Study on the catalytic performance of CO-PROX catalyzed by CuO-NiO/CeO2 in H2/CO2 rich atmosphere
-
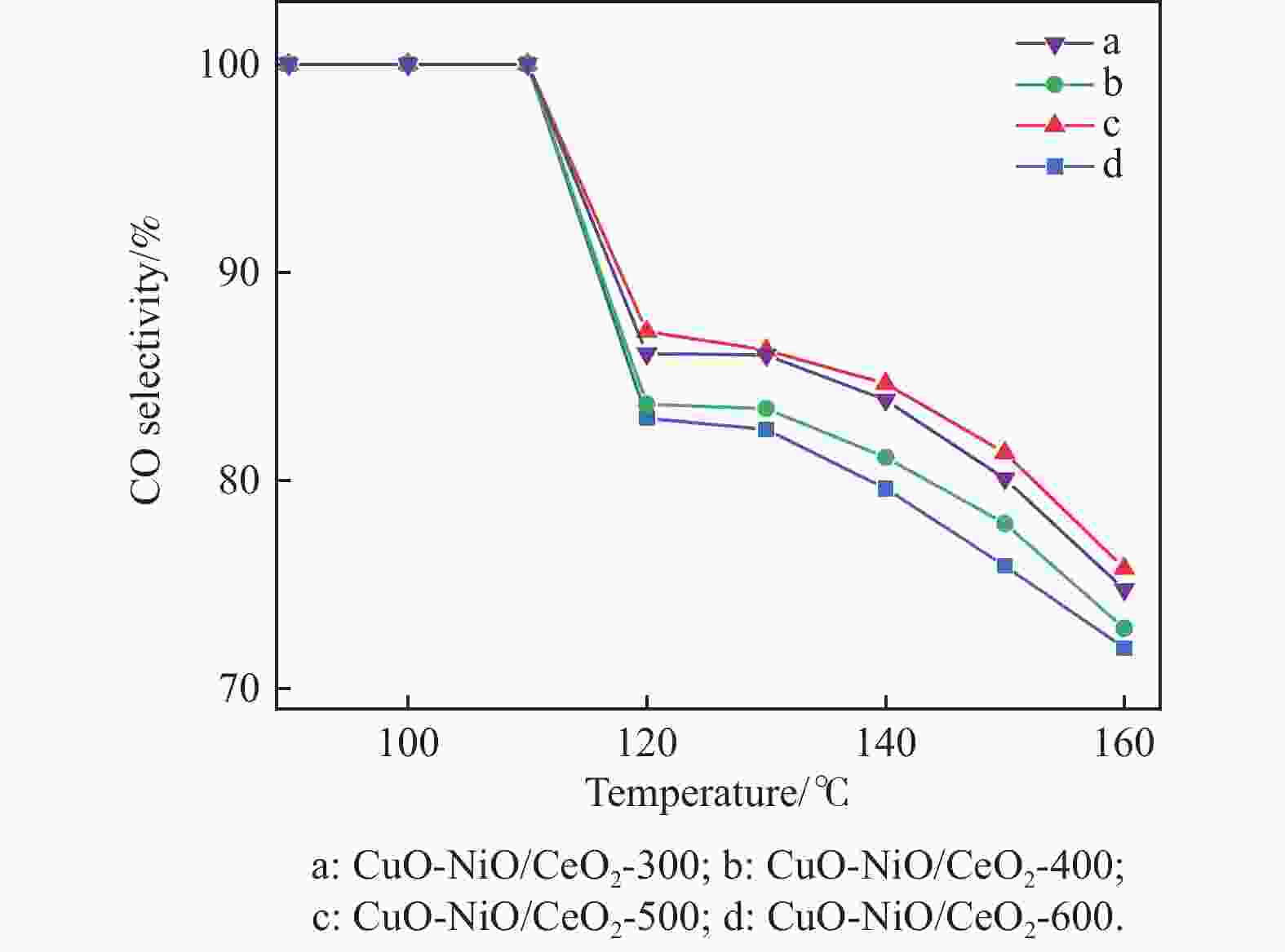
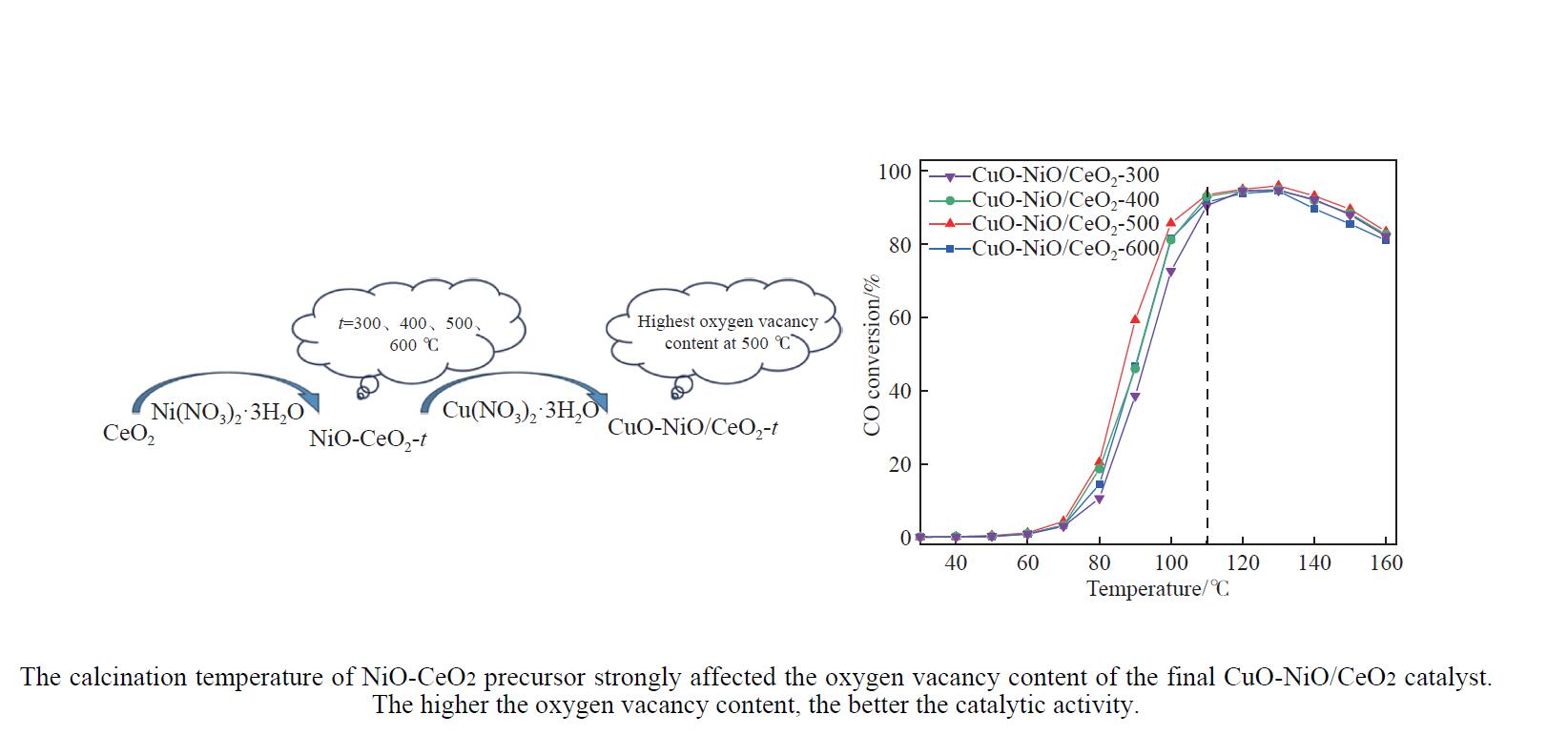
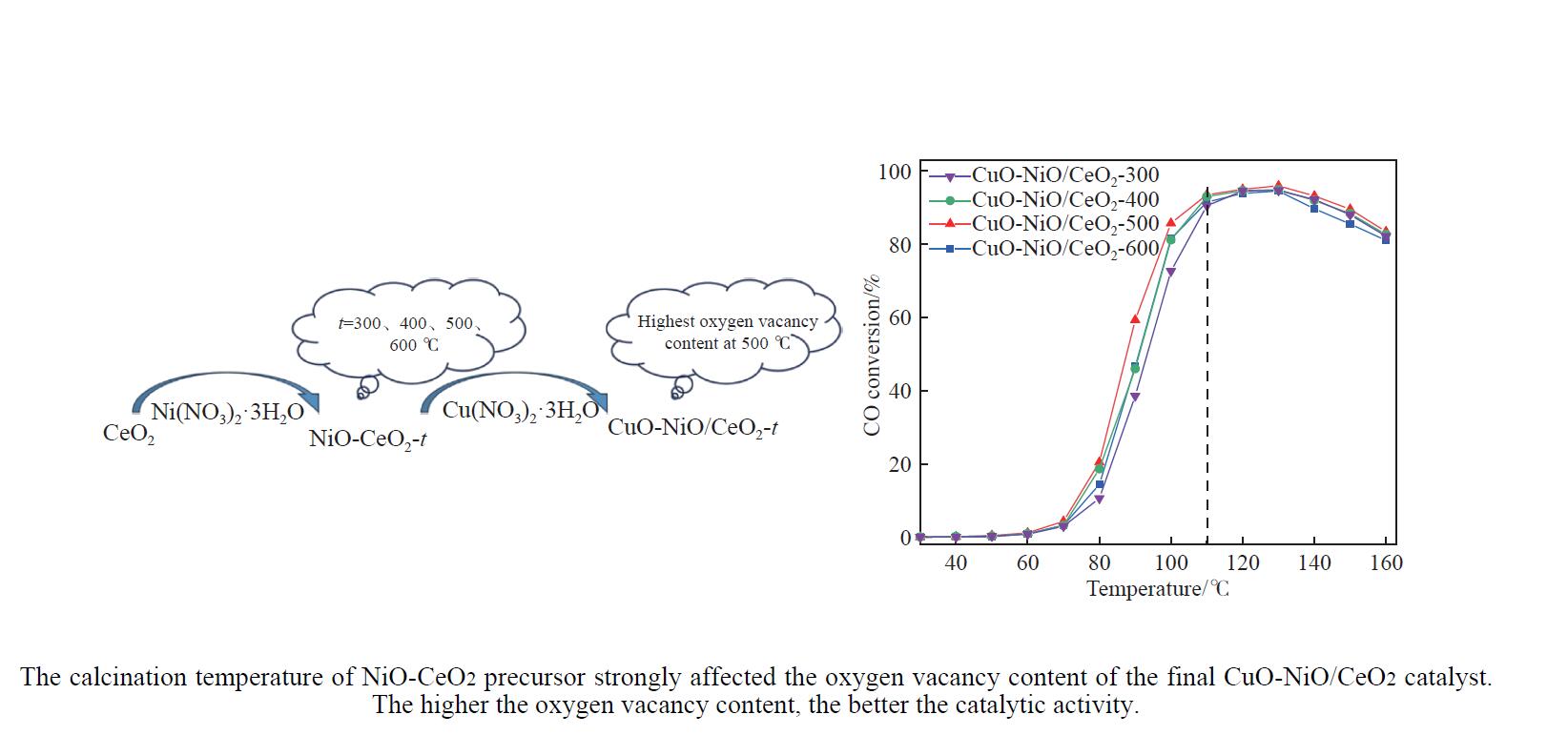
摘要: 采用分步浸渍法制备CuO-NiO/CeO2催化剂,通过XRD、BET、H2-TPR、Raman和XPS手段对催化剂进行表征,探究NiO-CeO2前驱体焙烧温度对催化剂物化性质及富H2/CO2气氛下CO选择性氧化性能的影响。结果表明,前驱体焙烧温度主要影响催化剂的还原性能和氧空位的含量。当焙烧温度为500 ℃时,催化剂中氧空位的含量较高,其催化性能较好。在反应温度为130 ℃,氧过量系数为1.2,空速为20266 mL/(g·h)时,CO转化率为95.9%,CO氧化选择性为86.3%。
-
关键词:
- 焙烧温度 /
- CuO-NiO/CeO2 /
- CO-PROX /
- 氧空位
Abstract: The CuO-NiO/CeO2 catalyst was prepared by step impregnation method. The catalyst was characterized by XRD, BET, H2-TPR, Raman and XPS, and the effects of the calcination temperature of NiO-CeO2 precursor on the physicochemical properties of the catalyst and the selective oxidation of CO in H2/CO2 rich atmosphere were investigated. The results showed that the precursor calcination temperature mainly affected the reduction performance and oxygen vacancy content of the catalyst. When the calcination temperature is 500 ℃, the content of oxygen vacancy in the catalyst is higher, and the catalytic performance is better. When the reaction temperature is 130 ℃, the oxygen excess coefficient is 1.2, and the air speed is 20266 mL/(g·h), the CO conversion rate is 95.9%, and the CO oxidation selectivity is 86.3%.-
Key words:
- calcination temperature /
- CuO-NiO/CeO2 /
- CO-PROX /
- oxygen vacancy
-
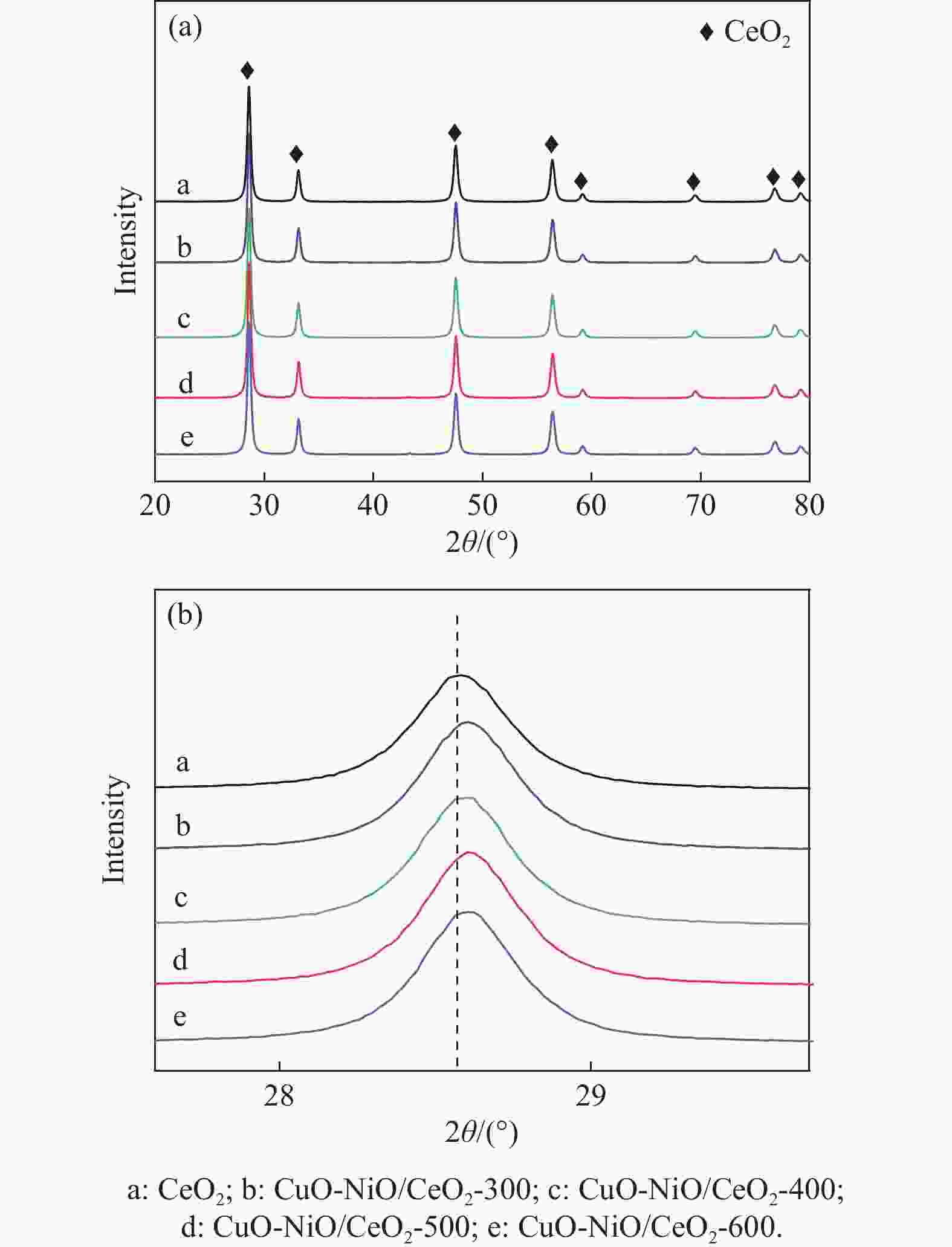
表 1 CeO2及CuO-NiO/CeO2-t催化剂的XRD分析
Table 1 XRD analysis of CeO2 and CuO-NiO/CeO2-t catalyst
Catalyst Cell parameter/Å Crystallite size/nm CeO2 5.4094 20.1 CuO-NiO/CeO2-300 5.4086 20.1 CuO-NiO/CeO2-400 5.4073 20.1 CuO-NiO/CeO2-500 5.4063 20.0 CuO-NiO/CeO2-600 5.4082 20.0 表 2 CeO2和CuO-NiO/CeO2-t催化剂的比表面积、孔体积、平均孔径
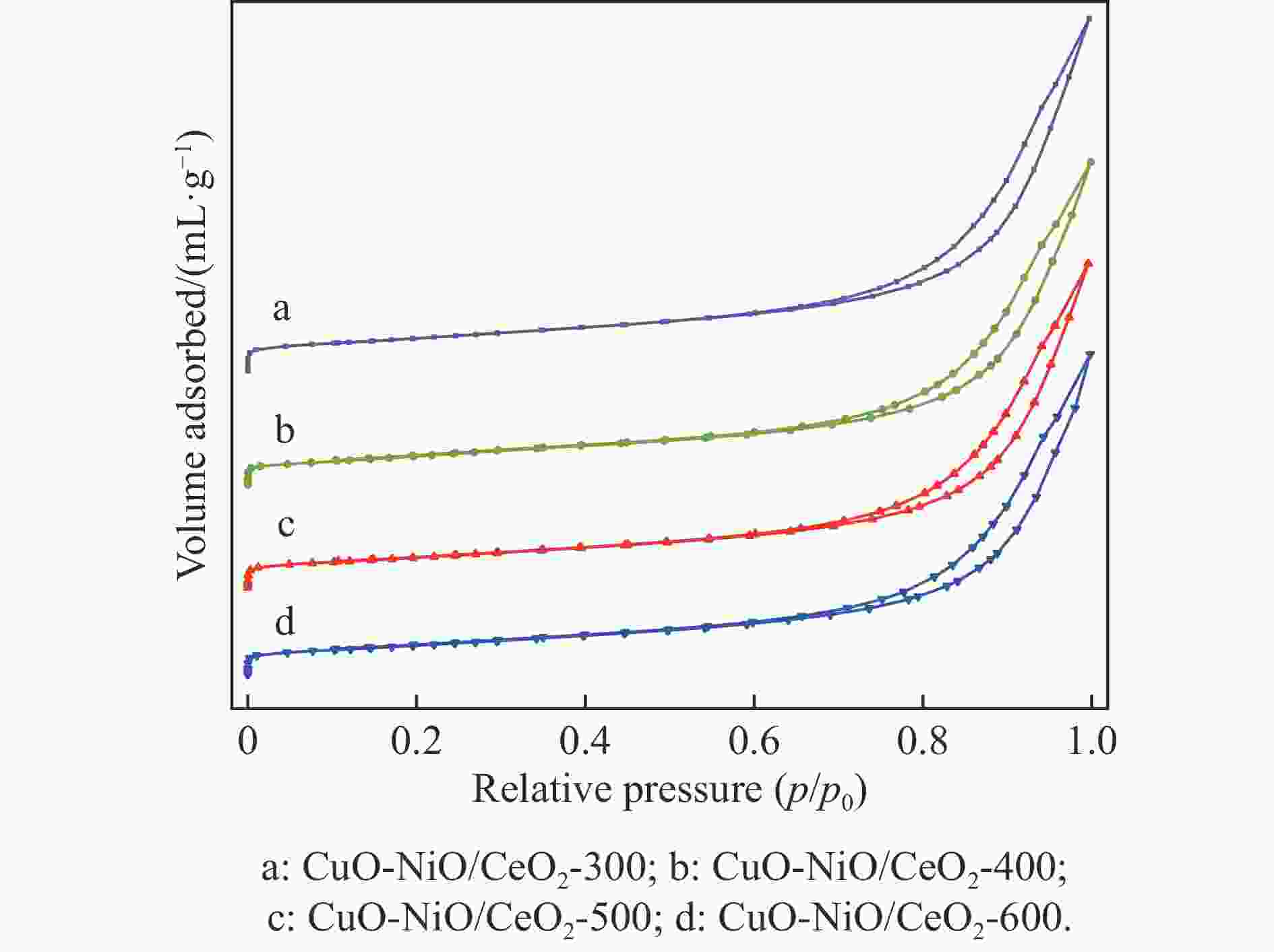
Table 2 Specific surface area, pore volume and average pore size of CeO2 and CuO-NiO/CeO2-t catalyst
Catalyst SBET/
(m2·g−1)Pore volume/
(mL·g−1)Average pore
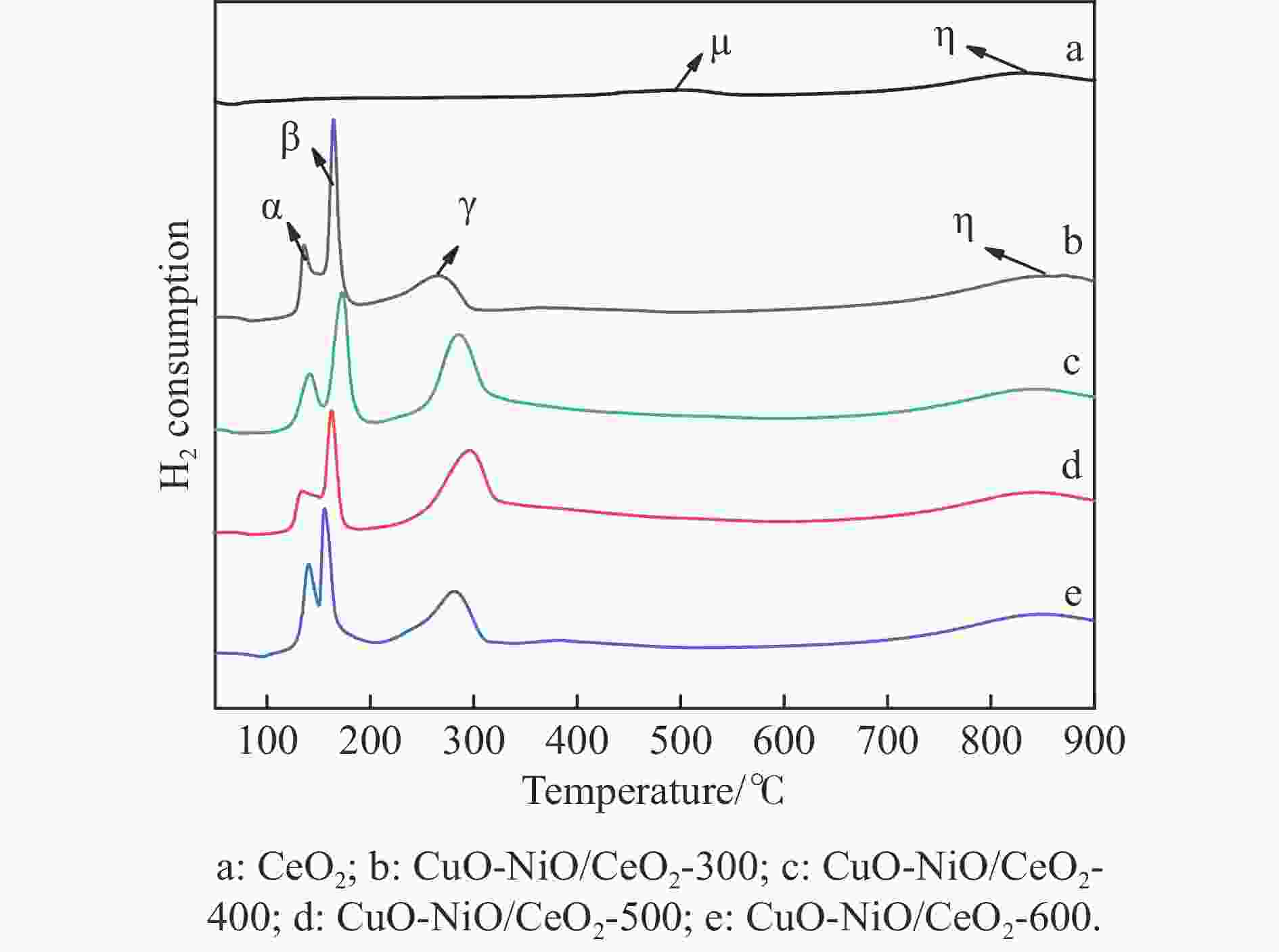
size/nmCeO2 34.2 0.134 15.67 CuO-NiO/CeO2-300 31.5 0.131 17.56 CuO-NiO/CeO2-400 28.5 0.124 17.44 CuO-NiO/CeO2-500 28.9 0.128 17.69 CuO-NiO/CeO2-600 28.3 0.122 17.27 表 3 CuO-NiO/CeO2-t催化剂的峰位置tpeak及峰面积占比area
Table 3 Peak position tpeak and peak area ratio of CuO-NiO/CeO2-t catalysts
Catalyst α β γ η α/β tpeak
/℃area
/%tpeak
/℃area
/%tpeak
/℃area
/%area
/%CuO-NiO/CeO2-300 135.9 6.9 163.7 14.6 266.2 23.9 55.3 0.47 CuO-NiO/CeO2-400 140.9 5.6 173.5 10.4 284.1 29.2 54.8 0.54 CuO-NiO/CeO2-500 132.6 5.3 162.4 7.4 293.5 33.2 54.2 0.72 CuO-NiO/CeO2-600 141.0 6.9 154.9 14.2 282.7 27.4 50.8 0.49 表 4 XPS结果分析
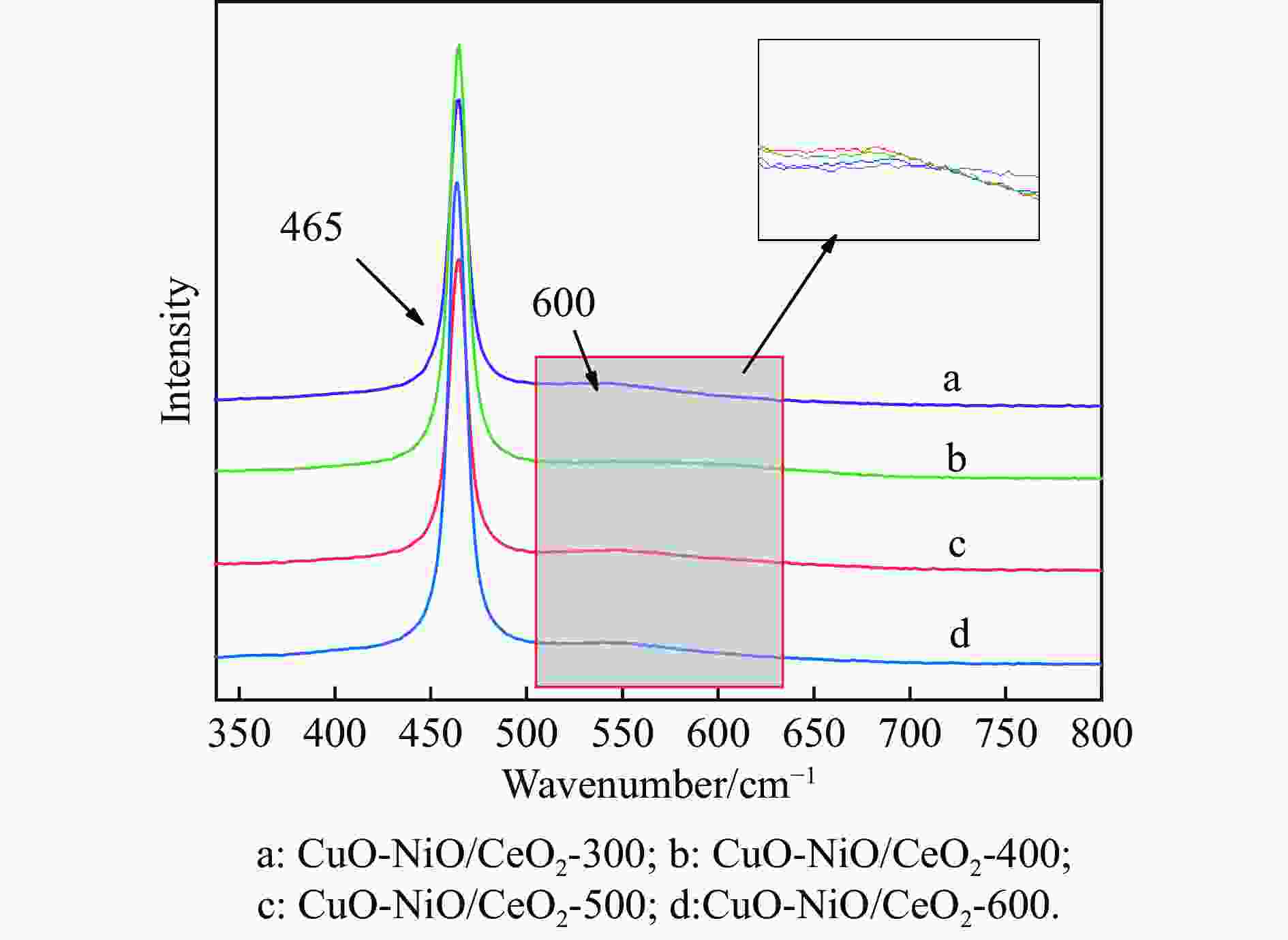
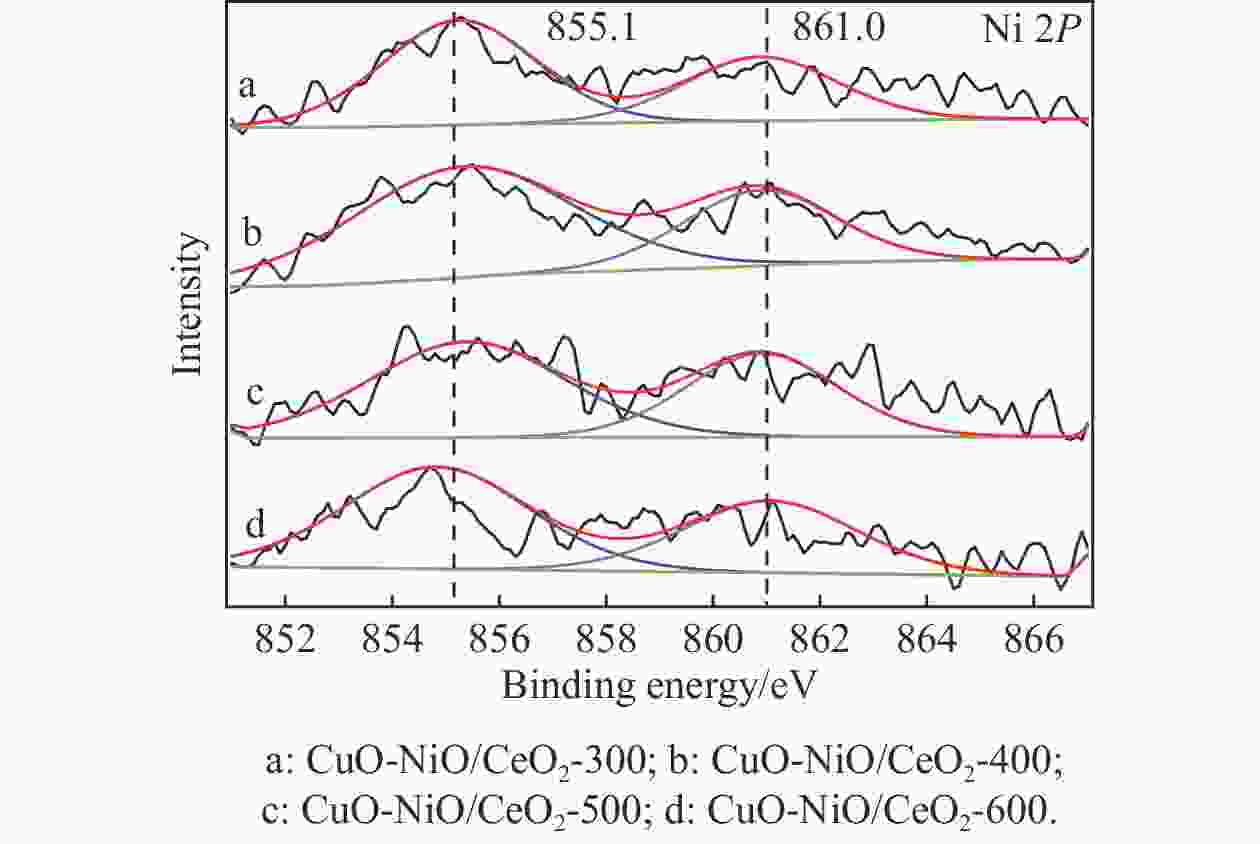
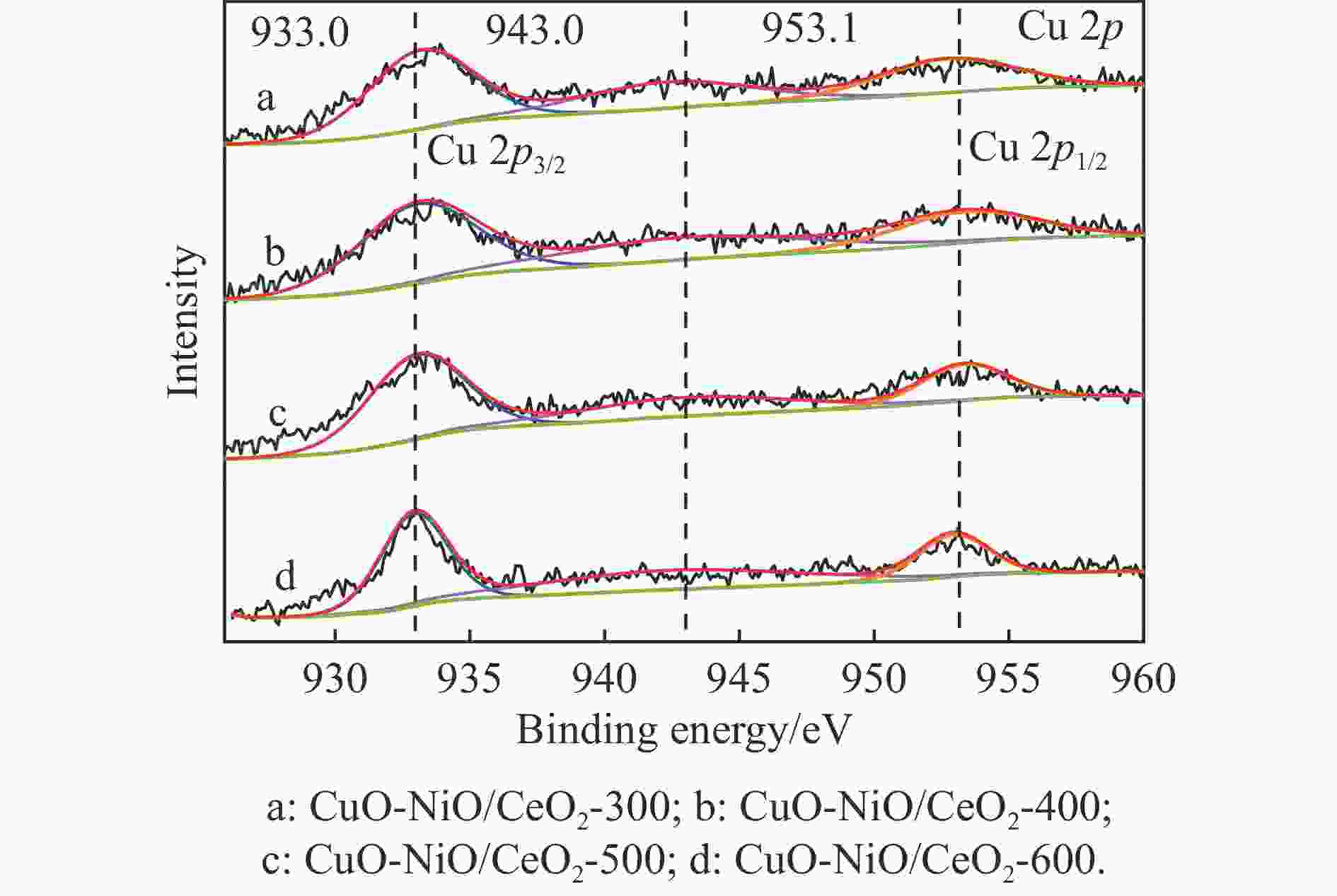
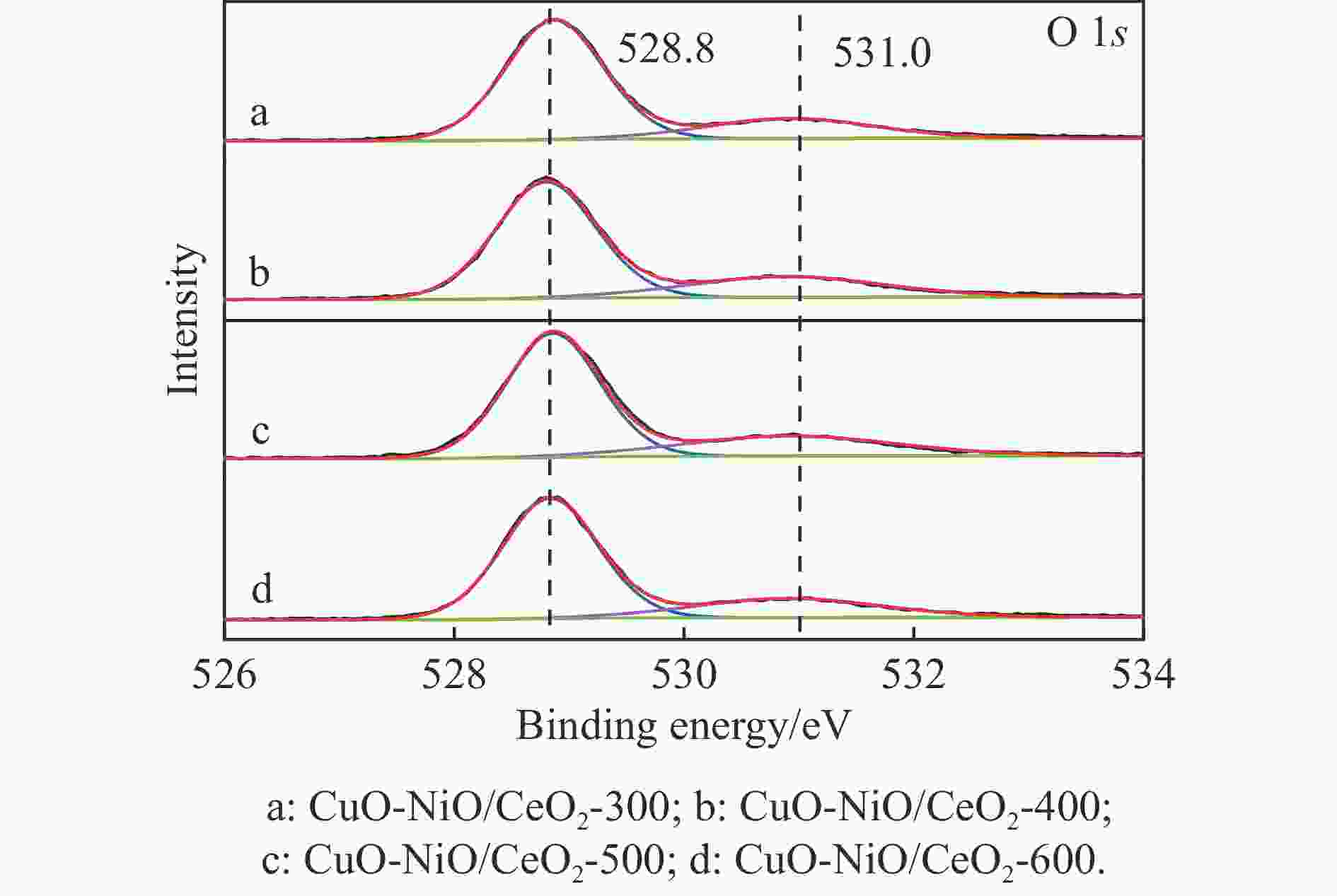
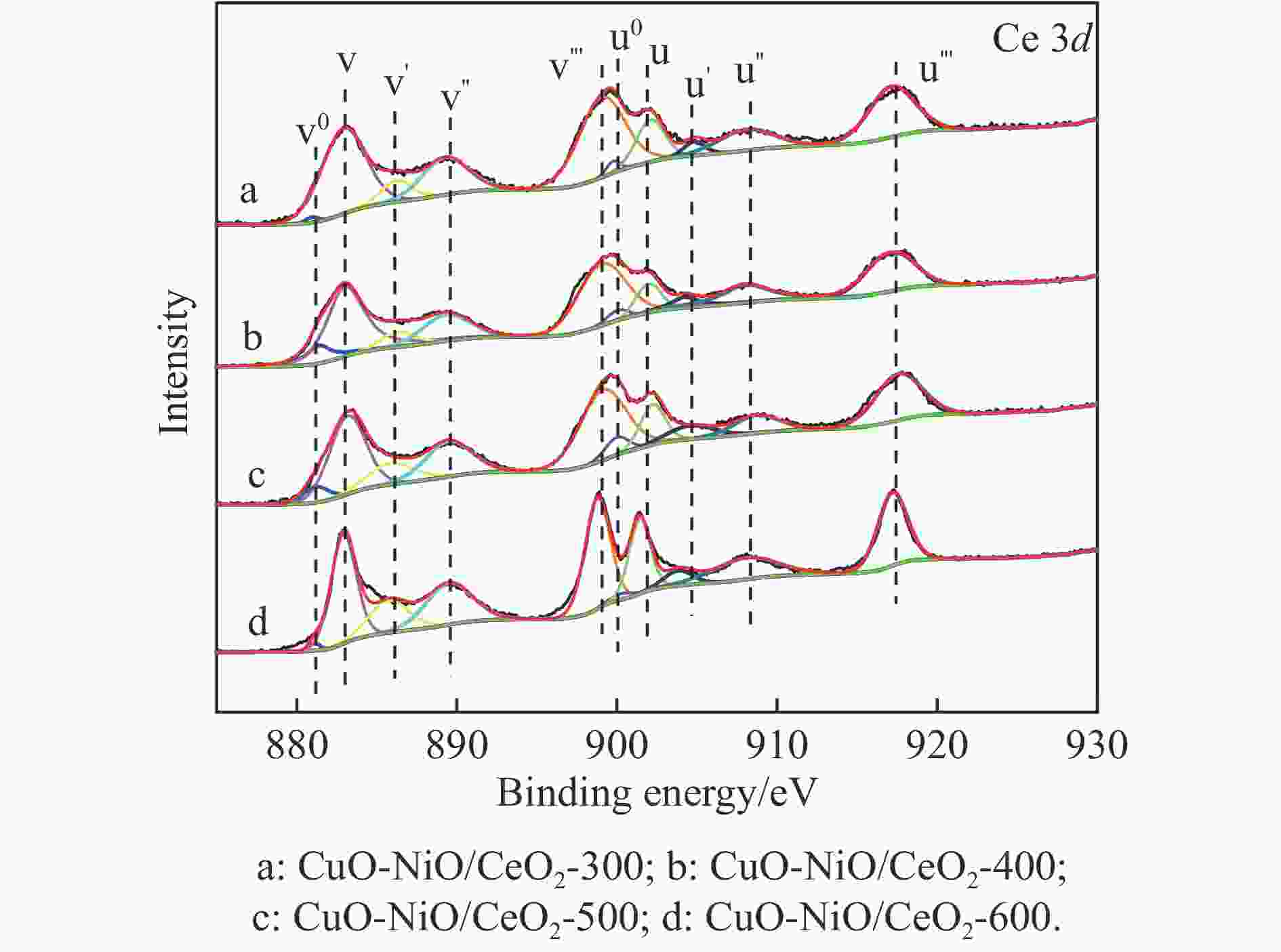
Table 4 XPS results analyzed
Catalyst Oads/% Ce3+/% CuO-NiO/CeO2-300 22.47 11.26 CuO-NiO/CeO2-400 25.76 13.98 CuO-NiO/CeO2-500 27.01 15.70 CuO-NiO/CeO2-600 23.70 13.32 表 5 CuO-NiO/CeO2-t催化剂的t50、ttop和xmax
Table 5 t50, ttop and xmax of CuO-NiO/CeO2-t catalysts
Catalyst t50/℃ ttop/℃ xmax/% CuO-NiO/CeO2-300 93 130 94.6 CuO-NiO/CeO2-400 91 130 94.8 CuO-NiO/CeO2-500 87 130 95.9 CuO-NiO/CeO2-600 91 130 94.5 表 6 本文及文献中催化剂的活性对比(130 ℃)
Table 6 Comparison of catalyst activity in this article and in the literature (130 ℃)
-
[1] MAJLAN E H, ROHENDI D, DAUD W R W, et al. Electrode for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A review[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev,2018,89:117−134. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.007 [2] 张楷文, 刘鑫尧, 张磊, 等. 甲醇水蒸气重整制Cu-Zn-Al尖晶石催化剂的研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2022,50(4):494−502.ZHANG Kaiwen, LIU Xinyao, ZHANG Lei, et al. Cu-Zn-Al spinel catalyst for hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2022,50(4):494−502. [3] 乔韦军, 张楷文, 张娜, 等. 甲醇水蒸气重整制氢CuAl2O4催化材料的研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2020,48(8):980−985.QIAO Weijun, ZHANG Kaiwen, ZHANG Na, et al. Study on CuAl2O4 catalytic material for methanol steam reforming[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2020,48(8):980−985. [4] 王丽宝, 王东哲, 张磊, 等. 铈源对甲醇水蒸气重整制氢CuO/CeO2催化剂的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2020,48(7):852−859.WANG Libao, WANG Dongzhe, ZHANG Lei, et al. Influence of cerium sources on CuO/CeO2 catalysts for hydrogen production from steam reforming of methanol[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2020,48(7):852−859. [5] YANG S Q, ZHOU F, LIU Y J, et al. Morphology effect of ceria on the performance of CuO/CeO2 catalysts for hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2019,44(14):7252−7261. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.254 [6] LIU H M, LI D Z, GUO J W, et al. Recent advances on catalysts for preferential oxidation of CO[J]. Nano Res,2023,16(4):4399−4410. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-5182-9 [7] 纪子柯, 包成. CO选择性甲烷化的研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2022,41(1):120−132.JI Zike, BAO Cheng. Research progress of selective CO methanation[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2022,41(1):120−132. [8] RELVAS F, WHITLEY R D, SILVA C, et al. Single-stage pressure swing adsorption for producing fuel cell grade hydrogen[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2018,57(14):5106−5118. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b05410 [9] 金石山, 张大山, 冯旭浩, 等. Ni含量对NiO/CeO2催化剂催化CO氧化性能的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2022,50(8):1034−1040.JIN Shishan, ZHANG Dashan, FENG Xuhao, et al. Effect of Ni content on catalytic oxidation of CO over NiO/CeO2 catalyst[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2022,50(8):1034−1040. [10] SCHMITT R, NENNING A, KRAYNIS O, et al. A review of defect structure and chemistry in ceria and its solid solutions[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2020,49(2):554−592. doi: 10.1039/C9CS00588A [11] 刘玉娟, 许骥, 佟宇飞, 等. 氧化铈纳米材料合成方法的研究进展[J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报,2017,37(5):8−12 + 37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6952.2017.05.002LIU Yujuan, XU Ji, TONG Yufei, et al. Progress in research of the synthesis methods of nanometer ceria[J]. J Liaoning Petrochem Univ,2017,37(5):8−12 + 37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6952.2017.05.002 [12] CENTENO M A, RAMÍREZ R T, IVANOVA S, et al. Au/CeO2 catalysts: Structure and CO oxidation activity[J]. Catalysts,2016,6(10):158. doi: 10.3390/catal6100158 [13] ZHOU G F, MA J, BAI S, et al. CO catalytic oxidation over Pd/CeO2 with different chemical states of Pd[J]. Rare Metals,2020,39:800−805. doi: 10.1007/s12598-019-01347-7 [14] WANG C, CHENG Q P, WANG X L, et al. Enhanced catalytic performance for CO preferential oxidation over CuO catalysts supported on highly defective CeO2 nanocrystals[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2017,422:932−943. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.017 [15] ARAUJO V D, BELLIDO J D, BERNARDI M I, et al. CuO-CeO2 catalysts synthesized in one-step: Characterization and PROX performance[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2012,37(7):5498−5507. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.12.143 [16] GUO X L, ZHOU R X. Identification of the nano/micro structure of CeO2(rod) and the essential role of interfacial copper-ceria interaction in CuCe(rod) for selective oxidation of CO in H2-rich streams[J]. J Power Sources,2017,361:39−53. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.06.064 [17] ALMERINDA D B, GIANLUCA L, LUCIANA L. Improved CO-PROX performance of CuO/CeO2 catalysts by using nanometric ceria as support[J]. Catalysts,2018,8(5):209. doi: 10.3390/catal8050209 [18] XIE Y, WU J F, JING G J, et al. Structural origin of high catalytic activity for preferential CO oxidation over CuO/CeO2 nanocatalysts with different shapes[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2018,239:665−676. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.08.066 [19] MACIEL C G, BELGACEM M N, ASSAF J M. Performance of CuO-CeO2 catalysts with low copper content in CO preferential oxidation reaction[J]. Catal Lett,2011,141(2):316−321. doi: 10.1007/s10562-010-0486-x [20] JIANG Y X, ZHANG D S, ZHANG C S, et al. Preparation of Cu0.1−xNixCe0.9O2−y catalyst by ball milling and its CO catalytic oxidation performance[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2023,48(33):12385−12395. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.12.183 [21] XING Y, WU J X, ZHANG C S, et al. Mn-induced Cu/Ce catalysts with improved performance for CO preferential oxidation in H2/CO2-rich streams[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2023,48(84):20667−20679. [22] CHEN G X, LI Q L, WEI Y C, et al. Low temperature CO oxidation on Ni-promoted CuO-CeO2 catalysts[J]. Chin J Catal,2013,34(2):322−329. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(11)60468-3 [23] CHAGAS C A, SOUZA E F, MANFRO R L, et al. Copper as promoter of the NiO-CeO2 catalyst in the preferential CO oxidation[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2016,182:257−265. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.09.033 [24] SOLSONA B, CONCEPCIÓN P, HERNÁNDEZ S, et al. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane over NiO-CeO2 mixed oxides catalysts[J]. Catal Today,2012,180(1):51−58. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.056 [25] GU D, JIA C J, BONGARD H, et al. Ordered mesoporous Cu-Ce-O catalysts for CO preferential oxidation in H2-rich gases: Influence of copper content and pretreatment conditions[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2014,152-153:11−18. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.01.011 [26] 杨昕毓, 孙舒, 石岩, 等. 水热时间对CuO/CeO2催化甲醇水蒸气重整制氢的影响[J]. 石油化工高等学校学报,2023,36(2):63−69. doi: 10.12422/j.issn.1006-396X.2023.02.008YANG Xinyu, SUN Shu, SHI Yan, et al. Effects of hydrothermal reaction time on the performance of CuO/CeO2[J]. J Petrochem Univ,2023,36(2):63−69. doi: 10.12422/j.issn.1006-396X.2023.02.008 [27] QIAO D S, LU G Z, GUO Y, et al. Effect of water vapor on the CO and CH4 catalytic oxidation over CeO2-MOx (M=Cu, Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni) mixed oxide[J]. J Rare Earth,2010,28(5):742−746. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(09)60192-7 [28] 王东哲, 冯旭, 张健, 等. 助剂M(M=Cr、 Zn、Y、La)对甲醇水蒸气重整制氢CuO/CeO2催化剂的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2019,47(10):1251−1257.WANG Dongzhe, FENG Xu, ZHANG Jian, et al. Effect of promoter M(M=Cr, Zn, Y, La) on CuO/CeO2 catalysts for hydrogen production from steam reforming of methanol[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2019,47(10):1251−1257. [29] MARTÍNEZ-ARIAS A, GAMARRA D, FERNÁNDEZ-GARCÍA M, et al. Redox-catalytic correlations in oxidised copper-ceria CO-PROX catalysts[J]. Catal Today,2009,143(3/4):211−217. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.018 [30] FATEMEH S S, MASOUD S N, MEHDI S N. Characterization of hydrogen storage behavior of the as-synthesized p-type NiO/n-type CeO2 nanocomposites by carbohydrates as a capping agent: The influence of morphology[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2018,43(31):14557−14568. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.06.007 [31] ZOU Q, ZHAO Y H, JIN X, et al. Ceria-nano supported copper oxide catalysts for CO preferential oxidation: Importance of oxygen species and metal-support interaction[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2019,494(15):1166−1176. [32] LIN X T, LI S J, HE H, et al. Evolution of oxygen vacancies in MnOx-CeO2 mixed oxides for soot oxidation[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2018,223:91−102. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.06.071 [33] 张迎, 朱文杰, 张黎明, 等. CeO2中氧空位形成、表征及其作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国稀土学报,2022,40(1):14−23.ZHANG Ying, ZHU Wenjie, ZHANG Liming, et al. Research progress on formation, characterization and mechanism of oxygen vacancies in cerium oxide[J]. J Mater Sci Technol,2022,40(1):14−23. [34] GUO X L, MAO J X, ZHOU R X. Influence of the copper coverage on the dispersion of copper oxide and the catalytic performance of CuO/CeO2(rod) catalysts in preferential oxidation of CO in excess hydrogen[J]. J Power sources,2017,371:119−128. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.10.055 [35] LIANG F L, YU Y, ZHOU W, et al. Highly defective CeO2 as a promoter for efficient and stable water oxidation[J]. J Mater Chem A,2015,3(2):634−640. doi: 10.1039/C4TA05770H [36] KIM D H, CHA J E. A CuO-CeO2 mixed-oxide catalyst for CO clean-up by selective oxidation in hydrogen-rich mixtures[J]. Catal lett,2003,86:107−112. doi: 10.1023/A:1022671327794 [37] MA W J, MASHIMO T, TAMURA S, et al. Cerium oxide (CeO2−x) nanoparticles with high Ce3+ proportion synthesized by pulsed plasma in liquid[J]. Ceram Int,2020,46:26502−26510. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.07.093 [38] LARACHI F, PIERRE J, ADNOT A, et al. Ce 3d XPS study of composite CexMn1−xO2−y wet oxidation catalysts[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2002,195:236−250. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(02)00559-7 [39] FAN J, WU X D, WU X D, et al. Thermal ageing of Pt on low-surface-area CeO2-ZrO2-La2O3 mixed oxides: Effect on the OSC performance[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2008,81(1/2):38−48. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.11.022 [40] LI J, HAN Y X, ZHU Y H, et al. Purification of hydrogen from carbon monoxide for fuel cell application over modified mesoporous CuO-CeO2 catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2011,108−109:72−80. [41] SUN J F, ZHANG L, GE C Y, et al. Comparative study on the catalytic CO oxidation properties of CuO/CeO2 catalysts prepared by solid state and wet impregnation[J]. Chin J Catal,2014,35(8):1347−1358. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60138-8 -




 下载:
下载: