Methane catalytic combustion over flame spray pyrolysis-synthesized Pd-Pt/CeO2 catalyst
-
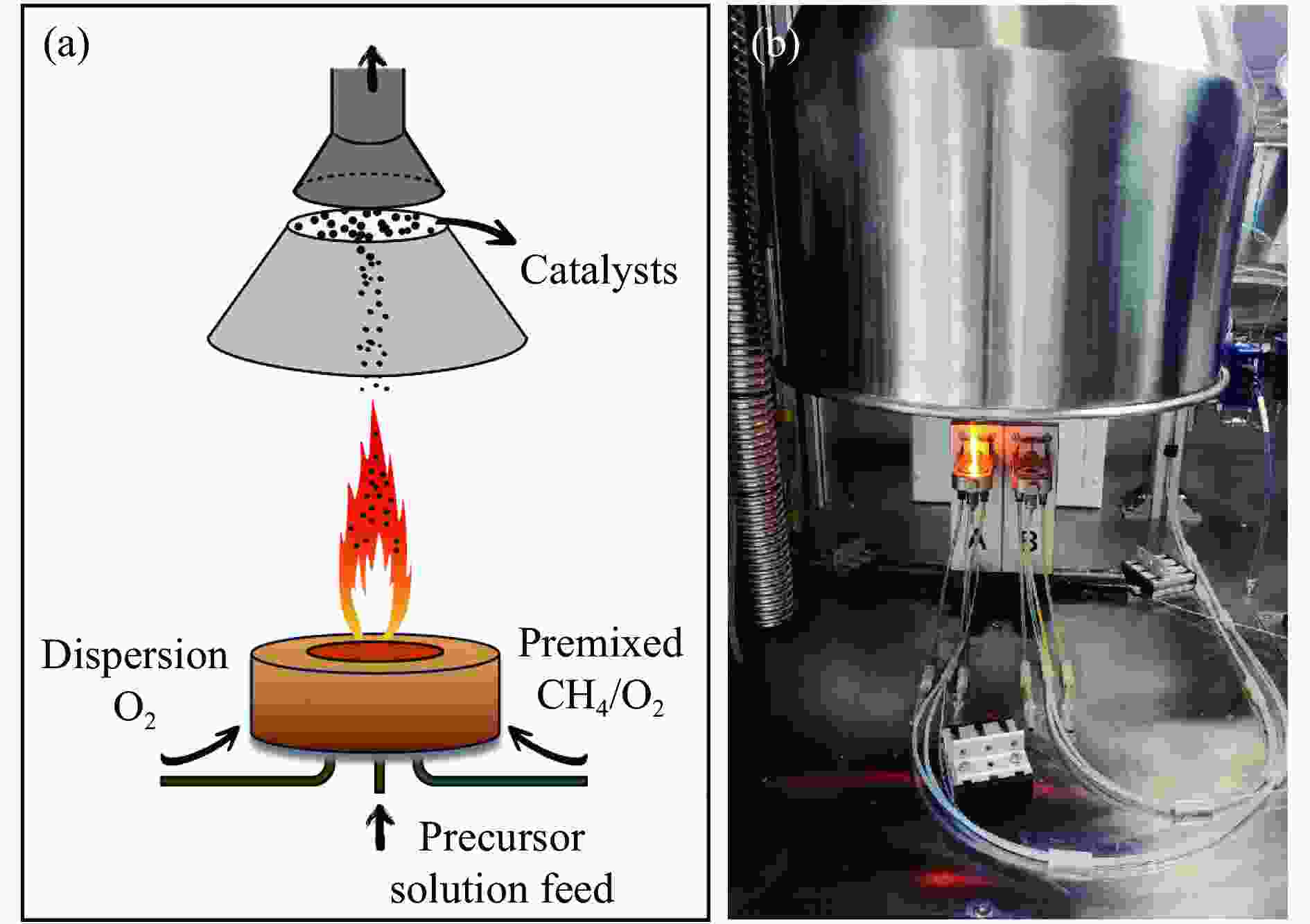
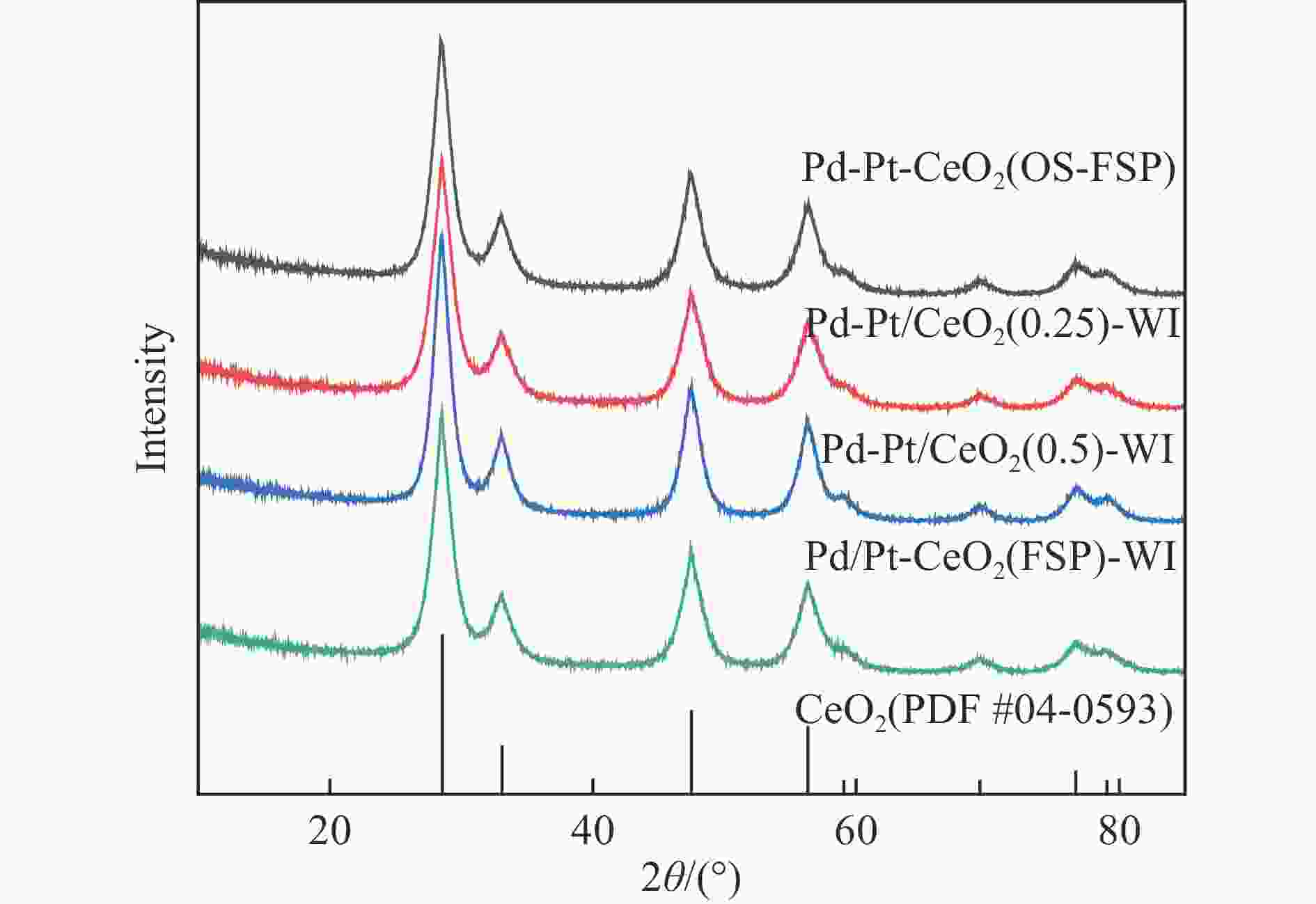
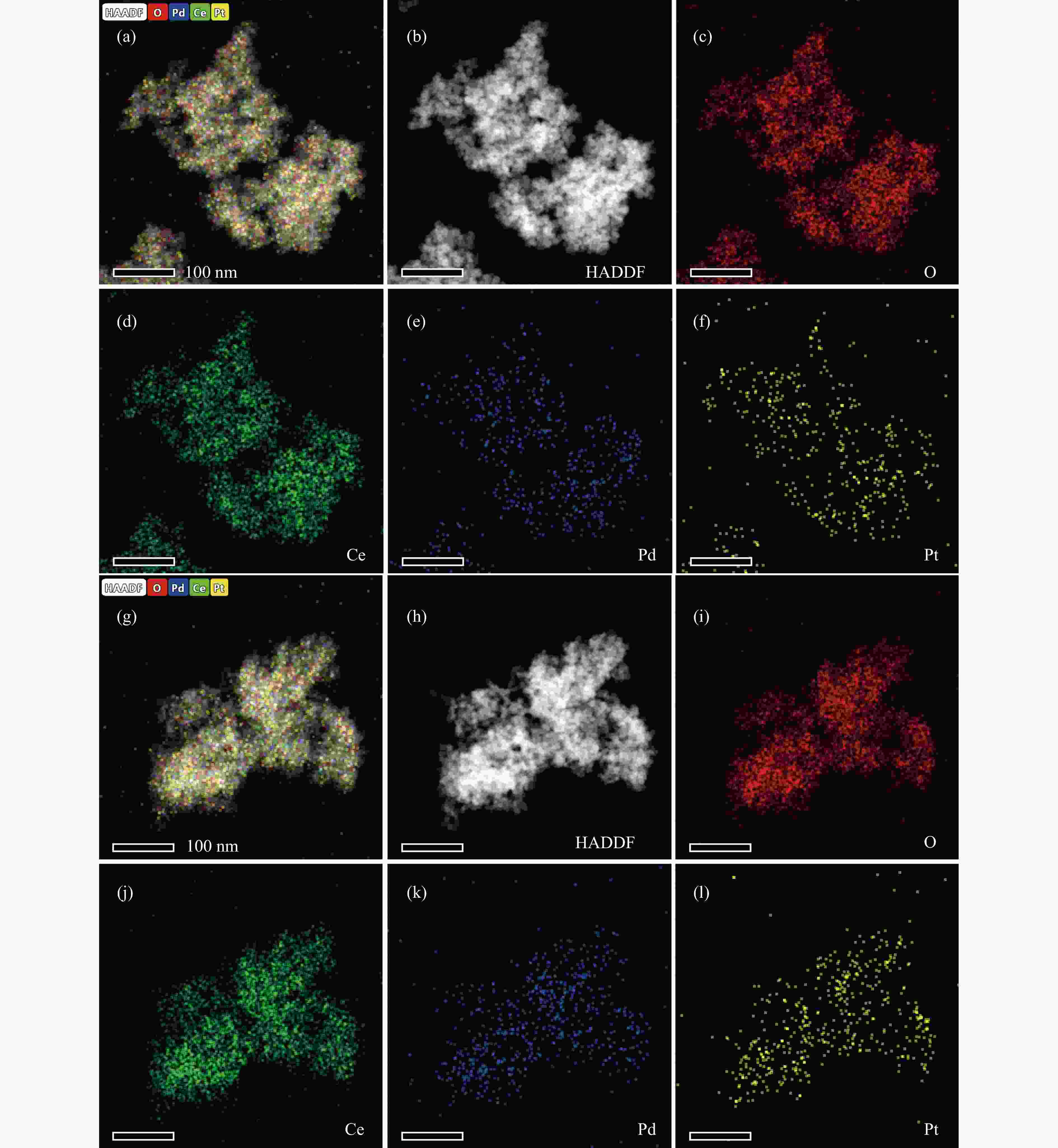
摘要: 火焰喷雾热解法(FSP)是一种简单、快速、可规模化制备纳米催化剂的技术。通过火焰喷雾热解法合成CeO2和Pt-CeO2载体、Pd-Pt-CeO2催化剂,采用浸渍法在CeO2和Pt-CeO2载体分别沉积Pd-Pt和Pd而制得Pd-Pt双金属催化剂,并考察其甲烷催化燃烧性能。利用ICP、XRD、TEM、BET、H2-TPR、XPS和Raman对催化剂的物化性质进行分析。TEM结果表明,Pd-Pt/CeO2催化剂中Pd和Pt物种高分散于CeO2载体。相比于一步法(one step)制得的Pd-Pt-CeO2(OS-FSP)催化剂,共浸渍法制得Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI的催化活性更高,其t50降低了60 ℃,且稳定运行60 h而没有明显失活。这归因于Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI催化剂表面上Pd0/Pd2+和Ce3+/Ce4+物质的量比更高、晶格氧更多,进而导致其具有良好的甲烷催化燃烧性能。Abstract: Flame spray pyrolysis (FSP) is a versatile, rapid, and scalable preparation technique for the nanocatalysts. CeO2 and Pt-CeO2 carriers, Pd-Pt-CeO2 catalyst were synthesized by flame spray pyrolysis, and then Pd-Pt bimetallic catalysts were prepared by impregnation method, and as-obtained Pd-Pt catalysts were tested in the methane combustion. The physicochemical properties of the catalysts were characterized by ICP, XRD, TEM, BET, H2-TPR, XPS, and Raman. TEM results showed that Pd and Pt species were highly dispersed in CeO2 carriers in Pd-Pt/CeO2 catalysts. Compared with the Pd-Pt-CeO2(OS-FSP) catalyst prepared by one-step flame spray pyrolysis, the catalytic activity of the Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI prepared by co-impregnation was higher, with its t50 reduced by 60 ℃, and no deactivation was seen for 60 h. It is attributed to the fact that the Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI catalyst has a higher molar ratio of Pd0/Pd2+ and Ce3+/Ce4+ on the surface of the catalyst and more lattice oxygen, resulting in an excellent performance during the methane combustion.
-
Key words:
- methane combustion /
- flame spray pyrolysis /
- impregnation /
- palladium /
- stability
-
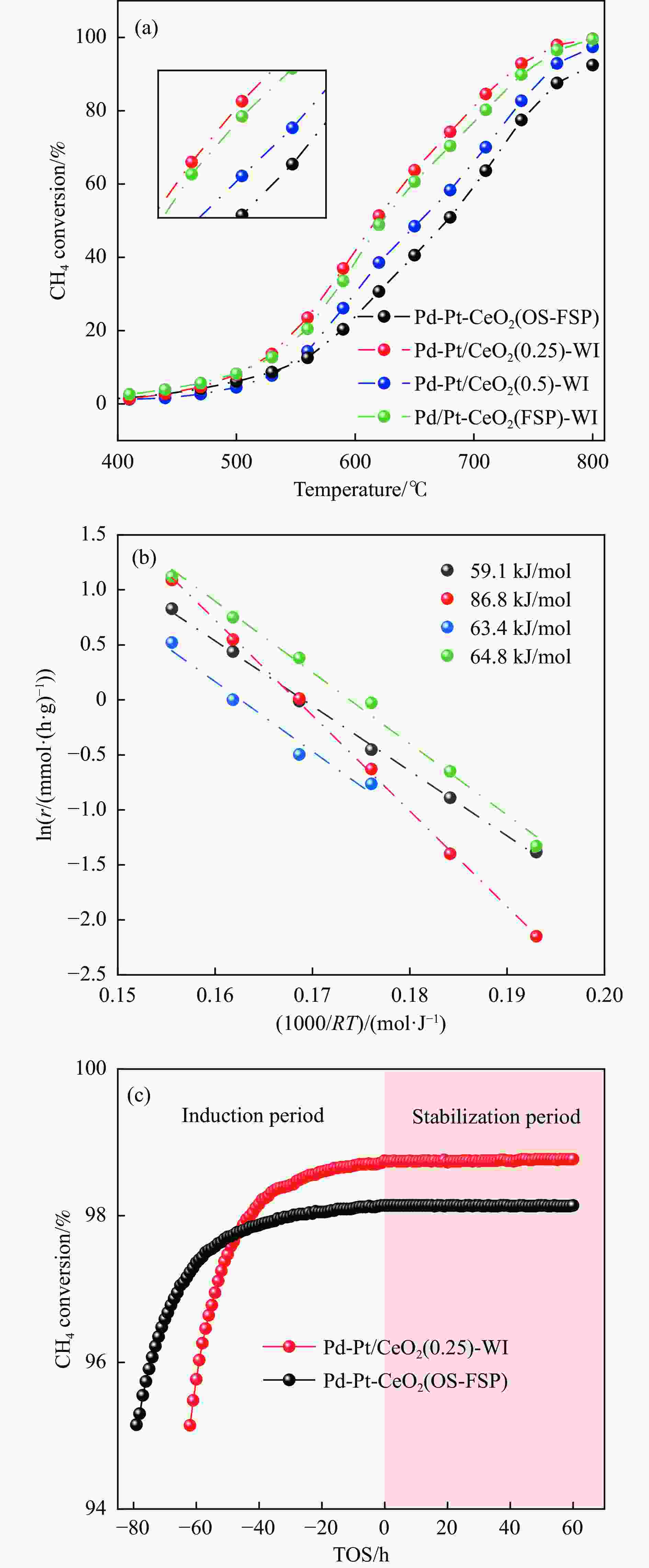
图 2 四种催化剂的(a) CH4转化率随反应温度的变化、(b) 表观活化能比较和(c) Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI和Pd-Pt-CeO2(OS-FSP)催化剂在710 ℃的稳定性比较
Figure 2 (a) CH4 conversion as a function of reaction temperature, (b) corresponding Arrhenius plots over four catalysts and (c) stability test over Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI and Pd-Pt-CeO2(OS-FSP) catalysts at 710 ℃ (0.1 g catalysts, CH4:O2:N2 = 0.5:10:89.5, GHSV = 15000 mL/(g·h))
表 1 四种催化剂的ICP-OES结果
Table 1 ICP-OES results of four catalysts
Catalyst Metal loading w/% Pd Pt Pd-Pt-CeO2(OS-FSP) 0.89 0.09 Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI 0.91 0.11 Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.5)-WI 0.89 0.10 Pd/Pt-CeO2(FSP)-WI 0.88 0.12 表 2 四种催化剂的t10,t50和t90
Table 2 t10, t50 and t90 results of four catalysts
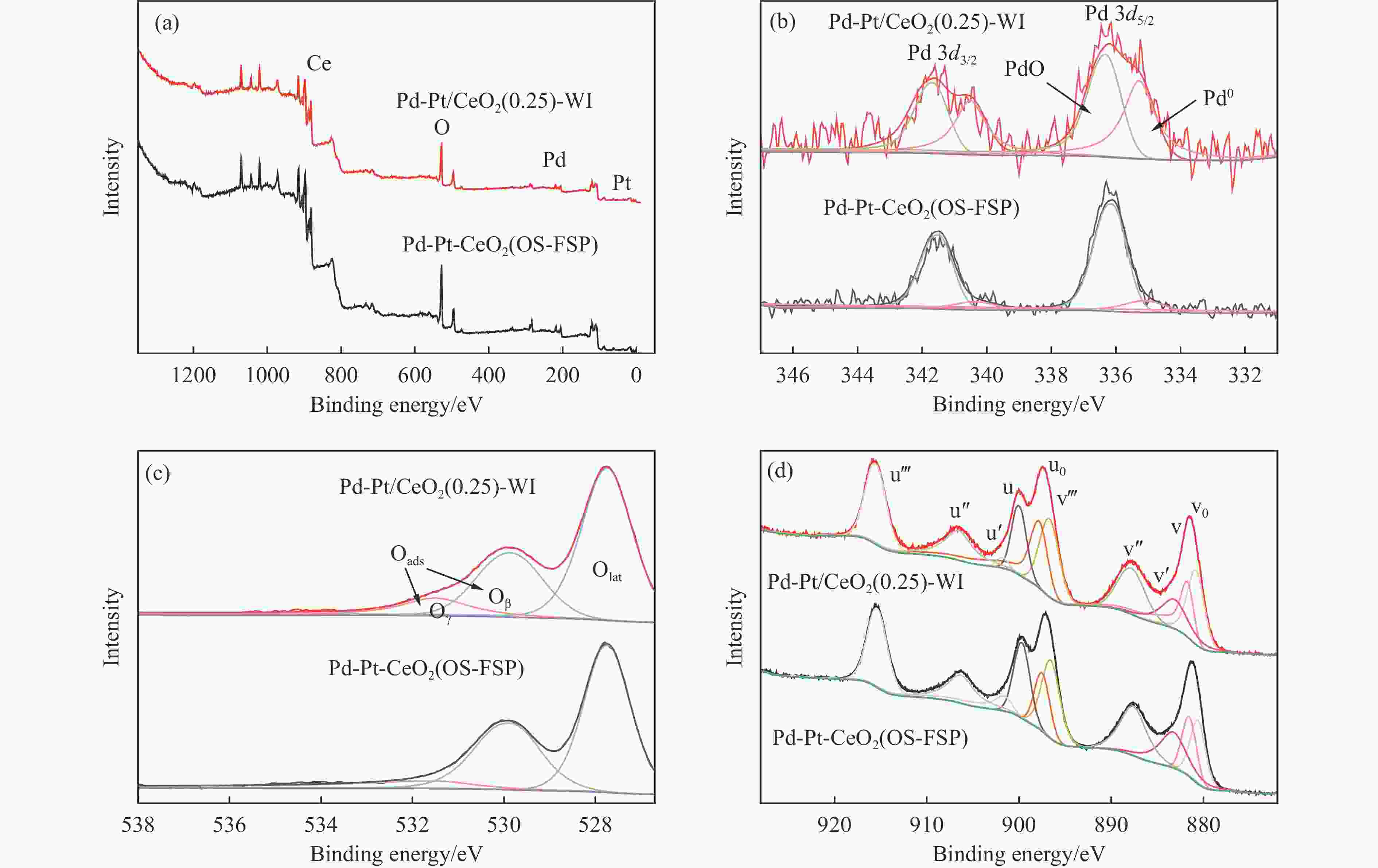
Catalyst t10/℃ t50/℃ t90/℃ Pd-Pt-CeO2(OS-FSP) 540 677 785 Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI 510 617 729 Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.5)-WI 540 654 761 Pd/Pt-CeO2(FSP)-WI 511 622 740 表 3 Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI和Pd-Pt-CeO2(OS-FSP)催化剂上Pd、Pt、Ce和O的表面原子浓度和不同元素的价态分布
Table 3 Surface atom concentration of Pd, Pt, Ce and O and valence distribution of different elements from XPS data on Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI and Pd-Pt-CeO2(OS-FSP) catalysts
Catalyst Surface atom concentration Pd0/Pd2+ Ce3+/Ce4+ Oads/Olat Pd Pt Ce O Pd-Pt/CeO2(0.25)-WI 0.57 0.10 17.39 81.94 0.85 0.53 0.54 Pd-Pt-CeO2(OS-FSP) 0.47 0.04 17.04 82.45 0.27 0.47 0.50 -
[1] MURATA K, KOSUGE D, OHYAMA J, et al. Exploiting metal-support interactions to tune the redox properties of supported Pd catalysts for methane combustion[J]. ACS Catal,2019,10:1381−1387. [2] LI T, YAO Y, HUANG Z, et al. Denary oxide nanoparticles as highly stable catalysts for methane combustion[J]. Nat Catal,2021,4:62−70. doi: 10.1038/s41929-020-00554-1 [3] 黄鑫, 焦熙, 黄国宝, 等. 甲烷催化燃烧钯基催化剂研究进展[J]. 低碳化学与化工,2023,48:147−154.HUANG Xin, JIAO Xi, HUANG Guobao, et al. Research progress on Pd-based catalysts for methane catalytic combustion[J]. Low-Carbon Chem Chem Eng,2023,48:147−154. [4] PENG S, LIN X, THOMPSON R L, et al. Wetland emission and atmospheric sink changes explain methane growth in 2020[J]. Nature,2022,612:477−482. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05447-w [5] KHOLOD N, EVANS M, PILCHER R C, et al. Global methane emissions from coal mining to continue growing even with declining coal production[J]. J Clean Prod,2020,256:120489. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120489 [6] YASUMURA S, SAITA K, MIYAKAGE T, et al. Designing main-group catalysts for low-temperature methane combustion by ozone[J]. Nat Commun,2023,14:3926. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39541-y [7] FENG X, JIANG L, LI D, et al. Progress and key challenges in catalytic combustion of lean methane[J]. J Energy Chem,2022,75:173−215. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2022.08.001 [8] HOU Z, DAI L, DENG J, et al. Electronically engineering water resistance in methane combustion with an atomically dispersed tungsten on PdO catalyst[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed,2022,61:202201655. doi: 10.1002/anie.202201655 [9] LIU Z, XU G, ZENG L, et al. Anchoring Pt-doped PdO nanoparticles on γ-Al2O3 with highly dispersed La sites to create a methane oxidation catalyst[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2023,324:122259. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.122259 [10] WANG X, ZHANG X, CAO M, et al. Ordered mesoporous Pd-La/Al2O3 catalysts for enhanced methane combustion[J]. Energy Fuels,2022,36:6999−7005. [11] PARRES-ESCLAPEZ S, ILLÁN-GÓMEZ M J, DE LECEA C S M, et al. On the importance of the catalyst redox properties in the N2O decomposition over alumina and ceria supported Rh, Pd and Pt[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2010,96:370−378. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.02.034 [12] PARK J, KIM D, BYUN S W, et al. Impact of Pd: Pt ratio of Pd/Pt bimetallic catalyst on CH4 oxidation[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2022,316:121623. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121623 [13] HUANG X, ZHANG X, DENG C, et al. Boosting methane catalytic combustion by confining PdO-Pd interfaces in zeolite nanosheets[J]. Fuel,2023,344:127693. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127693 [14] MURAVEV V, PARASTAEV A, VAN DEN BOSCH Y, et al. Size of cerium dioxide support nanocrystals dictates reactivity of highly dispersed palladium catalysts[J]. Science,2023,380:1174−1179. doi: 10.1126/science.adf9082 [15] VAN VEGTEN N, MACIEJEWSKI M, KRUMEICH F, et al. Structural properties, redox behaviour and methane combustion activity of differently supported flame-made Pd catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2009,93:38−49. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.09.010 [16] CHIARELLO G L, GRUNWALDT J D, FERRI D, et al. Flame-synthesized LaCoO3-supported Pd: 1. Structure, thermal stability and reducibility[J]. J Catal,2007,252:127−136. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2007.10.004 [17] STROBEL R, GRUNWALDT J D, CAMENZINDA, et al. Flame-made alumina supported Pd-Pt nanoparticles: Structural properties and catalytic behavior in methane combustion[J]. Catal Lett,2005,104:9−16. doi: 10.1007/s10562-005-7429-y [18] WANG N, LI S, ZONG Y, et al. Sintering inhibition of flame-made Pd/CeO2 nanocatalyst for low-temperature methane combustion[J]. J Aerosol Sci,2017,105:64−72. doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2016.11.017 [19] 康建东. 铜基催化剂氧化低浓度甲烷的反应动力学及性能调控[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2022.KANG Jiandong. Oxidation of low-concentration methane regulation of copper-based catalysts for reaction kinetics and performance[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2022. [20] XIONG H, KUNWAR D, JIANG D, et al. Engineering catalyst supports to stabilize PdOx two-dimensional rafts for water-tolerant methane oxidation[J]. Nat Catal,2021,4:830−839. doi: 10.1038/s41929-021-00680-4 [21] EGGART D, HUANG X, ZIMINA A, et al. Operando XAS study of Pt-doped CeO2 for the nonoxidative conversion of methane[J]. ACS Catal,2022,12:3897−3908. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.2c00092 [22] 王晓波, 邓存宝, 邓汉忠, 等. 缺陷钙钛矿LaMnO3催化煤矿乏风瓦斯燃烧性能[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47:1588−1595.WANG Xiaobo, DENG Cunbao, DENG Hanzhong, et al. Defective perovskite LaMnO3 catalysts for ventilation air methane combustion[J]. J China Coal Soc,2022,47:1588−1595. [23] YANG J, PENG M, REN G, et al. A hydrothermally stable irreducible oxide-modified Pd/MgAl2O4 catalyst for methane combustion[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed,2020,59:18522−18526. doi: 10.1002/anie.202009050 [24] GÄNZLER A M, CASAPU M, MAURER F, et al. Tuning the Pt/CeO2 interface by in situ variation of the Pt particle size[J]. ACS Catal,2018,8:4800−4811. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b00330 [25] LI F, LEI L, YI J, et al. Performance, structure and mechanisms of Pd catalyst supported on M-Doped (M= La, Ba and K) CeO2 for methane oxidation[J]. Catal Lett,2023,153:1847−1858. doi: 10.1007/s10562-022-04124-x [26] LEE J H, JO D Y, CHOUNG J W, et al. Roles of noble metals (M = Ag, Au, Pd, Pt and Rh) on CeO2 in enhancing activity toward soot oxidation: Active oxygen species and DFT calculations[J]. J Hazard Mater,2021,403:124085. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124085 [27] ZHANG L, SPEZZATI G, MURAVEV V, et al. Improved Pd/CeO2 catalysts for low-temperature NO reduction: activation of CeO2 lattice oxygen by Fe doping[J]. ACS Catal,2021,11:5614−5627. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.1c00564 [28] LI T, XIA D, ZHOU G, et al. Effect of the morphology on the vapor phase benzene catalytic hydrogenation over Pd/CeO2 catalyst[J]. Catal Commun,2018,112:35−38. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2018.04.011 [29] HUANG X, EGGART D, QIN G, et al. Methyl radical chemistry in non-oxidative methane activation over metal single sites[J]. Nat Commun,2023,14:5716. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41192-y [30] LEE J H, LEE B J, LEE D W, et al. Synergistic effect of Cu on a Ag-loaded CeO2 catalyst for soot oxidation with improved generation of active oxygen species and reducibility[J]. Fuel,2020,275:117930. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117930 [31] WANG B, CHEN B, SUN Y, et al. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on the catalytic activity of Pt/CeO2 catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2018,238:328−338. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.07.044 [32] MA J, LOU Y, CAI Y, et al. The relationship between the chemical state of Pd species and the catalytic activity for methane combustion on Pd/CeO2[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2018,8:2567−2577. doi: 10.1039/C8CY00208H [33] TU C, CHENG S. Ceria-modified palladium/activated carbon as a high-performance catalyst for crude caprolactam hydrogenation purification[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng,2014,2:629−636. doi: 10.1021/sc400501w [34] YUE Y, LI Y, WANG T, et al. Enhancement of methanol oxidation performance over Pd/CeO2 derived from MOF and mechanism investigation via in situ studies[J]. Catal Lett,2022,152:3437−3446. doi: 10.1007/s10562-021-03901-4 [35] LI S, ZHANG Y, SHI J, et al. Catalytic performance of palladium supported on sheaf-like ceria in the lean methane combustion[J]. Nanomaterials,2019,10:31. doi: 10.3390/nano10010031 [36] GUO T, DU J, LI J. The effects of ceria morphology on the properties of Pd/ceria catalyst for catalytic oxidation of low-concentration methane[J]. J Mater Sci,2016,51:10917−10925. doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-0303-z [37] DANIELIS M, DIVINS N J, LLORCA J, et al. In situ investigation of the mechanochemically promoted Pd-Ce interaction under stoichiometric methane oxidation conditions[J]. EES Catal,2023,1:144−152. doi: 10.1039/D2EY00067A [38] PENG H, DONG T, YANG S, et al. Intra-crystalline mesoporous zeolite encapsulation derived thermally robust metal nanocatalyst in deep oxidation of light alkanes[J]. Nat Commun,2022,13:295. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27828-x [39] CUI X, ZHANG X, YANG Y, et al. The noble metals M (M = Pd, Ag, Au) decorated CeO2 catalysts derived from solution combustion method for efficient low-temperature CO catalytic oxidation: effects of different M loading on catalytic performances[J]. Nanotechnology,2022,33:415705. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ac7ed3 -




 下载:
下载: