CH4 and CO2 activation[J]. ACS Catal,2021,11(14):8749−8765. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.1c01299 [30] OLSBYE U, WURZEL T, MLECZKO L. Kinetic and reaction engineering studies of dry reforming of methane over a Ni/La/Al2O3 Catalyst[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,1997,36(12):5180−5188. doi: 10.1021/ie970246l [31] MA Q, HAN Y, WEI Q, et al. Stabilizing Ni on bimodal mesoporous-macroporous alumina with enhanced coke tolerance in dry reforming of methane to syngas[J]. J CO2 Util,2020,35:288−297. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2019.10.010 [32] BARROSO-QUIROGA M M, CASTRO-LUNA A E. Catalytic activity and effect of modifiers on Ni-based catalysts for the dry reforming of methane[J]. Int J Hydrog Energy,2010,35(11):6052−6056. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.12.073 [33] ARBAG H, YASYERLI S, YASYERLI N, et al. Coke Minimization in dry reforming of methane by Ni based mesoporous alumina catalysts synthesized following different routes: Effects of W and Mg[J]. Top Catal,2013,56(18/20):1695−1707. doi: 10.1007/s11244-013-0105-3 [34] FENG J, DING Y, GUO Y, et al. Calcination temperature effect on the adsorption and hydrogenated dissociation of CO2 over the NiO/MgO catalyst[J]. Fuel,2013,109:110−115. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.08.028 [35] CASTRO LUNA A E, IRIARTE M E. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane over a metal modified Ni-Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2008,343(1/2):10−15. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2007.11.041 [36] DÜDDER H, KÄHLER K, KRAUSE B, et al. The role of carbonaceous deposits in the activity and stability of Ni-based catalysts applied in the dry reforming of methane[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2014,4(9):3317−3328. doi: 10.1039/C4CY00409D [37] LI L, ANJUM D H, ZHU H, et al. Synergetic effects leading to coke-resistant NiCo bimetallic catalysts for dry reforming of methane[J]. ChemCatChem,2015,7(3):427−433. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201402921 [38] GARCÍA-DIÉGUEZ M, HERRERA C, LARRUBIA M Á, et al. CO2-reforming of natural gas components over a highly stable and selective NiMg/Al2O3 nanocatalyst[J]. Catal Today,2012,197(1):50−57. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.06.019 [39] 张荣俊, 夏国富, 李明丰, 等. 载体类型对Ni基催化剂甲烷干重整反应性能的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2015,43(11):1359−1365. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(15)30040-2ZHANG Rongjun, XIA Guofu, LI Mingfeng, et al. Effect of support on catalytic performance of Ni-based catayst in methane dry reforming[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2015,43(11):1359−1365. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(15)30040-2 [40] SHEN J, REULE A A, SEMAGINA N. Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst for low-temperature oxidative dry methane reforming with CO2[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2019,44(10):4616−4629. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.027 [41] KARAM L, ARMANDI M, CASALE S, et al. Comprehensive study on the effect of magnesium loading over nickel-ordered mesoporous alumina for dry reforming of methane[J]. Energy Conv Manag,2020,225:113470. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113470 [42] DAS S, THAKUR S, BAG A, et al. Support interaction of Ni nanocluster based catalysts applied in CO2 reforming[J]. J Catal,2015,330:46−60. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.06.010 [43] ZHAO Y-H, GENG J-T, ZHU H-D, et al. Ordered mesoporous Ni-Mg-Al2O3 as an effective catalyst for CO2 reforming of CH4[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2023,48(20):7192−7201. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.11.205 [44] LU J, ZHANG Y, JIAO C, et al. Effect of reduction-oxidation treatment on structure and catalytic properties of ordered mesoporous Cu-Mg-Al composite oxides[J]. Sci Bull,2015,60(12):1108−1113. doi: 10.1007/s11434-015-0805-0 [45] ATANDA L, FRAGA G L L, AHMED M H M, et al. Conversion of agricultural waste into stable biocrude using spinel oxide catalysts[J]. J Hazard Mater,2021,402:123539. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123539 [46] REZAEI M, ALAVI S M. Dry reforming over mesoporous nanocrystalline 5% Ni/M-MgAl2O4 (M: CeO2, ZrO2, La2O3) catalysts[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2019,44(31):16516−16525. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.04.213 [47] LIU J, YU J, SU F, et al. Intercorrelation of structure and performance of Ni-Mg/Al2O3 catalysts prepared with different methods for syngas methanation[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2014,4(2):472−481. doi: 10.1039/C3CY00601H [48] 徐军科, 任克威, 周伟, 等. 制备方法对甲烷干重整催化剂Ni/La2O3/Al2O3结构及性能的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2009,37(4):473−479.XU Junke, REN Kewei, ZHOU Wei, et al. Influence of preparation method on the properties and catalytic performance of Ni/La2O3/Al2O3 catalyst for dry reforming of methane[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2009,37(4):473−479. [49] YUAN Q, YIN A-X, LUO C, et al. Facile synthesis for ordered mesoporous gamma-aluminas with high thermal stability[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2008,130(11):3465−3472. doi: 10.1021/ja0764308 [50] HAMBALI H U, JALIL A A, ABDULRASHEED A A, et al. Effect of Ni-Ta ratio on the catalytic selectivity of fibrous Ni-Ta/ZSM-5 for dry reforming of methane[J]. Chem Eng Sci,2020,227:115952. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2020.115952 [51] LIU Z, ZHOU J, CAO K, et al. Highly dispersed nickel loaded on mesoporous silica: One-spot synthesis strategy and high performance as catalysts for methane reforming with carbon dioxide[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2012,125:324−330. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.06.003 [52] ODEDAIRO T, CHEN J, ZHU Z. Metal-support interface of a novel Ni-CeO2 catalyst for dry reforming of methane[J]. Catal Commun,2013,31:25−31. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2012.11.008 [53] THOMMES M, KANEKO K, NEIMARK A V, et al. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report)[J]. Pure Appl Chem,2015,87(9/10):1051−1069. doi: 10.1515/pac-2014-1117 [54] LI B, YUAN X, LI L, et al. Lanthanide oxide modified nickel supported on mesoporous silica catalysts for dry reforming of methane[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2021,46(62):31608−31622. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.07.056 [55] BIAN Z, ZHONG W, YU Y, et al. Dry reforming of methane on Ni/mesoporous-Al2O3 catalysts: Effect of calcination temperature[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2021,46(60):31041−31053. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.12.064 [56] YUAN X, LI B, WANG X, et al. Synthesis gas production by dry reforming of methane over Neodymium-modified hydrotalcite-derived nickel catalysts[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2022,227:107104. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2021.107104 [57] TAN P, GAO Z, SHEN C, et al. Ni-Mg-Al solid basic layered double oxide catalysts prepared using surfactant-assisted coprecipitation method for CO2 reforming of CH4[J]. Chin J Catal,2014,35(12):1955−1971. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60171-6 [58] GUO J, LOU H, ZHAO H, et al. Dry reforming of methane over nickel catalysts supported on magnesium aluminate spinels[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2004,273(1/2):75−82. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2004.06.014 [59] DAMYANOVA S, PAWELEC B, ARISHTIROVA K, et al. Ni-based catalysts for reforming of methane with CO2[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2012,37(21):15966−15975. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.08.056 [60] LU X, GU F, LIU Q, et al. VOx promoted Ni catalysts supported on the modified bentonite for CO and CO2 methanation[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2015,135:34−46. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.10.009 [61] AGHAALI M H, FIROOZI S. Enhancing the catalytic performance of Co substituted NiAl2O4 spinel by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method for steam and dry reforming of methane[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2021,46(1):357−373. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.09.157 [62] DUAN X, WEN Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Intercalation of nanostructured CeO2 in MgAl2O4 spinel illustrates the critical interaction between metal oxides and oxides[J]. Nanoscale,2018,10(7):3331−3341. doi: 10.1039/C7NR07825K [63] JIANG F, WANG S, LIU B, et al. Insights into the influence of CeO2 crystal facet on CO2 hydrogenation to methanol over Pd/CeO2 catalysts[J]. ACS Catal,2020,10(19):11493−11509. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c03324 -




 下载:
下载: