The effect of alkali and alkaline earth metals in biomass ash on the bio-oil components derived from biomass fast pyrolysis
-
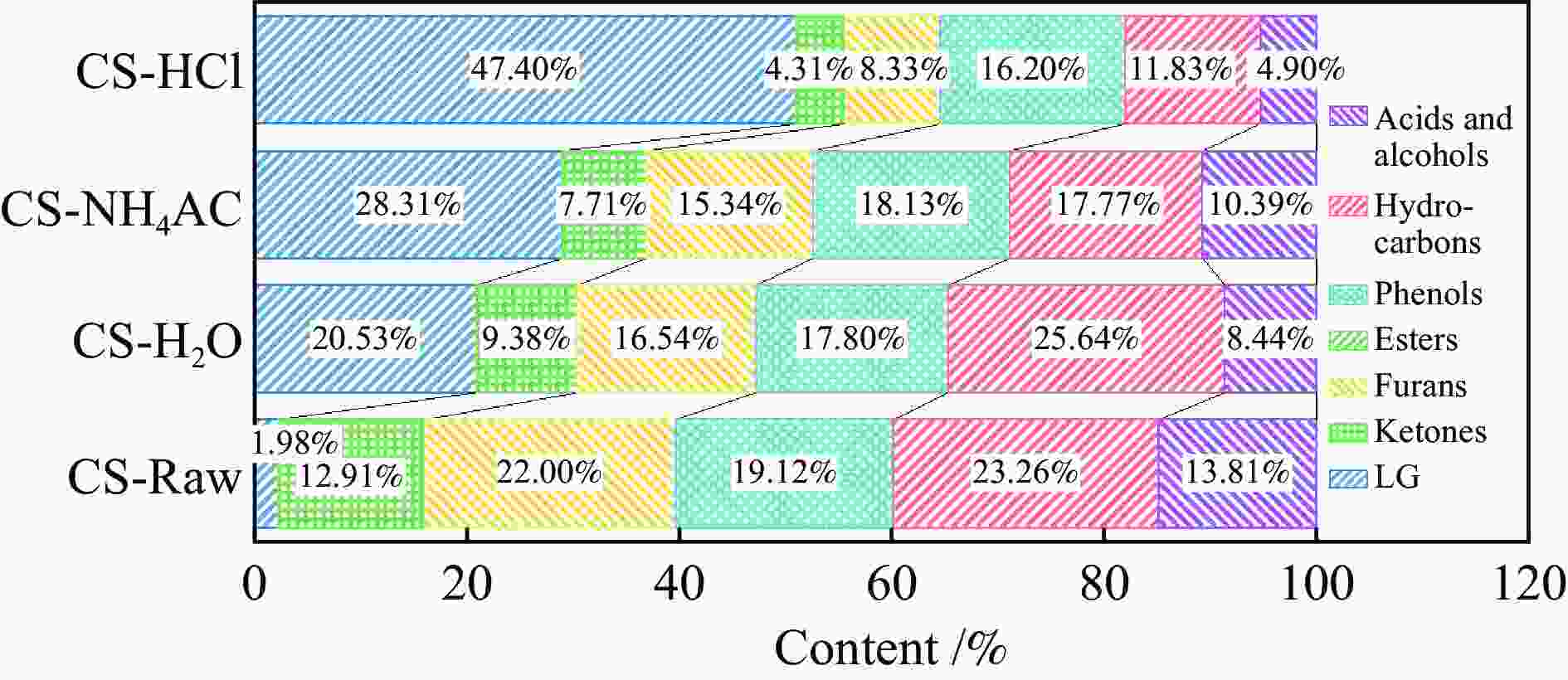
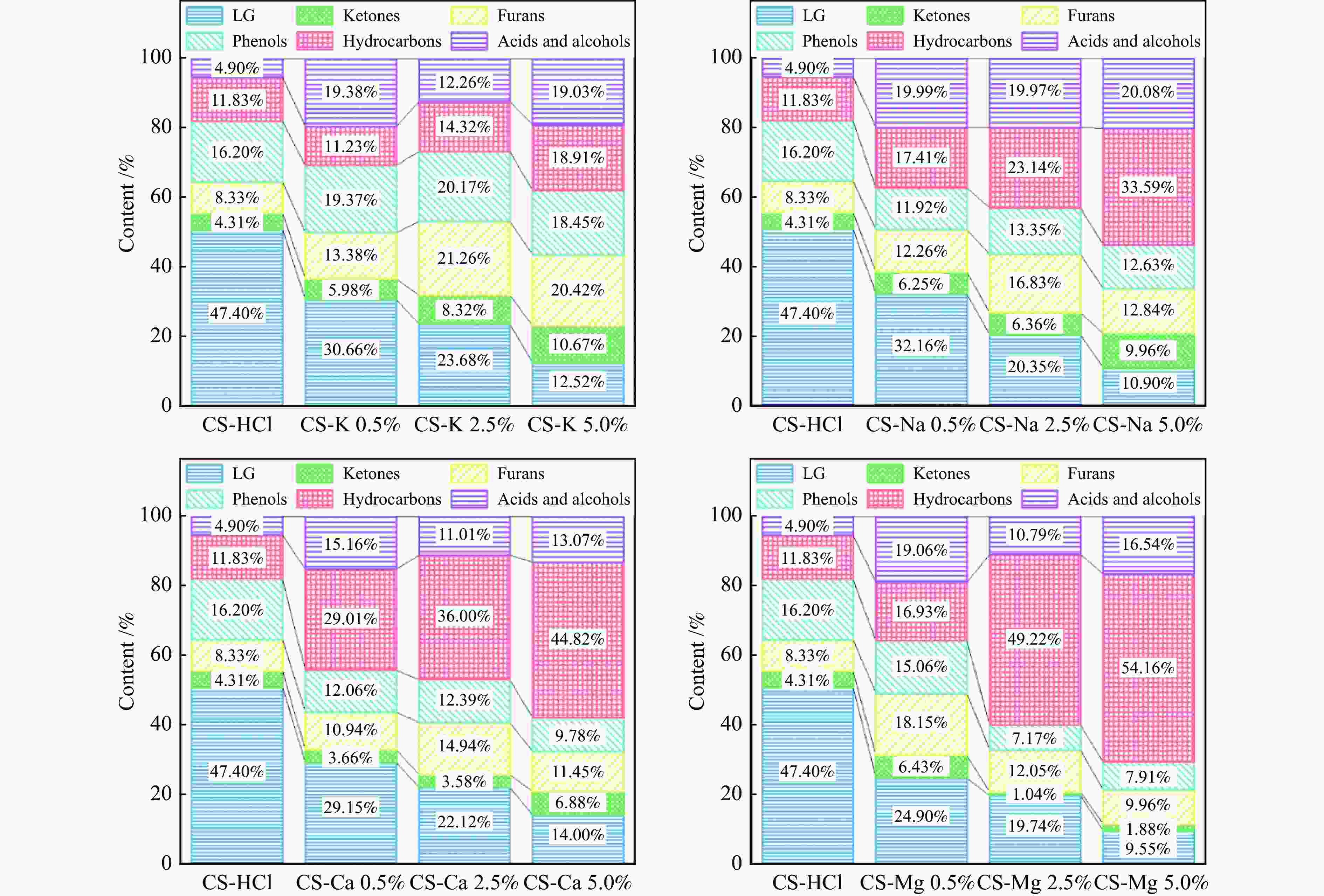
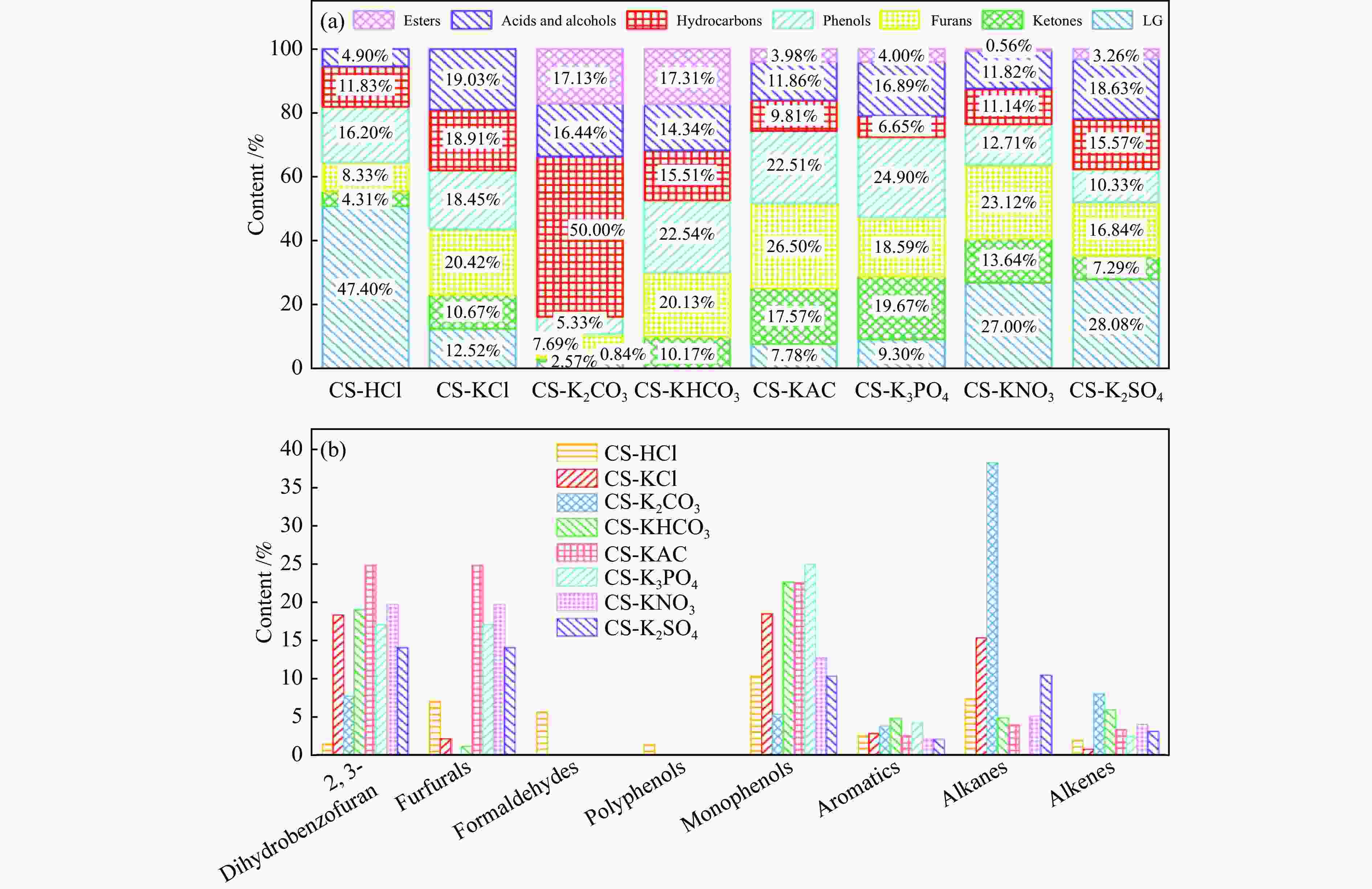
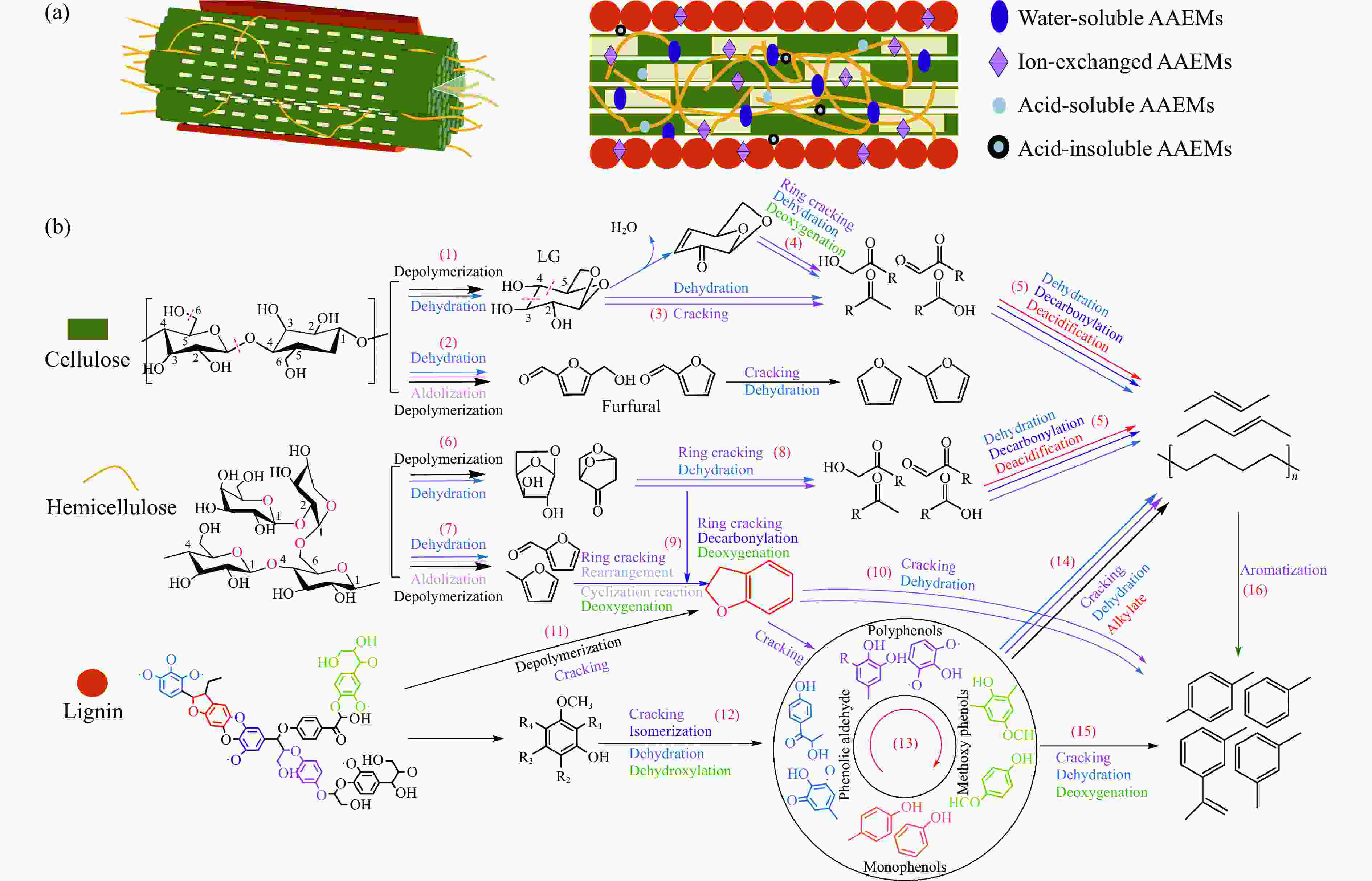
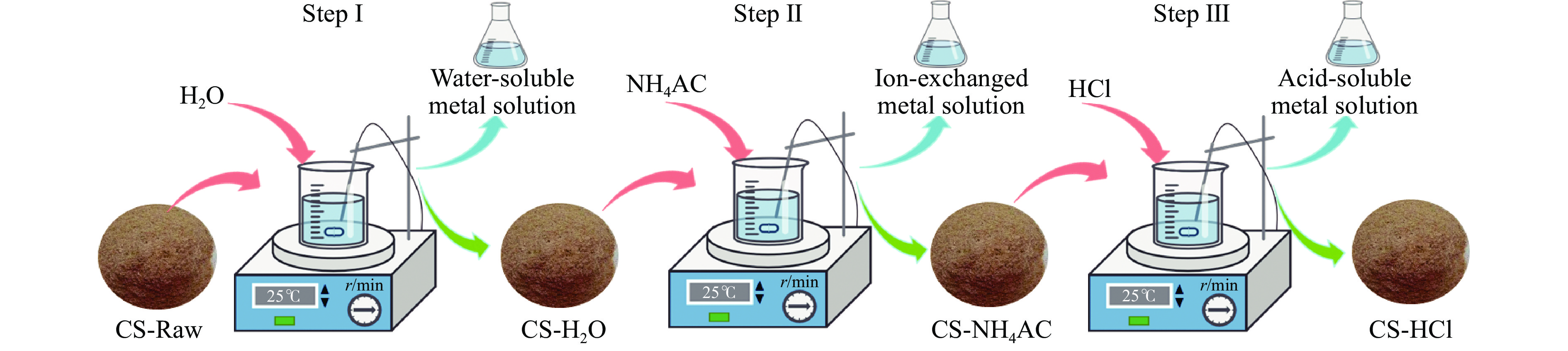
摘要: 生物质灰分中的碱和碱土金属(AAEMs)对快速热解生物油的产率和组分分布具有显著影响。本研究选取玉米秸秆为原料,研究梯级脱灰预处理(蒸馏水、醋酸铵和盐酸)对AAEMs的选择性脱除及其生物油组分的影响,研究了碱和碱土金属类别(K、Ca、Na和Mg)、盐浓度(0.5%、2.5%、5%)和不同钾盐的酸根(
${\rm{SO}}_{4}^{{2-}} $ 、${\rm{NO}}_{3}^{-} $ 、${\rm{CO}}_{3}^{{2-}} $ 、${\rm{HCO}}_{3}^{-} $ 、AC−和${\rm{PO}}_{4}^{{{3-}}}$ )对生物油组分的影响。结果表明,在梯级脱灰预处理过程中,随着脱灰溶液酸性程度加深,AAEMs的脱除率逐渐上升,根据AAEMs在梯级脱灰过程中的选择性脱除规律,可将其在生物质中的赋存形态分为水溶性(K)、离子交换性(Ca和Mg)和酸溶性(Na)等形态。经过碱和碱土金属盐浸渍后,AAEMs将起到催化剂的作用,促进热解中间产物左旋葡聚糖的二次降解,导致其相对含量显著降低,形成更多的呋喃和酮类等轻质含氧化合物,导致2, 3-二氢苯并呋喃、酮类和长链烷烃等组分的含量显著增加。不同钾盐酸根离子对脱水糖的二次裂解反应及木质素芳基醚键和酚羟基的裂解反应具有较大的影响,根据酸根的酸性强弱,对脱水糖裂解反应的影响大小顺序为${\rm{HCO}}_{3}^{-} $ >${\rm{CO}}_{3}^{{{2-}}}$ >AC−>${\rm{PO}}_{4}^{{{3-}}}$ >Cl−>${\rm{NO}}_{3}^{-} $ >${\rm{SO}}_{4}^{{{2-}}}$ ,而对木质素芳基醚键和酚羟基的裂解反应影响大小顺序为${\rm{CO}}_{3}^{{{2-}}}$ >Cl−>${\rm{HCO}}_{3}^{-} $ >${\rm{PO}}_{4}^{{{3-}}}$ ≈AC−>${\rm{SO}}_{4}^{{{2-}}}$ ≈${\rm{NO}}_{3}^{-} $ 。Abstract: The alkali and alkaline earth metals (AAEMs) in biomass ash have a significant impact on the yield and component distribution of rapid plytic biooil. In this paper, corn straw is selected as the raw material. First, the effect of cascade deash removal pretreatment (distillation water, ammonium acetate and hydrochloric acid) on the selective removal of AAEMs and its biological oil components is studied, and then the effect of the type of AAEMs (K, Ca, Na and Mg), the concentration of chloride salt (0.5%, 2.5% and 5%), and the acid radical in metal salt(${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ,${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ ,${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-} $ ,${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ , AC− and${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ )on the compound distribution of bio-oil was systematically investigated. The results show that in the process of ash removal pretreatment, with the deepening of the acidity of the ash removal solution, the removal rate of AAEMs gradually increases. According to the selective removal law of AAEMs in the process of cascade ash removal, their morphology in biomass can be divided into the following three groups, namely the water-soluble metal (K), the ion-exchanged metals (Ca and Mg), the acid-soluble metal (Na). The removal of AAEMs promoted the formation of levoglucosan (LG), while restrained the formation of ketones and furans. However, the incorporation of AAEMs in biomass presented an opposite variation trend. The AAEMs would act as catalyst during biomass pyrolysis which promoted the secondary cracking of LG, leading to the reduction of LG and increase of ketones and furans. In addition, different acid roots in potassium salt also have remarkable influence on the secondary cracking reaction of LG and the rupture of the aryl ether bond and the phenolic hydroxyl group in lignin. The influence of the acid roots on the secondary cracking reaction of LG was in the order of${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ >${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-} $ >AC−>${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ >Cl−>${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ >${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ , while the influence of acid roots on the rupture of the aryl ether bond and the phenolic hydroxyl group was in the order of${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-} $ >Cl−>${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ >${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ ≈AC−>${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ≈${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ .-
Key words:
- biomass /
- demineralization pretreatment /
- alkali and alkaline earth metals /
- fast pyrolysis /
- bio-oil
-
表 1 原料及梯级脱灰预处理样品的元素分析和工业分析
Table 1 Ultimate and proximate analysis of raw and pretreated biomass
Sample Ultimate analysis wdaf/% Proximate analysis wdb/% C H O S N A V FC CS-raw 45.42 6.18 47.81 0.09 0.60 3.39 77.58 19.03 CS-H2O 46.34 6.31 46.98 0.02 0.35 2.38 82.30 15.32 CS-NH4AC 46.36 6.28 47.04 0.03 0.29 1.73 85.21 13.06 CS-HCl 46.33 6.24 47.15 0.07 0.21 1.70 86.54 11.76 表 2 原料及梯级脱灰预处理样品的碱和碱土金属质量分数
Table 2 Contents of AAEMs in raw and stepwise demineralization pretreated biomass
Sample Contents of AAEMs/(μg·g−1) Removal rates of AAEMs after each washing step/% K Na Ca Mg K Na Ca Mg CS-raw 7375.47 417.06 663.03 789.85 − − − − CS-H2O 1486.73 376.00 397.81 393.89 79.84 9.85 40.00 50.13 CS-NH4AC 49.77 340.66 85.42 38.52 19.48 8.47 47.12 44.99 CS-HCl 14.48 349.93 2.60 11.54 0.48 0.00 12.49 3.42 -
[1] 黄明, 朱亮, 马中青, 周秉亮, 刘晓欢, 叶结旺, 赵超. 金属改性分子筛催化热解木质素制取轻质芳烃[J]. 燃烧化学学报,2021,49(3):292−302.HUANG Ming, ZHU Liang, MA Zhong-qing, ZHOU Bing-liang, LIU Xiao-huan, YE Jie-wang, ZHAO Chao. Production of light aromatics from the fast pyrolysis of lignin catalyzed by metal-modified H-ZSM-5 zeolites[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2021,49(3):292−302. [2] 朱亮, 黄明, 丁紫霞, 马中青. 烘焙脱氧毛竹与高密度聚乙烯共催化热解制备轻质芳烃[J]. 燃料化学学报,2022,50(8):993−1003. doi: 10.19906/j.cnki.JFCT.2022014ZHU Liang, HUANG Ming, DING Zi-Xia, MA Zhong-Qing. Production of light bio-aromatics from co-catalytic fast pyrolysis of torrefied bamboo and high-density polyethylene[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2022,50(8):993−1003. doi: 10.19906/j.cnki.JFCT.2022014 [3] WANG S R, DAI G X, YANG H P, LUO Z Y. Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis mechanism: A state-of-the-art review[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2017,62:33−86. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2017.05.004 [4] CAI W, CHIKAYA K B, MA Z Q, HUANG M, XU J L, SHI Y H. Synergetic deoxygenation and demineralization of biomass by wet torrefaction pretreatment and its influence on the compound distribution of bio-oil during catalytic pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis,2023,174:106134. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2023.106134 [5] CHEN D Y, CEN K H, CHEN F, MA Z Q, ZHOU J B, LI M. Are the typical organic components in biomass pyrolyzed bio-oil available for leaching of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species (AAEMs) from biomass?[J]. Fuel,2020,260:116347. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116347 [6] 刘金淼, 马欣欣, 燕黄, 何艳峰, 刘广青. 碱/碱土金属浸渍对酸洗生物质热解影响研究[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版),2015,42(5):24−31. doi: 10.13543/j.cnki.bhxbzr.2015.05.004LIU Jing-sen, MA Xin-xin, YAN Huang, HE Yan-feng, LIU Guang-qing. Effect of alkaline/alkaline earth metal impregnation on pyrolysis of acid-washing biomass[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology ( Natural Science),2015,42(5):24−31. doi: 10.13543/j.cnki.bhxbzr.2015.05.004 [7] HU R, WAN S Q, MAO F, WANG J. Changes in pyrolysis characteristics of agricultural residues before and after water washing[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2021,49(9):1239−1249. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60073-7 [8] ASTON J E, THOMPSON D N, WESTOVER T L. Performance assessment of dilute-acid leaching to improve corn stover quality for thermochemical conversion[J]. Fuel,2016,186:311−319. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.08.056 [9] ZHANG Y J, LV P, WANG J F, WEI J T, CAO P W, BIE N X, BAI Y H, YU G S. Product characteristics of rice straw pyrolysis at different temperature: Role of inherent alkali and alkaline earth metals with different occurrence forms[J]. Journal of the Energy Institute,2022,101:201−208. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2022.01.016 [10] GUREVICH MESSINA L I, BONELLI P R, CUKIERMAN A L. Effect of acid pretreatment and process temperature on characteristics and yields of pyrolysis products of peanut shells[J]. Renewable Energy,2017,114:697−707. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2017.07.065 [11] CHEN H D, CHEN X L, QIAO Z, LIU H F. Release and transformation characteristics of K and Cl during straw torrefaction and mild pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2016,167:31−39. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.11.059 [12] LIN X N, KONG L S, CAI H Z, ZHANG Q F, BI D M, YI W M. Effects of alkali and alkaline earth metals on the co-pyrolysis of cellulose and high density polyethylene using TGA and Py-GC/MS[J]. Fuel Processing Technology,2019,71−78. [13] LENG E, COSTA M, GONG X, ZHENG A Q, LIU S J, XU M G. Effects of KCl and CaCl2 on the evolution of anhydro sugars in reaction intermediates during cellulose fast pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2019,251:307−315. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.006 [14] ZHANG H Y, MA Y, SHAO S S, XIAO R. The effects of potassium on distributions of bio-oils obtained from fast pyrolysis of agricultural and forest biomass in a fluidized bed[J]. Applied Energy,2017,208:867−877. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.062 [15] ZHAO S L, LIU M, ZHAO L, LIU J H. Effects of organic and inorganic metal salts on thermogravimetric pyrolysis of biomass components[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering,2017,34(12):3077−3084. doi: 10.1007/s11814-017-0209-8 [16] 蒋丽群, 岳元茂, 徐禄江, 钱乐, 刘世君, 赵增立, 李海滨, 廖艳芬. 预处理促进木质纤维素快速热解生成左旋葡聚糖[J]. 化工学报,2021,72(4):1825−1832.JIANG Li-qun, YUE Yuan-mao, XU Lu-jiang, QIAN Yue, LIU Shi-jun, ZHAO Zeng-li, LI Hai-bing, LIAO Yan-fen. Pretreatments promote levoglucosan production from lignocellulose via fast pyrolysis[J]. CIESC Journal,2021,72(4):1825−1832. [17] WANG C Y, XIA S P, YANG X W, ZHENG A Q, ZHAO Z L, LI H B. Oriented valorization of cellulose and xylan into anhydrosugars by using low-temperature pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2021,291:120156. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120156 [18] ZHENG A Q, WANG Q, LIU S J, HUANG Z, WEI G Q, ZHAO K, WANG S, ZHAO Z L, LI H B. Selective sequential fractionation of biomass for quantitatively elucidating the compositional factors affecting biomass fast pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis,2021,156:105106. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105106 [19] HORNER H T, WAGNER B L. Calcium oxalate formation in higher plants [M]. Calcium Oxalate In Biological Systems. CRC Press. 2020: 53-72. [20] 钱乐, 蒋丽群, 岳元茂, 赵增立. 催化热解生物质生成左旋葡聚糖酮的研究进展[J]. 化工学报,2020,71(12):5376−5387.QIAN Yue, JIANG Li-qun, YUE Yuan-mao, ZHAO Zeng-li. Research progress of catalytic pyrolysis of biomass to yield levoglucosenone[J]. CIESC Journal,2020,71(12):5376−5387. [21] YANG H, LI S, LIU B, CHEN Y, XIAO J, DONG Z, GONG M, CHEN H. Hemicellulose pyrolysis mechanism based on functional group evolutions by two-dimensional perturbation correlation infrared spectroscopy[J]. Fuel,2020,267:117302. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117302 [22] LOU R, WU S B, LV G J. Fast pyrolysis of enzymatic/mild acidolysis lignin from moso bamboo[J]. BioResources,2010,5(2):827−837. doi: 10.15376/biores.5.2.827-837 [23] WANG S Q, LI Z H, BAI X Y, YI W M, FU P. Influence of inherent hierarchical porous char with alkali and alkaline earth metallic species on lignin pyrolysis[J]. Bioresource Technology,2018,268:323−331. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.117 [24] 王锐, 高明洋, 曹景沛. 碱/碱土金属催化松木屑快速热解机制[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(2):289−297.WANG Yue, GAO Ming-yang, CAO Jing-pei. Mechanism of rapid pyrolysis of pine chips catalyzed by alkali/alkaline earth metals[J]. Chinese Journal Of Applied Chemistry,2022,39(2):289−297. [25] 孔令伟, 张冰磊, 郭晨, 贺洁雅. 金属盐添加剂对生物质热解特性影响研究进展[J]. 广东化工,2022,49(23):119−20 + 56.KONG Ling-wei, ZHANG Bing-lei, GUO Chen, HE Jie-ya. Research Progress on the Effects of Metal Additives on Biomass Pyrolysis Characteristics[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2022,49(23):119−20 + 56. [26] CHEN H P, TANG Z Y, LIU B, CHEN W, HU J H, CHEN Y Q, YANG H P. The new insight about mechanism of the influence of K2CO3 on cellulose pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2021,295:120617. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120617 [27] WANG L C, SHEN Y F. Pyrolysis characteristics of cellulosic biomass in the presence of alkali and alkaline-earth-metal (AAEM) oxalates[J]. Cellulose,2021,28(6):3473−3483. doi: 10.1007/s10570-021-03756-3 [28] SUN T L, ZHANG L, YANG Y T, LI Y L, REN S X, DONG L L, LEI T Z. Fast Pyrolysis of Cellulose and the Effect of a Catalyst on Product Distribution[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2022,19(24):16837. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416837 [29] MARATHE P S, OUDENHOVEN S R G, HEERSPINK P W, KERSTEN S R A, WESTERHOF R J M. Fast pyrolysis of cellulose in vacuum: The effect of potassium salts on the primary reactions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,329:187−197. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.05.134 [30] MAYES H B, NOLTE M W, BECKHAM G T, SHANKS B H, BROADBELT L J. The Alpha–Bet(a) of Salty Glucose Pyrolysis: Computational Investigations Reveal Carbohydrate Pyrolysis Catalytic Action by Sodium Ions[J]. ACS Catalysis,2014,5(1):192−202. -


















 下载:
下载: